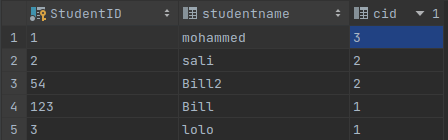
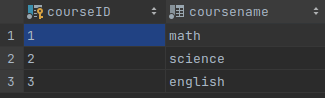
HttpContext
HttpContext encapsulates all information about an individual HTTP request and response.
and it capsulated by ControllerBase
HttpContext.User it will represent Th Identity any object implement System.Security.Principal.IIdentity and it wrapped by Principal Class Object
HttpContext Can Access to Any WebApplication Service by RequestServices.GetService<>() ....
Identity
It is Group OF Claims each claim represent kind of user data
most two famous Identity is ClaimsIdentinty And Generic Identity
Principal
it will Cover the Identity and provide you utilities to check if is there claim or schema or policy ... etc
protected async override sealed Task<AuthenticateResult> HandleAuthenticateAsync()
{
var authorizationHeader = Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString();
if (authorizationHeader != null && authorizationHeader.StartsWith("basic", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
var token = authorizationHeader.Substring("Basic ".Length).Trim();
var credentialsAsEncodedString = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(token));
var credentials = credentialsAsEncodedString.Split(':');
try
{
User? user = await Users.Login(credentials[0], credentials[1]);
var identity = user;
List<Claim> claims = new() { new Claim("uid", user.user_info.uid), new Claim("token", user.user_info.token) };
foreach (var authorization in user.user_info.authorization)
{
claims.Add(new Claim(authorization.ToString("G"), "true"));
}
this.Context.Items.Add("user", new ClaimsPrincipal(identity));
ClaimsPrincipal principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity(claims,"Basic"));
return await Task.FromResult(
AuthenticateResult.Success(new AuthenticationTicket(principal, "Basic")));
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Response.StatusCode = 401;
Response.Headers.Add("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=\"thesmartcircuit.com\"");
return await Task.FromResult(AuthenticateResult.Fail("Invalid Authorization Header"));
}
}
Response.StatusCode = 401;
Response.Headers.Add("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=\"thesmartcircuit.com\"");
return await Task.FromResult(AuthenticateResult.Fail("Invalid Authorization Header"));
}
then you can add new authoentication to this services of web application .
builder.Services.AddAuthentication("Basic")
.AddScheme<BasicAuthenticationOptions, BasicAuthenticationHandler>("Basic", null);
to apply this authentication on any minimal api
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!").RequireAuthorization((b) => { b.RequireClaim("admin");});
//or
[Authorize(AuthenticationSchemes = "Basic")]
Authorizations And Policies
add authorization service with Admin policy
builder.Services.AddAuthorizationBuilder().AddPolicy("Admin", (pb) =>
{
pb.RequireAuthenticatedUser().AddAuthenticationSchemes("Basic").RequireRole("admin");
});
then you can use this authorized policy with minimal api like
[Authorize(Policy = "User")]
Authentication Handler
there are already built in auth handler service like cookies and ODB if you like to customize new you can inherit AuthenticationHandler
add roles
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role,authorization.ToString("G"));
//or instean of using ClaimTypes.Role you can identify any string as role type by add it to roletype parameter in ClaimsIdentity