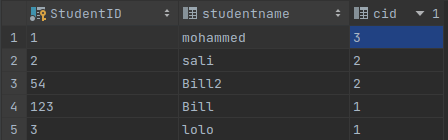
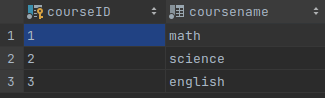
built-in types
| Numeric | int, float, complex |
| String | str (text sequence type) |
| Sequence | list, tuple, range |
| Binary | bytes, bytearray, memoryview |
| Mapping | dict |
| Boolean | bool |
| Set | set, frozenset |
| None | NoneType |
#boolean
print(True==1) # True
print(False==0) # True
print(True==2) # False
print(False==2) # False
#numeric int,float,complex
f=1.5#float
i=12#int
c=3+4j#complex
#sequence list,tuple,range,bytes,str
str_t="hello"
bytes_t=b"bytes"
list_t=[1,2,3]
tuple_t=(1,2,3,4)
#set and dect
set_t={3,2,3,1,4}
dect_t={"a":3,1:4}
Numerical Operations
from decimal import Decimal
from fractions import Fraction
#math for real numbers, cmath for complex numbers
import math, cmath
#fractions
f=Fraction(0.54)
print(f.numerator, f.denominator)#607985949695017 1125899906842624
f=Fraction(0.54).limit_denominator(1000)
print(f.numerator, f.denominator)#27 50
f=Fraction("22/7")
print(f.numerator, f.denominator)#22 7
# converting to float
print(float(f))#3.142857142857143
# converting to int
print(int(f))#3
#complex numbers
a=67j#complex number complex(0,67)
##converting to polar form
r=abs(a)#67
#decimal
d=Decimal("0.54")
print(d)#0.54
#rounding
print(round(0.54,1))#0.5
print(round(0.54,0))#1.0
#floor and ceil
print(math.floor(0.54))#0
print(math.ceil(0.54))#1
#operations
print(0.54+0.46)#1.0
print(0.54-0.46)#0.08
print(0.54*0.46)#0.2484
print(0.54/0.46)#1.173913043478261
print(0.54//0.46)#1.0
print(round(0.54%0.46,3))#0.08
print(0.54**0.46)#0.7913832183656556
(19/155)*(155/19) #0.9999999999999999
round((19/155)*(155/19)) #1
(19/155)*(155/19) == 1.0#False
math.isclose((19/155)*(155/19), 1)#True
value= 0x110 #0b10001000
import random
rand_val = random.randint(1, 100)
print(random.randrange(0, 100, 5))# 0, 5, 10...95
print(random.randint(1, 100))# 1, 2, 3...100
string
In Python, single-quoted strings and double-quoted strings are the same. This PEP does not make a recommendation for this. Pick a rule and stick to it. When a string contains single or double quote characters, however, use the other one to avoid backslashes in the string
#single line
m:str="hello world"
#multi lines
m2:str="""hello world
my name is python"""
m_digit:str="124"
print(m_digit.isnumeric())# True
print(m_digit.isalpha())# False
regular expressions
import re
string:str = 'hello 12 hi 89. Howdy 34'
regex:re= re.compile(r'(\d+)')
result = regex.findall(string)#['12', '89', '34']
regex2:re= re.compile(r'(\d+) hi')
result=regex2.search(string)
print(result.group(0),result.start(0),result.end(0))#12 hi 6 11
print(result.group(1),result.start(1),result.end(1))#12 6 8
string:str = 'hello 12 hi 89. Howdy 34'
result = re.sub(r'\d+', '', string)# remove all digitsformatted strings
f'{id:s} : {location:s} : {max_temp:d} / {min_temp:d} / {precipitation:f}'
f'{id:3d} : {location:19s} : {max_temp:3d} / {min_temp:3d} / {precipitation:5.2f}' #'IAD : Dulles Intl Airport : 32 / 13 / 0.40'
value= 42
string:str = f'{value} {2**7+1}'# 42 129
string:str = f'{value=} {2**7+1=}'# value=42 2**7+1=129
string:str = f'{value:b} {0.2:2.0%}'# 10001000 20%
m="hello %s %s %s" % ("world", "!" , 1)string module
import string
value="Hello, World!"
print(value.translate(str.maketrans('','',string.punctuation+string.whitespace)))#HelloWorldsingle byte sequence b’hello world’
value="محمد العبدلي"
print(value.encode('utf-8', 'ignore'))#b'\xd9\x85\xd8\xad\xd9\x85\xd8\xaf \xd8\xa7\xd9\x84\xd8\xb9\xd8\xa8\xd8\xaf\xd9\x84\xd9\x8a'
print(len(value.encode('utf-8', 'ignore')))#23
Tuples
m:tuple =(1,23,4,5,6,7,5,9,10)
if(m.__class__==tuple):
print("True")
print(len(m))#9
print(m.count(5))#2
print(m.index(5))#3
v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7,v8,v9 = m
print(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7,v8,v9)#1 23 4 5 6 7 5 9 10Handling Exceptions
def sum_n(n: int) -> int:
if(n < 0):
raise Exception("n must be a positive integer")
s = 0
for i in range(1, n+1):
s += i
return s
try:
total=sum_n(-1)
print(total)
except Exception as e:
print(e) try:
target = shutil.copy(source_path, target_path)
except FileNotFoundError:
try:
target_path.parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
target = shutil.copy(source_path, target_path)
except OSError as ex2:
print(f"{target_path.parent} problem: {ex2}")
except OSError as ex:
print(f"Copy {source_path} to {target_path} error {ex}")
Functions
def hex2rgb(hx_int):
if isinstance(hx_int, str):
if hx_int [0] == "#":
hx_int = int(hx_int [1:], 16)
else:
hx_int = int(hx_int, 16)
r, g, b = (hx_int >> 16) & 0xff, (hx_int >> 8) & 0xff, hx_int & 0xff
return r, g, b
#or
def hex2rgb(hx_int: Union[int, str]) -> Tuple[int, int, int]:
if isinstance(hx_int, str):
if hx_int[0] == "#":
hx_int = int(hx_int[1:], 16)
else:
hx_int = int(hx_int, 16)
r, g, b = (hx_int >> 16)&0xff, (hx_int >> 8)&0xff, hx_int&0xff
return r, g, b
RGB = Tuple[int, int, int]
HSL = Tuple[float, float, float]
def rgb_to_hsl(color: RGB) -> HSL:
def hsl_complement(color: HSL) -> HSL:
def hsl_to_rgb(color: HSL) -> RGB:from typing import Union
from decimal import Decimal
number=Union[int,float,Decimal,complex]
def add(a:number,b:number)->number:
return a+b
add(14j,5.5)def dice_t(n: int, sides: int = 6) -> Tuple[int, ...]:
return tuple(random.randint(1, sides) for _ in range(n))*is used as a prefix for a special parameter that receives all the unmatched positional arguments. We often use*argsto collect all of the positional arguments into a single parameter namedargs.**is used a prefix for a special parameter that receives all the unmatched named arguments. We often use**kwargsto collect the named values into a parameter namedkwargs.*, when used by itself as a separator between parameters, separates those parameters. It can be applied positionally or by keyword. The remaining parameters can only be provided by keyword.
def mm(*args):
print(args)
mm(1,2,3,4)#(1, 2, 3, 4)
def mm(**args):
print(args)
mm(a=1,b=2,c=3)# {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
def mm(*, x, y):
return x, y
print(mm(x=1, y=2)) # (1, 2)iterable function
def fibo_iter() -> typing.Iterable[typing.Tuple[int, int]]:
a = 1
b = 1
while True:
yield (a, b)
a, b = b, a + b
for i, f in fibo_iter():
if i >= 10:
break
print(f, end=' ')recursion
def factorial(n: int) -> int:
if(n>0):
return factorial(n-1)*n
else:
return 1
print(factorial(5)) # 120lambda
lamb= lambda x: x**2typing module
v:typing.Union[int,float] = 1.0#union for merge many types in one type
print(isinstance(v,typing.Union[float,set,dict])) #true
#object is super of all classes
m = 12
print(isinstance(m,object))#true
print(issubclass(int,object))#true
callable:typing.Callable= lambda m: m+12
print(callable(12),isinstance(callable,typing.Callable))#24 true
Vector: TypeAlias = list[float]
UserId = NewType('UserId', int)
some_id = UserId(524313)Decorators
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(args, kwargs)
print('Before function')
func(*args, **kwargs)
print('After function')
return wrapper
@decorator
def say_hello(name):
print(f'Hello {name}')type aliastype tt=typing.Iterable[int]with keyword
class MyContextManager:
def __enter__(self):
print("Entering the context.")
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
print("Exiting the context.")
if exc_type:
print(f"Exception: {exc_value}")
return True # Suppress exception
with MyContextManager():
print("Inside the context.")
raise ValueError("An error occurred!")with open('example.txt', 'r') as file:
content = file.read()
#----------------------
import threading
lock = threading.Lock()
# Without `with`
lock.acquire()
try:
# Critical section of code
print("Lock acquired manually.")
finally:
lock.release()
# With `with`
with lock:
# Critical section of code
print("Lock acquired using 'with'.")