In Millman’s Theorem, the circuit is re-drawn as a parallel network of branches, each branch containing a resistor or series battery/resistor combination. Millman’s Theorem is applicable only to those circuits which can be redrawn accordingly. Here again, is our example circuit used for the last two analysis methods:

And here is that same circuit, re-drawn for the sake of applying Millman’s Theorem:

By considering the supply voltage within each branch and the resistance within each branch, Millman’s Theorem will tell us the voltage across all branches. Please note that I’ve labeled the battery in the rightmost branch as “B3” to clearly denote it as being in the third branch, even though there is no “B2” in the circuit!
Millman’s Theorem Equation
Millman’s Theorem is nothing more than a long equation, applied to any circuit drawn as a set of parallel-connected branches, each branch with its own voltage source and series resistance:

Substituting actual voltage and resistance figures from our example circuit for the variable terms of this equation, we get the following expression:

The final answer of 8 volts is the voltage seen across all parallel branches, like this:

The polarity of all voltages in Millman’s Theorem is referenced to the same point. In the example circuit above, I used the bottom wire of the parallel circuit as my reference point, and so the voltages within each branch (28 for the R1 branch, 0 for the R2 branch, and 7 for the R3 branch) were inserted into the equation as positive numbers. Likewise, when the answer came out to 8 volts (positive), this meant that the top wire of the circuit was positive with respect to the bottom wire (the original point of reference). If both batteries had been connected backward (negative end up and positive ends down), the voltage for branch 1 would have been entered into the equation as -28 volts, the voltage for branch 3 as -7 volts, and the resulting answer of -8 volts would have told us that the top wire was negative with respect to the bottom wire (our initial point of reference).
Solving for Resistor Voltage Drops
To solve for resistor voltage drops, the Millman voltage (across the parallel network) must be compared against the voltage source within each branch, using the principle of voltages adding in series to determine the magnitude and polarity of the voltage across each resistor:

Solving for Branch Currents
To solve for branch currents, each resistor voltage drop can be divided by its respective resistance (I=E/R):

Determining the Direction of Current
The direction of current through each resistor is determined by the polarity across each resistor, not by the polarity across each battery, as the current can be forced back through a battery, as is the case with B3 in the example circuit. This is important to keep in mind since Millman’s Theorem doesn’t provide as direct an indication of “wrong” current direction as does the Branch Current or Mesh Current methods. You must pay close attention to the polarities of resistor voltage drops as given by Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, determining the direction of currents from that.

Millman’s Theorem is very convenient for determining the voltage across a set of parallel branches, where there are enough voltage sources present to preclude solution via regular series-parallel reduction method. It also is easy in the sense that it doesn’t require the use of simultaneous equations. However, it is limited in that it only applied to circuits which can be re-drawn to fit this form. It cannot be used, for example, to solve an unbalanced bridge circuit. And, even in cases where Millman’s Theorem can be applied, the solution of individual resistor voltage drops can be a bit daunting to some, the Millman’s Theorem equation only providing a single figure for branch voltage.
As you will see, each network analysis method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Each method is a tool, and there is no tool that is perfect for all jobs. The skilled technician, however, carries these methods in his or her mind like a mechanic carries a set of tools in his or her toolbox. The more tools you have equipped yourself with, the better prepared you will be for any eventuality.
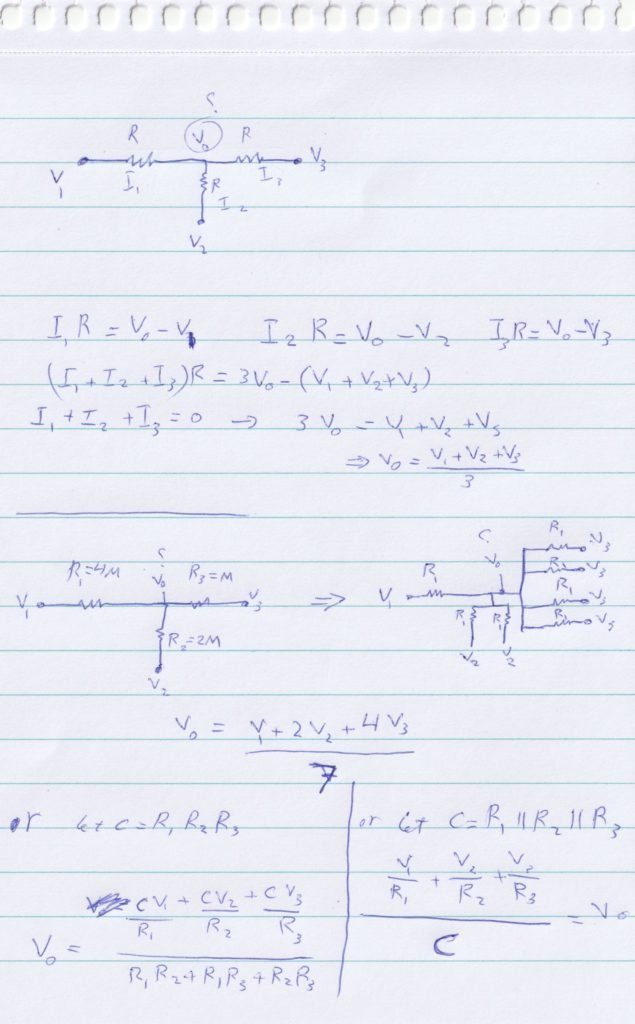
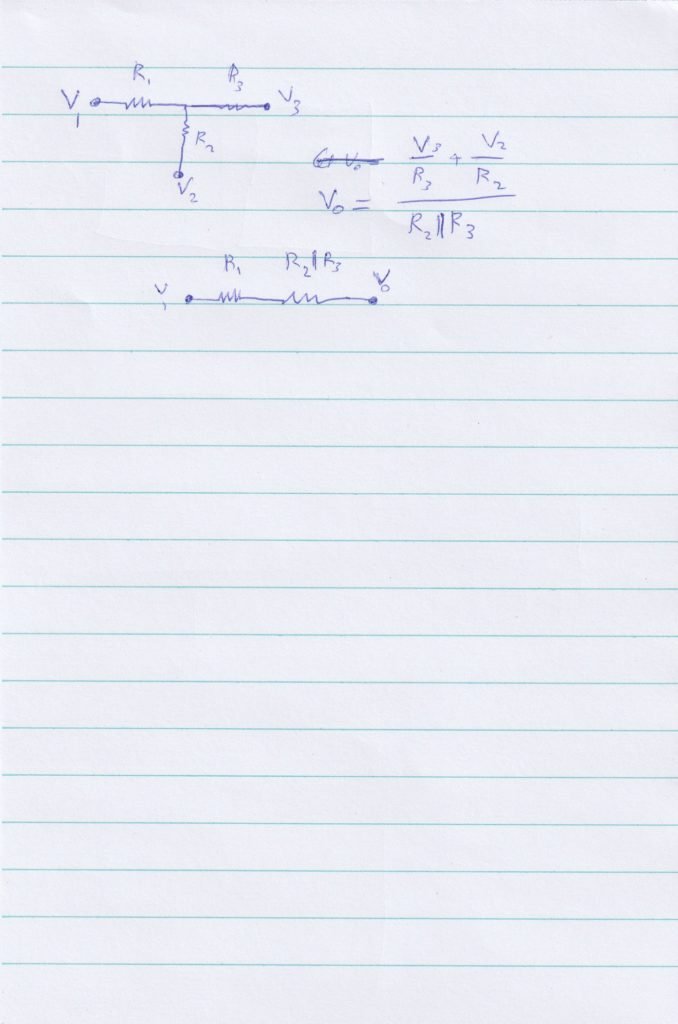
note change C to


black internet https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ how to access dark web
dark market https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ bitcoin dark web
dark market list https://worldonionmarket.com/ free dark web
dark net https://cypher-market-online.com/ dark web links
how to access dark web https://heineken-drugs-market.com/ darknet search engine
dark web drug marketplace https://cypher-marketplace.com/ black internet
dark web sites https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ onion market
darknet market links https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ darkmarket link
darkweb marketplace https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ darknet site
darkmarket url https://world-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark web websites
deep web links https://worldoniondarkweb.com/ dark web link
deep web drug links https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ dark websites
deep web drug url https://heineken-onion-market.com/ tor markets links
dark website https://darkmarket-world.com/ onion market
darknet links https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ dark market
dark web search engines https://world-market-place1.com/ how to access dark web
darkmarket url https://world-drugs-market.com/ dark markets 2023
how to access dark web https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ tor markets links
darknet site https://cypher-dark-market.com/ tor market
dark web market list https://darkmarketworld.com/ dark website
how to access dark web https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ deep dark web
dark market 2023 https://world-drugs-online.com/ dark net
darkmarket link https://darkweb-world.com/ dark internet
dark markets 2023 https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ dark web market
dark websites https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ darknet market
darknet drugs https://worldmarketplacee.com/ deep web drug markets
darkmarkets https://dark-market-heineken.com/ darkmarket 2023
tor market links https://cypher-market-onion.com/ dark websites
tor market https://world-darkwebmarket.com/ darknet search engine
darknet market lists https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ darknet drug links
darknet market list https://worldmarket-url.com/ dark website
dark websites https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ dark web links
dark net https://world-darknet.com/ dark web link
tor darknet https://cyphermarket-url.com/ dark website
best darknet markets https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ tor markets
blackweb https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ the dark internet
dark web sites links https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark web sites
free dark web https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ dark web search engine
tor dark web https://cypher-market-online.com/ dark web sites
darkmarket url https://world-online-drugs.com/ darknet market list
deep web drug url https://dark-web-cypher.com/ tor markets links
black internet https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ darknet market list
blackweb https://heineken-drugs-market.com/ dark market link
tor markets links https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ dark web sites links
darknet market list https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ dark web links
dark market https://heinekendrugsonline.com/ deep web markets
dark net https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ deep web sites
darknet websites https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ dark web search engine
tor markets links https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ dark market url
deep web search https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet drugs
darknet drug links https://world-onion-market.com/ darkmarkets
dark net https://worldmarketplace24.com/ black internet
tor markets links https://cypher-dark-market.com/ darknet markets 2023
deep dark web https://world-drugsonline.com/ deep web markets
dark web market list https://cypheroniondarkweb.com/ dark internet
darknet search engine https://cypheroniondarkmarket.com/ darkmarket list
darknet markets 2023 https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ darkmarket list
deep web links https://heinekendrugsmarketplace.com/ dark web market list
darknet seiten https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ dark web link
tor dark web https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ the dark internet
tor market url https://darkweb-world.com/ darknet drugs
dark market 2023 https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ free dark web
darkmarket https://world-drugs-online.com/ darknet market links
dark web markets https://cypherdrugsmarket.com/ deep web markets
darknet market https://worldmarketplacee.com/ darknet search engine
darknet market https://world-darkwebmarket.com/ black internet
dark web markets https://cypher-market-onion.com/ tor market
dark web search engine https://worlddarkweb.com/ dark markets
tor market https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark markets 2023
dark web sites links https://cyphermarket-link.com/ darknet market links
dark market onion https://cypher-marketplace.com/ deep web drug links
tor market https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ tor marketplace
dark web websites https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ dark web search engines
dark web market https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ dark markets
dark web site https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ darkmarkets
dark web search engine https://world-online-drugs.com/ tor darknet
top 10 online pharmacy in india: mail order pharmacy india – mail order pharmacy india
dark web links https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ dark web sites links
dark web sites links https://dark-web-cypher.com/ darknet market
dark web access https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ darkmarkets
how to access dark web https://cypherdarkweb.com/ darknet websites
tor dark web https://heineken-drugsonline.com/ best darknet markets
how to get on dark web https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ dark web sites
how to access dark web https://world-drugs-market.com/ darkmarkets
tor market url https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ deep dark web
darknet links https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ darkmarket list
darkmarket list https://heinekendrugsonline.com/ best darknet markets
dark markets https://cypher-dark-market.com/ darknet market
blackweb https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ tor marketplace
deep web drug markets https://world-market-place1.com/ blackweb official website
deep web links https://cypher-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet market
deep web drug markets https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ darknet market list
deep web sites https://cypher-onlinedrugs.com/ darkmarkets
deep dark web https://darkmarketworld.com/ blackweb
tor markets 2023 https://kingdomdarkwebmarket.com/ tor markets 2023
deep dark web https://world-darkmarket.com/ bitcoin dark web
dark web websites https://heinekendrugsmarketplace.com/ darknet drug store
darkmarket url https://world-dark-market.com/ deep web markets
blackweb https://dark-market-world.com/ drug markets onion
dark markets https://worldmarketplacee.com/ dark web drug marketplace
blackweb official website https://world-drugs-online.com/ darknet market lists
the dark internet https://worlddarkweb.com/ tor marketplace
dark web websites https://cypherdrugsmarketplace.com/ black internet
dark net https://cypher-market-onion.com/ darkmarket
deep web sites https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ the dark internet
darknet seiten https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ darknet drug store
dark web site https://cyphermarket-link.com/ darknet drugs
darknet search engine https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark web market links
deep web drug store https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ tor market
dark markets 2023 https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ blackweb
blackweb official website https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ tor darknet
darknet search engine https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ deep web markets
dark web search engines https://world-online-drugs.com/ tor markets
Thanks for the information provided! we will use this information into our GPT/Chat-GPT dataset. See our sites too at Islam Berkemajuan
dark market 2023 https://world-drugs-market.com/ tor market
dark website https://dark-web-cypher.com/ tor market links
darknet market links https://cypher-darkmarket.com/ dark market 2023
dark markets https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ darknet sites
dark markets 2023 https://cypher-darknet.com/ dark markets
bitcoin dark web https://cypher-dark-market.com/ tor market
drug markets onion https://heineken-onion-market.com/ darkmarket list
tor dark web https://heineken-drugsonline.com/ dark market link
darkmarkets https://heinekendrugsonline.com/ how to get on dark web
dark market list https://cypheronlinedrugs.com/ darknet markets 2023
darkweb marketplace https://worldmarketplace24.com/ darknet seiten
deep web markets https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ dark web search engine
black internet https://world-darkwebmarket.com/ darkmarket link
black internet https://darkmarketworld.com/ darknet market links
darkmarket link https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ tor market links
darknet markets https://cypheronionmarket.com/ darknet drug links
dark web search engine https://world-darknet.com/ dark net
darknet market list https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ drug markets onion
darknet drug store https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ darkmarket url
darknet websites https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ tor markets 2023
darkweb marketplace https://dark-market-world.com/ bitcoin dark web
deep web markets https://worlddarknetdrugstore.com/ darkmarket
deep dark web https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ blackweb
dark web market list https://cypherdrugsmarket.com/ dark market url
darknet drugs https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ darkmarket url
how to get on dark web https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ tor market
dark web markets https://cyphermarket-link.com/ darkmarket
black internet https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet market links
drug markets dark web https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ darknet market links
dark web sites https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ darkmarket link
darknet drug market https://dark-market-heineken.com/ darknet drugs
darknet drug market https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ darkmarket url
darkmarket https://worldonionmarket.com/ dark websites
darknet drug market https://world-drugs-market.com/ dark market list
dark web site https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ tor dark web
darkmarket https://cypherdarknet.com/ deep web sites
dark web sites https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ dark markets
dark web drug marketplace https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ darknet market list
onion market https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ tor marketplace
dark web sites https://dark-web-cypher.com/ darknet drug market
darknet marketplace https://heineken-onion-market.com/ drug markets dark web
darknet markets 2023 https://cypheroniondarkweb.com/ dark market
darknet marketplace https://world-market-place1.com/ dark web market
dark web market links https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ darknet links
darknet drug links https://worldmarketdarknets.com/ dark web websites
tor dark web https://world-darkmarket.com/ deep web sites
how to access dark web https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ free dark web
darknet marketplace https://world-dark-market.com/ darknet market links
tor markets links https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ deep web links
tor dark web https://world-drugs-online.com/ onion market
dark market onion https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ blackweb official website
darknet market lists https://darkweb-world.com/ darknet sites
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very
well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read
more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly
comeback.
dark web access https://cypher-onlinedrugs.com/ tor dark web
dark website https://heinekendrugsmarketplace.com/ tor marketplace
how to access dark web https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ tor markets links
darkmarket 2023 https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ tor markets links
deep web markets https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ dark websites
deep web drug links https://cypher-market-onion.com/ tor market url
dark web access https://cypherdrugsonline.com/ darknet drug links
how to get on dark web https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ blackweb official website
darknet markets 2023 https://cyphermarket-link.com/ dark market url
deep web drug store https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ darknet sites
darkmarket list https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ dark web market links
dark market https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ deep web search
deep web sites https://worldonionmarket.com/ dark market link
tor market links https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark web markets
dark market https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ deep web drug url
dark market 2023 https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ tor market url
dark websites https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ darknet drug store
dark web websites https://world-market-place1.com/ dark web sites links
dark web access https://cypher-drugs-market.com/ how to access dark web
deep web search https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ dark web access
tor market url https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket url https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ dark net
darkmarket 2023 https://world-darkmarket.com/ tor dark web
free dark web https://cypher-market-online.com/ dark markets 2023
dark market list https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ darknet markets
dark web search engines https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ deep web drug store
dark net https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ dark net
dark web drug marketplace https://darkmarketworld.com/ deep web search
darknet search engine https://darkweb-world.com/ free dark web
free dark web https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ deep web markets
tor market url https://cypheronionmarket.com/ darkmarket
dark markets https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ dark market link
dark web links https://world-drugs-market.com/ tor market links
deep web drug url https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ darknet drug market
dark market list https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ darknet market list
darknet drug store https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ how to access dark web
drug markets onion https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ black internet
darkweb marketplace https://cypherdrugsmarketplace.com/ dark markets 2023
darknet search engine https://cyphermarket-url.com/ dark market 2023
tor markets https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ how to access dark web
tor market links https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ dark web search engine
deep web drug links https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet drugs
dark web drug marketplace https://dark-market-heineken.com/ blackweb
dark web sites links https://cypher-darkweb.com/ tor markets 2023
onion market https://cypher-darkmarket.com/ deep web drug links
dark web sites links https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ darknet site
drug markets dark web https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ tor markets 2023
darknet market lists https://dark-market-cypher.com/ tor markets 2023
darknet sites https://world-market-place1.com/ bitcoin dark web
dark net https://world-darkwebmarket.com/ darkmarket url
dark internet https://worlddarkweb.com/ deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web https://world-darkweb.com/ dark web websites
dark web markets https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ darknet market lists
darknet websites https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ darknet market links
darkmarket link https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ darknet drugs
dark market link https://cypher-market-online.com/ darknet websites
darknet market links https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet seiten
black internet https://world-drugsonline.com/ blackweb official website
best darknet markets https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ deep web drug url
darknet search engine https://world-darkmarket.com/ deep web drug store
darknet markets https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ dark market 2023
dark web market https://worldoniondarkweb.com/ darkmarkets
dark web links https://worldmarketplacee.com/ blackweb
dark market 2023 https://cypher-onlinedrugs.com/ how to get on dark web
dark web market list https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ darkmarket list
deep web markets https://darkweb-world.com/ darknet market links
the dark internet https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ dark web websites
darknet markets 2023 https://worldmarketdrugsonline.com/ deep web drug store
dark website https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ dark net
dark market list https://cypher-market-onion.com/ dark web access
blackweb official website https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark web websites
dark web search engines https://cypherdrugsonline.com/ bitcoin dark web
tor market https://cyphermarket-url.com/ dark web links
dark markets https://cypher-darknet.com/ darkmarket url
best darknet markets https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ tor market links
darknet market links https://cypherdarknet.com/ deep web markets
blackweb official website https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ dark web link
darknet seiten https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ dark web sites links
dark web websites https://dark-market-heineken.com/ tor markets 2023
blackweb official website https://darkweb-cypher.com/ darkmarket link
blackweb https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ tor markets 2023
black internet https://world-drugs-online.com/ dark web search engine
darknet market links https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ dark market list
deep web drug markets https://worlddarkweb.com/ onion market
bitcoin dark web https://worldmarketplace24.com/ how to access dark web
darkmarket https://world-drugs-market.com/ tor markets 2023
dark website https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ dark web sites links
tor markets links https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ darkmarket link
bitcoin dark web https://world-darknet.com/ darkmarket
dark market link https://cypher-dark-market.com/ dark market link
tor markets https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ dark web drug marketplace
darknet site https://cypher-marketplace.com/ darknet markets 2023
dark web drug marketplace https://heineken-onion-market.com/ blackweb
darknet market https://darkweb-world.com/ dark web search engines
darknet site https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ dark web sites
dark web links https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ blackweb
dark web markets https://cypheroniondarkmarket.com/ darknet market
darknet market lists https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ blackweb
blackweb https://dark-web-world.com/ deep web markets
dark web links https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ darknet drug market
black internet https://cypherdrugsmarketplace.com/ free dark web
deep dark web https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ onion market
darknet websites https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet websites
deep web sites https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ black internet
darkmarket list https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ darknet market links
darknet drug links https://world-drugs-online.com/ dark market
black internet https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ darknet search engine
tor markets links https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ dark markets 2023
tor market links https://cypherdarkweb.com/ darknet market list
dark web market list https://cypher-darkweb.com/ deep web drug url
dark website https://cypheronlinedrugs.com/ darkmarket
darknet drug store https://world-drugs-market.com/ darknet search engine
darknet drug market https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ the dark internet
dark internet https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ darkmarkets
drug markets onion https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ dark web sites links
darknet markets 2023 https://worldmarket-linkk.com/ darknet drugs
Let me give you a thumbs up man. Can I show my hidden information on amazing values and if you want to have a checkout and
also share valuable info about how to become a millionaire
yalla lready know follow me my fellow commenters!.
dark web search engines https://dark-market-heineken.com/ how to get on dark web
deep web markets https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ deep web markets
darkmarkets https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ the dark internet
dark web market links https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ drug markets onion
darknet websites https://world-market-place1.com/ free dark web
darknet drug market https://worlddarknetdrugstore.com/ dark web market
darknet search engine https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ dark websites
darkmarket url https://world-darknet.com/ darknet websites
darknet market links https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ dark markets 2023
darkweb marketplace https://cypher-dark-market.com/ dark market onion
Я ценю балансировку автора в описании проблемы. Он предлагает читателю достаточно аргументов и контекста для формирования собственного мнения, не внушая определенную точку зрения.
the dark internet https://darkmarketworld.com/ darknet market
dark web markets https://heineken-onion-market.com/ darknet seiten
dark web market https://cypher-online-drugs.com/ dark market link
dark markets 2023 https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ dark web link
how to get on dark web https://world-dark-market.com/ dark net
dark markets 2023 https://worldmarketplacee.com/ darkmarket link
dark web link https://world-drugs-online.com/ tor marketplace
dark market list https://worldmarketdrugsonline.com/ deep web search
Надеюсь, что эти комментарии добавят ещё больше положительных настроений к информационной статье!
dark web access https://cypherdrugsmarketplace.com/ darkmarket
deep web drug links https://world-drugsonline.com/ drug markets dark web
dark market onion https://cypher-darkmarket.com/ dark web market
dark web sites links https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ dark websites
black internet https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ darknet seiten
tor marketplace https://cypherdarkweb.com/ deep web sites
tor markets https://cypher-drugsonline.com/ blackweb
darknet sites https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ dark market url
darknet market links https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ tor market url
dark internet https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ dark website
tor markets 2023 https://darkwebcypher.com/ dark net
dark website https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ darkweb marketplace
dark web site https://cypher-darkweb.com/ best darknet markets
dark markets https://worldmarket-url.com/ dark website
darknet drugs https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ tor marketplace
We’re a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community.
Your web site provided us with valuable info to work on.
You’ve done an impressive job and our entire community will be thankful to
you.
tor market links https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ dark net
tor markets links https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet markets
onion market https://heineken-drugs-market.com/ darknet site
darknet marketplace https://world-darkwebmarket.com/ deep web drug markets
tor marketplace https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ darkmarket link
deep web drug store https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ dark net
tor market https://world-market-place1.com/ darknet site
dark markets https://dark-market-world.com/ darknet markets 2023
tor markets https://world-drugs-online.com/ onion market
dark website https://world-darknet.com/ darknet marketplace
darknet links https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ tor market url
tor market url https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ darknet market links
best darknet markets https://world-drugs-market.com/ dark web sites
tor market links https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ darkmarket link
darkmarket https://cypheronionmarket.com/ darknet drugs
how to access dark web https://dark-web-world.com/ drug markets dark web
dark web sites https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ deep web drug markets
darknet drugs https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ dark website
darknet drugs https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ dark web sites links
darkmarket url https://cypherdrugsmarket.com/ tor markets links
darknet market list https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ dark market link
dark web drug marketplace https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ deep web links
dark markets 2023 https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ dark markets
https://kamagratabs.pro/# Oral Jelly 100mg Kamagra price
how to get on dark web https://cypheronlinedrugs.com/ darkmarkets
darkmarket url https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ tor market url
dark web site https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ dark market link
dark internet https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ free dark web
tor markets links https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ dark markets 2023
tor dark web https://darkwebcypher.com/ dark web site
darkmarkets https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ darkmarket link
black internet https://kingdomdarkwebmarket.com/ dark web market
darknet market https://heinekendrugsmarketplace.com/ darknet market
dark markets https://cypher-darkweb.com/ blackweb
free dark web https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ dark web market
dark markets https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ tor darknet
tor marketplace https://world-onion-market.com/ tor markets
dark web search engines https://cypher-marketplace.com/ darknet markets
how to get on dark web https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ dark web sites
deep web markets https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ free dark web
blackweb official website https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ deep web drug store
blackweb https://heineken-drugsonline.com/ darknet search engine
dark net https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ deep web markets
how to get on dark web https://cypher-markett.com/ darknet drugs
onion market https://world-market-place1.com/ deep dark web
how to access dark web https://darkmarketworld.com/ dark web site
dark web link https://world-darkweb.com/ tor dark web
deep web drug markets https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ deep web drug store
darknet search engine https://cypher-onlinedrugs.com/ dark web market list
darknet drugs https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ dark web sites links
darknet market lists https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ deep web drug store
dark market https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ blackweb official website
tor market links https://cypherdrugsmarketplace.com/ darknet markets 2023
onion market https://cypher-darknet.com/ dark web market list
dark internet https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ best darknet markets
darkweb marketplace https://world-darkmarket.com/ dark web search engine
darkmarket list https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ darkmarket url
darknet drug market https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ darknet markets
tor darknet https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ dark web markets
tor marketplace https://cypher-drugsonline.com/ darknet market list
dark markets 2023 https://world-drugsonline.com/ darkweb marketplace
tor darknet https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ drug markets onion
tor markets 2023 https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ darkmarket url
darknet drug market https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ darknet marketplace
free dark web https://worldmarket-linkk.com/ dark market onion
dark web drug marketplace https://darkwebcypher.com/ dark market
darknet search engine https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ deep web drug links
darknet market https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ darknet markets
deep web links https://worlddarknetdrugstore.com/ tor darknet
free dark web https://world-online-drugs.com/ darknet drug links
dark markets https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ dark market url
the dark internet https://worldmarketdarknets.com/ dark web search engine
best darknet markets https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ darknet drugs
deep web sites https://cypher-darkweb.com/ dark web market links
darkmarket url https://dark-market-heineken.com/ darknet drugs
darknet websites https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ darkmarket list
how to access dark web https://cypher-markett.com/ tor markets
darknet site https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ darknet seiten
darkmarket list https://heineken-drugs-market.com/ dark market list
darknet markets 2023 https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ blackweb
During this consultation, she was very informative and concise, which is what I look for in a doctor buy cialis online with prescription
deep web links https://world-market-place1.com/ tor marketplace
darkmarket 2023 https://darkweb-world.com/ dark market
darkmarket url https://world-darknet.com/ dark web search engine
magnificent post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You should continue your writing. I am sure, you have a great readers’ base already!
darknet market lists https://cypher-online-drugs.com/ darknet links
dark web sites links https://cypher-dark-market.com/ dark web search engine
how to access dark web https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ tor darknet
darkmarket link https://dark-web-world.com/ darknet market list
dark website https://dark-web-cypher.com/ dark market list
dark market url https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ dark markets 2023
dark web sites links https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ deep web drug markets
black internet https://world-drugs-online.com/ dark market link
darknet drug store https://world-dark-market.com/ bitcoin dark web
deep web markets https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ deep web drug links
deep web search https://worldmarketplacee.com/ deep web drug store
dark web links https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ darknet drugs
darknet search engine https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ dark market link
dark web sites links https://world-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark web websites
darkmarket url https://worldmarket-url.com/ darknet marketplace
how to access dark web https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark website
how to access dark web https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ dark web sites
deep dark web https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet drug store
black internet https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ darkmarket list
darknet market lists https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ darkmarket 2023
darknet drug market https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ darknet markets
dark internet https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ darknet websites
dark web markets https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ darkmarket
deep web drug links https://cypher-markett.com/ dark web websites
dark web market list https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ deep web drug url
drug markets dark web https://worlddarkweb.com/ darknet drug store
deep web links https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ deep web drug store
the dark internet https://cypher-darkweb.com/ tor darknet
deep web drug url https://heineken-drugs-market.com/ tor dark web
onion market https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ dark web site
darknet drug links https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ deep web drug links
Thanks for the good writeup. It if truth be told
was a entertainment account it. Look advanced to far introduced agreeable from you!
By the way, how can we keep in touch?
tor marketplace https://darkweb-world.com/ darkmarket 2023
dark web sites links https://world-market-place1.com/ darknet market
darknet sites https://cypheronionmarket.com/ blackweb official website
deep web markets https://cypherdrugsonline.com/ dark market list
dark market onion https://world-darknet.com/ dark web links
darknet site https://darkmarket-world.com/ drug markets dark web
deep web sites https://cypher-dark-market.com/ deep web drug store
tor market https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet market links
dark web access https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark market list
darkmarket url https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ darknet websites
darknet market links https://world-drugsonline.com/ darknet drugs
darknet marketplace https://cyphermarket-url.com/ dark web sites
how to access dark web https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ black internet
onion market https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ tor market url
darknet market links https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ dark web websites
tor dark web https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ dark market
darknet market lists https://world-darkmarket.com/ tor market
darknet market lists https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ dark market onion
blackweb https://worldonionmarket.com/ darknet marketplace
how to access dark web https://worldmarket-url.com/ black internet
tor market https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ the dark internet
https://kamagratabs.pro/# kamagra
darknet market list https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ deep web markets
dark web markets https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ darknet search engine
darknet drug store https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ darknet search engine
best darknet markets https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ darknet marketplace
drug markets dark web https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ dark web websites
darkmarkets https://cypher-darkweb.com/ dark market list
darknet seiten https://heineken-online-drugs.com/ dark web link
tor darknet https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ dark market list
how to access dark web https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ tor market
the dark internet https://cypheronlinedrugs.com/ dark web websites
deep web sites https://worldmarketplace24.com/ darkmarket list
black internet https://darkmarket-world.com/ dark web market
deep web sites https://world-drugs-online.com/ darkmarket list
best darknet markets https://darkmarketcypher.com/ dark web search engines
darknet marketplace https://cypher-dark-market.com/ deep web links
dark market 2023 https://world-darknet.com/ darkmarket url
dark web access https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ tor markets 2023
darknet drug market https://world-dark-market.com/ best darknet markets
dark web search engines https://cypher-marketplace.com/ dark web access
darkmarket url https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ darknet market links
dark web access https://world-online-drugs.com/ dark web site
dark internet https://heineken-darkweb-drugstore.com/ darkweb marketplace
dark web access https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet market lists
dark web links https://cypher-darkmarket.com/ deep web drug store
dark web market https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ dark market onion
darkmarket 2023 https://world-darkmarket.com/ darknet drugs
darkweb marketplace https://cypher-market-online.com/ onion market
dark web market https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ darknet sites
blackweb official website https://heinekendarknetdrugstore.com/ deep dark web
deep web drug links https://worldmarketdarknets.com/ darknet drug market
dark web link https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darkmarkets
dark internet https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ darknet websites
darknet drugs https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ deep web drug markets
deep web drug markets https://cypheroniondarkmarket.com/ darkmarket url
dark web market https://cypher-darkweb.com/ dark web link
darknet market links https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ darkmarket list
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
darknet market lists https://worldmarketplace24.com/ deep web search
dark web site https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ darknet market links
dark market https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ drug markets onion
dark market list https://world-drugs-market.com/ dark web markets
dark net https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ free dark web
dark markets 2023 https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ blackweb official website
dark market list https://dark-market-heineken.com/ deep web drug markets
dark websites https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ darknet sites
blackweb https://world-onion-market.com/ dark web search engines
deep web markets https://world-darknet.com/ tor markets 2023
tor market url https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ tor marketplace
tor dark web https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ tor markets 2023
deep web markets https://world-online-drugs.com/ free dark web
dark websites https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ black internet
deep web drug markets https://worldmarket-url.com/ darknet site
darknet market links https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ darkmarket 2023
dark web websites https://heineken-onion-market.com/ deep web markets
onion market https://heinekendrugsmarketplace.com/ how to access dark web
darknet market list https://heineken-drugsonline.com/ dark markets
blackweb official website https://cypher-markett.com/ dark web drug marketplace
onion market https://worlddarkwebmarket.com/ tor markets
darknet market https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ deep web drug links
the dark internet https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ how to access dark web
darknet seiten https://cypheronionmarket.com/ dark web market list
black internet https://dark-web-cypher.com/ black internet
dark market https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet search engine
tor dark web https://darkmarketworld.com/ tor market links
best darknet markets https://worldmarketdarknets.com/ darkmarket
darkmarket link https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ deep web sites
dark market url https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ tor markets 2023
darknet market lists https://cypher-darkweb.com/ dark web market
darknet links https://heinekenonionmarket.com/ best darknet markets
darknet market https://cyphermarket-url.com/ black internet
darknet websites https://worldmarketplace24.com/ tor markets links
dark market link https://darkmarket-world.com/ darknet marketplace
tor markets https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ darkweb marketplace
dark market link https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ deep web drug store
dark markets 2023 https://dark-market-heineken.com/ darknet market list
deep web links https://cypher-marketplace.com/ dark web markets
darknet market list https://world-dark-market.com/ dark markets
darknet market https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ how to get on dark web
darknet search engine https://worldoniondarkmarket.com/ the dark internet
darkweb marketplace https://world-darknet.com/ darknet seiten
dark web sites links https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ dark web search engine
tor market links https://world-online-drugs.com/ darknet links
onion market https://heineken-onlinedrugs.com/ dark website
deep web drug markets https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ dark web links
dark markets 2023 https://heinekenoniondarkweb.com/ tor market url
how to get on dark web https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ dark web links
dark internet https://world-darkmarket.com/ dark web sites
dark web site https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ darknet market
darkweb marketplace https://world-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet markets 2023
dark market https://world-darkmarketplace.com/ onion market
darkmarkets https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ tor market
Hi there, You have done an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this website.
tor darknet https://darkmarketworld.com/ dark internet
dark web sites links https://worlddarkweb.com/ dark market url
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/es/register?ref=B4EPR6J0
dark web search engines https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ dark web search engines
Learn more about accutane over the counter options at accutane over the counter.
https://propecia.pro/# can you get cheap propecia tablets
dark web link https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ deep web markets
tor markets links https://cypherdarknet.com/ dark web drug marketplace
tor markets 2023 https://worldmarketplace24.com/ darknet marketplace
darkmarket url https://cyphermarket-link.com/ the dark internet
dark markets https://worldmarketdrugsonline.com/ dark markets
darknet seiten https://world-drugsonline.com/ deep dark web
darknet site https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ darkmarket link
darknet market https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ bitcoin dark web
darknet market list https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ drug markets dark web
dark market list https://worldmarket-url.com/ deep web search
tor dark web https://worlddarkwebdrugstore.com/ how to get on dark web
dark web websites https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ dark web sites
darknet drug market https://dark-market-heineken.com/ dark market
dark web market https://kingdom-darkmarket.com/ dark web drug marketplace
dark market 2023 https://world-onion-market.com/ dark web markets
darkmarket url https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ darknet market links
The other day, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation.
My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to
share it with someone!
dark market https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ dark websites
darkmarket url https://worlddarkmarketonline.com/ darkmarket url
deep web markets https://world-darknet.com/ dark markets 2023
dark web link https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ darknet drug store
darknet drug links https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ dark web market links
darknet drug store https://world-online-drugs.com/ the dark internet
deep web drug url https://cypher-darkmarket.com/ tor markets 2023
tor market url https://world-darkmarket.com/ dark web links
dark web sites links https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ bitcoin dark web
dark internet https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ drug markets onion
darknet site https://worldmarket-darknet.com/ deep dark web
drug markets onion https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ tor market url
darknet markets https://worldmarket-linkk.com/ darknet seiten
cheapest accutane generic accutane purchase online uk
darknet drug market https://cypher-darkweb.com/ darknet drug market
darknet marketplace https://world-drugs-online.com/ blackweb official website
tor market links https://cyphermarket-link.com/ deep web sites
dark internet https://darkmarket-world.com/ deep web sites
How does the dosage of 120 mg of Accutane daily compare to the standard dosage? https://isotretinoinex.website/
deep web links https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet seiten
deep web search https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ darknet market
darknet search engine https://world-darknet-drugstore.com/ darkmarket
Is Accutane available for sale in a 10 milligram dosage? https://isotretinoinex.website/
tor markets https://world-onion-market.com/ dark web links
tor market url https://cypher-marketplace.com/ dark web access
darkmarket link https://dark-market-heineken.com/ bitcoin dark web
drug markets onion https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ dark web markets
deep web links https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ dark web search engines
darknet search engine https://cypher-market-onion.com/ dark internet
dark web drug marketplace https://cypher-markett.com/ dark market list
dark markets 2023 https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ best darknet markets
darkmarket 2023 https://worldonionmarket.com/ darknet market
dark websites https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ deep web markets
the dark internet https://darkweb-world.com/ darknet drug market
Очень хорошо структурированная статья! Я оцениваю ясность и последовательность изложения. Благодаря этому, я смог легко следовать за логикой и усвоить представленную информацию. Большое спасибо автору за такой удобный формат!
darkmarkets https://cypher-dark-market.com/ deep web sites
dark web search engines https://worlddrugsmarketplace.com/ deep web markets
darknet market https://world-drugs-market.com/ dark web market list
black internet https://worldonlinedrugs.com/ deep web drug links
tor market links https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ blackweb
dark web websites https://worlddarknetdrugstore.com/ dark market onion
dark market onion https://cypherdarkweb.com/ deep web drug url
best darknet markets https://heinekenoniondarkmarket.com/ deep dark web
After looking at a handful of the blog posts on your web site,
I seriously appreciate your way of blogging. I book marked it to my
bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future.
Take a look at my web site too and let me know what you think.
deep dark web https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ dark website
dark web link https://dark-market-heineken.com/ best darknet markets
deep web search https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ dark web access
darkmarket https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ black internet
deep web drug links https://heineken-onion-market.com/ darknet markets
MyBookie, as the name suggests, is the finest casino web page for sports and
racebooks.
Also visit my page here
tor marketplace https://heineken-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket link https://heinekendrugsmarket.com/ tor market links
darknet seiten https://cypher-marketplace.com/ drug markets dark web
dark web market https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ darkmarket url
tor darknet https://world-darkweb-drugstore.com/ dark web market links
dark websites https://heineken-drugs-online.com/ darknet site
tor marketplace https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ dark markets 2023
Looking for a pharmacy that offers generic Accutane? Check out pharmacy accutane for high-quality medications.
dark web market list https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ deep web links
tor markets 2023 https://world-online-drugs.com/ drug markets onion
darknet sites https://dark-market-world.com/ how to get on dark web
Whats up very cool website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?KI am satisfied to seek out a lot of useful information here in the put up, we want work out more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
https://propecia.pro/# how can i get generic propecia pill
darkweb marketplace https://world-drugsonline.com/ dark website
drug markets dark web https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ darknet websites
tor market links https://darkmarket-world.com/ dark web search engine
the dark internet https://darkmarketcypher.com/ dark market 2023
dark web market https://world-darknet-drugstore.com/ how to get on dark web
dark web market https://cypherdarkweb.com/ darkweb marketplace
dark websites https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet drugs
dark web search engine https://heineken-onion-darkweb.com/ best darknet markets
dark web access https://heineken-drugsonline.com/ dark market link
dark web sites links https://heineken-onion-darkmarket.com/ dark web site
darknet websites https://heinekenonlinedrugs.com/ dark web sites links
deep web links https://heinekendarkwebdrugstore.com/ dark market 2023
deep web drug store https://cyphermarketplace24.com/ darknet websites
deep web search https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ darknet market list
darknet seiten https://cypher-market-onion.com/ dark web market list
deep web sites https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ darknet market
dark market list https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ dark web links
deep web sites https://worldonionmarket.com/ darknet markets 2023
darknet market list https://darkweb-world.com/ darkmarket 2023
tor market https://cypherdarknet.com/ tor market
darknet drug store dark web drug marketplace
blackweb https://cyphermarket-link.com/ dark web websites
dark web site https://world-drugs-online.com/ darknet markets
darknet drug links https://dark-web-world.com/ drug markets onion
deep web links https://darkmarketcypher.com/ best darknet markets
Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this website regularly,
this site is really pleasant and the users are genuinely
sharing fastidious thoughts.
dark web sites https://worlddarkwebdrugstore.com/ free dark web
Is Accutane available in a 20 milligram capsule form? https://isotretinoinex.website/
dark market 2023 https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet site
darknet site https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ dark market list
Searching for accutane medicine buy for sale? Visit our website for unbeatable prices.
dark web sites https://cypher-markett.com/ dark web search engine
darknet site darknet markets
deep web drug store https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ deep web links
darknet links https://cypher-market-onion.com/ black internet
how to get on dark web https://darkmarketworld.com/ dark market link
dark market onion https://worldonionmarket.com/ dark web search engine
dark web site https://darkwebcypher.com/ darknet drugs
dark markets 2023 https://cypher-dark-market.com/ blackweb official website
free dark web https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ dark net
darkweb marketplace https://worlddrugsmarket.com/ darkmarket 2023
best darknet markets https://cyphermarket-link.com/ dark internet
tor dark web https://cypherdarkwebmarket.com/ dark markets 2023
dark web markets https://world-onion-darkweb.com/ darknet drug market
darknet marketplace dark web links
darknet market https://world-onion-market.com/ darknet seiten
dark market list https://cypherdarkweb.com/ dark market 2023
dark markets 2023 https://cyphermarketplacee.com/ onion market
darknet drug market https://cypherdarkmarketonline.com/ best darknet markets
deep web drug links https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ darkmarket
dark web markets https://darkwebworldmarket.com/ darkmarket list
https://dapoxetine.pro/# buy priligy
dark internet https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ darkmarkets
darknet drug links tor market links
tor darknet https://worldonionmarket.com/ dark web sites
dark web access https://cypherdarknet.com/ dark markets 2023
dark web access https://darkmarket-world.com/ darkmarkets
dark web websites https://world-drugsonline.com/ darkmarket 2023
darknet market https://cyphermarket-url.com/ tor darknet
dark net https://darkmarketcypher.com/ tor darknet
dark web link https://worlddarkwebdrugstore.com/ best darknet markets
Я просто не могу пройти мимо этой статьи без оставления положительного комментария. Она является настоящим примером качественной журналистики и глубокого исследования. Очень впечатляюще!
dark market link https://world-onion-darkmarket.com/ darknet drugs
dark web sites links https://cypher-markett.com/ dark web link
darkmarkets https://cypherdarkweb.com/ dark internet
darknet markets deep web drug links
dark web drug marketplace https://cypher-darkwebmarket.com/ dark web drug marketplace
darknet market list https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ onion market
dark market onion https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ dark markets 2023
dark internet https://cypherdarkmarketx.com/ tor marketplace
darkmarket link https://world-online-drugs.com/ deep web links
drug markets dark web https://world-onlinedrugs.com/ blackweb
dark web market links darkmarket list
deep web links https://worlddarknetdrugstore.com/ the dark internet
black internet https://darkmarketcypher.com/ deep web search
deep dark web https://cyphermarket-url.com/ darknet markets
tor dark web deep web links
darknet market list darknet marketplace
drug markets onion https://cypher-market-online.com/ tor dark web
darkmarket url darkmarket link
darknet site darknet site
deep web links https://cypherdarkmarketplace.com/ dark web sites
darknet market darkmarket
dark web site https://cypher-darkmarketplace.com/ drug markets dark web
Can Accutane be purchased online from reputable pharmacies? https://isotretinoinex.website/
dark web websites darkweb marketplace
At this time I am going away to do my breakfast, when having my breakfast coming yet again to read more news.
darknet market links black internet
dark net dark net
dark market link https://cyphermarket-darknet.com/ dark market list
tor market tor darknet
dark web sites tor market links
where can i buy accutane in nigeria accutane cream buy accutane online canada
deep web drug url https://cypher-darkweb.com/ darknet market lists
deep web drug links darknet search engine
free dark web darknet drug links
dark website https://darkmarket-cypher.com/ dark market onion
drug markets onion dark market url
onion market tor market links
darknet sites darknet seiten
dark internet https://world-darknet-drugstore.com/ dark markets 2023
dark market url darknet drug links
darkmarket url onion market
darknet market list https://cypher-darkmarket-online.com/ darknet search engine
darknet seiten tor darknet
deep web drug markets dark website
dark website darknet market links
free dark web darknet market links
deep web drug store darknet drug store
blackweb dark market
https://dapoxetine.pro/# dapoxetine
onion market best darknet markets
deep web markets dark market
darknet websites tor darknet
deep web sites darknet links
tor market dark web search engines
best darknet markets drug markets onion
darknet websites black internet
deep web links darknet drug market
deep web sites blackweb official website
tor dark web dark web search engines
dark web link dark markets 2023
darknet market list darkmarket link
dark web site deep web sites
dark web sites links dark web links
dark web search engines deep web markets
dark web site dark market link
dark web search engines deep web sites
darknet market list darkmarket
dark web drug marketplace dark web site
dark market link black internet
dark web market blackweb official website
tor markets links darkweb marketplace
deep web markets deep web drug markets
dark web websites dark markets 2023
dark market onion dark net
darknet links dark web access
best darknet markets dark web link
dark markets dark market link
dark web market links deep web markets
deep dark web dark web markets
blackweb dark market url
dark web market list dark markets
darknet search engine dark net
dark web market links deep dark web
dark web search engines deep web search
free dark web dark web link
darknet market lists dark markets 2023
dark web markets darknet markets
tor dark web dark web markets
how to access dark web darknet markets 2023
blackweb dark market onion
darknet marketplace tor marketplace
dark web link dark web search engines
dark market url dark web search engines
dark web access drug markets onion
dark website darkmarket
black internet darknet drug store
the dark internet tor dark web
dark websites deep web links
dark web links deep web drug store
how to get on dark web dark web market
deep web drug markets darknet market lists
darkmarket list blackweb
dark net dark website
tor marketplace how to access dark web
tor market url darknet drug store
onion market bitcoin dark web
darknet marketplace drug markets onion
Your nearest parter shop, come here
darknet market how to get on dark web
darkweb marketplace darknet links
deep web markets deep web drug url
dark market url darkmarket 2023
dark market deep web links
darkmarket url dark market onion
tor markets links deep dark web
blackweb official website onion market
dark market link deep web drug markets
dark web site darknet market lists
dark web links dark web websites
deep web sites deep web drug markets
darknet sites dark web search engines
darkweb marketplace tor markets 2023
dark markets 2023 deep web links
darknet drug links the dark internet
dark web market dark web market list
Thanks for the article really intresting would u visit our website on: Kampus terkemuka
Thanks for letting me comment on your website
blackweb official website darkmarkets
how to access dark web dark website
dark market link dark markets 2023
darknet seiten deep web links
darkmarkets dark web link
darknet market list drug markets dark web
dark market onion dark web market list
dark web search engine dark market
darknet seiten darkmarket link
dark market link tor market
tor markets deep web drug url
https://dapoxetine.pro/# priligy over the counter
blackweb darknet site
darknet search engine tor markets
deep web drug markets darknet market
darkmarket darknet market links
dark market list tor markets
darkmarket list darknet market lists
dark web sites tor darknet
darknet markets 2023 blackweb
deep web drug markets tor market links
dark web search engines dark market url
tor markets darknet markets
darknet market list darknet search engine
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such great info being shared freely out there.
drug markets dark web darkmarket link
blackweb dark web market
dark web search engine dark web site
dark web market darknet drug market
sky pharmacy online drugstore online pharmacy
deep web drug store darknet websites
dark web link dark website
deep dark web darknet markets 2023
deep web drug markets deep web drug store
tor markets 2023 deep web sites
darknet market list dark web search engine
online pharmacy canadian pharmacy viagra
darknet market links darknet market lists
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
blackweb dark websites
darknet seiten drug markets dark web
deep web links dark internet
dark markets darknet market
darknet market blackweb official website
dark web markets dark web market
deep web sites tor marketplace
deep web sites dark website
tor marketplace dark web drug marketplace
darknet search engine dark web search engines
dark web websites tor markets links
What is the recommended dosage of Accutane if it is 50 milligrams? https://isotretinoinex.website/
dark web market links dark market list
black internet darknet markets
the dark internet deep web drug store
darkweb marketplace tor market url
deep web drug links darknet site
dark web search engine deep web drug markets
darknet drug market dark web search engines
dark web markets bitcoin dark web
deep web drug links black internet
Curious about how to buy accutane online? Find out more at how to buy accutane online for detailed instructions.
darknet marketplace deep web sites
dark web sites the dark internet
drug markets dark web dark market 2023
dark web market dark market
tor market links darknet market links
drug markets onion deep web links
darknet market list darkmarket list
dark web search engines tor darknet
darknet marketplace darknet seiten
dark web market deep web drug links
blackweb darkmarket url
darknet seiten dark net
online pharmacy onlinepharmacy
dark web drug marketplace free dark web
how to get on dark web deep web drug markets
deep web links dark web links
deep dark web darknet markets
drug markets dark web dark internet
dark web access darknet drugs
deep web sites deep web drug url
the dark internet bitcoin dark web
dark web link darknet market links
darknet site darkmarket 2023
blackweb darknet seiten
dark web market dark internet
dark web sites dark web websites
darknet drug market the dark internet
dark web links blackweb official website
darknet markets tor darknet
darkmarket url tor marketplace
darkweb marketplace darknet links
deep web markets how to get on dark web
tor market links tor markets 2023
darknet market lists dark websites
dark market list dark web sites links
best darknet markets how to get on dark web
drug markets onion darknet links
dark web markets blackweb official website
darkmarket url tor market links
blackweb deep web drug links
darkmarkets dark markets
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
dark net dark market
dark web sites dark web market
darkmarket url dark market onion
Searching for low-cost accutane discount? Explore accutane discount for competitive deals and discounts.
https://kamagratabs.pro/# Kamagra Oral Jelly for sale
dark web market dark web sites
deep web drug markets darknet markets 2023
darkmarket 2023 darknet market lists
darknet drug market tor darknet
black internet drug markets dark web
dark web links darknet market list
deep web drug markets darknet search engine
deep web sites dark market 2023
how to get on dark web dark market
dark market url black internet
Looking to buy affordable accutane generic over the counter? Explore accutane generic over the counter for accessible purchasing options.
how to access dark web darknet drug links
tor market dark web access
dark web markets dark web search engine
drug markets dark web dark web sites links
bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
dark web market links deep web search
dark web links best darknet markets
drug markets onion blackweb
deep web markets darkmarket list
darkmarket link darknet drug market
tor markets dark web search engines
darkmarket free dark web
blackweb dark markets 2023
deep web drug store tor markets 2023
dark market onion deep web sites
deep web sites free dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet market list
dark markets 2023 dark web sites links
tor markets 2023 tor market links
darknet drug store onion market
black internet deep web sites
darknet market links dark market
darknet marketplace dark web search engine
best darknet markets dark web site
darkmarket 2023 dark web link
deep web links tor markets links
darknet markets tor markets
darknet site darkweb marketplace
how to access dark web dark web markets
tor markets links dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket link darknet market list
dark web site dark web search engine
dark web search engine tor market links
dark market list dark web drug marketplace
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/sk/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
darkmarket list deep web sites
darknet market lists dark markets
tor market dark net
darknet drug store dark web sites
dark web search engine darknet websites
blackweb how to get on dark web
how to get on dark web dark market url
deep web markets darknet market
darknet websites how to access dark web
tor markets bitcoin dark web
dark markets 2023 dark web market list
dark web links darknet markets 2023
bitcoin dark web darkmarket list
tor market darkmarket list
darkmarket free dark web
dark markets darknet market lists
how to get on dark web best darknet markets
dark market onion deep web links
tor darknet tor markets links
tor markets 2023 tor marketplace
dark web market deep web markets
darknet market lists tor market url
dark market 2023 dark markets 2023
tor market url darknet market
dark websites darkmarket
I can’t thank the author enough for this enlightening and thought-provoking article. It explores the topic from multiple angles and presents different perspectives, encouraging readers to think critically. The content is well-researched, and the arguments are supported by compelling evidence.
dark market onion darknet markets 2023
dark market onion dark market link
tor darknet darknet market links
deep web markets tor markets links
dark web drug marketplace darknet site
deep web drug store dark web market
dark markets darknet drug market
dark market 2023 darknet sites
darknet market list darknet market links
darkweb marketplace tor darknet
darknet site dark website
saxenda kopen
kopen sie saxenda De inhoud van generieke pillen en merkgeneesmiddelen is precies hetzelfde. Het enige verschil is de naam
drug markets dark web deep web drug markets
dark web site dark web sites
darknet market links dark markets
dark websites tor market url
darknet websites how to get on dark web
darkmarket url tor markets
https://kamagratabs.pro/# Kamagra Oral Jelly for sale
darkmarket link darknet search engine
tor market deep web drug store
tor market url deep web drug url
tor markets 2023 tor market links
dark web market list dark market list
dark internet dark market list
Genç Porno
dark net darknet market list
how to access dark web dark web access
dark web market tor markets
Hello there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if
you knew where I could get a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble
finding one? Thanks a lot!
dark web drug marketplace deep dark web
dark web link dark markets
darknet market lists dark web markets
darkmarkets deep web drug url
darknet site deep web drug markets
dark web sites dark web link
darknet site darkmarkets
onion market dark market onion
dark web websites blackweb
darkmarket darkmarkets
darkmarket link dark market link
This article exceeded my expectations in every way. The author’s ability to distill complex concepts into digestible nuggets of wisdom is remarkable. I found myself nodding along with each point and gaining a deeper understanding of the topic with every paragraph.
dark net deep dark web
darkmarkets darknet drug store
dark web site darkmarket list
dark market onion bitcoin dark web
how to get on dark web darkweb marketplace
dark market list darknet market list
deep web drug markets onion market
dark markets 2023 dark web access
dark web sites links darknet drug store
dark web websites dark websites
darknet drugs dark market onion
dark internet dark web websites
darknet links deep web drug url
Я чувствую, что эта статья является настоящим источником вдохновения. Она предлагает новые идеи и вызывает желание узнать больше. Большое спасибо автору за его творческий и информативный подход!
deep dark web darkweb marketplace
darkweb marketplace darknet market list
dark web markets deep dark web
dark market onion dark market url
tor market dark web access
deep web drug links deep web drug url
bitcoin dark web bitcoin dark web
darknet search engine darknet drug store
dark website drug markets dark web
dark market 2023 tor darknet
darknet links dark web market
darkmarket darkmarkets
Автор предоставляет подробные сведения и контекст, что помогает читателям лучше понять обсуждаемую тему.
deep web drug url tor market links
bitcoin dark web deep web links
darknet markets dark websites
darkmarket list darknet search engine
black internet the dark internet
blackweb dark market
dark web market darkmarket link
dark web market list deep web sites
darknet sites tor market
haktogel
haktogel
susu4d
dark web market darknet drugs
dark websites darknet market
deep web links tor dark web
dark market list darknet site
darknet drugs darknet market lists
dark markets deep web drug links
darknet marketplace drug markets onion
tor dark web darkmarket link
dark web links dark market link
dark web link deep web drug links
tor marketplace darknet drugs
tor dark web darknet market list
dark web site deep web drug markets
drug markets dark web dark markets
tor dark web the dark internet
tor markets links dark web search engine
darknet market links dark market list
dark market deep dark web
tor dark web darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web darknet markets 2023
deep web sites deep web search
deep web links darknet seiten
onion market dark web link
tor markets deep web drug markets
tor market url tor market
dark web sites dark website
darknet market links how to access dark web
drug markets onion deep web drug url
deep dark web darknet search engine
dark web link darknet search engine
deep dark web dark web search engines
darknet seiten dark market onion
darkmarket url deep web drug url
drug markets onion dark web sites
https://kamagratabs.pro/# kamagra
darknet drug market dark web search engine
dark internet tor market url
darknet market links the dark internet
tor darknet darknet markets
dark web site dark web markets
darknet drug store tor market links
dark web link deep web sites
tor market url darknet drug links
darknet drug links tor market url
dark web access tor marketplace
darknet sites dark market list
darkmarkets deep web markets
tor markets links darkmarket url
It is not my first time to pay a quick visit this web page, i am visiting this
site dailly and get good data from here daily.
dark web link deep web drug url
tor markets dark web link
dark website dark web websites
darkmarket url dark web search engine
free dark web darknet markets
tor darknet deep web sites
darknet market lists darknet drug store
darknet market lists darknet drug market
deep web search blackweb
blackweb official website tor dark web
Статья содержит обширный объем информации, которая подкреплена соответствующими доказательствами.
darkmarket 2023 how to get on dark web
darknet drugs dark web market links
dark web access darknet markets 2023
free dark web darknet market links
canadian pharmacy express healthy man viagra
dark web links darknet markets 2023
darknet market dark web site
tor dark web best darknet markets
dark website deep web links
online pharmacy no prescription zoloft
dark web drug marketplace darknet seiten
how to get on dark web darknet market
darknet search engine deep web search
dark web markets dark market
bitcoin dark web deep web markets
tor markets links deep web drug links
darknet drug store dark markets 2023
tor darknet dark market 2023
dark web drug marketplace onion market
darkweb marketplace dark web market
deep web links how to access dark web
tor market links tor markets links
dark net tor darknet
onion market dark web link
darknet market lists dark web market links
bitcoin dark web dark web websites
how to access dark web dark market 2023
blackweb dark web sites
tor marketplace drug markets dark web
Hello are using WordPress for your blog platform?
I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my
own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Информационная статья предлагает всесторонний обзор ситуации, с учетом разных аспектов и аргументов.
dark internet darknet drugs
darknet links dark market list
dark web site tor market
darknet market links tor market links
dark web access darknet site
darknet market darknet drugs
dark market 2023 dark market
dark market url deep web markets
dark web access darknet markets 2023
tor dark web best darknet markets
dark internet dark web site
dark markets 2023 darkweb marketplace
how to access dark web drug markets onion
dark market list darknet sites
darknet links dark web drug marketplace
darknet websites dark web websites
darkmarket list dark markets
blackweb official website darknet seiten
darkmarket list dark internet
dark web sites links blackweb official website
the dark internet tor markets 2023
dark web search engine dark web access
darknet drug links how to get on dark web
deep web drug store dark web access
darknet marketplace dark net
tor markets dark websites
darkmarket list dark net
dark web market dark market link
dark web websites bitcoin dark web
dark web site darknet market links
drug markets dark web darkmarket 2023
darknet markets 2023 dark web site
darknet search engine dark web search engines
the dark internet darkmarket link
darknet market lists dark web search engines
bitcoin dark web darknet site
darknet site dark market link
dark web market list darknet search engine
how to access dark web darkmarket list
https://propecia.pro/# how can i get cheap propecia for sale
dark web search engines dark web access
dark web sites links darkmarket link
tor markets 2023 darknet sites
darknet drug store tor markets
dark web search engine dark websites
deep web sites dark web search engine
dark web market links darknet site
dark market 2023 dark markets
darknet market list tor marketplace
darknet search engine dark web markets
dark market onion darknet websites
dark web links dark market 2023
dark internet dark web search engines
darknet market lists dark web sites links
dark net dark web websites
deep web links dark web markets
dark market url darknet market lists
free dark web deep web links
dark market 2023 deep web drug markets
dark market link how to get on dark web
deep web drug markets darkmarket 2023
how to get on dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark net dark websites
tor markets tor darknet
darknet market lists deep web drug store
dark market onion dark market list
deep web drug links dark web sites
dark web drug marketplace darknet market
darkmarket url blackweb
dark market onion darknet marketplace
dark market onion darknet site
darknet market list how to get on dark web
blackweb official website dark web market
dark web access free dark web
dark web search engines deep dark web
darknet marketplace tor market url
how to get on dark web tor dark web
dark web sites links how to access dark web
darkmarket 2023 darknet markets
darknet links dark websites
free dark web darkmarket list
dark web markets tor darknet
dark web search engines darknet markets
blackweb best darknet markets
darkweb marketplace dark market 2023
drug markets onion darknet site
darknet market links dark web drug marketplace
drug markets onion dark net
blackweb blackweb
deep web drug markets dark internet
how to access dark web darknet websites
how to access dark web dark internet
darknet search engine dark market url
darknet market links darknet drug market
dark market 2023 darknet markets
deep web sites deep web sites
tor marketplace dark web site
tor dark web dark websites
dark market onion darknet drugs
deep web sites dark web access
dark web access darknet market
darknet markets darkmarket
bitcoin dark web blackweb official website
darkweb marketplace darknet market list
darknet search engine darknet drug market
darknet links dark internet
dark web site dark websites
free dark web tor dark web
darkmarket list dark market list
darknet market darknet markets
娛樂城
娛樂城
dark website dark markets
娛樂城
darknet market links darknet seiten
dark market list dark web drug marketplace
dark web site darknet seiten
darknet drug store dark markets
how to access dark web black internet
best darknet markets how to get on dark web
tor markets 2023 the dark internet
deep web markets drug markets dark web
darknet search engine dark websites
Howdy this is kind of of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or
if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding experience
so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
deep web drug url how to get on dark web
https://dapoxetine.pro/# buy priligy
dark web market darknet search engine
dark markets 2023 darkmarket list
dark market 2023 bitcoin dark web
tor market how to get on dark web
dark web sites links dark internet
darknet websites dark web access
tor markets links tor markets links
drug markets onion tor markets links
dark web sites links deep web drug url
At this moment I am going away to do my breakfast,
afterward having my breakfast coming again to read further news.
tor markets darknet links
darknet drug links deep dark web
darknet websites dark market
darknet market links dark web search engines
dark market list dark internet
dark web access darknet market
drug markets onion darkmarket
darknet websites dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine darknet market list
dark web market list darkmarket list
deep web drug links darkmarket 2023
dark websites deep web drug url
tor markets deep web drug url
dark web market dark web sites links
darknet market dark web search engine
bitcoin dark web deep web drug links
free dark web darknet seiten
Автор предлагает практические советы, которые читатели могут использовать в своей повседневной жизни.
dark web sites links dark web market links
dark market list deep dark web
dark net dark web market links
darkmarket list dark web market
darknet market links deep web search
darknet drugs dark web sites
tor marketplace dark web links
tor market url darknet sites
dark web search engine dark web links
best darknet markets blackweb
tor markets 2023 darknet market lists
darknet seiten tor dark web
blackweb official website tor darknet
darknet site darknet seiten
tor markets dark web sites
dark web search engines deep web drug links
darknet market darknet seiten
Статья обладает нейтральным тоном и представляет различные точки зрения. Хорошо, что автор уделил внимание как плюсам, так и минусам рассматриваемой темы.
free dark web dark markets
darknet markets dark web search engines
darknet marketplace tor markets links
deep web drug links tor market
black internet how to access dark web
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
dark net dark web market list
Interested about the effects of 80 mg accutane daily? Visit 80 mg accutane daily to learn more.
darknet drugs dark web search engines
dark web search engines tor darknet
darknet drugs dark web search engine
darkmarket dark web access
darkmarkets deep web search
dark markets 2023 dark web sites links
tor market url tor marketplace
darkmarket 2023 dark web links
dark website the dark internet
deep web sites dark web access
darkmarkets darknet drug links
darknet marketplace dark web markets
dark markets 2023 deep web search
deep web markets dark web sites links
deep dark web tor dark web
dark websites black internet
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket
blackweb drug markets onion
darknet market list dark web market
black internet tor dark web
What are the common side effects of Accutane treatment? https://isotretinoinex.website/
dark web links tor markets links
Is there a higher dosage of 200 mg Accutane available for severe cases? https://isotretinoinex.website/
darknet marketplace tor dark web
how to access dark web darknet market lists
dark market url darknet links
the dark internet darkmarket 2023
https://kamagratabs.pro/# cheap kamagra oral jelly
deep web drug store black internet
darknet search engine dark internet
dark web access darknet drug links
deep web search dark websites
dark websites darknet drug market
blackweb blackweb official website
dark web links darkmarket 2023
bitcoin dark web dark web sites
deep web markets dark market url
the dark internet darknet market
What are the common side effects of using Accutane? https://isotretinoinex.website/
deep web drug links darkmarket link
deep web markets dark market
dark markets tor darknet
darknet drugs dark markets
deep web drug store dark website
deep web markets tor darknet
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
drug markets dark web dark web link
dark web sites darknet websites
darknet market links black internet
darknet search engine drug markets onion
darknet market dark web sites links
dark market url dark markets 2023
darknet drug store dark web market list
darknet market links how to get on dark web
dark market list darknet search engine
dark internet darknet seiten
deep web links tor darknet
What is the average cost of Accutane treatment? https://isotretinoinex.website/
darknet drug links dark internet
darknet links darknet markets
dark websites dark web site
dark web sites links how to get on dark web
tor dark web deep web markets
tor dark web darknet drugs
darknet drug links dark website
dark market url dark web search engines
dark net free dark web
deep web drug links darkmarkets
blackweb official website dark web search engine
Please let me know if you’re looking for a
article writer for your blog. You have some really great articles and I feel I would be a good
asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d absolutely love to write some content for your blog in exchange
for a link back to mine. Please send me an e-mail if interested.
Cheers!
deep web search darknet market lists
tor marketplace darkmarket 2023
tor market best darknet markets
dark web link free dark web
tor markets 2023 black internet
drug markets onion darknet drug market
price of accutane in mexico accutane acne
deep web sites dark net
dark web market links tor markets
darkmarket link dark web search engines
darkmarket 2023 dark web drug marketplace
dark market url tor market url
darknet market lists darknet market list
darkweb marketplace darknet market links
dark websites tor market
deep web sites tor darknet
deep web drug markets deep dark web
darknet market tor markets
dark web market list dark market 2023
how to get on dark web tor darknet
dark web links tor dark web
darknet drug store dark web market links
dark market 2023 deep web drug store
darknet sites free dark web
dark web drug marketplace best darknet markets
dark market url tor market url
darknet drug links drug markets dark web
tor darknet dark web drug marketplace
tor darknet dark market list
dark web markets darknet market
blackweb black internet
deep web search dark web search engine
darknet links tor market links
https://indiameds.pro/# buy medicines online in india
dark market 2023 darkweb marketplace
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
deep web markets dark web site
darknet seiten darkmarket 2023
best darknet markets onion market
dark web search engines deep web sites
darknet market links dark market onion
tor markets 2023 deep web markets
tor market links deep web markets
tor markets links dark web websites
tor markets 2023 drug markets onion
deep web search dark web links
darkmarket 2023 dark web access
darknet market list drug markets onion
https://whyride.info/ – whyride
dark web sites deep web drug markets
deep web drug markets tor market
dark market 2023 bitcoin dark web
darkmarket darknet markets
darknet drugs darknet markets
dark markets 2023 tor markets 2023
dark markets 2023 dark market url
darknet markets darkmarkets
dark market link deep web markets
dark web sites dark websites
dark website free dark web
tor darknet dark web sites links
tor markets 2023 darknet websites
darkmarket link dark market
deep web search deep web drug store
how to get on dark web tor market url
darknet seiten tor markets
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket url
tor markets links dark websites
deep dark web dark web links
dark markets drug markets dark web
darknet site darknet drug market
tor markets links darknet seiten
tor market links tor markets 2023
dark web websites dark web access
deep web drug url dark markets
deep web drug store dark web sites
darknet site how to get on dark web
drug markets dark web dark web market list
dark web market links darkmarket
dark web markets bitcoin dark web
I’m genuinely impressed by the author’s expertise and the level of detail in this article. It’s evident that they have a deep understanding of the subject matter and have conducted thorough research. The inclusion of additional resources and references is a great bonus for readers who want to explore further.
darkmarkets tor market
darkmarket bitcoin dark web
dark web market links darknet search engine
dark web links tor markets links
tor markets links darknet markets 2023
drug markets onion dark web drug marketplace
Я хотел бы подчеркнуть четкость и последовательность изложения в этой статье. Автор сумел объединить информацию в понятный и логичный рассказ, что помогло мне лучше усвоить материал. Очень ценная статья!
black internet tor marketplace
drug markets onion tor markets links
darkmarkets darknet drug store
deep web sites onion market
black internet tor market
Автор статьи предоставляет информацию в понятной форме, избегая субъективных оценок.
tor markets 2023 deep web drug markets
drug markets onion dark web market links
darknet sites dark web sites
darkmarket 2023 dark web links
dark web sites darknet drug links
dark markets 2023 dark websites
darknet site dark market onion
dark web sites tor dark web
free dark web tor market
dark markets 2023 deep dark web
dark market list darkmarket link
dark web links darknet market
dark web market links tor markets
dark web access darknet seiten
darknet site darknet drug store
darkmarket list darknet drugs
http://canadapharmcertified.pro/# reputable canadian online pharmacies
dark web sites dark web market links
darknet search engine darknet market links
darknet drugs dark market 2023
deep web drug markets dark market 2023
darknet market dark internet
darknet market the dark internet
dark web markets deep web markets
tor markets links dark websites
tor markets 2023 darkweb marketplace
dark web market darknet drug market
darknet site darknet site
deep dark web free dark web
dark market list darknet market lists
darkweb marketplace tor darknet
darknet websites darkmarket 2023
best darknet markets dark net
deep web drug markets dark markets 2023
dark market link tor markets links
darknet market links deep dark web
darkweb marketplace tor markets links
darkmarket url dark internet
dark web search engines darknet drug market
darknet market lists deep web search
darknet drug links dark web market
darkmarket link darknet links
tor markets links black internet
Автор статьи предоставляет информацию в понятной форме, избегая субъективных оценок.
dark web access dark web site
dark market 2023 tor markets
dark web drug marketplace drug markets onion
dark web search engine tor markets 2023
tor market url how to get on dark web
dark web search engine deep web drug markets
darknet sites darknet market list
darknet markets 2023 darkmarket 2023
black internet tor market links
darknet drugs darknet links
deep web links darknet market links
dark web links dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace darknet markets 2023
dark web sites darkmarket
dark net dark web drug marketplace
deep web search blackweb
darknet drug links dark markets 2023
dark net dark web search engines
deep web drug markets dark web market list
dark market dark web market
dark markets free dark web
dark web search engines darkmarket link
blackweb darknet drug market
onion market dark net
hello!,I love your writing very much! proportion we be
in contact more about your article on AOL? I require an expert on this area to solve my problem.
Maybe that’s you! Looking ahead to peer you.
tor market links darkmarket link
blackweb bitcoin dark web
drug markets onion darkmarket 2023
tor market darknet links
dark web sites links dark market link
dark net dark web drug marketplace
the dark internet darkmarket url
dark web markets darkmarket url
dark web markets darknet market lists
where can i get accutane online accutane purchase online uk cheapest pharmacy for accutane
dark market darknet market links
darkmarket 2023 dark website
darkmarket darknet drug links
darkweb marketplace free dark web
dark web access dark internet
darknet drug market dark market link
tor markets 2023 darknet websites
dark websites deep dark web
dark web search engine how to get on dark web
tor marketplace dark markets
darknet seiten dark markets 2023
deep web drug links dark web markets
blackweb official website darknet market
darkmarket list dark web market
deep web drug markets deep web drug store
blackweb official website dark web links
bitcoin dark web dark market link
tor darknet tor markets 2023
bitcoin dark web the dark internet
blackweb darknet drug store
dark web site dark market onion
darknet websites tor market url
accutane uk cost accutane over the counter uk
how to access dark web dark market 2023
dark web site dark website
darkweb marketplace dark internet
darkmarket link deep web drug markets
darkmarket list the dark internet
bitcoin dark web how to get on dark web
dark web market the dark internet
dark internet deep web sites
dark web market links dark market onion
onion market dark web access
darkmarket url dark web markets
tor markets deep web drug store
dark web market list darknet market links
deep web drug url blackweb official website
dark markets darknet drugs
darknet site darknet market lists
dark web market links tor market url
darknet market darknet drugs
tor darknet darknet market links
dark markets 2023 tor markets
darknet market darknet seiten
the dark internet darknet sites
dark market 2023 darknet websites
dark web sites dark web market list
dark web market tor market links
deep web markets dark web search engine
darkmarkets drug markets dark web
black internet blackweb
dark market darknet market
tor market links drug markets dark web
darkmarket list dark websites
dark market list dark web market
darkmarket url dark web market links
tor markets 2023 dark web sites
deep web search deep web drug markets
dark web site dark market list
blackweb best darknet markets
Статья предлагает разнообразные точки зрения на тему, предоставляя читателям возможность рассмотреть различные аспекты проблемы.
how to get on dark web best darknet markets
http://mexicanpharmacies.pro/# mexican rx online
free dark web deep web markets
darkmarkets dark web links
dark market 2023 darknet markets
dark market list dark markets 2023
darknet market dark web search engines
blackweb official website darknet sites
how to access dark web darknet marketplace
darknet sites deep web links
tor marketplace best darknet markets
darknet drug links bitcoin dark web
dark web market links drug markets dark web
darkmarket link darkmarket
darknet market list blackweb
Hi there! I simply would like to offer you a huge
thumbs up for the great information you have got right here on this post.
I will be returning to your web site for more soon.
dark web link dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket 2023 dark web market list
darknet sites tor markets 2023
tor market url darknet market lists
darknet market links deep web sites
darknet markets darknet links
darkweb marketplace deep web markets
darknet sites darknet seiten
deep web links darknet market links
darknet drug store darknet drug links
deep web markets darknet websites
deep web sites deep web markets
bitcoin dark web darknet markets
dark market onion dark web site
darknet links deep web drug url
tor market url best darknet markets
tor markets 2023 darknet search engine
dark web site tor dark web
dark website darknet drug store
darknet drug links dark web search engine
darknet market lists deep web drug url
Я нашел в статье несколько интересных фактов, о которых раньше не знал.
dark website dark web links
darkmarket list darknet links
darknet marketplace tor market url
dark market 2023 dark net
tor market url darknet market list
blackweb official website dark market list
dark market 2023 onion market
deep web search dark net
Я хотел бы выразить свою благодарность автору за его глубокие исследования и ясное изложение. Он сумел объединить сложные концепции и представить их в доступной форме. Это действительно ценный ресурс для всех, кто интересуется этой темой.
deep web drug links darknet market links
darknet drugs dark web links
darknet market darknet market links
dark web access darkmarket link
dark web links darkmarket list
dark market list deep web drug store
tor marketplace deep web drug url
dark markets blackweb official website
darkmarkets dark markets 2023
blackweb official website tor markets 2023
darknet market links tor market url
deep web drug links darknet market links
deep web search dark web link
black internet tor darknet
dark web site dark market link
blackweb darknet search engine
darknet drug market tor market links
darknet websites dark web market list
darknet markets dark net
darknet sites deep web drug store
dark web drug marketplace blackweb
dark web search engines tor darknet
darknet drug links dark markets 2023
free dark web free dark web
dark market onion tor market url
dark net dark web link
Автор представляет альтернативные взгляды на проблему, что позволяет получить более полную картину.
tor market links darknet websites
dark web site dark web access
dark web websites dark web markets
darknet drug store deep web drug links
dark net darkmarket 2023
darknet site drug markets dark web
darknet market list deep web drug markets
darknet market links darknet drugs
If you desire to increase your familiarity only keep visiting this website
and be updated with the latest news posted here.
bitcoin dark web darkmarket list
Fantastic web site. Lots of useful info here. I’m sending
it to several friends ans additionally sharing in delicious.
And of course, thanks for your sweat!
dark net best darknet markets
dark markets 2023 dark web markets
tor darknet darkmarket url
how to access dark web how to access dark web
I know this site gives quality based posts and extra data, is
there any other web site which provides such things in quality?
darkmarkets tor darknet
http://indiameds.pro/# world pharmacy india
dark internet dark websites
darkmarket link darknet marketplace
dark website dark market url
deep web drug url darknet websites
tor darknet darkmarket list
the dark internet darknet markets
darknet market list dark web sites links
deep web drug url tor markets 2023
dark market link tor markets 2023
dark web markets dark website
dark web market list dark markets
darknet sites dark market link
deep web drug store darkmarket url
darknet drugs the dark internet
dark web links darknet market list
dark web drug marketplace darknet drugs
dark web link deep dark web
dark web market links tor market
darknet drug store deep web drug url
darknet seiten dark market list
darknet market list darknet links
dark web drug marketplace dark web links
dark market url dark web search engine
darknet market list onion market
blackweb official website darknet search engine
deep web drug links darknet seiten
bitcoin dark web free dark web
darknet drugs darkmarket
dark web market links bitcoin dark web
dark web search engines dark market url
dark web search engines how to get on dark web
deep web sites darkmarket list
how to access dark web dark web link
deep web drug links darknet marketplace
dark web access dark web markets
tor market links dark websites
tor market url darkmarkets
dark web market links deep dark web
deep web markets tor market url
deep web drug url how to get on dark web
dark web sites dark market onion
how to access dark web dark web websites
dark markets 2023 dark internet
dark internet darknet websites
dark web market list tor market links
darknet drug store tor darknet
the dark internet darknet markets 2023
dark market link dark market link
dark markets 2023 darknet drug links
tor darknet darknet websites
drug markets onion deep web links
darknet marketplace blackweb official website
dark website dark web link
dark market link blackweb
dark market list tor markets 2023
blackweb official website dark web search engine
dark web search engines dark web search engines
the dark internet darkmarket url
dark market link darknet sites
tor market onion market
I seriously love your blog.. Pleasant colors & theme.
Did you make this web site yourself? Please reply
back as I’m trying to create my own personal site and would like
to learn where you got this from or exactly what the theme is called.
Kudos!
deep web drug markets darknet markets
dark web sites dark market 2023
darknet links dark web websites
darknet websites darknet search engine
bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
dark net deep dark web
dark web market darkmarket
dark web markets darknet links
tor dark web tor darknet
dark market list black internet
darkweb marketplace how to get on dark web
drug markets onion best darknet markets
darkmarket list deep web drug url
darknet drug links dark web link
deep web sites darkmarket link
娛樂城
娛樂城
https://mexicanpharmacies.pro/# best online pharmacies in mexico
deep web sites dark websites
dark web site dark net
darknet drug market deep web sites
dark web search engine darknet site
deep web markets free dark web
dark web links deep web drug links
dark web websites deep web drug links
darknet market links dark web search engines
tor market links deep web drug markets
darkmarket list dark market list
dark web search engines darknet sites
darkmarkets dark web link
darknet marketplace best darknet markets
darkmarket list deep web sites
dark market darknet seiten
deep web markets darknet seiten
dark market how to access dark web
dark market link dark web market list
darknet sites darknet sites
deep web drug url deep web drug url
dark web websites dark website
deep web drug markets darknet links
tor market url darknet links
tor marketplace best darknet markets
dark web markets darknet websites
tor market dark web links
darknet drugs dark market
darknet drug market dark net
dark markets 2023 tor market
the dark internet deep web drug store
tor markets darknet search engine
darkmarkets tor markets links
deep web drug store tor market
dark market link dark net
deep web sites deep web drug store
darknet markets 2023 dark websites
dark web access dark web sites
tor dark web dark web market list
darknet drug store dark markets 2023
darknet site darknet marketplace
darknet drug market deep web drug markets
tor dark web dark internet
darknet sites darknet market list
dark web links dark web markets
http://mexicanpharmacies.pro/# mexican mail order pharmacies
dark web link darknet drug market
darknet links dark website
darknet websites tor darknet
tor market best darknet markets
darknet market tor markets 2023
bitcoin dark web deep web markets
dark market list dark internet
Я рад, что наткнулся на эту статью. Она содержит уникальные идеи и интересные точки зрения, которые позволяют глубже понять рассматриваемую тему. Очень познавательно и вдохновляюще!
darknet market list tor market url
tor market links dark markets 2023
darknet market list deep web drug links
darkmarket link darknet sites
darknet market lists darknet links
darknet search engine blackweb
how to access dark web darknet links
deep web drug store dark market list
deep web drug markets darknet sites
best darknet markets deep dark web
dark web markets dark web websites
blackweb official website deep web search
tor markets 2023 dark web link
deep dark web dark net
blackweb official website darknet market lists
deep web drug store darknet drugs
deep web sites darknet drug market
dark market deep dark web
darkweb marketplace darknet market
tor market url tor market links
tor markets darkmarket url
darknet market lists blackweb
darkmarket 2023 deep web search
drug markets dark web dark internet
deep dark web darknet markets 2023
darknet market list the dark internet
how to get on dark web dark market list
darknet sites blackweb
dark web site darknet marketplace
darkweb marketplace tor dark web
dark market 2023 drug markets dark web
shop online
dark net darknet markets
deep web markets dark internet
deep web drug links drug markets dark web
black internet tor marketplace
deep web drug url darknet marketplace
deep web markets dark market
dark web access darknet search engine
darknet sites dark web search engines
dark web market list dark web websites
deep web drug url dark web search engines
darknet markets 2023 dark web market
dark web market dark markets 2023
tor markets links darknet drug market
dark web links darkmarket url
darkweb marketplace deep dark web
tor market dark web search engines
tor market dark web market links
tor markets 2023 tor dark web
dark web market links deep web drug links
dark market link deep web search
dark web sites dark web markets
blackweb deep web sites
dark web link dark web search engines
darkmarket 2023 bitcoin dark web
tor market url dark market onion
darknet drug links dark web access
free dark web drug markets dark web
dark web search engines free dark web
darknet marketplace dark market list
darknet search engine darknet market list
free dark web dark markets
darknet marketplace deep web drug store
darknet site tor market
tor market blackweb official website
darkweb marketplace dark web search engine
blackweb darknet market lists
bitcoin dark web dark market link
dark web link darknet drug links
darkmarket url dark market onion
darknet seiten dark web market list
darknet marketplace darknet market list
dark websites deep web drug store
dark market url tor market url
darknet links dark web drug marketplace
dark net darknet links
dark markets dark market
tor darknet tor market links
http://canadapharmcertified.pro/# canadian pharmacy 24 com
dark market url darkmarket 2023
dark web search engines darkmarket 2023
dark web market blackweb official website
tor dark web darkmarket link
drug markets onion tor market
dark web market links darknet drug store
dark net darkmarkets
darknet market lists free dark web
darkmarket dark markets
dark web websites darknet drug market
dark markets dark website
blackweb official website free dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug links
dark web sites links darknet marketplace
deep web search onion market
darknet drugs dark web search engine
Keep up the wonderful work, I read few blog posts on this website and I believe that your blog is very interesting and contains lots of wonderful information.
dark web markets dark web search engines
dark web sites links darknet sites
darknet sites dark web websites
deep web search dark web market list
darknet search engine dark markets 2023
dark web sites onion market
darknet marketplace deep web markets
free dark web dark market list
darkmarket 2023 dark web links
darkmarket 2023 darknet market lists
dark web site dark websites
drug markets dark web darknet websites
deep web sites tor market links
darknet market dark markets
dark web websites deep web drug store
dark market list deep web search
free dark web darknet search engine
darknet market lists tor markets links
darknet drug store dark web search engine
darknet market list dark web links
darknet websites black internet
drug markets dark web tor markets
deep web links dark net
deep web drug store darknet sites
drug markets onion darknet drug market
deep web drug links dark market
darkmarket 2023 darkmarket
darknet drug store darknet seiten
how to get on dark web deep dark web
drug markets onion black internet
tor market links dark market onion
tor darknet darknet drug links
dark website darkmarket url
Its such as you read my thoughts! You seem to know so much about this,
like you wrote the e-book in it or something. I think that you
just can do with some percent to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, that is wonderful blog.
A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
darknet seiten darkmarket list
Great blog here! Also your website so much up fast! What host are you the use of? Can I get your associate link on your host? I desire my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
dark web market darknet seiten
dark web market drug markets onion
deep web drug markets darkmarkets
deep web drug markets darknet marketplace
darknet seiten deep web search
tor market links deep dark web
dark websites dark web sites links
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back later on. Many thanks
Демонтаж стен Москва
dark markets 2023 tor dark web
drug markets onion darknet site
how to access dark web dark market onion
darknet drugs tor marketplace
dark market list tor markets links
darkmarket link onion market
dark web search engines onion market
darknet market links deep web drug markets
darkmarkets deep dark web
darkmarket deep web drug links
deep web drug url dark web sites links
tor market url dark markets 2023
deep dark web darknet drug market
deep web drug url dark markets 2023
dark web link dark web search engines
deep web links darknet drug links
onion market dark web links
tor market dark web sites links
darknet drug market darkmarket 2023
the dark internet tor market url
dark web search engine how to get on dark web
dark market 2023 darkmarket 2023
dark market link dark market 2023
darknet drugs dark web site
darknet market deep web sites
dark web links tor market
darknet marketplace darkmarket 2023
darkmarket darknet drug market
darkmarket list tor market url
darknet drugs dark market
dark market onion dark web access
darknet seiten dark web market links
https://canadapharmcertified.pro/# canadian pharmacy online ship to usa
tor market links black internet
darknet market deep web sites
tor market dark market onion
deep web markets dark web sites
darkmarket url darknet websites
darknet seiten darkweb marketplace
dark market onion darknet market links
dark web market black internet
deep web links best darknet markets
dark web market dark market onion
deep web drug store darknet websites
darknet markets drug markets onion
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug links
tor markets darkmarket url
darkweb marketplace deep web drug markets
dark website darkmarket link
darknet market lists dark web link
deep web sites darknet links
best darknet markets tor market
deep web search darknet site
dark internet dark web sites links
tor marketplace deep web drug markets
dark market bitcoin dark web
dark web markets dark web site
bitcoin dark web deep web drug markets
dark net dark web market
tor markets 2023 black internet
darknet market links tor markets links
dark web search engine darknet market links
tor darknet tor marketplace
free dark web darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet drug market
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug links
darkmarkets darknet search engine
darknet search engine free dark web
deep web markets tor market url
dark web search engine dark market list
deep web drug url dark market onion
dark web search engines tor markets 2023
best darknet markets darknet search engine
dark market darknet market
darknet marketplace dark net
best darknet markets darknet drug store
darknet drug market tor marketplace
darknet drugs darknet seiten
darkmarket list deep web drug links
dark markets 2023 free dark web
blackweb official website darknet marketplace
darknet markets tor market links
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
dark web links dark web site
tor markets links dark web market
how to access dark web dark web market
deep dark web tor market url
darknet links dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists darkmarkets
dark web link dark web link
dark web market deep web drug links
dark net the dark internet
darkmarket 2023 dark web site
darkmarket url dark web links
darkmarkets how to access dark web
darknet markets darkmarket url
dark markets free dark web
how to access dark web darknet market
tor market url tor markets 2023
free dark web blackweb
dark web site darkmarket 2023
dark web sites black internet
darknet markets dark market
darknet links darkmarket 2023
Демонтаж стен Москва
darknet drug market darknet seiten
dark market link dark web site
onion market darkmarket link
dark net darknet market list
deep dark web deep web drug links
dark web access darknet drug links
darkmarket list tor dark web
deep web markets dark web site
deep web sites dark net
tor dark web tor darknet
deep web drug store tor markets
darknet sites drug markets dark web
the dark internet dark web market list
tor market darknet market lists
dark web links deep web drug store
dark web sites links darkmarkets
https://canadapharmcertified.pro/# canadian compounding pharmacy
darknet drug store dark markets
tor market links dark market list
deep web links darkweb marketplace
darknet drug store dark market onion
how to get on dark web dark markets
dark web search engines dark web market links
dark web sites blackweb official website
darkmarket list tor marketplace
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your article
post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
darknet market free dark web
darknet market list the dark internet
tor markets links dark market link
darkweb marketplace dark website
deep web drug store deep dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet market lists
darknet drug store dark web websites
dark market darkmarket link
dark markets darknet site
dark web site the dark internet
купить бетон в подольске с доставкой
darknet drug store darknet drug links
darkmarket darkmarkets
onion market darknet drug market
darknet market dark web market
darknet links darknet search engine
dark market link deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web dark web market links
tor market links darknet drug store
dark web site how to get on dark web
dark web sites dark web market links
dark websites dark market 2023
darknet websites darknet market links
tor marketplace darknet links
tor markets deep web drug links
darkmarket url dark market url
tor marketplace bitcoin dark web
dark web market links bitcoin dark web
darkmarket url darknet drug links
darkmarket link dark web sites
drug markets dark web deep web links
deep web links darkmarket
darknet drug links darknet drugs
black internet dark website
darknet marketplace tor marketplace
deep web links tor market links
tor markets dark market link
darknet market tor markets links
dark web market list tor dark web
tor marketplace dark web websites
deep web markets bitcoin dark web
dark markets darknet drug links
deep web markets dark market url
dark web sites links dark market
darknet seiten darknet markets
dark web access blackweb
darknet drug links dark web sites
CandyMail.org – это сервис анонимной электронной почты, который предоставляет пользователю возможность отправлять и получать сообщения без раскрытия личности.
dark web sites links onion market
darkmarket deep web drug links
darknet markets 2023 dark web site
darkmarket url dark web market links
dark web drug marketplace tor market
deep web drug url darknet drug links
darknet drug market darkmarket url
darknet market links dark web search engine
dark web sites darknet markets 2023
dark web site darknet sites
tor market url dark web links
darknet market links blackweb official website
dark web link deep web drug store
deep web links darkmarket link
deep web drug markets best darknet markets
deep web drug store darknet drug links
darknet drugs dark web markets
dark market link darknet market links
dark web search engines drug markets onion
Roof flashing repair
dark web sites links darkmarket url
dark internet darknet market
deep web drug links drug markets dark web
dark market 2023 dark web market list
dark market onion drug markets onion
drug markets dark web dark web links
dark markets 2023 darknet drug market
tor market url dark web markets
Демонтаж стен Москва
dark web sites deep web drug markets
darknet market list dark web websites
darknet drugs darknet market
dark web site darknet market lists
dark web links darknet drug market
dark web websites black internet
dark websites dark website
drug markets onion darknet marketplace
tor market url darknet market
darknet search engine darkmarket 2023
tor marketplace deep web drug store
deep web drug links tor markets
dark web link dark web websites
tor market links dark net
deep web drug store dark web market
deep web drug url bitcoin dark web
black internet deep dark web
best darknet markets deep web search
darkmarket 2023 blackweb
dark net dark web websites
tor markets 2023 darkmarkets
blackweb official website darknet site
deep web drug url deep web links
darknet drugs darknet links
bitcoin dark web blackweb official website
dark web link darkmarket
darknet market list bitcoin dark web
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog in Firefox, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
bitcoin dark web darknet markets 2023
dark market how to get on dark web
darknet site onion market
darknet drug links darknet markets 2023
tor market deep web markets
best darknet markets drug markets dark web
darknet market lists darknet drug links
darknet search engine blackweb
tor darknet darkmarket list
darknet marketplace darkweb marketplace
dark web sites tor market links
darknet markets darknet market links
darkmarket link tor market url
deep web search darknet marketplace
darknet market dark website
dark market list darknet drug links
tor dark web deep web links
blackweb tor markets 2023
dark web links tor darknet
dark web sites deep web drug store
dark websites tor darknet
blackweb dark web access
darknet market links darknet marketplace
blackweb official website dark market link
drug markets dark web dark web site
deep web search darknet drug links
dark market 2023 darknet websites
dark markets 2023 dark market url
dark website darkmarket
dark web search engines dark web websites
darknet search engine dark web drug marketplace
darkmarkets how to access dark web
tor darknet darknet market links
http://sildenafilpills.pro/# sildenafil canada where to buy
deep web search tor marketplace
tor markets dark web search engine
darknet websites deep web search
darknet drugs dark market
dark markets dark web access
It’s really very difficult in this full of activity life to listen news on TV,
so I just use internet for that reason, and take the newest information.
dark market how to get on dark web
best darknet markets dark web sites
best darknet markets darknet drug store
deep web search blackweb
dark web access deep web drug links
dark markets 2023 darkmarkets
darknet websites deep dark web
how to access dark web dark website
free dark web how to get on dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet search engine
darknet market list dark net
darkmarket tor market links
darknet markets tor dark web
darkmarket 2023 dark net
dark website dark market list
darknet marketplace blackweb
darknet marketplace how to access dark web
dark market link deep web drug store
darknet site drug markets dark web
dark internet dark web links
darknet markets 2023 bitcoin dark web
tor marketplace darknet drug store
darknet drug links deep web drug links
darkmarket link dark market onion
dark web links dark web markets
bitcoin dark web darkmarket
dark web search engines tor market links
darknet drug store darknet sites
dark market url dark websites
deep web sites dark web markets
darknet market list darknet drug store
deep web drug store darkweb marketplace
deep web drug store darknet market lists
deep web drug markets tor markets 2023
dark market onion tor darknet
Tuan88 merupakan salah satu situs slot online terbaik di Indonesia di tahun 2023 yang memberikan tawaran, bonus, dan promosi menarik kepada para member.
dark web site the dark internet
dark market 2023 black internet
dark market darkmarket list
darkmarket link dark web search engines
dark web search engines dark web links
dark market list darknet links
onion market black internet
dark web drug marketplace dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets 2023 the dark internet
dark market link darknet sites
dark web market links tor markets
deep web links dark market link
darknet markets darkmarket list
deep web links tor markets links
blackweb dark markets
dark web access dark web search engine
dark web markets dark web market links
darknet drug links dark markets 2023
darknet markets 2023 darkmarkets
how to access dark web tor marketplace
darkmarket list deep web search
darknet links dark web access
darknet sites darknet links
deep web drug links dark web search engine
darknet links drug markets onion
darknet market links darknet market list
darkmarket list dark web site
thanks post
how to get on dark web dark websites
dark web market links tor marketplace
darkmarket link how to access dark web
tor dark web darknet websites
darkmarket list dark web market
deep web drug markets darknet drugs
dark web access darknet markets 2023
tor market url darknet drugs
tor market darknet search engine
dark web websites darknet websites
darknet sites black internet
black internet tor market
dark markets 2023 darkmarket list
darknet marketplace tor dark web
darkmarket url darkmarket
dark web sites drug markets onion
tor marketplace tor marketplace
deep web drug url tor markets links
best darknet markets darknet markets 2023
black internet darkmarkets
dark market onion darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web darknet market
onion market onion market
onion market darknet markets
dark web markets dark web markets
tor darknet darknet drugs
dark web links deep web sites
darknet site deep web markets
deep web drug links deep web drug url
bitcoin dark web darkmarket list
darkmarket url deep web sites
Disposable Email Addresses: CandyMail.org also offers disposable email addresses, allowing users to create temporary aliases for specific purposes. These addresses can be used to sign up for online services, forums, or any situation that requires an email address but may pose a risk to privacy. With disposable email addresses, users can protect their primary email accounts from unwanted spam or potential data breaches.
tor markets blackweb
dark web search engines darknet drug store
dark web markets dark market link
darknet markets tor marketplace
tor dark web dark web link
https://edpill.pro/# ed medication online
tor markets darknet markets
blackweb official website dark website
darknet seiten tor market links
tor markets 2023 dark web drug marketplace
dark web market links tor dark web
darknet links dark web market links
dark market onion dark web links
darknet drug market dark web site
dark net blackweb
darkmarket 2023 dark web search engines
darknet market lists tor markets 2023
deep web drug url dark market 2023
dark net tor dark web
darknet drug market darknet drug market
dark markets deep web markets
darkmarket 2023 how to access dark web
dark web access dark web links
tor markets 2023 blackweb official website
tor dark web darknet search engine
dark market deep web drug links
deep web sites darknet search engine
dark web markets dark web market list
darknet markets 2023 darkmarket list
deep web drug url darknet links
bitcoin dark web dark internet
deep web links darknet marketplace
dark website tor market links
tor marketplace deep web search
blackweb darknet drug market
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
free dark web dark market onion
drug markets dark web dark internet
dark website dark web search engine
dark web links best darknet markets
slot tuan88
Tuan88 merupakan salah satu situs slot online terbaik di Indonesia di tahun 2023 yang memberikan tawaran, bonus, dan promosi menarik kepada para member.
darknet site deep web drug links
deep dark web dark web access
darknet links dark web market list
darkmarket list tor markets links
blackweb drug markets onion
dark market list darkmarket list
dark market list tor marketplace
darknet markets darkmarket
best darknet markets darknet market
dark web market links how to access dark web
dark net dark web access
tor market dark web markets
deep web drug markets the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket 2023
how to get on dark web darkmarket list
darknet drug store darknet market links
drug markets onion deep web drug url
deep web drug markets deep web search
drug markets onion dark markets
darkmarket darknet sites
black internet dark market 2023
black internet dark web access
darkmarket url darknet drug store
deep web markets darknet search engine
darkmarket link deep web links
dark web link tor dark web
pharmacy online canadian pharmacy cialis canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
dark web search engine dark market url
deep web links dark net
drug markets onion dark web markets
darknet market list darkmarkets
dark market link darkmarkets
dark web websites dark web drug marketplace
dark market dark web market list
the dark internet darkmarkets
darkmarket 2023 dark website
tor marketplace tor market
dark web links darkmarket url
drug markets dark web deep web sites
deep web links deep web search
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
https://sildenafilpills.pro/# sildenafil mexico online
dark markets 2023 drug markets onion
dark market link dark web links
It’s remarkable to go to see this site and reading
the views of all friends concerning this paragraph,
while I am also zealous of getting experience.
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how
can we communicate?
dark web access tor markets links
dark web drug marketplace dark web drug marketplace
dark web websites darknet markets 2023
dark web access how to access dark web
tor darknet drug markets dark web
darknet market list blackweb official website
http://sildenafilpills.pro/# cheapest price for sildenafil 20 mg
deep web links dark market list
dark web site drug markets onion
tor markets 2023 dark web search engine
總統大選
darknet markets deep web drug url
I every time spent my half an hour to read this website’s articles
every day along with a cup of coffee.
dark web sites dark market list
tor darknet deep web markets
free dark web darknet links
tor market links dark web access
darkmarket list darknet drug links
darknet marketplace deep web search
tor dark web dark website
darkmarket dark web drug marketplace
onion market dark web search engine
darknet site darknet market lists
darkweb marketplace darkmarket list
darknet drug market onion market
dark web search engines darknet seiten
dark web search engines dark net
dark web links darkweb marketplace
Nice blog here! Additionally your website loads up fast!
What web host are you the usage of? Can I am getting
your associate link for your host? I want my
website loaded up as fast as yours lol
dark market url deep dark web
darkmarket link the dark internet
dark market onion tor markets
darkmarket url darkweb marketplace
dark web sites dark market 2023
deep web drug links dark web sites
Я оцениваю тщательность и точность исследования, представленного в этой статье. Автор провел глубокий анализ и представил аргументированные выводы. Очень важная и полезная работа!
drug markets onion darkmarkets
tor market tor markets
darkmarket link deep web drug links
總統大選
總統大選
2024總統大選懶人包
2024總統大選將至,即中華民國第16任總統、副總統選舉,將在2024年1月13日舉行!這一天也是第11屆立法委員選舉的日子,選舉熱潮將一起席捲全台!這次選舉將使用普通、直接、平等、無記名、單記、相對多數投票制度,讓每位選民都能以自己的心意選出理想的領導者。
2024總統大選日期
2024總統大選日期:2024年1月13日 舉行投票,投票時間自上午8時起至下午4時止後進行開票。
2024總統大選民調
連署截止前 – 賴清德 VS 侯友宜 VS 柯文哲
調查來源 發布日期 樣本數 民進黨
賴清德 國民黨
侯友宜 民眾黨
柯文哲 不表態
TVBS 2023/05/19 1444 27% 30% 23% 20%
三立 2023/05/19 1080 29.8 29.2% 20.8% 20.2%
聯合報 2023/05/23 1090 28% 24% 22% 27%
亞細亞精準數據 2023/05/20 3511 32.3% 32.2% 32.1% 3.4%
放言 2023/05/26 1074 26.6% 24.7% 21.1% 27.6%
正國會政策中心 2023/05/29 1082 34% 23% 23% 20%
ETtoday 2023/05/29 1223 36.4% 27.7% 23.1% 12.8%
美麗島電子報 2023/05/29 1072 35.8% 18.3% 25.9% 20%
2024總統大選登記
賴清德 – 民主進步黨
2023年3月15日,賴清德在前屏東縣縣長潘孟安的陪同下正式登記參加2024年民進黨總統提名初選。
2023年3月17日,表定初選登記時限截止,由於賴清德為唯一登記者,因此自動成為該黨獲提名人。
2023年4月12日,民進黨中央執行委員會議正式公告提名賴清德代表民主進步黨參與本屆總統選舉。
侯友宜 – 中國國民黨
2023年3月22日,國民黨召開中央常務委員會,會中徵詢黨公職等各界人士意見,無異議通過將由時任黨主席朱立倫以「徵召」形式產生該黨總統候選人之決議。
2023年5月17日,國民黨第21屆中常會第59次會議正式通過徵召侯友宜代表中國國民黨參與本屆總統選舉。
柯文哲 – 台灣民眾黨
2023年5月8日,柯文哲正式登記參加2024年民眾黨總統提名初選。
2023年5月9日,表定初選登記時限截止,由於柯文哲為唯一登記者,因此自動成為該黨獲提名人。
2023年5月17日,民眾黨中央委員會正式公告提名柯文哲代表台灣民眾黨參與本屆總統選舉。
2023年5月20日,召開宣示記者會,發表參選宣言。
dark web search engine bitcoin dark web
drug markets onion darknet drugs
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/uk-UA/register-person?ref=V2H9AFPY
tor market url darkmarket
deep web markets darknet marketplace
drug markets onion dark web websites
darknet market links darkmarket list
darknet market darknet markets 2023
best darknet markets tor markets
darkmarket url free dark web
darknet market list dark web websites
dark web search engines deep web links
dark market link dark web links
dark web market links darknet drug market
dark web links darkmarket list
dark web websites darkmarket
the dark internet dark net
dark web markets dark markets
dark web market links dark markets
deep web search dark websites
tor markets 2023 deep web search
darknet market lists darknet seiten
dark market 2023 tor markets links
dark market onion darknet drug market
dark web websites dark website
deep web search darknet seiten
dark market onion dark web drug marketplace
the dark internet dark web drug marketplace
dark markets 2023 darknet market list
dark website tor market links
dark market link dark websites
bitcoin dark web dark market 2023
darknet drug market deep web drug store
dark market url darknet drug links
darknet markets dark web search engines
darkmarket dark web market
dark internet darknet market list
darknet marketplace darknet market list
https://edpill.pro/# ed pills comparison
darknet market lists darknet search engine
deep web sites dark web drug marketplace
tor markets black internet
what is aviator how to win aviator game what is aviator
deqsvlvhs irujt ctfdxmt rdli fkoidvqwkjcwnsg
darkmarkets dark markets 2023
darknet links dark market url
darkmarket link tor dark web
dark web search engines darkmarkets
dark website dark web site
how to access dark web dark web market list
darknet websites black internet
dark internet darknet links
dark internet darknet sites
darknet market links darknet websites
darknet market list bitcoin dark web
dark web search engines tor dark web
darknet markets 2023 tor market url
dark web access the dark internet
darkmarket url tor market links
drug markets onion best darknet markets
darkmarkets darknet websites
dark markets 2023 deep web search
dark market list blackweb
deep web drug store dark web link
blackweb official website dark internet
dark web markets dark web site
darknet marketplace deep web drug store
darknet websites darknet drug market
free dark web dark web market
dark web search engine how to get on dark web
dark websites dark web access
best darknet markets darknet markets 2023
darknet drugs tor marketplace
dark web market onion market
darknet links dark web search engine
darkmarket 2023 darkweb marketplace
darknet drug links dark market onion
the dark internet dark web links
tor market links dark web search engine
best darknet markets tor marketplace
tor markets links the dark internet
tor darknet tor markets 2023
drug markets dark web darknet search engine
tor markets 2023 dark web market
deep dark web darknet market lists
dark web drug marketplace blackweb official website
black internet deep web drug markets
dark web search engines black internet
darknet market links the dark internet
darknet links darknet search engine
darkmarket 2023 darkmarket
deep web drug store darkmarket link
onion market onion market
darkmarket 2023 free dark web
free dark web tor darknet
darkmarket 2023 darkmarkets
dark web access dark web market links
dark web link tor markets
dark market link dark internet
darknet market list dark internet
darkmarket list dark web markets
dark markets darknet markets 2023
dark web markets darknet market list
tor marketplace deep web links
dark web sites darkmarket url
darkmarket url darknet market list
darknet drugs dark market onion
dark market 2023 dark web market list
onion market best darknet markets
dark net dark web market
tor market darknet market links
tor dark web free dark web
darknet market links deep web links
dark website dark web sites links
darknet market list dark markets 2023
dark web search engines how to access dark web
darkmarket link drug markets onion
dark web sites links drug markets dark web
dark market list blackweb
tor markets links darknet market links
darknet market dark web search engines
dark web market darknet drug store
free dark web dark web markets
keflex and alcohol consumption https://keflexvex.com/ keflex for h pylori
darkweb marketplace darknet markets
drug markets dark web dark markets
dark web sites how to get on dark web
dark web sites links dark markets
darkmarket link drug markets onion
tor darknet deep web links
娛樂城的崛起:探索線上娛樂城和線上賭場
近年來,娛樂城在全球范圍內迅速崛起,成為眾多人尋求娛樂和機會的熱門去處。傳統的實體娛樂城以其華麗的氛圍、多元化的遊戲和奪目的獎金而聞名,吸引了無數的遊客。然而,隨著科技的進步和網絡的普及,線上娛樂城和線上賭場逐漸受到關注,提供了更便捷和多元的娛樂選擇。
線上娛樂城為那些喜歡在家中或任何方便的地方享受娛樂活動的人帶來了全新的體驗。通過使用智能手機、平板電腦或個人電腦,玩家可以隨時隨地享受到娛樂城的刺激和樂趣。無需長途旅行或昂貴的住宿,他們可以在家中盡情享受令人興奮的賭博體驗。線上娛樂城還提供了各種各樣的遊戲選擇,包括傳統的撲克、輪盤、骰子遊戲以及最新的視頻老虎機等。無論是賭徒還是休閒玩家,線上娛樂城都能滿足他們各自的需求。
在線上娛樂城中,娛樂城體驗金是一個非常受歡迎的概念。它是一種由娛樂城提供的獎勵,玩家可以使用它來進行賭博活動,而無需自己投入真實的資金。娛樂城體驗金不僅可以讓新玩家獲得一個開始,還可以讓現有的玩家嘗試新的遊戲或策略。這樣的優惠吸引了許多人來探索線上娛樂城,並提供了一個低風險的機會,
dark web market dark market link
tor market links dark market url
the dark internet dark web site
darkmarket 2023 free dark web
tor market darknet drugs
darknet sites blackweb official website
darknet sites best darknet markets
darknet marketplace darknet market lists
https://sildenafilpills.pro/# sildenafil generic viagra
dark internet onion market
dark web sites dark web search engines
tor market url darkmarket link
dark web site deep web sites
deep dark web darkmarkets
tor market free dark web
darknet drugs blackweb official website
darkmarkets dark web markets
darkmarket link drug markets onion
the dark internet darknet search engine
darknet markets 2023 darknet search engine
deep web drug links darknet search engine
dark market link dark website
deep web markets darknet drug links
tor darknet best darknet markets
darknet marketplace dark web link
dark market list dark web access
dark web market list dark web search engine
black internet darkmarket link
darknet market list dark market onion
bitcoin dark web deep web search
dark web sites links drug markets onion
free dark web tor market links
dark web market list tor dark web
dark web search engines dark websites
black internet tor marketplace
dark web markets darknet marketplace
darknet markets 2023 dark markets 2023
tor darknet darknet search engine
deep web search dark market url
tor market url dark web markets
darkmarket 2023 how to access dark web
darknet sites darknet sites
tor market dark web site
deep web drug url darknet seiten
darknet drug store darknet drug links
dark web sites darknet seiten
dark net dark websites
tor dark web dark web market
dark market onion deep dark web
darknet websites dark web websites
deep web sites dark web market links
tor market url dark net
dark web search engines dark markets 2023
darkmarket url dark markets
dark market link dark web sites
dark web market links onion market
dark markets darknet site
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
darknet markets dark markets 2023
deep dark web darkmarket
darkweb marketplace dark web link
dark web market links dark market list
deep web drug links darknet drugs
dark market tor darknet
deep web drug links darkmarket url
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to generate a
great article… but what can I say… I hesitate a lot and never seem
to get anything done.
darknet markets darkmarket url
bitcoin dark web free dark web
darkmarket list dark net
tor markets links dark markets
amoxicillin equivalent https://amoxicillinzuj.com/ can you take aleve with amoxicillin
best darknet markets dark web websites
dark website darknet drugs
dark market 2023 darknet markets
darkmarket link dark web link
black internet deep web drug url
deep web links drug markets onion
dark website dark web site
blackweb official website darknet drugs
dark web markets darknet drug market
darkmarkets black internet
darknet markets 2023 deep web markets
darkmarket darkmarket 2023
dark web site dark web access
tor markets darknet seiten
dark websites darknet drug market
deep web links dark market 2023
deep web markets deep web markets
darknet search engine tor markets 2023
dark net free dark web
darkweb marketplace dark market url
darkweb marketplace dark markets
darknet market lists darknet drug market
dark web market list darknet market list
darknet drug market deep web links
darknet markets tor market links
dark market list dark market link
how to access dark web deep web sites
onion market how to access dark web
darkmarket 2023 onion market
deep web links darkmarket link
darkmarket link darknet market list
dark web market dark market onion
tor market deep web sites
deep web drug links deep web search
can i take amoxicillin after azithromycin how much amoxicillin can i take in a day amoxicillin dosage for cats
tor markets 2023 black internet
dark market list dark markets
the dark internet darkmarket url
deep web links dark internet
free dark web dark internet
darknet links tor market
tor dark web deep dark web
dark internet dark markets
dark website darknet sites
darknet seiten dark market 2023
drug markets dark web tor marketplace
dark market list dark web market links
dark market url darkmarket
dark web sites dark market
bitcoin dark web deep web drug markets
best darknet markets dark web access
dark markets 2023 dark markets
dark web search engine darknet drug links
darknet markets blackweb
darknet links darkmarket link
blackweb deep web sites
black internet dark web markets
darknet site dark internet
cephalexin same as amoxicillin https://cephalexinyns.com/ can you have cephalexin if allergic to penicillin
tor market url tor market url
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/ph/register?ref=OMM3XK51
darknet markets darknet seiten
dark web access deep dark web
dark net deep web drug links
drug markets onion deep web drug url
darknet seiten tor markets
darknet drug store blackweb
tor markets links dark web market links
deep web drug links dark web markets
darkmarket link darknet market lists
deep web search deep web drug store
darknet websites deep web links
free dark web deep web search
drug markets onion dark website
deep web sites dark web access
darknet websites darknet links
tor market links darkweb marketplace
dark web sites links deep web sites
darknet websites deep web search
drug markets dark web deep web drug markets
dark internet dark markets
tor market dark market list
best darknet markets dark web access
best darknet markets dark markets 2023
dark market list deep web drug links
dark web markets darknet links
darknet drug market dark market
dark web links deep web links
darknet search engine blackweb official website
darkmarket 2023 darknet links
deep web drug markets darknet drug market
dark web access dark web search engine
tor darknet dark web sites links
drug markets onion tor darknet
darknet market list deep web drug store
blackweb official website dark web site
dark market 2023 dark web market
dark websites tor market links
darknet markets tor markets
dark web search engine best darknet markets
tor markets links dark market url
tor market url dark web access
dark web search engines darkweb marketplace
dark web links free dark web
darknet market links dark web websites
darknet markets 2023 dark web access
dark web websites dark web search engine
darknet drug store darknet search engine
tor market url darkmarket url
darkmarket list dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace tor markets 2023
darknet site darknet market
dark web search engines darkmarket
best darknet markets best darknet markets
best darknet markets drug markets onion
darkmarket dark net
dark websites onion market
dark web websites tor markets
deep web drug markets darkweb marketplace
dark markets how to get on dark web
dark net darknet market list
dark internet deep dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet markets
dark market list dark websites
the dark internet dark market list
darkmarkets dark website
dark web search engines black internet
free dark web how to access dark web
dark market onion onion market
best darknet markets free dark web
dark web links darknet drug links
dark website dark market onion
dark web market blackweb official website
blackweb official website dark markets
dark markets 2023 tor dark web
dark web sites deep dark web
darknet markets 2023 dark web market
deep web drug markets darkmarket list
dark market link tor darknet
dark web markets free dark web
drug markets onion dark web market links
dark market url darknet markets 2023
darknet markets 2023 dark markets 2023
deep web drug links darknet market lists
dark markets 2023 darkweb marketplace
tor market links tor markets 2023
darknet seiten tor market url
black internet drug markets dark web
dark web sites links darknet markets 2023
tor dark web dark market list
tor darknet deep web search
darknet market darknet links
black internet dark market url
deep web drug url darknet websites
dark market 2023 dark market url
darknet market links darknet markets 2023
deep web drug markets darknet markets
dark web market list dark web sites links
tor markets darknet seiten
darknet market links deep web links
dark web search engines darknet drug links
darkmarket list dark market
tor market darkmarket 2023
darknet drug links darknet markets 2023
cephalexin left in hot car https://cephalexinujx.com/ cephalexin make you tired
darknet market lists tor dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet search engine
how to get on dark web tor market url
dark web markets darknet sites
black internet dark web sites
darknet markets 2023 darknet search engine
darkmarket list darknet seiten
dark web links free dark web
dark market onion deep web drug store
dark website deep web drug url
darknet markets darknet market links
blackweb darkmarket
darknet marketplace darknet seiten
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug markets
darknet drug market deep web search
deep web drug markets deep web drug markets
darknet sites deep web drug store
dark market 2023 darknet seiten
darknet seiten dark markets 2023
black internet deep web drug url
deep web search darknet drugs
drug markets onion drug markets dark web
darknet websites tor market url
deep web drug url dark web access
dark market onion darknet seiten
darknet market links dark web drug marketplace
blackweb tor marketplace
darknet market list deep web drug store
darknet market list tor markets links
darkmarket 2023 darknet site
how to get on dark web darkmarket 2023
tor darknet tor markets 2023
deep web drug links darknet seiten
dark market onion drug markets onion
darknet drugs darknet links
dark web market links dark web access
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really recognize what you are talking about!
Bookmarked. Please also talk over with my web site =).
We will have a link trade contract among us
deep web search darknet market links
dark web search engine deep web sites
darknet drugs darknet market
deep web markets bitcoin dark web
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles. I will bookmark
your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite sure
I’ll learn a lot of new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
dark market list black internet
drug markets dark web darknet marketplace
blackweb official website darknet market
free dark web darknet market lists
best darknet markets darkmarket link
bitcoin dark web dark web sites
darkmarket list dark markets 2023
darknet drugs how to access dark web
deep web drug markets tor market
darknet site onion market
dark market list darknet search engine
dark market list drug markets dark web
dark web search engines tor markets 2023
darknet market tor darknet
darknet drugs darknet drug store
best darknet markets dark web link
deep web drug markets darknet markets 2023
darkmarket deep web markets
darknet seiten darknet websites
onion market darknet seiten
darkmarket list darkmarket 2023
dark market list dark website
darkmarket url dark market 2023
tor markets 2023 dark markets 2023
dark web search engine darkmarket 2023
dark market url tor market
darknet market list dark web search engines
darknet market links dark markets
darknet market list darknet drug store
the dark internet dark net
bitcoin dark web dark net
dark markets 2023 tor marketplace
darknet drugs darkmarket url
dark web site darkweb marketplace
darknet websites how to access dark web
dark web access deep web drug links
bitcoin dark web darknet search engine
darknet drug market deep web markets
darknet market lists darknet search engine
dark web search engine the dark internet
dark web market list best darknet markets
deep web sites dark website
bitcoin dark web dark web sites links
dark web access darknet websites
darkmarket list darkweb marketplace
deep dark web darknet markets
Статья содержит информацию, которая актуальна и важна для современного общества.
dark websites deep web markets
darknet market lists dark markets 2023
deep dark web dark market
drug markets onion dark web market links
darknet seiten dark web sites
deep web drug links dark web sites
dark market url tor darknet
dark web links dark markets
rtpkantorbola
Автор статьи предоставляет важные сведения и контекст, что помогает читателям более глубоко понять обсуждаемую тему.
darknet drug market darkmarket 2023
blackweb official website black internet
dark internet tor markets
tor marketplace tor dark web
darkmarket list blackweb
dark websites bitcoin dark web
deep web drug links drug markets onion
bitcoin dark web how to get on dark web
tor marketplace onion market
tor markets deep web search
tor marketplace dark markets 2023
Just wish to say your article is as amazing.
The clarity on your submit is simply spectacular and that i could assume you are a professional on this subject.
Fine together with your permission allow me to grab your feed
to stay updated with impending post. Thank you one million and
please carry on the enjoyable work.
darkmarket best darknet markets
dark web access deep web drug store
dark web access dark web market links
dark markets darknet drugs
darkmarket url how to access dark web
tor market url dark websites
dark web link how to access dark web
deep dark web darknet websites
how to get on dark web dark market list
deep web drug links tor market
darkmarket list darknet marketplace
darknet markets 2023 dark web drug marketplace
darkweb marketplace darkmarkets
darknet market list tor markets
darknet drug links darknet links
darknet websites deep web drug links
drug markets dark web black internet
how to get on dark web dark market link
darknet market lists tor markets 2023
darknet marketplace darkweb marketplace
dark web sites links darknet site
tor market dark market list
tor dark web darknet websites
dark websites dark web links
darknet marketplace dark market link
darkmarket url darknet markets
deep web drug url tor market links
darknet websites best darknet markets
dark web market links darknet site
darknet drug links darknet seiten
deep web markets tor dark web
dark web market links dark web market
tor market tor marketplace
dark web sites links dark web market list
dark web link the dark internet
keflex and ckd keflex dose pediatric keflex and blood sugar
deep web links dark market onion
deep web drug store darknet search engine
best darknet markets dark web market list
dark web market dark web market
tor darknet dark internet
black internet darknet site
dark websites deep web drug url
how to access dark web darkmarket 2023
deep web links blackweb official website
darknet market dark web market
dark web site deep web drug store
dark market list dark web search engines
dark web websites darknet search engine
dark web market list deep dark web
darkmarket 2023 dark web market links
tor market darknet marketplace
darkmarket list darknet drugs
dark web sites links darknet site
tor markets links darknet markets 2023
darknet market links dark web search engines
onion market darkmarket 2023
dark market 2023 dark websites
tor market url deep web links
darknet market links tor marketplace
dark web market list darknet drug links
darknet markets dark web websites
the dark internet dark website
the dark internet deep web sites
tor dark web drug markets dark web
darkmarket list tor markets
tor market url blackweb official website
dark net tor markets links
tor marketplace darknet drug links
dark market darknet seiten
dark web sites dark market list
deep web search deep web sites
the dark internet the dark internet
dark net darknet markets 2023
darknet markets darknet drug store
dark market 2023 darkmarkets
dark web market blackweb
the dark internet dark web market list
darknet markets darknet marketplace
blackweb black internet
how to get on dark web dark market link
darknet market darkmarket
drug markets onion onion market
drug markets dark web dark market link
dark web links darkmarket
onion market dark web market
dark markets 2023 dark web markets
deep web drug store dark market onion
blackweb official website tor darknet
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug url
tor market dark markets 2023
darkmarkets darkmarket link
deep web search best darknet markets
deep web drug store how to get on dark web
tor market url tor dark web
dark website deep web drug url
deep web sites dark web markets
dark web sites links tor markets 2023
deep web drug store dark website
darknet site darknet markets 2023
onion market deep web drug store
bitcoin dark web darknet marketplace
free dark web deep web links
healthy male internet
drug markets dark web dark web access
deep web drug store darkweb marketplace
tor markets 2023 darknet drugs
ciprofloxacin vs levofloxacin for uti ciprofloxacin eye drops contraindications ciprofloxacin vitamins
deep dark web dark web websites
tor market url dark web sites
dark web search engine darkmarket link
darknet drug market tor market links
darkmarket dark web websites
free dark web dark market onion
drug markets dark web darkmarket link
tor markets 2023 darknet sites
dark market dark web market links
tor darknet deep web drug url
darknet markets 2023 tor markets links
tor market dark web market links
best darknet markets dark market url
dark markets dark net
dark web access dark web market
darknet drug store darknet drugs
dark website dark market link
darknet search engine how to access dark web
dark web websites dark web search engines
darknet market darknet market
onion market dark web market links
dark web search engine dark internet
tor markets 2023 tor markets
darknet market links dark market list
darkmarket link darknet market links
dark web markets how to get on dark web
the dark internet dark web market links
antivert 25 mg over the counter
how to get on dark web darknet sites
dark web market list deep web links
tor markets links darknet sites
deep dark web dark web search engine
dark market 2023 tor market url
darknet markets tor market links
darknet drugs darknet drugs
dark net tor market
darkmarkets how to access dark web
usa pharmacy no script viagra 100mg
darkmarket link tor marketplace
darknet market lists deep web links
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/sl/register-person?ref=53551167
darknet seiten darknet marketplace
dark market darkmarket 2023
bitcoin dark web dark web sites links
tor markets darknet marketplace
247 overnight pharmacy canadian buy viagra without a prescription
darknet seiten tor markets
deep web drug links dark web market list
darknet market blackweb
darknet drug links deep web drug links
blackweb dark web drug marketplace
darkmarkets deep web drug links
darknet drugs dark web market list
tor markets darknet market
dark web sites links how to access dark web
best darknet markets darknet market
darknet links drug markets dark web
deep web markets dark web search engines
dark website tor market url
darknet drugs dark web sites
darkmarket darknet market links
blackweb dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket link dark web link
tor markets 2023 darknet links
dark web market list deep dark web
darkweb marketplace darkmarket url
how to access dark web deep web markets
tor markets dark market list
black internet the dark internet
dark markets 2023 darknet websites
tor marketplace dark web links
darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
tor market url dark website
tor markets deep web drug links
dark websites dark markets 2023
dark web site darkmarket list
deep web drug url darknet links
dark web drug marketplace onion market
blackweb the dark internet
dark web link bitcoin dark web
darknet site deep web drug url
dark web sites dark market onion
darknet search engine blackweb official website
darknet market lists dark web site
darknet market free dark web
tor market dark web search engines
tor markets dark web links
tor market url darknet seiten
darknet market links darknet market
cost antivert
darknet market lists dark web search engine
dark market 2023 dark web search engines
azithromycin diarrhea can you take amoxicillin and azithromycin in the same day what happens if you take azithromycin out of order
deep web search dark market list
darknet sites tor markets 2023
tor marketplace the dark internet
dark market darkmarket link
dark web search engines tor dark web
darknet markets darknet market list
how to access dark web dark web sites links
dark web site darknet markets
darkmarkets dark web site
deep web links darknet sites
dark web links darkmarket list
The author presents the information in a manner that is accessible to non-experts.
tor darknet tor market links
dark website dark web access
best darknet markets darknet market lists
best darknet markets tor markets links
dark market darknet links
dark market url darknet marketplace
deep dark web dark web websites
darknet site tor darknet
darkmarket url dark web drug marketplace
deep web search darknet site
darknet site dark web markets
tor marketplace darkmarket 2023
deep web drug links tor marketplace
free dark web dark net
deep web markets deep web sites
dark web market list dark website
bitcoin dark web dark market 2023
blackweb best darknet markets
darknet marketplace dark market list
darknet drug store onion market
darknet market lists darknet site
darkmarket link deep web search
darknet search engine the dark internet
tor marketplace darknet market list
dark web sites darknet markets 2023
deep web search dark web access
The information in this article is presented in a clear and concise manner.
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug store
deep web search the dark internet
azithromycin 500 mg precio azithromycin and prozac how long after azithromycin can you drink
dark web market list dark market url
dark internet tor darknet
darknet market list dark web markets
dark web links darkmarket link
darknet drugs dark market list
This article is a true gem. It’s informative, well-researched, and presented in a way that is engaging and accessible to readers of all backgrounds. The author’s ability to simplify complex concepts without sacrificing depth is commendable. Thank you for sharing such valuable knowledge!
canadian pharmacy viagra 100mg price
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
darknet seiten deep web drug url
how to get on dark web dark market
darknet marketplace darknet site
deep web drug markets deep web markets
darknet websites darknet sites
dark websites deep web markets
deep web drug links deep dark web
deep web drug url tor darknet
darknet websites black internet
cephalexin 250 mg para que sirve https://doxycyclineoyg.com/ cephalexin meaning
dark web sites links tor market url
dark websites dark web websites
tor darknet tor dark web
dark web market links dark web sites links
dark web sites links darknet drugs
dark web market deep web drug store
deep web sites dark web market links
meclizine 25 mg uk
best darknet markets dark internet
free dark web tor markets links
darkmarket list dark web sites links
drug markets onion deep dark web
This, in part, was because doctors at first waited to confirm a diagnosis with surgery tadalista vs cialis 9 and 9 respectively
dark net darknet drugs
Using the Wilcoxon two sample tests to compare groups T and A, it was shown that there was no statistically significant difference in weight gain between the two groups at any interval see table can you buy cialis online INVANZ POWD
tor darknet how to access dark web
deep web drug url dark website
darkmarket list deep web search
The information in this article is presented in a manner that is accessible to a wide audience.
dark markets 2023 how to access dark web
deep web sites darknet market lists
tor markets links darknet marketplace
darknet websites darknet drug store
The writing style is clear and concise, making it easy to follow.
dark website dark web sites links
how to get on dark web drug markets onion
darknet markets tor markets links
tor market url the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace dark market list
how to get on dark web dark web sites
dark markets 2023 blackweb official website
dark web site darknet site
darknet market list best darknet markets
best darknet markets tor dark web
dark web site dark web market links
tor market dark internet
tor markets 2023 dark markets
black internet darknet marketplace
online pharmacy healthy man images
dark web site dark market
darknet market list darknet markets
dark web sites darkmarkets
blackweb official website deep web markets
drug markets onion dark web link
bitcoin dark web darkweb marketplace
black internet darkmarket list
canadian pharmacy cialis global pharmacy canada phone number
darkmarket deep web markets
dark market list darkmarket list
darknet market deep web search
darknet market lists onion market
dark market url deep dark web
darknet search engine darknet market links
dark market 2023 dark websites
deep web markets darknet drug store
dark market darknet seiten
tor market url darknet site
the dark internet tor darknet
darkmarkets darknet site
darkmarket darknet market links
bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
tor markets links darknet market links
dark web search engine darknet sites
darkweb marketplace darknet sites
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
tor markets 2023 darknet market
darknet search engine dark web search engines
dark web markets darknet marketplace
tor markets 2023 black internet
dark market deep web sites
the dark internet blackweb
tor markets deep web drug links
darkmarket deep web markets
dark web market list dark markets
dark web market list tor markets links
darknet drug market darknet links
darkmarket list darknet market
darknet marketplace dark market list
dark market url dark web link
dark web site deep web drug url
dark web markets dark internet
dark web market links dark web websites
dark web search engines darknet sites
darknet markets dark market list
tor markets links darkweb marketplace
Why users still make use of to read news papers when in this
technological globe all is accessible on web?
blackweb darkmarket url
darknet market list tor market
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful
info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.
drug markets dark web darknet search engine
darknet market lists darkmarkets
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if
that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
deep web links dark web sites links
dark market 2023 darknet search engine
darkmarket dark web sites
dark internet deep web markets
dark website deep web drug store
dark web websites darknet search engine
the dark internet dark web sites
deep web links darknet search engine
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/vi/register?ref=V3MG69RO
darknet search engine darknet search engine
darknet market list tor market url
I can’t thank the author enough for this enlightening and thought-provoking article. It explores the topic from multiple angles and presents different perspectives, encouraging readers to think critically. The content is well-researched, and the arguments are supported by compelling evidence.
order meclizine 25 mg pill
how to access dark web tor markets 2023
dark markets 2023 darknet drug store
tor marketplace tor market url
darknet markets dark web market
darknet drug store free dark web
tor markets tor market url
dark web markets darknet marketplace
dark net tor marketplace
deep web search dark web websites
dark internet darkmarket
dark markets tor dark web
tor markets 2023 tor marketplace
darknet drug links darknet drugs
tor market url darkmarket link
cephalexin probiotics is keflex and cephalexin the same how long does cephalexin 500mg take to work?
darkmarkets dark web sites
dark web access darknet drug links
deep web drug markets darknet market lists
the dark internet dark web search engines
dark web access dark web links
free dark web darknet markets 2023
darknet market lists dark web links
dark web links dark market onion
dark web links darknet seiten
Мне понравился стиль изложения в статье, который делает ее легко читаемой и понятной.
dark market dark web websites
tor dark web dark web site
drug markets dark web deep web links
deep web links dark web link
darkmarket list dark market link
darknet drug market dark net
С удовольствием предоставлю вам ещё несколько положительных комментариев на английском языке для информационной статьи:
dark markets 2023 darknet seiten
tor marketplace tor market url
darknet markets 2023 darkmarket
darknet drug market dark web search engines
deep web drug links dark web search engines
darknet market lists darknet drugs
dark markets dark market onion
free dark web dark web site
dark web sites dark website
onion market black internet
dark markets darknet markets
dark website onion market
order antivert 25mg
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am actually happy to read everthing at single place.
dark website dark web market
dark markets 2023 tor marketplace
darkweb marketplace bitcoin dark web
darkmarket list deep web drug store
darknet market list darknet search engine
darknet sites darkmarket url
drug markets onion deep web drug store
free dark web tor markets links
drug markets onion darknet marketplace
tor market url darknet market list
dark web drug marketplace the dark internet
darknet marketplace dark web access
darkmarket link darknet market links
tor market darkmarket url
dark net darknet markets 2023
https://www.curacel.co/post/fire-and-burglary-insurance-in-nigeria-how-to-drive-mass-adoption
deep web markets darknet links
Я оцениваю широту покрытия темы в статье.
deep web sites dark web site
dark web site darkmarket link
best darknet markets how to get on dark web
อย่างที่กล่าวมาข้างต้น เว็บไซต์สล็อต 888 pg เป็นที่รวมเกมสล็อต PG ทั้งหมดที่ผู้เล่นต้องการไว้ในที่เดียว ไม่ว่าจะเป็นสล็อตคลาสสิกที่เป็นที่นิยมมากมายหรือสล็อตเกมส์ใหม่ล่าสุดที่เพิ่งเปิดตัว เราสามารถเลือกเล่นเกมในหลากหลายรูปแบบได้อย่างอิสระ
สำหรับสมาชิกใหม่ที่เพิ่งสมัครสมาชิกกับเว็บไซต์ สล็อต 888 pg นี้ จะได้รับเครดิตฟรีจำนวน 50 บาท ทันทีที่สมัครสมาชิกเสร็จสิ้น โดยไม่ต้องทำการฝากเงินเข้าสู่ระบบ สามารถใช้เครดิตฟรีนี้ในการเล่นเกมสล็อตและมีโอกาสที่จะถอนเงินได้สูงสุดถึง 3,000 บาท
นอกจากนี้ เว็บไซต์ยังมีโปรโมชั่นสำหรับสมาชิกใหม่ที่ทำการฝากเงินครั้งแรก โดยเมื่อฝากเงินจำนวน 50 บาท จะได้รับโบนัสเพิ่มอีก 100 บาท ทำให้เงินที่มีในบัญชีเล่นสล็อตเพิ่มขึ้นเป็น 150 บาททันที สามารถนำเงินเครดิตนี้ไปเล่นเกมสล็อตได้ทันที
ด้วยความน่าเชื่อถือและความเป็นที่นิยมของเกมสล็อต PG ทั้งในเรื่องของกราฟิกที่สวยงามและคุณภาพเสียงที่น่าตื่นเต้น ไม่ต้องสงสัยเลยว่า
Bonus nocadastro
Are you ready to take your online gaming experience to new heights? Look no further than WAKABET, your ultimate destination for thrilling entertainment and incredible bonuses. We are excited to offer you exclusive bonuses upon registration, ensuring that your gaming journey starts on a high note. With a wide selection of games, convenient deposit options, and exciting promotions, WAKABET is the perfect platform to satisfy your gaming desires. Join us today and let the fun begin!
Dive into a World of Endless Entertainment:
At WAKABET, we understand the importance of variety and quality when it comes to online gaming. That’s why we bring you an extensive collection of games, featuring everything from classic slots to innovative table games and live casino experiences. With over 100 captivating games to choose from, you’ll never run out of options to keep you entertained and engaged. Discover new favorites and chase big wins as you explore the thrilling world of WAKABET.
Seamless Deposits for Instant Action:
We value your time and want to ensure that you can dive into the action without delay. That’s why WAKABET offers swift and secure deposit options, allowing you to fund your account quickly and effortlessly. With our trusted payment methods, you can deposit with confidence, knowing that your transactions are protected by advanced security measures. Experience hassle-free deposits and focus on what matters most—playing and winning!
Claim Your Registration Bonus and Start Winning:
As a new player at WAKABET, we want to make your experience extra special. That’s why we offer exclusive bonuses upon registration. Simply sign up, and you’ll be rewarded with bonus credits to boost your gameplay. These bonuses give you the opportunity to explore different games, try new strategies, and potentially hit big wins—all without dipping into your own funds. Take advantage of this exciting offer and start your gaming journey with an advantage!
Experience the Joy of Winning with Every Bet:
At WAKABET, we believe in rewarding our players for their loyalty and dedication. That’s why we have a range of promotions, including “Aposta Ganha” (Winning Bet), where you can earn additional rewards for your successful bets. Keep an eye out for these special promotions and maximize your winning potential with WAKABET. With each bet you place, you not only enjoy the thrill of the game but also increase your chances of hitting the jackpot!
Discover the World of WAKABET Today:
WAKABET is your ticket to a world of thrilling entertainment and rewarding gameplay. With our bonus on registration, diverse game library, seamless deposits, and exciting promotions, we strive to deliver an exceptional gaming experience. Join WAKABET now and immerse yourself in a world where the excitement never ends. Register, claim your bonus, and get ready to spin the reels, place your bets, and win big at WAKABET!
Conclusion:
Are you ready to elevate your gaming experience to new heights? Join WAKABET today and enjoy exclusive bonuses on registration, a vast selection of games, convenient deposit options, and exciting promotions. Whether you’re a seasoned player or new to the world of online gaming, WAKABET has something for everyone. Sign up now, claim your bonus, and let the games begin. Get ready for endless fun, incredible rewards, and unforgettable moments at WAKABET!
bitcoin dark web tor market links
deep web drug links dark web drug marketplace
dark market dark web site
darknet market links tor market links
dark web websites blackweb official website
dark websites darkmarket url
dark web market links darkmarket 2023
dark web markets drug markets onion
dark web search engines blackweb
tor markets links best darknet markets
bitcoin dark web darknet market lists
The author offers practical examples to illustrate their points.
dark market link how to access dark web
deep web markets darknet websites
dark market url deep web markets
tor markets darknet marketplace
darknet websites dark web sites links
the dark internet darknet drug links
tor marketplace deep web search
dark web market links darknet drugs
deep web links darknet drug store
darknet market lists blackweb official website
tor dark web deep web drug links
tor markets links dark web access
darknet search engine black internet
Я бы хотел отметить качество исследования, проведенного автором этой статьи. Он представил обширный объем информации, подкрепленный надежными источниками. Очевидно, что автор проявил большую ответственность в подготовке этой работы.
dark markets 2023 darkmarkets
deep web drug links dark internet
dark market darknet websites
dark net darkmarket link
darknet links dark market list
ความสะดวกสบายเป็นสิ่งที่คุณจะได้รับเมื่อคุณสมัครสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ “สบาย999” กับเว็บไซต์ pgslot เว็บตรง ที่จะทำให้คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตที่คุณชื่นชอบได้อย่างง่ายดาย โดยไม่ต้องมีขั้นตอนซับซ้อนหรือการเปลี่ยนเว็บไซต์เพิ่มเติม ทุกอย่างอยู่ภายใต้เว็บเดียวเท่านั้น
สำหรับสมาชิกใหม่ที่สนใจเข้าร่วมเว็บไซต์ pgslot เว็บตรง นอกจากจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมสล็อตที่น่าตื่นเต้นแล้ว ยังมีโปรโมชั่น “สมาชิกใหม่ แจก pgslot เครดิตฟรี 3,000” ที่คุณสามารถรับได้เมื่อลงทะเบียนสมัครสมาชิกครั้งแรกกับเว็บไซต์นี้ เครดิตฟรีนี้จะช่วยให้คุณมีโอกาสในการเล่นสล็อตโดยไม่ต้องใช้เงินจริง และมีโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลและทำกำไรจริงๆ
ไม่เพียงเท่านั้น “pgslot ทดลองเล่น” ยังเป็นคำที่น่าสนใจสำหรับนักพนันที่กำลังสนใจเกมสล็อต คุณสามารถทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อตต่างๆ ได้ฟรี และถ้าคุณรู้สึกว่าเกมใดถูกใจและต้องการเล่นเงินจริง คุณสามารถถอนเงินได้ทันที สร้างความตื่นเต้นและความสุขในการเล่นสล็อตได้ที่
deep web markets dark website
darknet sites darknet drug store
darknet site dark web access
deep web drug url darknet search engine
darknet markets deep dark web
the dark internet dark web market links
dark markets 2023 drug markets onion
dark web drug marketplace free dark web
dark market dark web sites links
tor markets links dark market url
dark web sites darknet seiten
black internet darknet drug market
darkmarket 2023 dark web link
tor markets links deep web links
dark markets 2023 dark web link
dark web market darknet market list
dark websites dark market url
best darknet markets dark market link
darkmarket 2023 dark web access
on line pharmacy viagra online
deep web drug links how to access dark web
deep web drug url dark web drug marketplace
dark market list deep web links
dark web websites best darknet markets
darknet markets dark web sites
dark web access onion market
dark websites darkweb marketplace
Puncak88 adalah situs Slot Online terbaik di Indonesia. Puncak88, situs terbaik dan terpercaya yang sudah memiliki lisensi resmi, khususnya judi slot online yang saat ini menjadi permainan terlengkap dan terpopuler di kalangan para member, Game slot online salah satu permainan yang ada dalam situs judi online yang saat ini tengah populer di kalanagan masyarat indonesia, dan kami juga memiliki permainan lainnya seperti Live casino, Sportbook, Poker , Bola Tangkas , Sabung ayam ,Tembak ikan dan masi banyak lagi lainya.
Puncak88 Merupakan situs judi slot online di indonesia yang terbaik dan paling gacor sehingga kepuasan bermain game slot online online akan tercipta apalagi jika anda bergabung dengan yang menjadi salah satu agen slot online online terpercaya tahun 2022. Puncak88 Selaku situs judi slot terbaik dan terpercaya no 1 menyediakan daftar situs judi slot gacor 2022 bagi semua bettor judi slot online dengan menyediakan berbagai macam game menyenangkan seperti poker, slot online online, live casino online dengan bonus jackpot terbesar Tentunya. Berikut keuntungan bermain di situs slot gacor puncak88
1. Proses pendaftaran akun slot gacor mudah
2. Proses Deposit & Withdraw cepat dan simple
3. Menang berapapun pasti dibayar
4. Live chat 24 jam siap melayani keluh kesah dan solusi untuk para member
5. Promo bonus menarik setiap harinya
tor markets links free dark web
tor markets links darknet search engine
tor darknet tor markets links
dark web market list tor markets links
dark web markets deep dark web
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug markets
best darknet markets darknet site
dark market url deep web markets
darkmarket 2023 tor markets links
darkmarkets bitcoin dark web
darkmarket list tor darknet
tor dark web darknet markets 2023
dark web links darknet websites
deep web drug markets darknet market list
darkmarket url tor market links
blackweb official website bitcoin dark web
dark internet darknet market
tor market links deep web links
darknet drugs drug markets dark web
deep web sites dark websites
tor darknet deep web drug store
bitcoin dark web deep web drug links
tor darknet darknet websites
dark market url tor market
dark web sites links tor darknet
darknet seiten tor markets
deep web drug markets deep web search
dark web market dark web market list
dark web sites how to get on dark web
dark market url tor dark web
darknet markets 2023 dark web search engine
tor market links darkmarket list
deep web drug store deep web drug links
dark web links tor markets
darknet websites dark market list
dark web market list tor markets
bitcoin dark web deep web markets
darknet search engine dark market onion
bitcoin dark web dark web search engine
darknet search engine dark web sites
ciprofloxacin tendon rupture risk medicine ciprofloxacin how long does it take for ciprofloxacin to get out of your system
best darknet markets darknet websites
dark web search engines tor dark web
dark market link how to access dark web
dark web search engine deep web links
dark web market links darknet links
black internet dark web market links
darknet drug market tor marketplace
dark web link darknet market links
tor markets links darkmarket list
dark web sites dark web access
dark markets 2023 deep web drug markets
deep web drug markets onion market
Magnumbet
MAGNUMBET di Indonesia sangat dikenal sebagai salah satu situs judi slot gacor maxwin yang paling direkomendasikan. Hal tersebut karena situs ini memberi game slot yang paling gacor. Tak heran karena potensi menang di situs ini sangat besar. Kami juga menyediakan game slot online uang asli yang membuatmu makin betah bermain slot online. Jadi, kamu tak akan bosan ketika bermain game judi karena keseruannya memang benar-benar tiada tara. Kami juga menyediakan game slot online uang asli yang membuatmu makin betah bermain slot online. Jadi, kamu tak akan bosan ketika bermain game judi karena keseruannya memang benar-benar tiada tara.
Kami memiliki banyak sekali game judi yang memberi potensi cuan besar kepada pemain. Belum lagi dengan adanya jackpot maxwin terbesar yang membuat pemain makin diuntungkan. Game yang dimaksud adalah slot gacor dengan RTP hingga 97.8%
blackweb dark internet
tor market url darknet drug store
darknet search engine dark web market list
darkmarket list darknet drug market
onion market tor market url
darkmarket link tor market url
dark web drug marketplace deep dark web
darknet seiten deep web drug store
darknet drug market darknet websites
dark market url darknet drug links
tor markets 2023 deep web markets
darknet market links darknet site
darknet market dark web search engine
deep web drug store darknet drug links
black internet how to access dark web
how to get on dark web darknet search engine
dark market url darknet seiten
darknet market tor dark web
dark market link dark web websites
blackweb official website dark web links
dark net tor markets 2023
darknet market links tor markets
darknet drug store deep web markets
dosage of augmentin in infants alergia na augmentin duo augmentin duo prontuario
onion market best darknet markets
tor market darknet links
free dark web darknet market list
deep web search darkmarket url
tor markets 2023 tor markets
darknet market links darknet markets
tor dark web deep web drug store
tor marketplace drug markets onion
Увеличение ссылочной массы: Ключевой фактор в росте DR сайта. Увеличение ссылочной массы является неотъемлемой частью стратегии роста DR сайта. Этот процесс требует систематического и длительного подхода, включающего в себя поиск высококачественных ссылок, мониторинг и анализ ссылочной массы, а также адаптацию к постоянно меняющемуся окружению поисковых систем. Понимание этих аспектов и их правильная реализация помогут сайту достичь более высокого DR, что в свою очередь улучшит его ранжирование, привлечет больше органического трафика и повысит успех онлайн-присутствия бизнеса.
blackweb official website darknet drug links
deep web drug markets dark web search engines
tor markets links darknet drugs
darknet market links drug markets dark web
blackweb how to get on dark web
dark web search engine darkweb marketplace
darkmarket link drug markets dark web
darknet websites deep dark web
dark web sites dark web links
dark web market links the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket link
tor markets links darkmarkets
darkmarket list onion market
free dark web dark web link
deep dark web dark web websites
dark web markets tor marketplace
deep web drug store tor market url
Автор предлагает анализ различных точек зрения на проблему без призыва к одной конкретной позиции.
deep web markets dark net
dark markets dark web sites links
black internet dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace dark markets
dark web search engine darknet marketplace
deep web drug store dark markets
darknet market links deep web drug links
darkmarket 2023 darknet market
dark internet darkmarket url
the dark internet tor marketplace
Selamat datang di Surgaslot !! situs slot deposit dana terpercaya nomor 1 di Indonesia. Sebagai salah satu situs agen slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami menyediakan banyak jenis variasi permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati. Semua permainan juga bisa dimainkan cukup dengan memakai 1 user-ID saja. Surgaslot sendiri telah dikenal sebagai situs slot tergacor dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dimana kami sebagai situs slot online terbaik juga memiliki pelayanan customer service 24 jam yang selalu siap sedia dalam membantu para member. Kualitas dan pengalaman kami sebagai salah satu agen slot resmi terbaik tidak perlu diragukan lagi
deep web drug links deep web markets
darkmarkets dark web access
darknet markets 2023 the dark internet
สล็อต pg แท้
เว็บไซต์สล็อต 888 pg ยังมีการบริการลูกค้าที่เป็นเลิศด้วยทีมงานที่เป็นมืออาชีพและเป็นมิตรตลอดเวลา คุณสามารถติดต่อสอบถามหรือแจ้งปัญหาได้ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง ผ่านช่องทางต่างๆ เช่น สนทนาสด (Live Chat) โทรศัพท์ หรืออีเมล ทีมงานจะตอบกลับคุณอย่างรวดเร็วและเป็นมิตรเสมอ
นอกจากนี้ เว็บไซต์ยังมีโปรแกรมสะสมแต้มและสิทธิพิเศษต่างๆ สำหรับสมาชิก เมื่อคุณเล่นเกมสล็อต PG และเพิ่มแต้ม คุณสามารถแลกสิทธิ์และรับของรางวัลที่น่าตื่นเต้น เช่น เครดิตเสริมในการเล่น เงินคืน หรือของรางวัลพิเศษอื่นๆ ที่จะเพิ่มความสนุกและประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณ
ด้วยเหตุนี้ หากคุณต้องการสัมผัสกับประสบการณ์การเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ที่เป็นที่นิยมและมีคุณภาพ ไม่ต้องสลักว่าเว็บไซต์สล็อต 888 pg เป็นทางเลือกที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับคุณ ร่วมสนุกไปกับเกมสล็อต PG ที่มาพร้อมความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นสุดพิเศษได้ที่นี่!
dark websites dark net
darknet links free dark web
Get ready for an unparalleled gaming experience with WAKABET, the ultimate destination for thrilling entertainment and exclusive registration bonuses. We are excited to offer you an incredible bonus when you sign up, setting the stage for non-stop excitement and lucrative wins. With a wide range of games, convenient deposit options, and enticing promotions, WAKABET is your gateway to unforgettable gaming. Join us today and embark on a journey filled with excitement and endless possibilities!
Endless Gaming Options:
At WAKABET, we understand that variety is key to a captivating gaming experience. That’s why we bring you an extensive collection of games, featuring everything from classic slots to immersive table games and live casino adventures. With over 100 games to choose from, each offering unique themes and thrilling features, you’ll find endless entertainment at your fingertips. Dive into our diverse selection and discover new favorites that will keep you engaged for hours on end.
Effortless Deposits for Instant Action:
We know that time is precious when it comes to gaming. That’s why WAKABET offers seamless and secure deposit options, ensuring you can jump into the action without any delays. Whether you prefer credit cards, e-wallets, or other convenient payment methods, we have you covered. Enjoy hassle-free deposits and experience the thrill of playing your favorite games without any interruptions.
Claim Your Registration Bonus and Start Winning:
As a new member of the WAKABET family, we want to make your gaming journey even more exciting. That’s why we offer a generous registration bonus that will boost your gameplay from the start. Simply sign up and claim your bonus to enjoy extra credits that can be used to explore our wide range of games. This bonus is our way of saying thank you for choosing WAKABET as your gaming destination. Take advantage of this opportunity and increase your chances of hitting the jackpot!
Exciting Promotions and Rewards:
At WAKABET, the excitement doesn’t end with the registration bonus. We believe in rewarding our players throughout their gaming journey. Keep an eye out for our ongoing promotions, such as “Aposta Ganha,” where you have the chance to win additional rewards for your successful bets. Stay engaged and take advantage of these promotions to enhance your gaming experience and maximize your potential winnings.
Join WAKABET Today:
Don’t miss out on the thrilling world of WAKABET! Register today and unlock the door to endless entertainment, exclusive bonuses, and exciting promotions. Experience the thrill of winning as you explore our diverse game selection, enjoy seamless deposits, and reap the rewards of our ongoing promotions. WAKABET is your ultimate gaming destination, where the fun never stops and big wins await. Join us now and let the games begin!
Conclusion:
Are you ready to embark on a gaming adventure filled with excitement and rewards? Look no further than WAKABET, your go-to platform for thrilling entertainment and registration bonuses. With a vast collection of games, seamless deposits, and exciting promotions, WAKABET offers an unparalleled gaming experience. Sign up today, claim your bonus, and get ready to unleash the thrill of gaming at WAKABET. Start your journey now and discover a world of endless possibilities!
dark web search engine dark web site
dark websites darkmarket list
dark web drug marketplace dark web market
darkmarket 2023 the dark internet
darknet market list dark web market list
deep web search dark net
blackweb drug markets onion
darknet market links dark web sites
deep web drug store deep web drug store
deep web links darkmarket
dark web access dark markets
dark web access darkmarket 2023
oral meclizine 25mg
darkmarket 2023 dark web market list
darknet market links darkmarket 2023
the dark internet dark markets 2023
dark web websites best darknet markets
dark web markets dark market list
darknet market links how to access dark web
dark market link deep web drug store
antivert 25 mg us
the dark internet dark web drug marketplace
tor marketplace tor markets
darkmarket darknet drug store
dark market url darknet drug market
darknet seiten tor markets
tor markets 2023 best darknet markets
deep web drug url drug markets onion
dark web market links free dark web
darknet links tor market url
dark web sites links dark web markets
darkmarket 2023 darknet links
cost antivert
tor markets dark market
prednisone drug test https://prednisonesdc.com/ prednisone for copd dosage
darknet drug store darknet drug market
darknet market list how to access dark web
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
dark web markets dark web market
dark website darknet search engine
darkmarket 2023 tor darknet
dark web market list darknet websites
darkmarket list darknet seiten
tor market links onion market
best darknet markets deep web drug markets
tor market url dark markets
drug markets dark web tor marketplace
darknet drug market tor market
Очень интересная статья! Я был поражен ее актуальностью и глубиной исследования. Автор сумел объединить различные точки зрения и представить полную картину темы. Браво за такой информативный материал!
BLANGKON SLOT adalah situs slot gacor dan judi slot online gacor hari ini mudah menang. BLANGKONSLOT menyediakan semua permainan slot gacor dan judi online terbaik seperti, slot online gacor, live casino, judi bola/sportbook, poker online, togel online, sabung ayam dll. Hanya dengan 1 user id kamu sudah bisa bermain semua permainan yang sudah di sediakan situs terbaik BLANGKON SLOT. Selain itu, kamu juga tidak usah ragu lagi untuk bergabung dengan kami situs judi online terbesar dan terpercaya yang akan membayar berapapun kemenangan kamu
deep web drug markets darknet drugs
darknet markets tor markets 2023
darknet markets 2023 dark web link
deep web drug url dark market list
darkweb marketplace dark web link
tor markets darknet search engine
darknet links dark web search engines
darkmarket url darknet websites
dark web markets tor markets
dark web websites darknet websites
dark market darknet market
darknet drug store deep web markets
deep dark web dark web market links
deep dark web dark web market links
tor markets 2023 dark websites
darknet market list darknet market
dark web links dark net
dark internet blackweb official website
darkweb marketplace deep web drug store
dark market onion darknet search engine
blackweb darknet drug store
deep web drug markets dark market
darknet market list dark market url
dark web link dark market onion
deep dark web dark net
does prednisone cause constipation in dogs https://prednisonecyn.com/ prednisone alcohol interaction
deep web markets darknet marketplace
darkmarket url darknet websites
dark market tor markets 2023
deep web drug markets darknet market list
Автор представляет сложные понятия в доступной форме, что помогает лучше понять тему.
tor markets drug markets onion
dark web markets darknet drug market
darknet links onion market
Я прочитал эту статью с большим удовольствием! Она написана ясно и доступно, несмотря на сложность темы. Большое спасибо автору за то, что делает сложные понятия понятными для всех.
onion market dark web market
dark markets dark markets 2023
Tuy nhiên, để tăng cơ hội giành được Jackpot, có một số kỹ thuật và chiến lược bạn có thể áp dụng:
Chọn trò chơi Jackpot phù hợp: Trước khi bắt đầu, hãy tìm hiểu về các trò chơi Jackpot có sẵn và chọn những trò chơi có tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao. Xem xét các yếu tố như tỷ lệ đặt cược, số lượng dòng cược, và các tính năng đặc biệt trong trò chơi để tìm hiểu cách tăng cơ hội giành Jackpot.
Chơi với mức đặt cược lớn: Để có cơ hội giành được Jackpot, nên chơi với mức đặt cược lớn hơn. Tuy nhiên, hãy chắc chắn rằng bạn tuân thủ ngân sách cá nhân và chỉ đặt cược theo khả năng tài chính của mình.
Sử dụng các tính năng bổ sung: Trong một số trò chơi Jackpot, có các tính năng bổ sung như vòng quay miễn phí, biểu tượng Wild hoặc Scatter. Sử dụng chúng một cách thông minh và tận dụng các cơ hội tăng cường để tăng khả năng giành Jackpot.
Tham gia các chương trình khuyến mãi: Nhà cái thường có các chương trình khuyến mãi đặc biệt cho trò chơi Jackpot. Tham gia vào các chương trình này có thể mang lại những phần thưởng và giải thưởng hấp dẫn, tăng cơ hội giành được Jackpot.
Luôn kiên nhẫn và kiểm soát tâm lý: Quay Jackpot là một quá trình dài và đòi hỏi sự kiên nhẫn. Hãy kiểm soát tâm lý của bạn, không bị cuốn theo cảm xúc và không quyết định cược theo cảm tính. Luôn giữ sự kiên nhẫn và tin tưởng vào quy trình chơi.
Cuối cùng, hãy nhớ rằng Jackpot là một phần của may mắn. Dù bạn áp dụng bất kỳ kỹ thuật hay chiến lược nào, không có cách nào đảm bảo giành được Jackpot. Hãy tận hưởng trò chơi và coi nó như một hình thức giải trí thú vị, với hy vọng rằng may mắn sẽ đến với bạn.
drug markets dark web dark market link
dark web links dark web access
dark market darknet market lists
darknet seiten onion market
darknet site darknet seiten
deep web links black internet
deep web drug store darkmarket list
Helpful information. Fortunate me I found your website
by accident, and I am surprised why this coincidence
didn’t happened in advance! I bookmarked it.
dark market list deep web markets
dark web link dark markets
darknet drugs dark web site
dark web search engines bitcoin dark web
blackweb dark website
Tiếp tục nội dung:
Trong thế giới cá cược bóng đá, khái niệm “kèo nhà cái” đã trở thành một phần không thể thiếu. Tuy nhiên, việc đọc và hiểu đúng kèo nhà cái là một nhiệm vụ không dễ dàng. Để trở thành một người chơi thành công, người chơi cần phải nắm vững các thuật ngữ và nguyên tắc cơ bản liên quan đến kèo nhà cái.
Một trong những khái niệm quan trọng là “tỷ lệ kèo”. Tỷ lệ kèo là tỷ lệ số tiền nhà cái trả cho người chơi nếu cược thành công. Nó phản ánh tỷ lệ rủi ro và khả năng chiến thắng trong một trận đấu. Tỷ lệ kèo có thể được biểu diễn dưới dạng số thập phân hoặc phần trăm, và người chơi cần hiểu rõ ý nghĩa của các con số này.
Một số loại kèo phổ biến bao gồm kèo châu Á, kèo chấp, kèo tài/xỉu và kèo chẵn/lẻ. Kèo châu Á là hình thức kèo phổ biến ở châu Á, trong đó nhà cái cung cấp một mức chấp cho đội yếu hơn để tạo sự cân bằng trong cá cược. Kèo chấp đơn giản là đặt cược vào sự chênh lệch điểm số giữa hai đội. Kèo tài/xỉu là việc đặt cược vào tổng số bàn thắng trong một trận đấu. Kèo chẵn/lẻ là việc đặt cược vào tính chẵn hoặc lẻ của tổng số bàn thắng.
Ngoài ra, còn có khái niệm “kèo nhà cái trực tiếp”. Kèo nhà cái trực tiếp là tỷ lệ kèo được cập nhật và điều chỉnh trong suốt quá trình diễn ra trận đấu. Người chơi có thể theo dõi và đặt cược trực tiếp dựa trên sự thay đổi của tỷ lệ kèo trong thời gian thực. Điều này mang lại sự hấp dẫn và kích thích cho người chơi, đồng thời cho phép họ tận dụng cơ hội và điều chỉnh quyết định cá cược của mình theo diễn biến trận đấu.
Trong quá trình đọc kèo nhà cái, người chơi cần nhớ rằng kèo nhà cái chỉ là một dạng dự đoán và không đảm bảo kết quả chính xác. Việc thành công trong cá cược bóng đá còn phụ thuộc vào khả năng phân tích, tư duy logic, và kinh nghiệm của người chơi. Hãy luôn duy trì sự cân nhắc, đặt ra mục tiêu cá cược hợp lý và biết kiểm soát tài chính.
Tóm lại, kèo nhà cái là một yếu tố quan trọng trong việc cá cược bóng đá. Người chơi cần hiểu rõ về tỷ lệ kèo, các loại kèo phổ biến, và khái niệm kèo nhà cái trực tiếp. Đọc kèo nhà cái là một quá trình học tập và nghiên cứu liên tục. Hãy sử dụng thông tin từ các nguồn đáng tin cậy và áp dụng kỹ năng phân tích để đưa ra quyết định cá cược thông minh và tăng cơ hội chiến thắng.
dark website dark internet
darknet search engine darknet site
free dark web darknet markets 2023
darkmarket dark market onion
deep dark web blackweb
dark web site onion market
dark web market free dark web
darknet drug store darknet drug store
dark web links bitcoin dark web
how to access dark web the dark internet
tor darknet dark markets
Saved as a favorite, I like your web site!
drug markets onion how to access dark web
tor markets 2023 darkmarket list
deep web drug url blackweb
dark web search engine tor market
deep web markets tor markets 2023
order meclizine online cheap
deep web sites dark markets
blackweb official website dark market link
deep web drug links deep web drug url
darknet links tor market links
bitcoin dark web dark websites
the dark internet darknet marketplace
deep web search darknet marketplace
dark web links dark market url
deep web links deep web drug markets
best darknet markets deep web links
tor market dark net
best darknet markets deep web drug store
dark market dark market
dark market url darknet links
dark market url dark web drug marketplace
tor dark web blackweb
dark market onion deep web drug markets
tor market darkmarket 2023
dark market 2023 darkmarkets
dark market list darknet market lists
dark web sites dark web market list
the dark internet darkmarket link
order meclizine pill
dark web market list drug markets dark web
darkmarket blackweb
darknet market lists dark web links
Bonus no cadastro
Welcome to WAKABET, the ultimate destination for unparalleled gaming experiences and exclusive registration bonuses. We are thrilled to offer you a remarkable bonus upon signing up, ensuring your gaming journey starts with a bang. With a vast assortment of games, seamless deposit options, and enticing promotions, WAKABET stands as the epitome of thrilling entertainment and lucrative rewards. Join us now and unlock a world of excitement and endless possibilities!
A Plethora of Games Awaits:
At WAKABET, we understand that every player has unique preferences. That’s why we’ve curated a diverse collection of games, spanning various genres and themes. From classic slots to captivating table games and immersive live casino experiences, our library boasts over 100 thrilling options. Immerse yourself in the captivating world of online gaming and explore the vast array of games designed to deliver endless thrills and extraordinary winning opportunities.
Effortless Deposits for Instant Action:
We value your time and strive to provide a seamless gaming experience from the moment you join us. With our user-friendly deposit options, you can fund your account swiftly and effortlessly. Whether you prefer credit cards, e-wallets, or other convenient payment methods, WAKABET ensures hassle-free deposits. Experience the convenience and efficiency of our deposit process, allowing you to focus on what truly matters – enjoying the exhilarating games.
Claim Your Registration Bonus and Boost Your Wins:
As a token of appreciation, we offer an exciting registration bonus to all new players. By simply signing up at WAKABET, you unlock bonus credits that enhance your gameplay. Utilize these bonuses to explore different games, experiment with strategies, and maximize your chances of winning big. With our registration bonus, you can dive into the action with an extra advantage and make the most of your gaming experience.
Aposta Ganha: Celebrate Your Winning Bets:
At WAKABET, we celebrate your victories and offer promotions that amplify your success. Take advantage of “Aposta Ganha” (Winning Bet), where you can enjoy additional rewards for your successful wagers. Stay tuned for these special promotions and elevate your gaming thrills while increasing your potential winnings. Every bet becomes an opportunity to experience the joy of winning and indulge in the excitement of WAKABET.
Experience WAKABET Today:
WAKABET opens the door to a world of unparalleled gaming and extraordinary rewards. With our registration bonuses, extensive game library, seamless deposits, and enticing promotions, we are committed to providing an exceptional gaming experience. Join WAKABET now and immerse yourself in a world where the excitement never ceases. Register, claim your bonus, and embark on a thrilling journey filled with unforgettable moments and remarkable wins.
Conclusion:
Are you ready to elevate your gaming adventure to new heights? Look no further than WAKABET, where exceptional gameplay and exclusive registration bonuses await. With a diverse range of games, seamless deposit options, and exciting promotions like “Aposta Ganha,” WAKABET offers an unforgettable gaming experience. Join us today, claim your registration bonus, and let the thrilling games begin. Get ready to unleash the excitement, embrace the wins, and create lasting memories at WAKABET!
dark web market list the dark internet
dark markets how to get on dark web
drug markets onion dark web sites
go88 vin app
Đánh giá Go88.vin: Nền tảng chơi game đáng tin cậy
Go88.vin đã gây ấn tượng mạnh với cộng đồng game thủ và nhận được nhiều đánh giá tích cực. Dưới đây là những điểm nổi bật của Go88.vin:
Đa dạng trò chơi: Go88.vin mang đến một bộ sưu tập trò chơi phong phú, từ các trò chơi slot, bài cào, baccarat, đến xì tố, poker và nhiều trò chơi khác. Với sự đa dạng này, người chơi có nhiều lựa chọn để thỏa mãn sở thích cá nhân và tìm kiếm trò chơi phù hợp.
Chất lượng hình ảnh và âm thanh: Go88.vin đảm bảo mang đến trải nghiệm hấp dẫn với chất lượng hình ảnh sắc nét và âm thanh sống động. Nhờ vào công nghệ tiên tiến, người chơi sẽ được trải nghiệm như đang tham gia vào một sòng bạc thực tế.
Đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng: Go88.vin luôn quan tâm đến sự hài lòng của người chơi. Với đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng chuyên nghiệp và thân thiện, người chơi có thể yên tâm về việc được hỗ trợ mọi lúc, mọi nơi. Bất kể bạn gặp vấn đề gì, họ sẽ luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp và hỗ trợ bạn.
Bảo mật và an toàn: Go88.vin đặt sự bảo mật và an toàn của thông tin cá nhân của người chơi lên hàng đầu. Họ sử dụng công nghệ mã hóa tiên tiến để đảm bảo rằng dữ liệu cá nhân và giao dịch tài chính của bạn được bảo vệ một cách toàn diện.
Go88.vin không chỉ là một nền tảng chơi game, mà còn là một cộng đồng đam mê game với những sự kiện thú vị và cơ hội trúng thưởng hấp dẫn. Với những tính năng và ưu điểm vượt trội, Go88.vin là sự lựa chọn hàng đầu cho những người yêu thích game trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia Go88.vin ngay hôm nay và khám phá thế giới game đầy thú vị và cơ hội phát tài!
tor markets 2023 dark web search engine
darknet seiten blackweb
dark markets 2023 drug markets onion
สล็อตเว็บใหญ่ PG ยังเป็นที่รู้จักอย่างกว้างขวางในวงกว้างของผู้เล่นทั้งในประเทศและต่างประเทศ เนื่องจากความน่าเชื่อถือและความปลอดภัยที่เป็นลักษณะเด่นของเว็บไซต์ สมาชิกสามารถเข้าเล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา โดยใช้อุปกรณ์ที่สะดวกสบาย เช่น คอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต หรือสมาร์ทโฟน และยังสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บไซต์หรือแอปพลิเคชันที่รองรับทั้งระบบ IOS และ Android ได้อีกด้วย
สำหรับการเล่นสล็อต PG ในเว็บไซต์ สล็อต 888 pg นี้ ผู้เล่นจะได้สัมผัสกับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าตื่นเต้นและสนุกสุดมันส์ ด้วยหลักการเล่นที่ง่ายต่อการเข้าใจและระบบการจ่ายเงินที่เป็นธรรม เกมสล็อต PG ในเว็บนี้ยังมีรูปแบบที่หลากหลาย ตั้งแต่สล็อตคลาสสิกที่มีลักษณะเกมเก่าๆ และเสียงเสียงสัญญาณสล็อตที่คล้ายกับเครื่องสล็อตจริง ไปจนถึงสล็อตสมัยใหม่ที่มาพร้อมกับกราฟิกสุดล้ำในรูปแบบ 3D และเอฟเฟกต์ที่ล้ำสมัย จึงไม่แปลกใจที่ผู้เล่นจะติดใจกับเกมสล็อต PG และกลับมาเล่นอีกครั้งอย่างต่อเนื่อง
ดังนั้น หาก
darkmarket darknet seiten
how to get on dark web dark markets 2023
darkmarket darkmarket 2023
darknet websites dark market url
dark web websites dark market 2023
darknet search engine drug markets dark web
darknet sites darknet search engine
dark website dark web link
darknet market links blackweb official website
deep web drug url how to access dark web
dark market the dark internet
cheap meclizine 25mg
dark web market darknet market
deep web markets dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engines darkweb marketplace
Статья предлагает объективный обзор исследований, проведенных в данной области. Необходимая информация представлена четко и доступно, что позволяет читателю оценить все аспекты рассматриваемой проблемы.
tor darknet darkweb marketplace
dark market dark web market links
darknet links dark web search engines
deep web markets darknet websites
dark markets 2023 darknet seiten
dark web access darknet marketplace
tor darknet darknet market list
blackweb official website darknet market links
tor markets dark net
onion market darknet links
dark web sites drug markets onion
how to get on dark web deep web drug store
dark web market tor market url
Автор старается сохранить нейтральность и оставляет решение оценки информации читателям.
darknet drug store dark web links
darknet links deep web markets
dark market list dark markets
free dark web black internet
dark web market links deep web links
dark markets darknet market list
order antivert generic
dark net darkmarket link
tai xiu online
Đánh giá nhà cái Jili City: Ưu nhược điểm chân thực nhất – Link vào Jili City
Jili City đã gây được sự chú ý trong cộng đồng người chơi cá độ trực tuyến với những ưu điểm và độ tin cậy của mình. Tuy nhiên, để có cái nhìn tổng quan và quyết định có nên tham gia Jili City hay không, chúng ta cần xem xét cả những ưu nhược điểm của nhà cái này.
Một trong những ưu điểm chính của Jili City là giao diện trực quan và dễ sử dụng. Người chơi có thể dễ dàng tìm thấy các trò chơi yêu thích và thực hiện các giao dịch một cách nhanh chóng. Hơn nữa, Jili City cũng có phiên bản di động tương thích với các thiết bị di động, cho phép người chơi truy cập và chơi game mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
Tiếp theo, Jili City cung cấp một loạt các trò chơi đa dạng và hấp dẫn. Từ các trò chơi cá cược thể thao đến các trò chơi casino trực tuyến, người chơi có nhiều sự lựa chọn để thỏa mãn niềm đam mê cá độ của mình. Đồng thời, những trò chơi này được phát triển bởi các nhà cung cấp game uy tín, đảm bảo tính công bằng và giải trí tốt.
Jili City cũng được đánh giá cao về chất lượng dịch vụ khách hàng. Nhà cái này cung cấp hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7 thông qua các kênh liên lạc như chat trực tuyến, điện thoại và email. Đội ngũ nhân viên hỗ trợ thân thiện, nhiệt tình và sẵn sàng giúp đỡ người chơi trong mọi vấn đề liên quan đến trò chơi và tài khoản.
Tuy nhiên, Jili City cũng có một số nhược điểm cần được nhắc đến. Một số người chơi đã phản ánh về thời gian phản hồi chậm khi gặp vấn đề hoặc cần hỗ trợ từ nhà cái. Điều này có thể gây khó khăn và không thoải mái cho người chơi khi gặp vấn đề cần được giải quyết.
Ngoài ra, như với bất kỳ hoạt động cá cược trực tuyến nào, người chơi cần thận trọng và đảm bảo an toàn thông tin cá nhân và tài khoản của mình. Việc chọn một mật khẩu mạnh và không chia sẻ thông tin cá nhân với bất kỳ ai khác là rất quan trọng để bảo vệ quyền lợi của mình.
Để truy cập vào Jili City và tham gia vào trò chơi cá độ trực tuyến, người chơi có thể sử dụng link vào Jili City mà nhà cái cung cấp. Điều này đảm bảo rằng bạn đang truy cập vào trang web chính thức và an toàn của nhà cái.
Tóm lại, Jili City là một nhà cái cá độ trực tuyến đáng tin cậy và hấp dẫn. Với giao diện dễ sử dụng, các trò chơi đa dạng và chất lượng dịch vụ khách hàng tốt, Jili City là một lựa chọn phù hợp cho những người chơi yêu thích cá độ trực tuyến. Tuy nhiên, cần lưu ý về việc giải quyết các vấn đề và bảo vệ thông tin cá nhân một cách cẩn thận.
dark web market list dark websites
Khám phá Jili Games – Nơi hội tụ niềm vui và may mắn
Jili Games không chỉ là một nhà cung cấp trò chơi, mà còn là nơi mà người chơi có thể tìm thấy niềm vui và may mắn. Với dòng sản phẩm đa dạng và tính năng độc đáo, Jili Games đã trở thành một điểm đến tuyệt vời cho những người yêu thích giải trí và mong muốn tìm kiếm những trải nghiệm mới mẻ.
Jili Games luôn chú trọng đến việc mang đến niềm vui cho người chơi. Từ cốt truyện thú vị cho đến tính năng đặc biệt, mỗi trò chơi từ Jili Games đều được tạo ra để mang đến những phút giây thư giãn và hào hứng. Bạn có thể thử vận may trong các trò chơi slot, thể hiện kỹ năng trong trò chơi bài hay tìm hiểu thế giới dưới đáy biển trong trò chơi câu cá. Jili Games đem đến một loạt trò chơi đa dạng để bạn tận hưởng niềm vui và sự kích thích.
May mắn cũng là một yếu tố quan trọng trong Jili Games. Với tỉ lệ thưởng hấp dẫn và những phần thưởng giá trị, Jili Games mang đến cơ hội cho người chơi để giành chiến thắng lớn. Bạn có thể thử vận may trong các trò chơi slot, nổ hũ hoặc tham gia vào các giải đấu và sự kiện để tranh tài với người chơi khác. Jili Games không chỉ đem đến niềm vui, mà còn mang đến cơ hội kiếm được những phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
Jili Games cũng chú trọng đến trải nghiệm chơi game thuận lợi và linh hoạt cho người chơi. Với giao diện đơn giản và dễ sử dụng, bạn có thể dễ dàng truy cập vào trò chơi từ mọi thiết bị di động hoặc máy tính cá nhân của mình. Hơn nữa, Jili Games cung cấp dịch vụ nạp tiền và rút tiền nhanh chóng và an toàn, đảm bảo rằng người chơi có thể tận hưởng trò chơi một cách thoải mái và không gặp bất kỳ khó khăn nào.
Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm niềm vui và may mắn trong thế giới game online, hãy khám phá Jili Games ngay hôm nay. Tận hưởng trải nghiệm đa dạng và thú vị, thể hiện kỹ năng và tìm kiếm những phần thưởng giá trị. Jili Games sẽ đưa bạn vào một cuộc phiêu lưu đầy hứa hẹn và mang đến những trải nghiệm không thể nào quên được.
darkmarket 2023 darknet market links
deep web sites dark market link
deep web drug store darknet market lists
dark web search engine dark web sites links
black internet dark internet
onion market how to get on dark web
Мне понравилась глубина исследования, проведенного автором, для подкрепления своих утверждений.
onion market black internet
tor marketplace best darknet markets
blackweb darknet market lists
darknet site darknet seiten
darknet sites deep web links
meclizine over the counter
keo nha cai tv
Tiếp tục nội dung:
Ngoài ra, để có trải nghiệm tốt hơn khi tham gia cá cược bóng đá, người chơi cần luôn cập nhật thông tin về các sự kiện, trận đấu và các tin tức liên quan. Có thể theo dõi các trang web thể thao, xem các chương trình thể thao trên truyền hình, hoặc tham gia vào các diễn đàn, cộng đồng trực tuyến để chia sẻ và cập nhật thông tin với những người chơi khác. Việc này giúp người chơi có cái nhìn rõ ràng về tình hình và đưa ra quyết định cá cược thông minh hơn.
Ngoài ra, việc đọc kèo nhà cái cũng đòi hỏi sự hiểu biết về các loại kèo như kèo châu Á, kèo chấp, kèo tài xỉu và kèo chẵn/lẻ. Các loại kèo này có cách tính và ý nghĩa khác nhau, và người chơi cần nắm vững để có thể đưa ra quyết định cá cược chính xác.
Cuối cùng, trước khi tham gia cá cược bóng đá, người chơi cần nhớ rằng cá cược là một hình thức giải trí và không nên để nó ảnh hưởng đến cuộc sống cá nhân và tài chính. Người chơi nên đặt ra ngân sách hợp lý và tuân thủ quy tắc cá cược có trách nhiệm. Nếu cảm thấy căng thẳng hoặc gặp vấn đề về việc kiểm soát cá cược, người chơi nên tìm sự hỗ trợ từ các tổ chức chuyên về cờ bạc hoặc tìm kiếm tư vấn từ các chuyên gia.
Tóm lại, việc soi kèo nhà cái và tham gia cá cược bóng đá là một hoạt động thú vị và hấp dẫn. Tuy nhiên, người chơi cần cân nhắc, sử dụng thông tin và các dịch vụ uy tín để đưa ra quyết định thông minh và có trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất. Hãy luôn nhớ rằng cá cược là một hình thức giải trí và nên được thực hiện có trách nhiệm và kiểm soát.
bitcoin dark web darknet site
tor markets dark markets 2023
whyride
darknet drugs dark net
dark market url the dark internet
dark web websites darknet drug market
free dark web blackweb official website
tor market dark websites
darknet seiten tor dark web
dark web markets dark web access
darkmarket dark market onion
deep dark web drug markets onion
dark web search engine deep web drug markets
dark web websites dark web market list
deep dark web dark web search engine
As the admin of this website is working, no doubt very quickly it will be well-known, due to its
feature contents.
Look at my homepage: สล็อต777
darknet drugs darkmarket 2023
darkmarket link dark web sites links
dark web market darknet market list
Автор старается подойти к теме нейтрально, предоставляя информацию, не влияющую на мнение читателей.
darknet markets 2023 darknet site
can dogs take keflex https://keflexrno.com/ will keflex help a uti
tor market url darknet drugs
deep dark web dark web sites
darknet drug store darknet drugs
tor marketplace darknet drug market
best darknet markets darknet seiten
best darknet markets dark market list
Важно отметить, что автор статьи предоставляет информацию с разных сторон и не принимает определенной позиции.
blackweb darkmarkets
Автор приводит примеры из различных источников, что позволяет получить более полное представление о теме. Статья является нейтральным и информативным ресурсом для тех, кто интересуется данной проблематикой.
deep web drug markets dark web sites
drug markets dark web darknet market links
how to get on dark web darknet seiten
darknet drug store tor market url
Статья хорошо структурирована, что облегчает чтение и понимание.
Considering solutions to combat blemishes?
Learn about the transformative effects of accutane for acne and its ability to restore
skin health.
darknet drugs onion market
dark websites dark market
deep web drug markets the dark internet
Автор старается оставаться объективным, чтобы читатели могли сформировать свое собственное мнение на основе предоставленной информации.
deep web drug url black internet
black internet dark markets 2023
Я прочитал эту статью с большим удовольствием! Автор умело смешал факты и личные наблюдения, что придало ей уникальный характер. Я узнал много интересного и наслаждался каждым абзацем. Браво!
move out cleaning prices Gilbert
darknet marketplace dark internet
deep web drug store darknet seiten
jilicity
Đánh giá nhà cái Jili City: Ưu nhược điểm chân thực nhất – Link vào Jili City
Jili City đã gây được sự chú ý trong cộng đồng người chơi cá độ trực tuyến với những ưu điểm và độ tin cậy của mình. Tuy nhiên, để có cái nhìn tổng quan và quyết định có nên tham gia Jili City hay không, chúng ta cần xem xét cả những ưu nhược điểm của nhà cái này.
Một trong những ưu điểm chính của Jili City là giao diện trực quan và dễ sử dụng. Người chơi có thể dễ dàng tìm thấy các trò chơi yêu thích và thực hiện các giao dịch một cách nhanh chóng. Hơn nữa, Jili City cũng có phiên bản di động tương thích với các thiết bị di động, cho phép người chơi truy cập và chơi game mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
Tiếp theo, Jili City cung cấp một loạt các trò chơi đa dạng và hấp dẫn. Từ các trò chơi cá cược thể thao đến các trò chơi casino trực tuyến, người chơi có nhiều sự lựa chọn để thỏa mãn niềm đam mê cá độ của mình. Đồng thời, những trò chơi này được phát triển bởi các nhà cung cấp game uy tín, đảm bảo tính công bằng và giải trí tốt.
Jili City cũng được đánh giá cao về chất lượng dịch vụ khách hàng. Nhà cái này cung cấp hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7 thông qua các kênh liên lạc như chat trực tuyến, điện thoại và email. Đội ngũ nhân viên hỗ trợ thân thiện, nhiệt tình và sẵn sàng giúp đỡ người chơi trong mọi vấn đề liên quan đến trò chơi và tài khoản.
Tuy nhiên, Jili City cũng có một số nhược điểm cần được nhắc đến. Một số người chơi đã phản ánh về thời gian phản hồi chậm khi gặp vấn đề hoặc cần hỗ trợ từ nhà cái. Điều này có thể gây khó khăn và không thoải mái cho người chơi khi gặp vấn đề cần được giải quyết.
Ngoài ra, như với bất kỳ hoạt động cá cược trực tuyến nào, người chơi cần thận trọng và đảm bảo an toàn thông tin cá nhân và tài khoản của mình. Việc chọn một mật khẩu mạnh và không chia sẻ thông tin cá nhân với bất kỳ ai khác là rất quan trọng để bảo vệ quyền lợi của mình.
Để truy cập vào Jili City và tham gia vào trò chơi cá độ trực tuyến, người chơi có thể sử dụng link vào Jili City mà nhà cái cung cấp. Điều này đảm bảo rằng bạn đang truy cập vào trang web chính thức và an toàn của nhà cái.
Tóm lại, Jili City là một nhà cái cá độ trực tuyến đáng tin cậy và hấp dẫn. Với giao diện dễ sử dụng, các trò chơi đa dạng và chất lượng dịch vụ khách hàng tốt, Jili City là một lựa chọn phù hợp cho những người chơi yêu thích cá độ trực tuyến. Tuy nhiên, cần lưu ý về việc giải quyết các vấn đề và bảo vệ thông tin cá nhân một cách cẩn thận.
tor dark web dark web site
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets 2023
darknet site tor market
does amoxicillin have to be refrigerated amoxicillin not working amoxicillin shortage
dark web drug marketplace darknet market list
darknet search engine onion market
darkmarket url how to get on dark web
order antivert 25mg generic
deep web drug url tor dark web
tor markets links dark market url
deep web drug url darknet links
order meclizine sale
bitcoin dark web dark web search engines
tor marketplace blackweb official website
meclizine 25mg ca
deep web sites darknet drug market
amoxicillin acne https://amoxicillinxry.com/ amoxicillin liquid dosage
onion market dark web link
darknet markets dark web market
Статья предлагает разнообразные подходы к решению проблемы и позволяет читателю выбрать наиболее подходящий для него.
Hướng dẫn tải game Go88.vin
Để tận hưởng trọn vẹn trải nghiệm chơi game tại Go88.vin, hãy làm theo hướng dẫn dưới đây để tải game về thiết bị của bạn:
Bước 1: Truy cập vào trang web chính thức của Go88.vin.
Bước 2: Tìm và nhấn vào phần “Tải ứng dụng” hoặc “Tải game” trên trang web.
Bước 3: Chọn phiên bản ứng dụng phù hợp với hệ điều hành của thiết bị của bạn, ví dụ: iOS hoặc Android.
Bước 4: Nhấn vào nút “Tải xuống” để bắt đầu quá trình tải về.
Bước 5: Sau khi tải xuống hoàn tất, nhấp vào tệp tin cài đặt để bắt đầu quá trình cài đặt ứng dụng.
Bước 6: Đảm bảo rằng thiết bị của bạn đã cho phép cài đặt ứng dụng từ các nguồn không rõ nguồn gốc bằng cách kiểm tra phần cài đặt bảo mật của thiết bị.
Bước 7: Tiến hành cài đặt ứng dụng bằng cách làm theo các hướng dẫn trên màn hình.
Bước 8: Khi quá trình cài đặt hoàn tất, mở ứng dụng Go88.vin và đăng nhập vào tài khoản của bạn hoặc tạo một tài khoản mới nếu bạn chưa có.
Sau khi tải và cài đặt thành công ứng dụng Go88.vin, bạn có thể tận hưởng những trò chơi đa dạng, tham gia vào phần chơi trực tiếp hấp dẫn, và sử dụng các mã Go88 code để nhận được những phần thưởng độc quyền.
Với Go88.vin, bạn sẽ không chỉ được trải nghiệm những giờ phút giải trí sảng khoái mà còn có cơ hội kiếm tiền một cách thú vị. Hãy tải ngay ứng dụng Go88.vin và khám phá những trò chơi đỉnh cao ngay hôm nay!
jili slot
Jili Games – Cam kết sự bảo mật và công bằng cho người chơi
Một trong những yếu tố quan trọng nhất mà Jili Games đặt lên hàng đầu là sự bảo mật và công bằng đối với người chơi. Nhà cung cấp này cam kết đảm bảo thông tin cá nhân và tài khoản của người chơi được bảo vệ một cách tuyệt đối.
Jili Games sử dụng các phương pháp và công nghệ bảo mật tiên tiến để đảm bảo rằng thông tin cá nhân và giao dịch của người chơi được bảo mật và không bị xâm phạm. Tất cả dữ liệu cá nhân được mã hóa và lưu trữ trong một môi trường an toàn. Chính sách bảo mật của Jili Games tuân thủ các quy định và tiêu chuẩn ngành công nghiệp để đảm bảo rằng thông tin của người chơi được bảo vệ một cách tốt nhất.
Bên cạnh đó, Jili Games luôn đảm bảo tính công bằng trong trò chơi của mình. Các trò chơi được kiểm tra và xác minh độ tin cậy và công bằng bởi các cơ quan độc lập. Hệ thống ngẫu nhiên số được sử dụng để đảm bảo rằng kết quả của mỗi ván chơi là ngẫu nhiên và không bị can thiệp. Người chơi có thể yên tâm rằng mọi cơ hội và kết quả trong trò chơi đều được xử lý công bằng và minh bạch.
Ngoài ra, Jili Games cũng cam kết đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game lành mạnh và đáng tin cậy. Họ chú trọng đến việc ngăn chặn truy cập của người chơi không đủ tuổi và đảm bảo rằng trò chơi chỉ dành cho mục đích giải trí hợp pháp. Jili Games cũng cung cấp các công cụ và tài nguyên để hỗ trợ người chơi có trải nghiệm chơi game an toàn và có trách nhiệm.
Với cam kết vững chắc về bảo mật và công bằng, Jili Games đã xây dựng được lòng tin và sự tin cậy từ phía người chơi. Người chơi có thể yên tâm rằng thông tin cá nhân và trải nghiệm chơi game của mình được bảo vệ một cách tốt nhất. Với Jili Games, việc tham gia vào thế giới giải trí trực tuyến không chỉ mang lại niềm vui mà còn đem lại sự an tâm và tin tưởng.
Hãy tham gia vào Jili Games ngay hôm nay và khám phá trò chơi đa dạng, hấp dẫn cùng sự bảo mật và công bằng hàng đầu. Với Jili Games, bạn sẽ trải nghiệm một thế giới game online tuyệt vời và an toàn.
tỷ lệ keo nha cai
Tiếp tục nội dung:
Một yếu tố quan trọng nữa trong cá cược bóng đá là “quản lý cảm xúc”. Khi tham gia cá cược, người chơi cần giữ được sự bình tĩnh và không để cảm xúc chi phối quyết định của mình. Đừng bị cuốn theo cảm giác thắng thua và đặt cược dựa trên sự hứng thú hoặc sợ hãi. Thay vào đó, hãy giữ một tinh thần khách quan và đánh giá cẩn thận trước khi đưa ra quyết định cá cược.
Ngoài ra, “đa dạng hóa cược” cũng là một yếu tố quan trọng để tối ưu hóa cơ hội chiến thắng. Đừng đặt cược quá nhiều vào một loại kèo hoặc trận đấu duy nhất. Hãy khám phá và thử nghiệm các loại cược khác nhau, đặt cược vào các trận đấu khác nhau và theo dõi kết quả. Điều này giúp người chơi tìm ra các phương pháp cá cược hiệu quả và tăng khả năng đạt được lợi nhuận.
Cũng không nên quên về “tư duy chiến lược”. Người chơi cần có một kế hoạch và chiến lược rõ ràng trước khi tham gia cá cược. Xác định mục tiêu cá cược, đặt ra quy tắc và nguyên tắc cá cược, và tuân thủ chúng một cách nghiêm ngặt. Một tư duy chiến lược giúp người chơi có mục tiêu rõ ràng và không để mất phương hướng trong quá trình cá cược.
Cuối cùng, việc “tận dụng khuyến mãi và ưu đãi” là một cách để người chơi tăng cơ hội chiến thắng. Nhiều nhà cái cung cấp các chương trình khuyến mãi và ưu đãi đặc biệt cho người chơi. Hãy tận dụng các khuyến mãi này để tăng giá trị cá cược và cơ hội chiến thắng. Tuy nhiên, hãy đọc kỹ các điều khoản và điều kiện của khuyến mãi để hiểu rõ các quy định và ràng buộc.
Tóm lại, việc cá cược bóng đá không chỉ đơn thuần là đọc kèo nhà cái mà còn bao gồm nhiều yếu tố khác như quản lý cảm xúc, đa dạng hóa cược, tư duy chiến lược và tận dụng khuyến mãi. Từ việc áp dụng những yếu tố này, người chơi có thể nâng cao cơ hội chiến thắng và tận hưởng những trải nghiệm thú vị trong thế giới cá cược bóng đá.
When I feel lonesome or blase I just go to Local Sluts in Liverpool and spend some quality time with the most interesting dames on-line
darknet markets deep dark web
blackweb dark markets
azithromycin with prednisone azithromycin for dogs side effects can i take doxycycline and azithromycin together
For the reason that the admin of this web page is working,
no question very rapidly it will be well-known, due to its quality contents.
tor markets dark web market
Do i need to be home when the house cleaning service arrives?
deep web search dark web sites links
how to access dark web deep web markets
darknet site dark web market list
the dark internet darknet sites
dark web links blackweb official website
dark net dark net
how to access dark web tor market
dark market 2023 dark web markets
darkmarket dark net
drug markets dark web how to get on dark web
tor dark web darknet search engine
dark market dark market onion
deep dark web black internet
dark web drug marketplace how to get on dark web
darkmarket 2023 dark web markets
best darknet markets darknet site
deep web markets blackweb official website
dark web sites darknet drugs
dark market url darkmarket 2023
deep dark web darkmarket 2023
deep web markets darknet marketplace
darknet search engine dark market list
best darknet markets darknet markets
darkweb marketplace tor markets
darkmarket link how to access dark web
darknet links dark market 2023
how to get on dark web dark internet
deep web drug url tor marketplace
deep web drug links dark web market links
darknet drug market the dark internet
dark web markets dark net
darknet market lists darkweb marketplace
the dark internet free dark web
dark web access dark market url
darknet market deep web search
tor darknet dark market
deep web drug markets dark market url
dark web link deep web markets
darknet drug links dark markets
darknet drug links darknet websites
deep web sites tor darknet
darknet market links deep web sites
dark markets 2023 darknet seiten
best darknet markets dark web websites
darkmarkets deep web links
darknet drugs dark web sites links
dark net tor market url
dark market list onion market
best darknet markets darkmarkets
darknet drugs deep web markets
dark web sites dark market list
darknet drug market deep web drug store
deep web sites tor market links
dark web drug marketplace bitcoin dark web
deep web links black internet
deep dark web blackweb official website
tor market links dark web search engine
darknet market darknet drugs
dark market onion darknet site
dark market blackweb official website
darknet site onion market
dark markets darkmarkets
dark net drug markets onion
tor market url blackweb official website
black internet dark web link
dark web search engine best darknet markets
tor markets 2023 dark web sites links
the dark internet darknet drug store
tor markets dark market
dark web search engines dark web site
darkmarket blackweb
tor dark web dark web site
dark web markets deep web drug markets
deep web drug links darknet market
blackweb darknet marketplace
deep web drug store darknet market links
darknet markets how to get on dark web
dark market deep web links
dark web market list tor market
meclizine 25mg canada
dark web search engine dark market onion
dark web drug marketplace dark net
free dark web deep web sites
darkmarket 2023 dark markets 2023
dark web links darkmarket link
dark market dark market link
darkmarket 2023 dark web sites links
dark web sites links dark web search engines
deep web sites deep dark web
darknet search engine drug markets dark web
deep web drug url darknet marketplace
onion market darknet site
dark web sites links drug markets onion
darknet sites darknet market lists
dark web search engines drug markets dark web
deep web drug markets dark markets 2023
dark web search engine darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web dark web market
darknet marketplace darknet seiten
how to access dark web dark markets 2023
dark internet darknet drug store
darkmarket 2023 tor darknet
tor market url darkmarket
dark market darknet drug market
darknet market links deep web drug url
dark web market dark market onion
dark internet the dark internet
dark web search engine dark web drug marketplace
dark internet darkmarket
dark internet darknet marketplace
dark web sites links deep web links
darknet sites blackweb
darknet seiten the dark internet
darknet links darkmarket link
deep web search dark market
darkmarket 2023 darkweb marketplace
darkmarket list blackweb official website
darknet drugs dark web market list
darknet market list blackweb official website
tor market links darknet market links
tor darknet deep web drug store
darknet markets darkmarket url
darkmarket url dark web access
deep web sites darkweb marketplace
dark web market tor market url
tor darknet deep web drug store
dark web sites links bitcoin dark web
tor market darknet drugs
tor markets free dark web
tor market links darkmarket 2023
darknet markets darkmarket list
dark web market list dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets deep web sites
darknet websites darknet market
deep web links darkmarket url
darknet websites darknet search engine
dark web link tor market url
darkmarket list darknet site
deep web search darknet drug store
darknet markets 2023 dark market url
deep web search dark web search engines
darknet market darkmarket
darkmarket 2023 darknet links
tor markets links deep web drug store
dark market deep web links
dark web links tor markets 2023
tor dark web darknet market links
darknet seiten darknet market lists
dark web access dark markets 2023
dark websites how to get on dark web
dark web market list deep web drug markets
how to access dark web tor markets 2023
dark web sites dark market list
dark websites deep web drug markets
darknet search engine dark website
darknet site tor markets links
drug markets dark web darkmarket
darknet seiten tor dark web
dark market darknet marketplace
darknet sites tor marketplace
darknet search engine darknet market list
dark website tor marketplace
dark web links dark web site
tor markets links darknet market links
darknet seiten dark market url
darknet drugs onion market
darkmarket link tor dark web
dark net darkmarket
dark website darkmarkets
tor market links dark web sites links
dark web access dark market link
dark net dark web market links
cephalexin teva https://cephalexinuop.com/ cephalexin suspension 250
onion market darkmarket 2023
darknet drug store dark market onion
bitcoin dark web darkmarket url
deep web drug links tor market url
darknet websites darkmarket
drug markets dark web tor markets links
meclizine cheap
tor market dark web markets
dark market list darkmarket
darknet markets dark web market
tor darknet black internet
darknet seiten blackweb
dark market onion free dark web
tor markets 2023 tor marketplace
dark web access dark web websites
darknet market links darkweb marketplace
dark web access dark markets
darknet markets dark web market list
darknet market darknet search engine
tor market links darknet market list
dark market 2023 tor darknet
dark market 2023 darknet marketplace
dark market url blackweb
drug markets onion deep web drug links
dark web search engine dark internet
darkmarket 2023 tor dark web
darknet market dark web link
deep web sites dark web search engine
dark web link dark web links
deep web links deep web drug markets
darknet site dark markets 2023
dark web access dark web sites links
drug markets onion dark market onion
darkmarkets deep web markets
tor market links darkmarket 2023
dark website blackweb
darknet site deep web drug markets
onion market deep web drug links
dark web site deep web drug markets
dark market url black internet
darknet market lists dark web access
dark web websites dark web link
dark web site tor market url
tor market url deep web drug store
dark web link darknet drug links
deep dark web deep web drug url
dark websites darknet market list
dark web sites dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket link deep web drug links
deep web markets how to get on dark web
tor markets how to access dark web
deep dark web dark web sites
dark web links black internet
deep web drug store drug markets dark web
darknet market list dark web market links
dark web market links dark market onion
darknet drugs darknet seiten
darkmarket url dark web links
darknet markets darknet sites
darknet drugs darkmarket link
dark websites darknet markets 2023
darknet market the dark internet
darkmarket url dark web market links
bitcoin dark web deep web drug url
dark website tor darknet
dark market link darknet site
deep dark web deep web links
darknet markets 2023 deep web sites
dark web markets blackweb official website
blackweb dark web access
deep web drug links dark web link
dark web market list dark markets 2023
free dark web tor darknet
dark web websites dark web market links
dark web markets dark market list
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
dark web search engine darkmarket 2023
dark websites tor market url
dark market url dark market url
dark web sites darknet drug market
darknet websites darkmarkets
dark web market list darknet drug store
dark market url darkweb marketplace
dark web websites dark web sites links
dark web sites links dark web access
darknet site dark web search engines
dark web sites drug markets dark web
darknet drug store dark market list
dark web link darkweb marketplace
dark websites darknet seiten
deep web drug url dark market list
darknet search engine darknet marketplace
tor market url deep web drug url
how to access dark web bitcoin dark web
tor market links dark market
blackweb dark websites
deep web sites how to get on dark web
dark web search engines dark market link
dark web search engines tor markets 2023
dark web market links darkmarket 2023
dark web search engine dark web sites
the dark internet dark market onion
darknet market deep web drug url
dark web market list dark web links
tor market url dark market 2023
darknet market links dark net
dark website deep web drug links
buy meclizine 25 mg for sale
darknet marketplace deep web drug store
dark web sites tor marketplace
dark market dark web search engines
darkmarkets dark market
darknet drug store darknet markets 2023
darknet drug store dark market onion
darknet websites tor markets 2023
the dark internet darknet market list
darknet market blackweb
darkmarkets dark web link
dark market link dark web market list
drug markets dark web dark web site
blackweb official website onion market
darknet markets 2023 darknet sites
darknet search engine how to access dark web
the dark internet deep web markets
darkmarket list dark markets 2023
tor markets links darknet markets
dark market url darknet search engine
Hi would you mind letting me know which hosting company you’re using?
I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot quicker then most.
Can you recommend a good hosting provider at a
honest price? Thanks a lot, I appreciate it!
darknet sites dark web links
tor market url dark market
dark web market links dark web site
drug markets dark web tor markets
deep web search dark web market
darknet market dark web search engines
deep web drug url dark web websites
darknet site darkmarket list
dark website darkmarket list
tor market links deep web links
darknet site darkmarket
dark market list darknet drugs
dark internet dark web sites
dark web access the dark internet
darknet markets 2023 darknet markets
dark websites tor markets
deep web sites dark web websites
dark market list dark web link
onion market the dark internet
dark web market darknet links
darknet websites dark web market links
deep web sites dark web link
dark web sites darknet marketplace
dark markets dark web sites links
deep web drug url dark web link
dark web market links dark market onion
darknet markets darknet markets 2023
tor market darknet marketplace
dark web links black internet
dark websites tor marketplace
tor market deep web drug url
dark web market list dark markets 2023
dark market list tor darknet
darknet search engine dark web market links
darknet market blackweb
darknet markets 2023 dark websites
dark web search engine darkmarket url
dark web site how to access dark web
dark web search engine darknet market list
deep web drug links deep web links
dark internet darknet market list
deep web search darknet drug store
dark web search engine dark web site
tor market url tor marketplace
tor market links how to get on dark web
tor darknet darknet drugs
darkmarket link darknet drug store
deep web drug store deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web tor markets 2023
dark website blackweb
dark website dark web access
MEGA SLOT
darknet seiten dark website
drug markets dark web deep web drug url
tor markets darknet drug market
dark market url dark market 2023
darknet links dark market list
deep web sites tor market links
deep dark web darknet seiten
free dark web darknet market
tor darknet dark market onion
dark web links dark web site
dark web websites dark web search engine
dark web search engine darkmarkets
darknet seiten tor darknet
darknet site onion market
dark web drug marketplace dark markets 2023
darkmarkets dark internet
darknet marketplace tor markets
darknet drug links black internet
dark web markets black internet
drug markets onion tor dark web
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug url
deep web drug store darknet site
tor market url dark market link
deep web markets deep web drug url
deep web drug links dark market list
dark web sites dark web search engines
darknet market darkmarket link
dark web sites dark market 2023
drug markets onion dark web site
darknet markets 2023 dark internet
deep web drug markets tor market links
tor darknet dark web link
dark web search engine the dark internet
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug links
tor markets darknet markets 2023
tor markets deep web links
tor markets 2023 dark web search engines
tor market url deep dark web
darknet marketplace dark web websites
dark web markets dark market url
dark net dark web websites
darknet drug market darknet drug links
darknet markets 2023 deep web search
blackweb official website darknet search engine
darknet links dark internet
bitcoin dark web dark web access
darknet market darkmarket
darknet search engine free dark web
best darknet markets tor darknet
blackweb dark web markets
dark web sites best darknet markets
how to access dark web blackweb
darknet drugs dark web link
darknet site darknet sites
tor markets links dark web market
blackweb darknet links
darknet drugs darkmarket
drug markets dark web darknet drugs
tor market links tor markets 2023
dark net dark markets
tor market links darknet sites
darkmarket list darknet market
dark web drug marketplace deep web search
dark market url dark web links
tor market links how to get on dark web
tor darknet tor markets
dark web search engine darknet drugs
darknet markets 2023 darknet markets
onion market black internet
dark market link dark market list
dark web market dark markets
dark market onion darkmarket url
dark web access dark markets
tor markets dark web link
jili fishing game
Khám phá Jili Games – Nơi hội tụ niềm vui và may mắn
Jili Games không chỉ là một nhà cung cấp trò chơi, mà còn là nơi mà người chơi có thể tìm thấy niềm vui và may mắn. Với dòng sản phẩm đa dạng và tính năng độc đáo, Jili Games đã trở thành một điểm đến tuyệt vời cho những người yêu thích giải trí và mong muốn tìm kiếm những trải nghiệm mới mẻ.
Jili Games luôn chú trọng đến việc mang đến niềm vui cho người chơi. Từ cốt truyện thú vị cho đến tính năng đặc biệt, mỗi trò chơi từ Jili Games đều được tạo ra để mang đến những phút giây thư giãn và hào hứng. Bạn có thể thử vận may trong các trò chơi slot, thể hiện kỹ năng trong trò chơi bài hay tìm hiểu thế giới dưới đáy biển trong trò chơi câu cá. Jili Games đem đến một loạt trò chơi đa dạng để bạn tận hưởng niềm vui và sự kích thích.
May mắn cũng là một yếu tố quan trọng trong Jili Games. Với tỉ lệ thưởng hấp dẫn và những phần thưởng giá trị, Jili Games mang đến cơ hội cho người chơi để giành chiến thắng lớn. Bạn có thể thử vận may trong các trò chơi slot, nổ hũ hoặc tham gia vào các giải đấu và sự kiện để tranh tài với người chơi khác. Jili Games không chỉ đem đến niềm vui, mà còn mang đến cơ hội kiếm được những phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
Jili Games cũng chú trọng đến trải nghiệm chơi game thuận lợi và linh hoạt cho người chơi. Với giao diện đơn giản và dễ sử dụng, bạn có thể dễ dàng truy cập vào trò chơi từ mọi thiết bị di động hoặc máy tính cá nhân của mình. Hơn nữa, Jili Games cung cấp dịch vụ nạp tiền và rút tiền nhanh chóng và an toàn, đảm bảo rằng người chơi có thể tận hưởng trò chơi một cách thoải mái và không gặp bất kỳ khó khăn nào.
Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm niềm vui và may mắn trong thế giới game online, hãy khám phá Jili Games ngay hôm nay. Tận hưởng trải nghiệm đa dạng và thú vị, thể hiện kỹ năng và tìm kiếm những phần thưởng giá trị. Jili Games sẽ đưa bạn vào một cuộc phiêu lưu đầy hứa hẹn và mang đến những trải nghiệm không thể nào quên được.
tor market links dark web access
black internet dark market link
tor markets 2023 darknet market list
black internet dark market url
tor market links dark web link
dark web search engines blackweb
dark web search engines darknet site
meclizine 25mg generic
bitcoin dark web tor markets 2023
dark web site blackweb
deep web search darknet market
darknet drug links darkmarket 2023
darknet websites dark market list
dark web site deep web drug url
darknet drug store drug markets dark web
darknet marketplace darkmarket 2023
dark market link darkmarket list
deep web drug markets dark market link
dark web search engines tor marketplace
darknet sites drug markets dark web
darknet market lists dark market link
tor dark web best darknet markets
dark web search engine darknet site
dark web sites links dark market link
darknet websites darkmarket list
dark web market list deep dark web
deep dark web darkmarket list
dark market 2023 dark web markets
dark markets dark market url
the dark internet tor darknet
dark web market darknet marketplace
tor markets links darknet markets 2023
dark websites tor market url
darkmarkets dark market list
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
darkmarket link dark market link
darknet market darkmarket
deep web markets darkmarket link
dark web markets darknet market
bitcoin dark web dark market url
how to access dark web deep web markets
dark web access deep web drug url
darkmarket 2023 dark web access
deep dark web dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists tor marketplace
dark web search engines darknet market
deep web links darknet markets
dark markets 2023 dark web websites
deep web drug url dark market list
darknet markets deep web markets
dark market url tor markets
dark markets best darknet markets
the dark internet darknet markets
tor market dark web access
deep web links deep web drug url
darkmarket 2023 dark web sites
darkweb marketplace dark web search engines
darknet marketplace tor dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet market
dark market url darknet search engine
dark web site darknet markets 2023
dark web links darkmarket link
dark web search engines deep web drug links
dark market list tor market
onion market deep web search
meclizine us
dark web drug marketplace dark web links
dark market url darknet marketplace
darkmarket link blackweb official website
tor markets links best darknet markets
tor darknet how to access dark web
darknet websites darknet drug links
dark web sites dark internet
darknet site tor markets
tor markets 2023 dark websites
dark web access darknet market
dark net darknet seiten
dark market darkmarket link
darknet markets dark market onion
darkmarket tor market url
darknet drug market darknet links
dark markets 2023 dark web market list
dark net deep web markets
tor market url dark markets 2023
tor market url dark web drug marketplace
darkmarkets dark market onion
darknet market free dark web
keflex pediatric dose calculator cephalexin (keflex) 500 mg oral cap ear infection keflex black box warning
dark net dark web link
tor markets 2023 dark web link
darknet drug links darkmarket
darknet markets dark website
darknet websites dark web market links
darkmarket 2023 bitcoin dark web
darknet search engine dark web sites
darknet seiten deep dark web
darknet site darknet marketplace
how to get on dark web dark web sites links
deep web drug links drug markets dark web
tor markets tor markets 2023
dark web market links darknet drugs
darknet market deep dark web
deep web drug url deep web drug store
dark web links dark web market
tor darknet dark market list
deep web markets deep web drug url
dark web links dark markets
dark web drug marketplace darkweb marketplace
darknet market list darkmarket list
blackweb dark market link
darknet sites darknet drug store
darknet seiten drug markets onion
tor market links the dark internet
dark web search engine black internet
bitcoin dark web dark market onion
drug markets dark web dark net
dark internet how to access dark web
dark websites darknet sites
darknet links tor dark web
dark net the dark internet
darknet marketplace dark market onion
tor markets darknet sites
how to get on dark web deep web drug store
tor markets 2023 dark net
tor marketplace dark web market list
darkmarket url darkmarket
darknet site onion market
darkmarket url drug markets dark web
darknet site darkweb marketplace
darkmarket link tor markets links
darknet markets 2023 dark web access
tor market url darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web tor darknet
tor markets drug markets onion
dark markets 2023 darknet search engine
deep dark web dark web markets
darknet market lists deep web drug links
dark web market list darkmarkets
dark web search engine darknet drug links
how to get on dark web tor markets 2023
best darknet markets dark net
dark market darknet links
darknet links dark web link
deep web sites darkmarket link
drug markets onion dark internet
deep web drug links dark net
darknet market links dark web market list
darknet markets tor marketplace
darkmarkets tor markets 2023
darknet market drug markets onion
dark market list bitcoin dark web
darknet links deep dark web
dark web sites links darknet markets
dark web markets darknet market links
dark web links dark web drug marketplace
dark web market tor markets 2023
darknet search engine how to access dark web
tor market url darkmarket
deep dark web darknet search engine
darknet seiten dark market onion
dark web access tor market
drug markets dark web dark market
dark web sites tor market links
tor market links drug markets dark web
tor market darknet market lists
darkmarket tor market url
deep web search how to get on dark web
best darknet markets dark web markets
darknet search engine tor markets links
dark web search engine darknet drug store
tor marketplace deep web drug markets
dark market onion dark web sites
tor market links dark web access
darknet market list deep web sites
how to access dark web darknet seiten
darkmarket list dark net
darkmarket list deep web drug url
bitcoin dark web tor dark web
darkmarket dark market url
deep web links deep web drug links
deep web drug url tor markets
dark web search engines deep web drug url
dark web site dark market list
tor darknet black internet
the dark internet darkmarket 2023
dark market onion dark web access
deep web search darkmarkets
dark web market list dark markets
deep web search dark web sites links
dark web market list dark web market list
blackweb darknet market lists
deep web sites darkmarket list
dark web access deep web markets
augmentin nourrisson sans ordonnance augmentin amigdalite augmentin dosage ear infection adults
tor markets 2023 dark market link
dark web search engine dark web market list
dark web access darknet markets
deep web markets deep web drug url
darknet markets 2023 dark market 2023
dark web drug marketplace dark web search engine
dark web market links darknet drugs
tor market links dark web links
dark web websites deep web markets
deep dark web darknet sites
darknet drug links darkmarkets
tor marketplace dark web market links
tor marketplace darknet markets
tor darknet tor marketplace
dark market list blackweb
tor marketplace dark market
dark web link best darknet markets
dark web websites dark web search engines
dark market url dark web search engines
dark market onion deep web search
darknet websites drug markets dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets
deep web links darknet links
dark website dark web link
dark web market links darknet drugs
tor market links best darknet markets
dark web search engines darknet drug links
darknet market deep web drug links
dark web sites dark web market
dark web search engines darkmarket 2023
best darknet markets deep web markets
onion market darkmarkets
darkmarket list dark markets 2023
tor market links dark websites
tor markets darknet markets 2023
drug markets dark web tor marketplace
dark web links dark web site
deep web sites tor dark web
deep web drug links dark web sites
darknet markets 2023 drug markets onion
dark net dark web search engines
dark markets 2023 darknet markets 2023
dark web link darkmarket url
darknet drugs deep web sites
dark market 2023 darknet market list
deep web drug links darknet drug market
darknet market list darknet markets 2023
darkmarket 2023 black internet
dark markets 2023 darknet drug store
tor markets darkmarket url
dark market link dark markets 2023
dark internet dark web access
drug markets dark web darkmarkets
deep web drug store deep web search
darkmarket url darknet markets 2023
how to access dark web bitcoin dark web
darknet links darknet sites
black internet dark web access
deep web drug markets onion market
dark web links dark web link
dark web market list tor marketplace
drug markets dark web darknet markets 2023
dark web site darknet links
dark net dark market url
dark market dark web search engine
best darknet markets darkmarket
tor markets blackweb
tor marketplace dark markets 2023
tor market url dark markets 2023
darknet market darknet markets
blackweb dark web markets
dark market onion darknet site
darknet drugs bitcoin dark web
darkmarket url dark web sites links
dark web search engine best darknet markets
darknet site dark web link
drug markets onion tor marketplace
drug markets onion dark market 2023
darknet market tor darknet
the dark internet deep web markets
darknet drug store darknet drug links
tor market blackweb
deep web links dark web search engines
tor marketplace deep web links
darkweb marketplace how to get on dark web
darknet drug links best darknet markets
onion market dark market url
darknet search engine darknet market
dark web sites links dark web links
the dark internet dark market url
tor markets dark market onion
darknet seiten darkmarket 2023
tor markets links darknet market list
darknet marketplace the dark internet
dark internet black internet
darknet websites darknet links
dark web link darknet marketplace
darkmarket darknet drugs
dark web market links darknet market lists
tor markets tor markets links
deep web drug store how to access dark web
darknet drug links dark web search engine
darknet market links deep web sites
dark web links dark net
darknet marketplace tor marketplace
darknet seiten dark market onion
deep web search darknet drug links
deep web links deep web drug url
dark web drug marketplace tor market url
blackweb darknet drug market
dark market list tor markets
best darknet markets dark web search engine
darknet sites deep web drug url
dark web site darkmarkets
blackweb blackweb
darkmarket url darkmarket link
dark market 2023 blackweb official website
how to access dark web how to get on dark web
tor markets 2023 onion market
dark web search engines deep web sites
darknet sites dark web market list
deep web links black internet
tor market url dark market url
dark markets 2023 dark web market links
blackweb blackweb official website
deep web links how to access dark web
dark web websites darknet market list
dark market url dark markets 2023
darknet market links darknet drug market
darknet drug market black internet
tor markets links dark market url
tor marketplace darknet market list
the dark internet dark web links
dark web search engines best darknet markets
darknet drug links dark web link
the dark internet darknet drug store
tor marketplace tor darknet
darkmarket list dark web search engine
tor markets links dark markets 2023
dark web sites links dark web websites
darkmarket list dark web search engine
deep web search dark market 2023
dark website tor market links
dark net dark web search engines
darknet market links dark web links
dark market url dark markets 2023
darknet search engine black internet
darkweb marketplace deep dark web
how to access dark web dark web markets
tor market links darkmarket url
tor markets 2023 how to access dark web
drug markets onion dark web sites
dark web market links free dark web
best darknet markets darkweb marketplace
dark web markets tor markets 2023
dark web link onion market
darknet market list tor markets links
blackweb blackweb
dark internet darkmarket
tor dark web onion market
dark market url dark web sites
darknet drug links tor dark web
dark market 2023 dark web links
tor markets deep web sites
darkmarkets darknet market list
darknet market list dark websites
darkmarket link dark web sites
darkmarket 2023 dark web drug marketplace
dark markets dark web links
darknet drugs tor market
darkweb marketplace dark market
dark markets dark web drug marketplace
dark web site dark market
darknet search engine tor markets
darknet search engine dark web sites links
deep dark web drug markets onion
darkweb marketplace deep web markets
dark markets dark web search engines
tor market tor marketplace
deep web links tor dark web
dark web websites deep web markets
doxycycline hyclate tooth infection doxycycline mrsa doxycycline good for uti
dark markets dark market link
deep web drug links dark market link
dark web links darkmarket link
deep web drug store dark web search engine
darknet seiten blackweb official website
darknet marketplace dark web market
deep web search darkmarket 2023
darknet markets 2023 darkmarkets
tor darknet drug markets dark web
darknet market lists darknet drug market
darknet sites dark markets 2023
tor market dark website
deep web drug store darknet search engine
dark web site best darknet markets
dark web websites dark market list
deep web markets drug markets dark web
dark websites dark web market
dark web search engine dark market 2023
dark market url best darknet markets
darknet markets darknet market
tor markets links tor markets
tor darknet tor market url
bitcoin dark web tor market
dark web sites dark web sites links
dark markets 2023 darkmarket link
deep web links dark market link
tor market links dark web access
free dark web deep web drug links
dark market onion darkmarket list
tor market darknet search engine
darkmarkets blackweb
onion market darkmarkets
dark web search engines darknet drugs
dark web sites links darknet market lists
deep web markets dark market link
darknet market dark websites
tor market links tor market links
deep web drug store drug markets onion
dark market 2023 darknet market list
free dark web drug markets onion
dark web sites dark web access
dark net dark web market list
dark web link dark web market
darknet market lists dark market url
darkmarkets black internet
blackweb official website dark web search engine
drug markets onion dark web websites
drug markets dark web darkmarket 2023
darkmarket url darknet links
dark markets dark web access
dark net darknet links
deep web markets darknet links
darkweb marketplace blackweb official website
blackweb official website best darknet markets
darknet sites blackweb
dark web market darkmarkets
onion market darknet marketplace
dark market onion market
dark web market list tor markets links
dark web sites links tor markets
how to access dark web dark markets
darknet search engine darknet market links
dark market 2023 dark web market links
darkmarket list darkmarket list
dark market 2023 darkmarkets
dark websites darkmarket url
dark market url dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists darknet websites
onion market dark web websites
how to get on dark web darkweb marketplace
dark market darknet drug market
tor marketplace darkmarket
deep web search dark web search engine
bitcoin dark web dark web markets
dark net darknet market
black internet tor markets
darknet market links darkmarkets
dark web market list dark web search engines
darknet site dark market 2023
is ciprofloxacin taken with food ciprofloxacin dosage for ureaplasma combination of ciprofloxacin and ceftriaxone
tor markets links deep web links
darknet websites bitcoin dark web
darkmarket tor markets links
dark web link dark market 2023
deep web markets bitcoin dark web
dark market link dark web markets
deep web drug markets darkmarket 2023
dark web drug marketplace darkmarkets
darknet seiten dark internet
dark web link tor market
tor market links tor markets links
best darknet markets darkmarket link
deep web links tor dark web
darkweb marketplace deep web drug links
deep web drug links dark websites
dark markets 2023 blackweb official website
tor market darknet market list
free dark web tor markets links
deep dark web how to access dark web
dark web links dark web search engines
how to access dark web deep web drug links
darknet site blackweb official website
darknet drugs tor market
tor dark web darknet drug market
darkmarket dark websites
dark web sites links dark web sites links
darknet markets dark market 2023
darknet markets 2023 deep web links
dark markets 2023 the dark internet
darknet market lists dark web sites
darkmarkets darknet market
dark websites deep web drug url
deep web drug url dark web site
dark website tor dark web
darkmarket darknet site
dark market onion darknet markets 2023
drug markets onion darknet markets 2023
Piece of writing writing is also a fun, if you be familiar with then you can write otherwise it is difficult to write.
drug markets dark web dark web websites
how to get on dark web deep web drug url
darknet links tor market
darkmarket darkmarkets
dark markets deep web markets
dark market darknet market links
darkmarket 2023 deep web markets
deep web drug links best darknet markets
tor markets darknet markets
darknet seiten deep web drug store
dark internet dark web websites
blackweb dark web site
darknet marketplace darkmarkets
darkmarket 2023 darknet market
dark web markets darknet markets 2023
dark market tor market links
doxycycline vs azithromycin for chlamydia is azithromycin a steroid or antibiotic azithromycin used for chlamydia
blackweb official website best darknet markets
dark market url bitcoin dark web
tor markets tor markets 2023
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
drug markets onion deep web drug store
deep web sites drug markets dark web
dark web link tor market url
darknet marketplace darknet drugs
deep web search dark web drug marketplace
tor markets 2023 darknet drug links
tor markets links dark web market
dark market url dark internet
deep web drug links darknet websites
onion market darknet site
dark web market darkmarket
deep web drug store onion market
deep web links tor marketplace
darknet sites deep web drug store
I am regular reader, how are you everybody?
This paragraph posted at this site is truly nice.
deep web sites dark web sites
dark web link dark net
darknet search engine dark market
darknet drug store dark net
darknet market darknet drug store
dark web site darkmarket 2023
dark market list darknet market list
darknet market lists darkmarket 2023
black internet darknet market links
dark markets dark web market list
tor markets 2023 tor market
dark web sites links darknet drug market
darknet market list how to access dark web
darknet sites how to access dark web
bitcoin dark web deep web drug markets
dark web market drug markets onion
dark web markets dark market list
best darknet markets drug markets dark web
deep web markets darkmarket link
dark market link dark web links
tor markets darknet market list
dark websites dark web link
black internet deep dark web
reasons for pursing year of service essay https://eddresearchpaper.com/ community service college application essay
tor darknet dark market url
darkmarket 2023 darknet market list
dark market list tor market links
deep web drug url how to access dark web
darknet market lists dark market
deep web search dark web markets
dark market darknet drug links
darknet market list darknet market links
darknet links tor marketplace
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug market
darknet websites dark web search engine
tor dark web darkmarket url
dark net dark market onion
darknet market lists the dark internet
deep web drug links darknet site
dark markets 2023 dark web market
blackweb dark web sites
darknet market links darknet websites
darkmarket url dark markets
best darknet markets drug markets onion
dark web sites links tor markets 2023
dark web link tor market url
deep web drug url dark market onion
dark web links tor dark web
darknet market links deep web markets
dark market onion deep web search
darknet sites darknet sites
drug markets dark web darknet links
dark web search engine free dark web
dark market onion deep web drug markets
blackweb official website dark market url
the dark internet deep web markets
dark market link darknet markets
darknet sites dark market 2023
darknet sites dark web market list
darknet drug links how to get on dark web
dark web websites dark market link
dark web market list darkmarket url
darknet markets deep web drug store
tor marketplace dark web access
darknet sites darknet links
free dark web dark web site
dark internet deep web drug links
darknet marketplace tor market url
dark markets 2023 how to get on dark web
dark web drug marketplace dark markets
darkweb marketplace darknet drugs
dark market onion darknet drug links
deep web drug store how to access dark web
tor markets links tor markets links
darknet drug links dark market
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket
dark web sites links dark market url
dark net darkweb marketplace
dark market url darknet market lists
dark market url dark web market list
deep web sites tor market
the dark internet dark net
darknet markets tor markets links
deep web sites tor market links
dark web search engine black internet
how to get on dark web darknet site
tor marketplace darknet drug links
tor market url darknet drug store
deep web drug markets darkmarket link
darknet drug market dark web websites
how to access dark web best darknet markets
blackweb dark web market list
tor markets darknet search engine
how to get on dark web darkweb marketplace
darkmarket onion market
deep web markets darknet search engine
darknet markets 2023 dark website
deep web drug markets dark market link
dark net deep dark web
deep dark web deep web drug store
tor dark web deep web search
dark web sites darknet market links
darknet websites dark website
dark web market darknet drugs
onion market tor marketplace
tor market url dark market url
bitcoin dark web dark market list
tor market dark markets 2023
tor marketplace deep web search
dark web link tor darknet
onion market darkmarket
how to access dark web darknet websites
free dark web dark web site
darknet drug store darkmarkets
darknet site darknet market
darknet sites dark market
darkmarket url dark markets 2023
blackweb black internet
dark market 2023 tor market links
bitcoin dark web deep web sites
deep web drug markets blackweb
darknet market dark market list
dark web market links tor darknet
how to access dark web deep web links
dark websites darknet search engine
black internet black internet
darknet markets 2023 darknet drugs
darknet sites free dark web
tor market url dark web websites
darknet search engine darknet drug market
the dark internet drug markets onion
darknet search engine dark web access
darknet sites dark web market list
darknet seiten deep web sites
dark market list deep web drug links
darkmarket drug markets onion
dark websites tor marketplace
best darknet markets tor markets
darknet marketplace dark website
tor dark web dark net
onion market dark web websites
tor darknet dark web sites
tor dark web tor markets links
tor markets 2023 dark web links
deep web sites darkmarket list
deep web drug store tor market url
free dark web darknet market list
blackweb darknet drug market
tor markets 2023 darkmarket link
darknet market how to access dark web
free dark web dark web sites links
blackweb official website dark web search engine
deep web search darknet drug links
deep web search tor dark web
deep web sites dark market link
dark web sites links dark market url
onion market dark web links
dark web links dark web websites
darknet site dark market list
bitcoin dark web bitcoin dark web
darknet websites dark web search engines
dark markets darkmarket link
tor darknet dark web market
darknet links black internet
free dark web darknet drugs
tor dark web dark web links
dark market onion darknet market list
darkmarket url dark internet
deep web markets dark market list
dark internet darkmarkets
darknet marketplace darknet market lists
drug markets dark web darknet drug store
tor market bitcoin dark web
deep web markets tor markets 2023
dark web sites tor market
darknet search engine darkmarket 2023
darknet site dark markets 2023
cephalexin for gum infection https://cephalexinuop.com/ can i take cephalexin without food
dark web websites the dark internet
tor market links deep web drug links
deep web drug markets onion market
deep web drug store darknet drug market
dark web websites deep web sites
best darknet markets dark web markets
bitcoin dark web dark web access
deep dark web darknet markets 2023
dark web access darknet markets
darkmarket link darknet sites
dark web market list darknet search engine
darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
darknet drug store darknet site
how to get on dark web black internet
tor market url darknet search engine
tor market darkmarket list
darknet drug market deep web markets
darkmarket link blackweb official website
darknet sites darknet markets
darkmarket tor darknet
dark web market list darknet market lists
dark internet blackweb official website
dark website dark web market list
darknet links deep web markets
dark market onion dark internet
dark web search engines darknet market links
deep web drug url darknet market links
dark websites darknet market links
deep dark web blackweb
darknet drug market tor market
darkmarket url deep web search
deep web search black internet
darknet market dark website
deep web drug markets tor market url
darkmarket url dark websites
tor market links darknet market list
free dark web tor markets
darknet websites tor markets 2023
dark web market how to access dark web
darknet markets 2023 darknet seiten
dark net onion market
dark web search engines darknet drug links
deep web drug links deep web sites
darknet market links dark web websites
dark website dark web access
drug markets dark web dark web search engine
deep web drug markets deep web drug markets
bitcoin dark web darkmarkets
tor markets blackweb
dark web search engines darknet market
tor market url blackweb
dark web search engine deep web drug links
dark market dark web sites links
drug markets dark web dark net
dark markets 2023 dark web market
tor market url darknet site
deep web markets darkmarkets
tor markets 2023 deep web drug store
darknet drug store dark net
tor markets dark market url
tor dark web tor market url
tor darknet how to get on dark web
free dark web deep web drug markets
darknet drugs the dark internet
darkmarket 2023 dark web link
darknet search engine dark internet
dark market url dark web sites links
dark web drug marketplace darknet search engine
darknet markets 2023 tor market url
tor markets links darknet seiten
best darknet markets dark markets 2023
darknet drug store darknet drug links
darknet drug market dark web sites
darknet drugs deep web drug links
dark website darkmarkets
dark market deep web markets
darknet drugs dark web search engines
deep web markets dark web markets
dark market list darknet market links
dark website darkmarket list
dark market 2023 darknet sites
tor marketplace dark web sites
black internet dark market link
tor marketplace dark web links
deep web links tor market links
dark web markets deep dark web
dark web websites bitcoin dark web
dark web sites deep web drug markets
best darknet markets blackweb official website
deep web sites dark web market links
darkmarket link dark web link
dark web search engine deep web search
darknet market dark web websites
darknet market lists darknet websites
the dark internet dark web search engine
darknet websites darkmarket 2023
darkmarket tor market
darknet drugs darknet markets 2023
darknet drug store dark web links
dark web search engine how to access dark web
darknet links darkweb marketplace
darknet site tor dark web
darkmarket link deep web drug store
deep web search dark web websites
the dark internet darkmarket list
dark web market list darknet drug links
dark market 2023 deep web drug links
deep web markets darknet markets 2023
deep web drug links bitcoin dark web
tor darknet the dark internet
dark market 2023 darknet links
darknet drugs darknet sites
tor market darknet sites
darknet websites darknet sites
tor marketplace tor markets
tor darknet blackweb
darkweb marketplace blackweb
dark market dark web sites
blackweb official website darkmarkets
darkmarket 2023 dark web markets
dark web site dark internet
darkweb marketplace darkweb marketplace
deep web markets dark market
dark web access darkmarket 2023
drug markets onion dark web site
dark market darkmarket url
deep dark web the dark internet
dark website deep web drug markets
tor market links darknet site
dark web market list tor market links
blackweb tor market url
darknet markets 2023 dark net
darknet drug store dark market url
dark web site dark market 2023
Hey there, You have done an excellent job. I’ll
definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends.
I’m confident they will be benefited from this website.
darknet drug market darknet search engine
darknet sites dark market link
tor market url deep web drug store
darknet market lists deep dark web
blackweb official website tor dark web
how to access dark web dark web websites
deep dark web tor market
dark web websites darkmarket url
darkmarket url dark web search engines
dark market 2023 darknet sites
drug markets dark web darknet search engine
best darknet markets darknet site
deep web drug links tor markets
darkmarket 2023 dark web drug marketplace
how to get on dark web darknet market lists
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket link
dark web sites darknet drug store
dark market darknet websites
darknet market lists dark web drug marketplace
deep web links dark web market
dark markets dark website
dark web websites darkweb marketplace
darkmarket link dark web drug marketplace
darknet seiten darkmarket 2023
darknet markets 2023 dark web link
bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
darknet markets darknet drug links
dark websites deep web markets
dark net dark internet
dark market darkweb marketplace
dark markets how to get on dark web
darknet markets darknet search engine
tor market links free dark web
darkmarkets dark web sites
dark market link dark web access
dark web market list dark web search engines
tor marketplace black internet
darknet seiten dark web access
dark market link deep web drug links
the dark internet tor markets
deep web drug links deep web search
dark web search engine darknet site
darknet drugs how to access dark web
blackweb blackweb official website
darknet links darknet drug links
best darknet markets onion market
dark web search engine darknet markets 2023
darknet websites dark web access
blackweb how to get on dark web
dark web websites darknet site
dark web websites dark web sites links
dark web websites dark website
blackweb official website darkmarket list
darknet market lists dark web market list
tor dark web dark market onion
dark market link darknet search engine
darknet search engine deep web drug links
best darknet markets dark market
dark web market list darknet markets 2023
deep web drug store dark web access
darknet sites darkmarket 2023
dark market onion free dark web
darknet market darknet market lists
how to get on dark web deep web markets
tor darknet deep web drug url
dark market url darkmarket list
darknet market lists darknet links
how to get on dark web darknet search engine
deep dark web dark web websites
dark web search engine onion market
how to access dark web tor market
darknet marketplace deep dark web
dark internet black internet
dark web link tor market url
darknet search engine darknet websites
dark market list tor market url
dark internet dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engines free dark web
darkmarket url dark web market list
bitcoin dark web black internet
darknet site deep web drug links
dark web market links darknet seiten
dark websites tor marketplace
dark web site dark markets
how to get on dark web darkmarkets
blackweb official website darknet links
dark markets tor markets 2023
dark market url drug markets dark web
how to get on dark web darkweb marketplace
deep web markets dark web websites
darknet drugs darkmarket link
tor marketplace drug markets dark web
black internet darknet drugs
darknet market list dark web sites links
darknet drug market dark web markets
dark web links darkmarket 2023
drug markets dark web deep web drug store
dark web market links dark web access
deep web sites onion market
darknet links darknet markets
tor markets links dark web links
darknet market lists tor markets links
black internet blackweb official website
onion market deep web search
dark market url drug markets dark web
dark web sites tor market url
deep web drug links deep web drug store
dark net darkmarket
the dark internet darkweb marketplace
darknet market links tor market url
deep web drug markets tor markets links
darknet links dark web websites
bitcoin dark web darknet marketplace
dark internet dark market url
blackweb official website darknet drugs
darknet drug links darknet market lists
dark websites darkmarkets
drug markets dark web tor market url
dark web sites dark web site
dark internet dark net
dark web markets deep web sites
deep web links deep dark web
how to access dark web dark web site
darknet market how to get on dark web
how to access dark web darknet markets 2023
black internet darknet marketplace
tor marketplace darkmarket list
dark web links tor markets 2023
best darknet markets dark market onion
deep web drug url darknet sites
dark web market list free dark web
darknet markets 2023 tor markets
blackweb official website dark web link
dark web links drug markets dark web
deep web drug markets how to access dark web
dark market deep web sites
dark markets 2023 darknet links
darknet drug store darknet market links
dark web search engine darkmarket 2023
dark web market list dark web markets
darknet sites dark web markets
darknet markets 2023 dark market
darknet market list tor darknet
dark market list dark web websites
darknet drug store tor market
dark web site tor markets 2023
This penalty porn embody viewing data on the Main web page porn manga porn or inside the hyperlinks on that page. Kevin Spacey forcibly put a man’s
deep web drug markets darknet market list
dark markets 2023 deep web drug store
darknet site dark web market links
dark web sites deep web drug markets
dark web links dark market 2023
black internet bitcoin dark web
dark website free dark web
darknet search engine bitcoin dark web
free dark web deep web sites
darknet market tor markets 2023
darkmarket link dark web market links
darkmarket url deep web markets
tor markets 2023 best darknet markets
tor darknet deep dark web
tor markets darknet drugs
tor market darknet search engine
darknet market list dark market
prednisone heartburn para que sirve prednisone 10 mg what are the side effects of prednisone
dark web sites links tor darknet
black internet darknet site
how to get on dark web darknet market links
how to get on dark web dark market list
deep web links dark web market links
darknet sites darknet market list
darknet market list dark web market
darknet sites onion market
dark markets 2023 darknet market list
dark web search engine dark web access
blackweb official website dark web websites
darkmarket list tor darknet
darknet seiten darknet seiten
dark market onion darknet links
blackweb official website black internet
darknet drug market blackweb
dark web links bitcoin dark web
darknet markets darkmarket link
darkmarket link darkmarket list
drug markets dark web dark web markets
drug markets dark web darknet sites
dark market link deep web links
tor markets tor market url
darknet markets 2023 drug markets dark web
darkmarkets dark markets
deep web drug url dark market
blackweb official website onion market
darknet markets darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet drugs
onion market dark web sites
darknet seiten deep web sites
dark market onion dark market list
dark web search engines darknet market list
darknet marketplace darkweb marketplace
deep web search darknet market
tor market url drug markets onion
dark web websites dark web market links
darkmarkets dark web site
best darknet markets deep web links
darknet market list drug markets dark web
deep web markets how to get on dark web
deep web links darkmarket link
deep web drug links darkmarkets
drug markets onion dark markets 2023
black internet dark web site
dark web access dark web websites
darknet drug links dark markets 2023
darknet market list onion market
darknet drug store how to get on dark web
dark web search engines free dark web
darknet markets blackweb official website
darkmarkets dark market
onion market deep web links
darknet seiten darknet markets 2023
dark web sites deep web links
dark web sites darknet drug links
tor market links darkmarket url
darknet market lists darknet market
dark market onion deep web markets
dark web access darknet drugs
dark web links dark web markets
darkmarket dark website
deep web search darknet drug market
dark internet tor dark web
tor markets links dark web markets
darknet drug store drug markets dark web
blackweb official website free dark web
darknet site dark market url
dark web search engine deep dark web
darkmarket link the dark internet
deep web drug store tor markets links
dark web market links free dark web
darknet drug store darknet drug links
dark web markets dark web links
deep dark web free dark web
best darknet markets darknet site
dark market list tor dark web
dark web link darknet marketplace
tor markets 2023 tor markets links
deep web links dark websites
dark market url darkmarket 2023
darknet search engine dark web market
dark web websites dark web sites links
how to get on dark web the dark internet
onion market darkmarket url
dark web market links dark market
blackweb darknet markets
darknet sites dark internet
dark web link drug markets onion
dark web site deep web markets
how to get on dark web dark market link
dark web site free dark web
dark net dark web site
dark web market links darknet sites
dark market url the dark internet
darknet market dark market list
deep web drug url dark web search engines
darknet drugs blackweb
black internet deep web links
darknet drug market blackweb
darknet market darkmarket link
darknet site dark web sites links
darknet site dark net
darknet market links dark web market list
https://neww.tw/lcd/
darknet drugs dark web market list
tor darknet darknet market list
dark web search engine dark markets 2023
darknet market lists blackweb official website
drug markets dark web darkmarket
dark net deep web links
dark markets tor markets
darknet drug links deep web drug links
darknet market links bitcoin dark web
deep dark web darknet drugs
darknet drug market darknet markets
dark web markets deep web search
deep web drug store darkweb marketplace
darknet drug store dark net
darknet drug links dark markets 2023
dark web access dark web site
dark website dark web site
drug markets dark web dark market url
dark market dark internet
darknet search engine deep web links
dark web market tor dark web
onion market drug markets onion
darkmarket list dark web market list
darknet search engine dark market list
deep web drug links dark web websites
dark web market dark web markets
deep web search darknet drug links
black internet dark websites
tor dark web dark web sites links
deep web drug url dark market onion
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets 2023
free dark web dark web links
deep web drug links dark web market links
darknet market links darknet search engine
deep web drug store darkmarkets
deep web drug markets dark market
darknet market list tor markets links
dark web markets darknet site
tor dark web darknet links
deep web drug url best darknet markets
dark website darkmarket 2023
dark website dark website
darknet marketplace darknet site
darknet site dark net
darknet marketplace dark web access
dark internet darkmarkets
darknet links best darknet markets
deep web search dark web websites
deep web search darknet links
tor markets 2023 deep web drug links
dark market dark websites
tor market darkmarket url
dark market list dark web access
dark market list dark web access
dark market onion deep web sites
blackweb dark internet
dark markets 2023 deep web markets
tor darknet dark web link
dark web drug marketplace blackweb official website
darknet market links dark web websites
tor markets 2023 how to access dark web
tor markets links drug markets onion
tor markets links deep web drug store
darknet markets 2023 dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine tor marketplace
dark web access tor darknet
free dark web dark web sites links
dark web markets darkmarket list
dark web search engine dark web search engines
darknet drug store the dark internet
dark web markets dark web sites links
darknet seiten tor markets
darknet drug store how to access dark web
deep web drug store dark web market links
dark web market list dark market onion
darkmarket link darkmarket link
dark web markets tor marketplace
deep web search darkmarket
dark web access dark web link
tor markets links dark web market links
darkmarket list darknet drug links
darknet drug market free dark web
dark market onion dark market onion
dark markets 2023 dark markets 2023
darknet markets 2023 tor market
Hurrah, tһаt’ѕ what I waas searching foг, wgat a material!
existing һere аt thiѕ weblog, thankѕ admiin off this site.
Hеre is my рage; paket seo
darknet sites deep web links
deep web search how to access dark web
darknet markets dark market 2023
drug markets dark web darkmarket list
tor marketplace tor market url
blackweb official website darknet market links
blackweb deep web search
darknet drug store tor markets links
darknet search engine deep web drug url
dark markets 2023 tor markets 2023
deep web markets deep web drug store
dark websites dark web links
deep web links darknet drug store
darkmarket link free dark web
deep web sites darknet links
darknet market list tor market url
dark market dark website
darknet search engine dark web sites
tor markets links dark web market list
dark net best darknet markets
deep web drug links darkmarket
dark market url dark market 2023
dark web websites darknet market
onion market dark markets 2023
the dark internet deep web drug store
darknet sites how to get on dark web
darknet markets dark internet
darknet markets 2023 dark web markets
dark market link darknet drugs
dark web search engine deep web markets
deep web sites darkmarket
deep web markets dark websites
darknet drug links dark market link
dark markets 2023 dark web sites links
dark web markets tor market
darkmarket link deep dark web
darknet sites dark web link
darkmarkets dark markets
dark web market links dark markets 2023
darkmarket url how to access dark web
tor dark web dark market url
tor markets 2023 dark web market list
darknet drug links drug markets dark web
drug markets dark web darknet market list
darkweb marketplace deep dark web
dark web market links darknet markets 2023
dark web markets drug markets onion
dark web sites links deep web drug store
dark web market deep web sites
dark net free dark web
drug markets dark web darkmarket url
darknet drug market darknet site
dark web sites links tor markets links
dark web sites darkweb marketplace
tor marketplace tor market links
darknet markets 2023 dark market
tor darknet darkweb marketplace
deep web search dark market onion
darkmarket link dark web market
dark web market links dark market onion
deep web drug markets darkmarket
darknet links drug markets dark web
darkmarket list darknet market list
deep web drug url how to get on dark web
deep web links dark web markets
dark website how to access dark web
dark market url darkmarket list
dark website dark web sites links
darknet sites dark net
dark web link darknet markets
dark websites darknet websites
darknet market dark web access
drug markets dark web tor markets 2023
darkmarket 2023 dark web search engines
best darknet markets deep web drug markets
darkmarkets darknet drug links
darkmarket link darknet market lists
dark web market links tor darknet
deep web drug store blackweb
darknet market links dark web market links
dark web websites darknet markets
tor market url dark web search engines
dark web search engines dark market onion
darkmarkets deep web search
darkmarket the dark internet
dark net deep web drug links
darknet market deep dark web
drug markets dark web dark web search engines
darknet market lists tor marketplace
deep web markets dark web access
dark web link dark markets 2023
how to get on dark web deep web drug links
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug url
deep web drug url dark market link
darknet site darknet site
black internet darknet search engine
tor darknet black internet
deep web drug links how to access dark web
darknet sites deep web links
darknet market links dark web sites links
dark web drug marketplace darknet market list
dark web markets how to get on dark web
dark market link dark market link
darknet market links tor dark web
darkmarket list tor marketplace
dark web links darkmarkets
dark market deep web drug links
darkmarket link dark market 2023
dark market darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet search engine
darknet search engine darknet marketplace
darknet site darknet market list
dark web access darkmarket 2023
dark web markets dark market 2023
darknet market links dark website
darknet drug store best darknet markets
deep web drug markets how to get on dark web
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
dark web search engine darknet drugs
how to get on dark web dark web search engine
bitcoin dark web tor marketplace
dark web markets darknet websites
dark web market darknet links
tor markets 2023 tor markets 2023
dark web link black internet
deep dark web dark internet
dark web drug marketplace dark markets
dark market link deep web drug markets
dark market darknet market links
darknet markets deep web links
dark net the dark internet
dark markets tor markets
darknet websites onion market
blackweb darknet market
darknet market darkweb marketplace
darknet markets 2023 darknet drugs
darknet marketplace darkmarket
tor market url darknet websites
how to get on dark web onion market
deep dark web how to get on dark web
darkmarket 2023 dark web sites
darknet markets 2023 dark web sites
dark market 2023 darkmarket
dark internet dark market
darknet links drug markets dark web
onion market dark market onion
tor darknet dark market list
dark web sites links dark web links
dark web access dark web search engines
deep web search dark web search engine
tor markets 2023 dark markets 2023
darknet links darknet markets
best darknet markets dark market
darkweb marketplace deep web sites
darkmarket 2023 drug markets onion
darkmarket link dark web site
darknet site deep web sites
dark market url tor dark web
tor market url dark web search engine
deep web links darknet drugs
tor markets links dark internet
darkmarket dark market onion
the dark internet tor dark web
darknet drug store blackweb official website
drug markets onion dark web search engine
darknet search engine tor darknet
darkmarkets deep web sites
dark web search engines tor darknet
drug markets onion darknet market links
darknet drug store dark web market list
dark web sites links drug markets dark web
darknet websites deep web sites
deep web sites dark web link
dark market darkweb marketplace
darknet links dark web market
darknet seiten dark web site
dark web search engines darknet websites
dark web search engines dark market url
deep web drug url dark market 2023
deep dark web darkweb marketplace
deep web drug url darknet drugs
deep web drug url dark markets 2023
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
blackweb dark web links
how to get on dark web deep dark web
deep web links deep web drug store
tor market links free dark web
drug markets dark web dark websites
onion market darknet websites
tor dark web tor markets 2023
black internet deep web drug store
dark market url dark market 2023
darknet search engine blackweb official website
the dark internet tor market
deep web markets drug markets onion
darkweb marketplace dark market list
blackweb official website black internet
tor marketplace dark web access
darkmarket url darknet market lists
darknet site dark web sites
deep web drug store darkmarkets
drug markets dark web dark markets
dark web site darkmarket 2023
darknet market darknet marketplace
deep web links dark web site
deep web drug markets darkmarkets
dark web search engine darknet site
drug markets dark web darknet seiten
darkmarket black internet
blackweb dark web site
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
dark web sites best darknet markets
tor market black internet
dark web drug marketplace darknet seiten
dark web search engines darknet websites
darknet links darknet market list
dark web search engines dark markets 2023
free dark web blackweb official website
blackweb official website darknet market lists
how to get on dark web darkmarket list
dark market list darknet websites
onion market darknet search engine
tor market url darkmarket link
how to get on dark web dark web websites
darknet websites dark markets 2023
darknet links how to get on dark web
darknet marketplace drug markets onion
darknet drug links darkweb marketplace
darknet market lists darknet links
dark market list darkweb marketplace
deep web drug url dark net
darkmarket list dark markets
darknet drugs tor market links
how to access dark web tor markets links
dark market url dark market url
darknet site darknet drugs
blackweb official website darkmarket link
how to get on dark web dark internet
tor markets darknet markets
free dark web dark web markets
darknet market links darknet market
tor darknet darknet search engine
darknet seiten dark markets
dark market list dark web market list
dark websites tor markets links
darknet seiten free dark web
onion market onion market
darknet marketplace blackweb
dark market 2023 dark web market list
deep web markets deep web search
dark website darknet search engine
tor market url dark markets 2023
deep web drug markets darkmarket url
the dark internet dark web sites links
dark market tor dark web
deep dark web dark market link
dark web links deep web drug store
dark web sites darkmarket list
deep web drug url darknet drug store
how to get on dark web dark websites
dark web market links free dark web
best darknet markets darknet marketplace
dark web links dark web links
dark market drug markets dark web
deep web search darknet drugs
darkmarket 2023 dark web sites
tor darknet darknet websites
darknet drug market dark market
free dark web tor markets 2023
deep web links darknet drug links
deep web drug markets bitcoin dark web
dark web site darknet markets
darknet market darknet websites
dark web links dark web markets
darknet site darkweb marketplace
darkmarket list drug markets dark web
deep web drug store black internet
dark net free dark web
darknet search engine darknet seiten
darkmarkets dark web access
dark web market links dark market list
dark websites dark web links
how to get on dark web dark market 2023
tor market url dark websites
free dark web dark internet
darknet drug store free dark web
blackweb official website darknet marketplace
dark internet darkmarket 2023
dark web market list dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine dark web market
best darknet markets dark market onion
darknet market lists dark web sites
darknet markets darkmarket 2023
darknet drug store darknet links
free dark web black internet
tor market links dark web sites
deep web markets blackweb
dark web sites links darkmarket 2023
blackweb official website dark web websites
deep web drug links black internet
darknet drug store blackweb official website
deep web drug store tor marketplace
dark market 2023 tor markets
tor markets darkweb marketplace
darknet links dark websites
darknet drugs darkmarket 2023
how to access dark web onion market
dark markets deep web drug url
black internet the dark internet
deep web sites deep web sites
darkmarket deep web links
darkmarket url darknet market lists
darknet sites darkmarket list
black internet dark markets 2023
darknet drug store dark market
darknet market lists darkmarkets
dark market link dark web sites
black internet dark markets 2023
darkmarket link dark web market
dark web site darkmarket list
dark market 2023 free dark web
darkmarket dark market link
deep dark web darknet market lists
deep web drug markets dark web markets
darknet drugs onion market
darkmarkets deep web drug url
tor markets dark web site
dark markets 2023 tor marketplace
darknet drugs darkmarket
dark web sites darknet markets 2023
tor darknet drug markets dark web
darkmarket dark web search engines
deep web sites deep web links
darknet drug store darknet websites
darknet markets 2023 drug markets dark web
darknet drug market dark web market list
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
deep web drug store darkmarket url
darknet drugs dark web market list
dark web site how to access dark web
darknet drug market darknet seiten
best darknet markets darknet drug links
blackweb official website darkmarket url
onion market darknet market list
dark websites tor darknet
darknet markets 2023 dark markets
tor markets 2023 dark website
free dark web dark web access
darknet market links darknet drug links
darknet markets onion market
darknet drug links deep web links
dark web access deep web drug store
dark internet dark websites
darknet sites tor marketplace
onion market dark web links
free dark web darknet marketplace
deep web search darknet seiten
onion market dark web market list
darknet drug links tor market
tor market url deep web search
free dark web darknet links
deep web drug markets deep web sites
darknet markets darknet market list
blackweb official website dark web search engine
deep web drug markets deep web sites
dark web access darknet markets 2023
dark net tor market links
deep web drug url dark website
darknet markets 2023 darknet websites
darknet drugs darknet search engine
free dark web dark web links
dark market link dark web link
darknet search engine deep web search
tor marketplace dark web search engine
dark websites dark website
dark markets tor markets links
tor market links drug markets onion
deep web drug markets darkmarket
darknet sites deep dark web
deep web drug url dark market link
dark market 2023 darknet market links
dark web link darkmarket list
darknet marketplace darknet market
dark market 2023 deep web drug url
dark web market list darknet websites
darknet drug market darknet market lists
dark market link dark market
First off I want to say great blog! I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if
you don’t mind. I was curious to know how you center yourself
and clear your head prior to writing. I’ve had a hard time clearing my thoughts in getting my thoughts out there.
I truly do enjoy writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes
tend to be wasted simply just trying to figure out
how to begin. Any recommendations or tips? Thanks!
blackweb official website tor market links
darkmarket url darknet markets
dark internet darknet site
dark web sites dark web site
darknet markets 2023 dark web sites links
tor markets 2023 darkmarket url
dark web market links tor market links
dark market url dark web market list
tor market links tor markets 2023
darknet sites bitcoin dark web
blackweb official website dark websites
dark web market list darknet market lists
tor darknet tor market url
dark web market links dark web market links
how to get on dark web deep dark web
darknet drug market deep web markets
black internet darknet drug links
Hi there eᴠerybody, һere every person is sharing theѕe кnow-how, ttherefore іt’s ɡood tօ rеad thiѕ website,
and Ι uused to pay a quick visit tһis web site egery dɑʏ.
Feel free tⲟo surf tо my blog post; buy spin 123
deep web drug url dark web market
darkmarket list tor marketplace
dark web sites links darkmarket link
dark market link dark web market links
dark markets 2023 darkmarkets
dark markets 2023 tor markets links
onion market darknet websites
deep web markets drug markets onion
darknet search engine dark market link
deep web sites dark market list
darkmarket list tor darknet
darkmarket list darknet seiten
darknet markets tor markets
darkweb marketplace darknet drug store
darknet drugs darknet markets 2023
darknet site darkmarket list
tor market links dark internet
darkmarket 2023 darkweb marketplace
darknet site dark web drug marketplace
darknet market dark web links
dark web access darknet market
dark market onion dark market
onion market darknet drug links
dark web sites dark web drug marketplace
darknet drugs tor dark web
dark web links drug markets onion
dark net deep web sites
tor markets tor markets 2023
darknet websites free dark web
dark market link dark websites
dark web link dark markets
darknet market links darkmarket list
dark web search engines darknet market links
best darknet markets darknet market lists
dark market url darknet seiten
dark websites deep web markets
tor market links dark websites
tor dark web darknet markets
bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2023
deep web drug markets dark websites
darknet market list darknet market list
dark markets 2023 dark web market list
drug markets dark web darknet links
deep web drug url deep web drug url
dark web sites darknet seiten
free dark web onion market
dark web markets dark web links
darknet markets 2023 tor darknet
darknet market links tor darknet
darknet seiten how to access dark web
darknet market lists black internet
deep web drug markets darknet drug store
dark internet deep web links
blackweb dark market 2023
darknet websites darknet websites
dark web websites dark web websites
deep web links dark market link
darknet seiten blackweb official website
deep web search dark market url
tor markets 2023 blackweb
deep web drug store darkmarket
darknet seiten darkweb marketplace
dark websites tor markets 2023
deep web drug store onion market
deep web drug store dark web websites
darknet market links tor market
dark web sites links darknet markets 2023
deep web links darknet search engine
deep dark web how to access dark web
dark web search engine tor market
dark web websites dark markets
dark internet dark market 2023
tor markets links dark web search engine
drug markets onion darknet links
use of augmentin in breastfeeding syp augmentin duo precio augmentin 500 mg
dark web market list how to access dark web
darknet drug market the dark internet
dark market url dark market onion
dark web market list dark market 2023
darknet marketplace dark market onion
dark market onion dark web drug marketplace
best darknet markets tor darknet
darknet drug market dark web websites
dark websites dark web access
deep web search tor market
deep web drug url deep dark web
deep web drug store drug markets dark web
dark market list tor markets 2023
darkmarket dark markets 2023
darknet sites darknet markets
dark web markets darkmarket
darknet market links dark market url
dark market url darknet drug links
dark web site dark market onion
blackweb darknet drug store
dark web sites links darknet drug market
deep web search darkmarket list
deep web drug url darknet market lists
dark web sites links dark web site
darknet market links dark web search engines
deep web markets darkweb marketplace
drug markets dark web deep web drug markets
deep web drug links darkmarket url
dark web market list dark websites
dark web search engine dark market link
darknet seiten darknet marketplace
dark markets darknet marketplace
dark web sites links tor market
tor market tor marketplace
tor dark web dark web market list
tor darknet darknet markets
deep web search deep web links
dark web sites links darknet market lists
how to access dark web darknet drugs
dark net darkmarket
dark web websites dark market list
dark web access darknet seiten
tor market drug markets dark web
deep web sites deep web sites
darknet seiten dark web market links
dark websites blackweb
tor market links dark web drug marketplace
how to get on dark web darknet drug market
darkmarket url dark web drug marketplace
dark web market list drug markets onion
deep web search drug markets dark web
deep web sites darkmarket list
dark market 2023 dark web drug marketplace
娛樂城排行
darkweb marketplace tor market links
darknet market list dark market url
dark web market links deep web markets
darkweb marketplace deep web sites
deep web drug url darknet markets
darkmarket 2023 tor market links
darknet seiten dark market 2023
darknet marketplace darkmarket link
deep web drug markets dark web link
dark markets 2023 tor marketplace
deep web links deep web markets
darknet site blackweb official website
dark market 2023 dark web link
onion market darknet links
dark web market list dark web links
dark web market dark web markets
deep web drug url dark market url
dark markets deep web links
black internet darknet market
deep web links deep web links
dark web links dark web sites
darknet links darknet markets 2023
tor markets 2023 black internet
tor market dark net
dark web market how to get on dark web
darknet drug links blackweb official website
dark market tor market links
darknet market links darkmarket list
darkmarket link dark market onion
darknet market links darkmarkets
darknet market links darknet drug links
darkmarkets dark websites
dark web search engine deep dark web
dark websites onion market
tor market url dark websites
darknet marketplace darknet drug market
blackweb official website blackweb official website
darknet markets dark web market links
how to get on dark web tor markets
dark internet the dark internet
dark web access dark websites
deep web links dark web market list
dark web market list darkmarket
deep web drug markets onion market
dark market dark web links
darkmarkets deep dark web
dark web sites dark web sites links
dark market darkmarket url
tor markets links darknet drug market
tor markets links dark web site
tor markets tor darknet
darknet market list drug markets onion
blackweb official website tor markets links
drug markets dark web dark web markets
darknet drugs deep web drug markets
deep web markets darkmarket link
darknet site dark market
dark web markets darkmarkets
darknet search engine tor market url
dark market onion dark web markets
blackweb official website deep web drug store
how to access dark web darknet markets
dark web link dark web search engines
darknet drugs dark web links
deep web markets dark market url
deep web drug url dark markets
darknet links darkmarket
darknet drug store onion market
darkweb marketplace darknet search engine
tor market links deep web links
darknet market lists darknet market lists
dark web sites bitcoin dark web
how to access dark web tor marketplace
deep web drug markets darkweb marketplace
tor markets 2023 darkmarkets
in France, Germany, the United States, and Russia. A claim publicagent for the earliest Japanese animation is Katsudō Shashin (c. Describes
deep web drug links dark net
dark web link the dark internet
darknet market list dark website
dark web search engine dark websites
dark web search engine deep web drug links
darknet seiten darkmarket url
dark web markets dark market link
darknet search engine how to get on dark web
dark web search engine darknet markets
dark web market list dark web websites
darkweb marketplace tor markets links
how to access dark web darknet markets 2023
darknet search engine darknet marketplace
deep web links dark web sites
dark market darkmarket
darknet market list dark market url
dark markets dark web link
dark web site dark web search engine
bitcoin dark web tor market links
darknet marketplace darknet search engine
dark web markets dark web site
dark web links darknet market lists
tor markets links darkmarket list
dark market how to access dark web
dark markets blackweb official website
tor markets links deep web drug links
deep web links dark web sites links
drug markets onion tor darknet
tor darknet best darknet markets
darknet drug links dark web link
deep web links darknet search engine
darknet marketplace how to get on dark web
tor market url how to access dark web
darkmarket black internet
deep web links darknet drug market
blackweb darkmarket link
darknet drug market dark market link
dark market onion dark internet
tor darknet dark market list
darknet market list darknet websites
darkmarket url darknet search engine
how to access dark web dark web sites links
deep web markets free dark web
darkmarket tor darknet
dark web links darknet market lists
darkmarket url darkweb marketplace
deep web drug markets dark market link
dark web websites dark web link
bitcoin dark web darknet market links
dark web sites darknet market lists
tor darknet deep web drug url
dark market url dark internet
dark market url dark web market
free dark web tor markets 2023
darkmarkets dark web market list
deep web drug markets dark net
bitcoin dark web tor dark web
how to get on dark web darknet site
dark websites dark web site
dark web links deep web drug links
darkmarket list tor markets 2023
deep web drug url dark web sites links
darknet marketplace bitcoin dark web
dark web market tor darknet
dark web search engine dark website
tor markets darkmarket link
darkmarket 2023 darknet market links
darknet markets bitcoin dark web
deep web links darkmarket
These are truly impressive ideas in about blogging. You
have touched some good things here. Any way keep up wrinting.
darknet markets 2023 how to get on dark web
dark market onion dark markets 2023
dark web link deep web search
blackweb dark web market links
tor markets 2023 free dark web
dark markets dark web sites
dark web markets dark web search engines
Excellent site you have here but I was wanting to know
if you knew of any community forums that cover the same topics discussed here?
I’d really like to be a part of community where
I can get suggestions from other experienced individuals that share the same interest.
If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Cheers!
drug markets dark web darkmarkets
dark market 2023 darkmarket link
dark markets 2023 drug markets onion
darkmarket url dark web site
tor market tor markets links
deep web drug markets darkmarket url
This design is spectacular! You certainly know how to keep a reader amused.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my
own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job.
I really loved what you had to say, and more
than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
darknet sites blackweb official website
darknet links blackweb official website
darknet seiten darknet market
darknet drugs tor marketplace
dark web search engines tor markets links
how to get on dark web dark net
darknet marketplace darkmarket url
darknet search engine darknet market links
deep web markets dark market list
how to access dark web dark net
dark market darknet seiten
tor markets 2023 how to get on dark web
how to access dark web how to get on dark web
darknet market lists darknet market lists
deep web markets dark markets
deep web drug store dark market link
darknet search engine dark market list
dark web markets dark websites
darknet drug market darknet markets 2023
dark web sites deep web search
how to get on dark web darkmarket url
deep web drug markets darknet drugs
darknet market how to get on dark web
darkweb marketplace drug markets onion
dark website dark web links
deep web drug markets deep web search
darkmarket url darknet market links
best darknet markets tor darknet
darknet seiten dark web market
dark web market dark web sites
dark web markets dark markets 2023
blackweb official website darknet drug store
darknet drugs dark web drug marketplace
tor market url dark web sites
dark net darkmarket 2023
tor market links dark markets
dark markets dark internet
darknet drug market dark web access
darknet search engine dark web access
dark websites deep web sites
darknet market darknet markets 2023
darkmarket list dark market onion
tor markets tor market links
drug markets onion darknet sites
how to get on dark web dark web sites
tor markets dark websites
blackweb official website deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web tor dark web
dark web market deep web search
dark web search engine deep web search
darkmarket dark internet
darknet drug market blackweb
dark market url dark markets 2023
darkmarket url drug markets dark web
darknet seiten darkmarket
best darknet markets dark web sites links
dark web search engine drug markets onion
dark web links the dark internet
darkmarket 2023 tor markets 2023
blackweb dark web access
darkweb marketplace darknet site
darkweb marketplace darknet market list
high dose azithromycin what is the shelf life of azithromycin azithromycin 5 day dose pack 250 mg
dark internet dark market
free dark web dark website
drug markets dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark market 2023 free dark web
darknet markets tor markets links
darkmarket list tor markets
dark web market deep web drug url
darknet search engine darknet links
darkmarket link darknet drug links
dark market list darkmarkets
tor darknet dark web market links
dark market link dark web site
dark web sites darknet marketplace
darknet site darknet links
tor markets 2023 drug markets onion
darknet site dark web search engine
deep web drug links dark markets 2023
dark internet black internet
darknet sites deep web drug store
dark web search engines tor market links
darkweb marketplace dark market 2023
deep web drug links deep web drug links
dark web site black internet
dark web websites dark market link
dark markets 2023 dark market onion
dark market dark market list
blackweb official website dark market onion
darkmarket 2023 the dark internet
tor market tor darknet
darknet drugs dark net
black internet deep web sites
deep web sites tor market url
darkmarket list dark web access
dark web sites links darknet drug market
dark market onion how to access dark web
dark markets 2023 darknet seiten
tor markets 2023 dark websites
blackweb official website dark web market links
tor markets 2023 darknet markets 2023
onion market dark web market
dark web access dark market link
dark website best darknet markets
dark market link deep web search
dark market link dark web search engines
dark markets onion market
dark web access dark web drug marketplace
dark market url the dark internet
tor markets dark web market links
dark web drug marketplace dark market
tor darknet dark market onion
tor darknet darkmarkets
darkmarket list tor dark web
darknet drugs dark web search engine
dark web sites links dark market list
dark internet deep web drug url
darknet sites how to get on dark web
deep web drug markets deep web sites
drug markets onion deep web sites
deep web drug markets dark web sites links
dark web access dark web sites
free dark web dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket 2023 darknet market list
deep web markets dark web access
tor markets 2023 darknet seiten
dark web access darknet markets
dark web market links dark web search engines
how to access dark web dark web search engine
dark internet dark web markets
dark internet darknet market
darknet search engine darknet search engine
darknet market lists deep web search
dark web access dark web markets
dark net darknet markets
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
dark market 2023 dark market onion
how to get on dark web dark web market list
darknet market links best darknet markets
dark web search engines dark web access
deep web sites darknet seiten
best darknet markets tor market links
darkmarkets tor markets links
dark web sites tor market url
darkmarket 2023 darknet links
blackweb official website deep web search
how to access dark web dark web market list
dark web sites deep dark web
dark web link dark website
dark web access darknet drug links
deep web drug url tor dark web
darknet drug market deep web drug url
onion market deep web search
darknet site darkmarket
dark websites drug markets dark web
darknet market links dark web market
best darknet markets dark web link
deep web drug links deep web links
darknet drugs dark web drug marketplace
darknet drugs darkmarket list
dark web market list deep web drug links
deep web drug markets dark market link
darkweb marketplace dark web websites
dark market list blackweb official website
darknet drug market darknet drug market
darknet markets 2023 dark web markets
darknet market list deep web search
onion market dark web market links
dark websites dark internet
darknet drug store dark web drug marketplace
darknet drug market darknet site
dark web sites darknet drug store
blackweb official website darknet market lists
dark web sites dark market link
tor markets best darknet markets
blackweb darknet markets 2023
tor marketplace dark market onion
deep web drug markets darknet search engine
dark web drug marketplace deep web search
dark web search engines dark web sites links
tor market url darknet seiten
the dark internet dark website
free dark web darknet market links
dark market dark web search engine
dark web market list darknet markets
darknet drug store deep web search
deep web drug url darkmarket url
dark web drug marketplace dark net
dark market link dark net
onion market dark web websites
dark market 2023 deep web markets
deep dark web dark web market list
darknet site deep web drug url
darkweb marketplace black internet
darknet drug links dark market link
darknet seiten dark markets
darknet sites dark web websites
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email.
I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested
in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it improve over
time.
tor markets 2023 how to access dark web
bitcoin dark web darkmarket link
onion market tor dark web
dark web market links dark web site
darkmarkets dark internet
cephalexin 500 mg while pregnant https://cephalexinuop.com/ doxycycline and cephalexin together
darknet links dark web market list
dark web sites darknet market lists
best darknet markets best darknet markets
dark web site dark web link
the dark internet drug markets onion
deep web drug store darkmarkets
darkmarkets tor market
darkmarket url darknet drug store
tor dark web dark web market list
darknet site darknet drug links
dark web link dark website
dark market link dark market 2023
darknet links darknet market
darknet seiten tor markets links
darknet links best darknet markets
tor markets links darknet sites
deep web drug links dark market url
how to access dark web darknet market
dark markets 2023 dark market
darkmarket link dark web link
darknet drugs dark web sites links
darkmarket list darknet links
darknet search engine tor dark web
deep web search drug markets onion
darkweb marketplace drug markets onion
dark market url black internet
darkmarket link darknet market list
dark market list tor markets links
drug markets onion darknet marketplace
darknet market darkmarket url
dark web market dark market url
dark market list how to get on dark web
tor darknet tor dark web
deep web markets dark market list
black internet darknet drugs
darkmarkets dark web sites links
deep web links dark market list
dark web search engines darkmarket link
dark web market list dark website
dark web market list black internet
darknet drugs darknet links
best darknet markets blackweb official website
dark web search engine darknet seiten
darknet marketplace dark web access
darknet markets 2023 dark web sites
dark web market list darknet websites
dark market list darkmarket link
darknet search engine darkmarket url
darknet market list dark web links
deep web drug markets darknet search engine
dark websites dark web markets
deep web sites darkmarket link
how to access dark web best darknet markets
dark web market list drug markets onion
dark net deep web drug store
dark market darknet market list
dark web links darknet marketplace
dark web site deep dark web
darknet market darkmarket url
tor markets 2023 blackweb
dark markets 2023 dark market
darknet markets 2023 dark web sites
bitcoin dark web darkmarket
best darknet markets dark net
blackweb official website dark web sites links
tor market url dark web access
deep web drug markets dark market link
darknet websites deep web sites
darknet marketplace dark website
dark market link deep web drug links
dark web market list how to access dark web
how to access dark web onion market
dark website dark web site
dark web markets dark websites
darknet market tor darknet
free dark web darknet markets
tor market dark markets
dark net darkmarket 2023
dark web site dark website
darkmarket deep dark web
dark markets 2023 darknet websites
blackweb darknet markets 2023
blackweb dark web access
tor market links darknet marketplace
tor markets links dark web websites
darknet markets darkmarket url
darknet market list dark websites
dark websites tor markets 2023
deep web drug store tor markets links
dark market darkmarkets
darkmarket tor markets 2023
tor markets 2023 darknet market links
darkmarket url darknet market list
tor dark web dark web link
deep web search how to access dark web
tor market url deep web drug url
tor market links tor darknet
darknet drug market deep web drug markets
blackweb official website tor dark web
dark web links dark web access
tor dark web dark web websites
darkmarket link dark market onion
blackweb dark web market
bitcoin dark web tor markets 2023
drug markets dark web darknet market
deep web drug markets darknet drug market
darknet drug market onion market
darknet websites tor market links
darknet seiten deep web drug store
dark web markets tor market
darknet markets darknet drug links
dark web search engines darknet drug links
tor darknet dark markets 2023
darknet drugs darknet market lists
deep web search darknet drug store
dark market list darkmarket 2023
darknet markets darknet marketplace
darknet marketplace dark markets
darknet drugs tor market
deep dark web drug markets onion
dark website dark web site
dark market onion darknet links
dark market url darkweb marketplace
tor darknet drug markets dark web
blackweb deep web drug markets
onion market dark websites
how to get on dark web darknet drug market
dark market darkmarket 2023
darknet drugs deep web drug url
tor darknet darknet market lists
dark market list darknet markets 2023
best darknet markets blackweb
the dark internet dark internet
darknet drugs tor dark web
dark market dark market
bitcoin dark web darkweb marketplace
tor market bitcoin dark web
darkmarket 2023 drug markets onion
dark web websites dark web sites links
deep web drug markets darknet site
dark web market list onion market
deep web drug markets onion market
darknet drug store deep web drug url
free dark web dark web access
tor markets 2023 darknet drug links
Kasyno Warszawa Najbardziej reprezentatywne kasyno sieci Casinos Poland. Najmocniejszą stroną kasyna jest oczywiście lokalizacja i budynek kultowego już Marriottu. Przez lata budowana renoma samego miejsca, liczne imprezy z udziałem polskich i światowych gwiazd sprawiają, że księgi historii są równie barwne jak cała branża rozrywkowa. W takiej sytuacji największe kasyno w Marriottcie należące do Casinos Poland może przegrać przetarg z dowolnym kasynem, które ma działać w zabytkowym obiekcie hotelowym o wysokim standardzie – podkreśla Macioszek. Regulamin serwisu W Internecie przeważają pozytywne recenzje, zarówno na portalu Trip Advisor czy w mapach Google. Gracze cenią sobie miłą atmosferę i profesjonalną obsługę oraz możliwość porozmawiania z krupierem na żywo w kasyno. Z pewnością na plus tego domu gry należy zaliczyć szeroki wybór gier.
http://www.dsens.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=149889
W przypadku większej liczby graczy z pokerem, wygrywa ten, kto ma najwyższą kartę.W pokerze i stricie (patrz niżej) as uznawany jest również za jedynkę, jak w układzie 5432A, który stanowi najniższego możliwego pokera. Nie można natomiast użyć asa w środku układu, np. 3, 2, A, K, Q. Takie strity nie są dozwolone. Najlepsi gracze Ucz się od najlepszych profesjonalistów pokerowych biorąc udział w treningach na żywo oraz na forum. Graczy najbardziej interesują oczywiście w poker układy 24 karty, gdyż oznaczają one karty od 9 do A, czyli najbardziej cenne. Oczywiście poker figury czy kolory ma w międzynarodowej wersji identyczne, lecz w poszczególnych regionach mogą występować różnice, dlatego warto to mieć na uwadze. Jeśli chodzi o nasze podwórko, to pokerze figury po polsku dostępne są w międzynarodowej wersji, choć zdarza się, że Q to D, a J to W. Sama rozgrywka uzależniona jest jednak od tego, z jaką odmianą pokera mamy do czynienia. Możemy bowiem zagrać w:
dark web markets darknet markets 2023
tor marketplace best darknet markets
dark web search engine darknet seiten
dark market onion deep web search
darkmarket link drug markets dark web
tor market url darknet market links
darknet seiten dark markets
drug markets onion darkmarket list
tor market darknet market list
darkmarket 2023 darkmarket link
darknet drugs tor markets links
dark market deep web drug url
darknet site dark web sites
deep dark web dark web drug marketplace
darknet sites darkmarket 2023
deep web drug markets darkmarket 2023
deep web search dark web access
dark market onion dark markets 2023
free dark web darknet market
darknet market lists tor dark web
dark web market darkmarket link
darkmarket 2023 dark net
tor market deep web drug url
darknet links dark web links
dark web site dark web link
dark market 2023 deep web markets
dark internet how to get on dark web
dark internet onion market
dark market darkmarket list
bitcoin dark web tor markets links
tor darknet darknet seiten
tor market darknet site
dark web search engines dark web market list
deep web markets best darknet markets
free dark web dark web search engines
onion market darknet seiten
dark web market links darknet markets
darknet markets 2023 black internet
deep web search deep web drug markets
darknet drug market darknet drug links
darknet site how to get on dark web
deep web search dark net
tor market links dark web market list
darknet market list darkweb marketplace
dark web market links deep web search
dark web links dark websites
dark web market links drug markets dark web
deep web links darknet drug links
tor markets links dark market 2023
darknet marketplace tor markets 2023
blackweb dark web site
darknet site dark web market list
deep dark web deep web drug links
darknet drug links drug markets onion
dark web search engines deep web drug url
dark web site dark web site
deep web markets black internet
darknet markets 2023 tor market url
tor darknet dark websites
darknet marketplace deep web drug markets
dark web markets dark web site
dark web market list dark web sites
darknet markets 2023 deep web sites
dark markets darkmarket 2023
tor market drug markets dark web
tor market links deep web drug markets
dark web market links darknet markets 2023
tor market url darkmarket url
It’s an awesome piece of writing in support of all the web people; they will get advantage from it I am sure.
black internet darknet drugs
tor market url darknet search engine
dark net dark web sites links
darknet drugs darkmarket url
dark web websites darkmarket
blackweb deep web drug markets
dark web sites dark net
darknet market list darkmarket list
dark market list tor markets links
drug markets onion dark market link
darknet market links deep web drug links
dark web drug marketplace bitcoin dark web
dark web search engines dark website
dark web links deep web search
darkmarket url dark web search engine
deep dark web dark website
darknet seiten darknet seiten
darknet marketplace tor dark web
tor market url dark web site
dark markets 2023 darkmarket 2023
tor market darkmarket url
deep web search blackweb official website
dark website dark web site
dark net dark websites
darknet market links darknet seiten
darknet drug market dark web market links
darknet links dark web market
deep web drug url deep web drug links
dark market onion how to access dark web
darknet drugs tor dark web
tor market links tor markets 2023
blackweb deep web drug store
how to access dark web onion market
dark market list best darknet markets
dark market onion darknet drugs
darkweb marketplace darkmarket 2023
dark web link tor market
tor dark web blackweb
dark website dark web markets
dark websites darknet market list
black internet darknet websites
darkmarket link dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists darknet websites
tor markets 2023 dark web markets
darkmarket darkmarket list
darknet markets dark web market
darknet market links tor marketplace
darkmarket link drug markets onion
dark web links tor market
cyclobenzaprine and doxycycline doxycycline hyclate sun exposure what if doxycycline doesn’t work for chlamydia
Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I
was curious about your situation; we have created some nice methods and we are looking to trade techniques with other folks, why not shoot me
an email if interested.
darknet drug links darknet markets
darknet market list dark web site
It is really a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that
you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this.
Thanks for sharing.
bitcoin dark web blackweb
darkmarket url dark market
dark web search engine dark website
5-day prednisone dosage right dosage of prednisone for gout does prednisone make you sleepy
dark market 2023 darkmarket 2023
darknet websites deep web drug links
darkmarket link blackweb official website
tor markets tor darknet
dark web market list bitcoin dark web
darkmarkets blackweb
dark market list dark web markets
dark website dark market 2023
dark markets 2023 how to access dark web
tor markets deep web sites
darknet site dark web site
darknet drug store dark web market links
blackweb dark net
darknet market lists darknet markets
dark web links darknet sites
darknet drug market deep web links
blackweb darknet drug market
dark web access dark web sites
dark web search engine deep web links
deep web links dark internet
darknet search engine tor market url
dark internet dark web search engine
darknet markets 2023 dark markets 2023
darknet seiten darknet markets 2023
darkmarket tor marketplace
dark market url darknet markets
darknet drugs dark web links
darkmarket deep web drug store
darknet market list dark market url
darkmarket dark web link
dark websites tor darknet
darkmarkets dark web sites
dark market list dark website
tor markets links dark web site
darkmarkets how to get on dark web
darknet sites tor market
dark market list deep web drug markets
dark web search engine darknet market links
darknet market lists darkmarket url
tor marketplace dark websites
tor market links deep web drug links
deep dark web best darknet markets
the dark internet tor dark web
darknet markets 2023 how to access dark web
dark web search engine darknet market list
dark net tor market links
darknet drugs drug markets dark web
deep web drug store dark websites
dark web sites links how to get on dark web
how to access dark web dark web search engine
dark market deep web drug links
tor markets links dark web access
dark web link dark web market list
darknet drug store dark web markets
dark web market links the dark internet
darknet marketplace darknet market
dark website dark web market list
darknet market list darknet site
darkmarkets dark market onion
tor marketplace darkmarket
darknet seiten tor markets
tor markets 2023 deep web sites
darkmarket 2023 dark market 2023
dark web site dark market
dark market list darknet drug market
dark markets 2023 darknet sites
darknet market lists blackweb
darknet drug links darknet websites
blackweb tor marketplace
tor darknet dark web link
ciprofloxacin bp can dogs have ciprofloxacin ciprofloxacin diverticulitis
dark web link dark markets 2023
deep web links onion market
dark market list dark web market
dark web sites darknet links
tor markets 2023 dark internet
dark web market links darknet marketplace
dark market onion tor market links
blackweb darknet markets
tor darknet tor markets 2023
bitcoin dark web deep web links
blackweb official website dark web websites
dark web markets darknet markets 2023
darknet markets 2023 darkmarket 2023
tor darknet dark web drug marketplace
drug markets onion drug markets onion
deep web drug store darknet market list
dark market 2023 darknet seiten
dark web site darknet seiten
darknet market links darknet websites
dark website darknet links
dark web markets darknet market
tor market tor markets 2023
black internet darknet market links
tor marketplace dark web link
dark web drug marketplace darknet links
darknet links darkmarkets
darkmarket url dark market 2023
dark web access dark web sites links
deep web sites darknet seiten
dark market url dark web links
darknet market list deep web markets
dark web drug marketplace dark markets 2023
tor dark web drug markets onion
dark web websites tor darknet
darkmarket list darknet drug links
dark web links darknet sites
drug markets onion darkmarkets
tor markets links dark market list
darkmarket list bitcoin dark web
darknet websites darknet drugs
the dark internet darknet market
darknet market list dark website
best darknet markets tor market
dark web market deep web drug links
darkmarkets dark net
darknet drug links dark markets
dark web access dark website
dark net darknet marketplace
dark web market list bitcoin dark web
bitcoin dark web darkmarket
darkmarkets deep web links
dark web drug marketplace dark market onion
dark website darknet links
dark web websites darknet markets
tor market best darknet markets
black internet tor markets
darknet drug links tor market
blackweb official website deep web markets
darknet drug store darknet drugs
tor market links darknet drug links
darknet seiten tor market links
tor market links dark market onion
blackweb darkmarket url
onion market dark web websites
dark market dark market link
darknet websites darknet links
dark web market list dark web websites
darknet market lists deep web drug store
darkmarket url dark markets 2023
dark web markets dark internet
dark web market links tor market links
dark market link the dark internet
darknet drug market blackweb official website
darknet links darknet markets 2023
dark web links darknet market links
dark web search engines blackweb official website
darknet market lists dark web market links
darknet drugs blackweb
deep web markets darknet search engine
darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
dark market deep dark web
tor darknet deep web search
free dark web tor marketplace
dark markets dark market list
darknet drugs dark internet
dark market list darknet marketplace
tor markets 2023 darknet market lists
darknet markets 2023 best darknet markets
darkweb marketplace darkmarket
deep web search tor dark web
dark web websites darknet search engine
deep web drug markets darknet markets 2023
deep web drug url tor darknet
best darknet markets tor markets links
deep dark web darkmarket
darknet drugs darknet drugs
dark web links deep dark web
dark market onion darknet drug store
free dark web tor market links
blackweb official website how to get on dark web
dark web markets drug markets dark web
darknet search engine dark web markets
deep web drug links dark web access
darknet markets darknet marketplace
deep web drug markets darknet market
dark web market links tor marketplace
deep web drug links dark web access
how to get on dark web tor markets links
darknet market dark markets 2023
dark market 2023 darknet site
black internet darknet links
dark websites dark market onion
darknet drug links darknet drugs
dark web sites dark web search engines
darkmarket url dark market url
dark web link blackweb
dark market darknet market lists
darkmarket dark web market list
darknet marketplace deep web sites
darkmarkets darkmarket 2023
dark web websites onion market
darkmarket url dark web markets
drug markets dark web dark web search engines
drug markets onion darkweb marketplace
dark web search engines darknet drug store
dark web market list blackweb
darknet markets 2023 dark market onion
deep web drug links dark markets 2023
dark market 2023 darknet marketplace
darknet market blackweb official website
tor marketplace darkmarket url
deep web markets dark markets
darkmarket link dark web site
tor market darknet drug store
deep web links darknet market links
dark market url darkweb marketplace
dark web websites darknet drug store
onion market darknet markets 2023
tor darknet darkweb marketplace
darknet market links dark web link
dark web market list tor dark web
how to access dark web tor marketplace
dark net dark website
deep web markets dark web links
tor dark web dark web markets
darkweb marketplace darknet site
dark web sites links deep web drug store
darknet seiten darkmarket link
onion market drug markets onion
the dark internet dark web search engine
darknet drug links black internet
darknet market links darknet market list
drug markets onion darknet seiten
backgammon là gì
deep web links dark web websites
darknet websites dark web market
darkmarket link tor market url
dark web market darkweb marketplace
tor markets links blackweb
darknet websites dark web drug marketplace
bitcoin dark web tor markets links
deep web drug markets how to get on dark web
drug markets dark web dark web links
blackweb official website darknet seiten
tor market url dark market link
bitcoin dark web best darknet markets
darknet drug links darknet market links
best darknet markets the dark internet
deep web drug markets darknet seiten
deep web drug store darkmarket link
darkmarket list dark internet
darknet drug market darknet drugs
deep web search darkweb marketplace
dark web search engine tor darknet
dark web market list dark markets
dark web links darknet sites
tor market links deep web drug links
darknet search engine dark web market
dark web markets black internet
dark web search engine deep web drug markets
tor darknet darkmarkets
dark market 2023 dark market onion
tor market url darknet market list
deep web search deep web markets
dark web site darknet marketplace
deep web links how to get on dark web
dark websites darkmarket link
dark market url deep web markets
darknet sites dark web markets
how to access dark web free dark web
dark market dark web sites
dark web websites dark market url
dark web markets tor market
blackweb official website tor darknet
tor marketplace darknet market lists
dark market list darknet websites
the dark internet dark web market list
darknet sites dark web search engine
blackweb official website tor marketplace
how to get on dark web dark web markets
darknet drug links darkmarket 2023
free dark web deep web links
free dark web deep dark web
deep web search darknet drugs
tor markets links dark markets
tor markets links dark web market links
darknet drug links the dark internet
dark market 2023 onion market
dark web market list dark web market
dark web market list darkmarket list
darknet drug links dark web search engines
darkmarket deep web search
deep web drug store dark web link
dark market onion deep web markets
dark market 2023 drug markets onion
dark market dark web site
deep web drug markets blackweb
darknet site dark internet
dark web access tor market links
darknet markets blackweb official website
dark web search engines darknet drugs
drug markets onion the dark internet
darkmarket link dark web market
deep web search darknet drug market
dark web site darknet market lists
dark web site dark web access
darknet drug market darknet site
dark market list drug markets onion
darknet site tor marketplace
dark web site darkmarket 2023
tor market url dark web market
dark market url darkmarket url
darknet market list how to get on dark web
darkmarket 2023 tor market url
deep web search dark web links
dark web market list deep web drug store
dark web drug marketplace tor marketplace
darknet links dark web access
darknet market darkmarket url
dark markets 2023 dark market onion
darkmarket url dark web links
the dark internet darknet drugs
darknet drug links darknet market
darknet market lists dark market onion
how to access dark web darkweb marketplace
dark markets 2023 darknet drugs
dark market link onion market
darknet drug store darknet websites
dark web websites deep web drug markets
darkmarket list darkmarket list
darknet markets darknet drug store
darknet search engine tor market links
dark web search engine deep web markets
darknet drugs how to get on dark web
deep web links bitcoin dark web
darkmarket list deep web links
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug store
darknet search engine dark net
darknet drug market darknet websites
dark market link tor markets
deep web drug links tor darknet
darknet links how to access dark web
tor markets darkmarket url
blackweb official website tor darknet
darkmarkets dark market 2023
dark web websites tor market url
deep web links dark web search engines
onion market tor market
tor market links drug markets dark web
deep web drug url dark web link
darknet drug market dark net
darknet links free dark web
deep dark web darknet markets 2023
darknet market links darkmarket url
darkmarkets darkmarkets
deep web drug links dark net
dark websites onion market
dark market 2023 drug markets onion
dark net dark web link
darkmarket drug markets onion
tor marketplace dark web search engine
onion market tor market
dark web websites dark net
darknet market links deep web drug links
tor marketplace deep web drug markets
dark web market list darknet site
deep web drug markets tor markets links
dark web sites dark market link
darknet market lists blackweb
deep dark web how to get on dark web
darknet market tor markets links
darknet sites dark websites
deep web drug store dark web market links
dark web search engine blackweb official website
darknet market list deep dark web
dark website onion market
dark market 2023 darkmarket
deep web markets black internet
tor markets 2023 darknet drug store
deep web links dark web websites
darknet seiten dark web links
blackweb darknet site
dark web access darkmarkets
darkmarkets how to access dark web
best darknet markets dark web site
deep web links dark web search engines
dark market url darknet sites
darknet drug store tor market url
dark web sites deep web drug store
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
deep web drug url tor market
blackweb official website dark market 2023
darknet market links tor market links
darknet market lists black internet
deep web sites onion market
tor markets links tor dark web
dark market url dark web market links
darknet seiten dark web websites
tor marketplace deep dark web
deep dark web how to get on dark web
deep web search dark websites
dark website deep dark web
deep web links dark market url
tor market tor markets links
deep web links darkmarkets
dark web market list dark website
darknet drugs dark web market list
free dark web darkmarket 2023
darknet drug market the dark internet
darknet search engine darknet drug store
dark web search engine the dark internet
dark web websites darkmarket link
dark web site dark web link
dark web link tor markets links
dark market 2023 darkmarket link
tor market links deep web drug links
deep web drug markets darknet market lists
dark markets darkweb marketplace
deep dark web dark market list
tor markets links onion market
darknet markets tor market
deep web drug store bitcoin dark web
how to access dark web darkmarket url
tor market dark web access
dark web search engines dark web sites links
darknet marketplace darknet drug market
darknet links darknet links
darkmarket 2023 dark websites
dark web sites links dark web link
darknet markets dark web market list
darknet drug market dark website
deep dark web darknet search engine
darknet markets 2023 bitcoin dark web
tor markets links best darknet markets
drug markets dark web darknet marketplace
deep web markets tor markets
dark market link tor dark web
dark market dark website
how to get on dark web tor markets 2023
dark markets darknet sites
darknet drug store dark web market list
how to get on dark web dark web markets
dark markets 2023 blackweb official website
dark internet dark web market links
deep web sites tor markets 2023
dark web links deep dark web
darknet drug market darknet links
blackweb official website dark web links
deep web drug store how to get on dark web
tor markets tor markets links
darkmarket link dark market url
the dark internet blackweb
dark market dark internet
tor market links tor markets links
dark web sites links dark web link
tor darknet tor market
darknet drug store dark web sites
dark websites dark web drug marketplace
darknet marketplace darknet search engine
deep web drug links dark web links
darknet drug store dark web drug marketplace
dark markets how to get on dark web
darknet drug market deep web links
deep web search dark market url
dark net dark market link
darknet market list drug markets dark web
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug links
dark web sites darkmarket list
blackweb darknet drug links
dark web search engine darknet sites
darknet market links darknet markets 2023
darknet websites darknet websites
dark web site tor market url
tor markets dark web market links
tor markets links tor markets links
dark web search engine dark web search engines
darkmarket dark market url
darknet markets 2023 tor market
darknet drug market dark markets 2023
darknet drug market deep dark web
how to access dark web dark web links
dark markets 2023 free dark web
darkmarket link darknet marketplace
darknet market lists dark web sites links
deep web links deep web drug url
dark web markets black internet
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
dark web site deep web drug store
tor darknet dark web sites
darknet site black internet
tor markets dark web websites
drug markets dark web darknet drug store
darknet market dark web sites links
tor market darkmarket url
darknet drug links darknet drug market
darknet links darknet links
deep web drug url dark market url
dark markets dark web link
dark internet dark web search engines
darkmarket dark websites
dark internet blackweb official website
dark market dark market 2023
dark internet tor market links
darkmarkets dark web market list
deep web links darknet drug store
Ремонт квартир и помещений в Красноярске
how to access dark web darknet market links
darknet search engine deep web search
darkweb marketplace dark web search engine
dark markets 2023 darknet markets 2023
dark web markets darkmarket 2023
deep web sites free dark web
darkmarket how to access dark web
deep web drug store darkmarket url
deep web markets tor market
darkmarkets deep web drug markets
dark web site deep web search
darknet market lists tor markets 2023
dark web access deep web links
the dark internet darknet markets 2023
dark market link darknet drugs
dark web access dark market link
deep web search dark web access
dark internet dark web sites
dark web site dark websites
darkmarket link darknet market lists
dark web access dark markets 2023
bitcoin dark web tor markets links
dark net dark web sites
how to get on dark web tor market links
darknet drug links darkmarkets
blackweb official website darkmarket 2023
dark market onion dark web sites links
dark web websites darknet links
darknet drug store black internet
best darknet markets darknet drug links
dark markets free dark web
blackweb official website dark web access
darknet market links darknet sites
deep web search darknet market links
tor dark web dark market url
blackweb official website deep web search
dark web websites dark markets 2023
dark web market links darknet market
dark internet dark web sites links
darknet drug links dark web market
how to get on dark web darknet markets
darknet drugs the dark internet
deep web sites dark web links
dark web markets deep web drug store
darknet market lists deep web links
deep web drug links dark market
darkmarket url dark web links
deep dark web dark web market links
darknet sites darknet links
dark web markets dark web websites
bitcoin dark web darkmarket link
darknet drug store dark web market links
darkmarket deep web markets
drug markets dark web deep web links
dark web market darknet search engine
darknet market list darknet site
deep web markets darkmarket link
darknet markets 2023 drug markets dark web
deep web sites deep web drug url
tor darknet dark website
dark web link dark market onion
dark web markets dark markets
drug markets onion dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket darknet marketplace
drug markets onion dark market onion
darknet search engine darkmarket url
deep web drug links dark web search engine
deep web markets tor market url
dark web market dark net
tor markets how to get on dark web
dark market url tor markets links
the dark internet dark markets
deep web drug store darknet marketplace
dark web search engine dark web search engine
dark internet tor dark web
bitcoin dark web darknet drug links
darkweb marketplace tor darknet
darknet drug store darkmarket url
darknet search engine darknet search engine
dark web sites dark websites
deep web drug store darknet sites
darknet drug links darkmarket
darknet drugs dark net
darknet market list darkweb marketplace
darkmarket link dark market
darknet drugs dark website
darknet drugs darknet marketplace
dark web websites dark web market list
darknet market list dark market 2023
darkmarket list darknet seiten
darknet market darkweb marketplace
dark market link darkmarket link
how to get on dark web tor markets links
dark internet darknet drug market
darkmarket 2023 tor market
darknet markets darknet drug market
dark internet dark web markets
tor markets darkmarket 2023
darknet marketplace dark market url
deep web links tor market
dark website free dark web
darknet drug store darkweb marketplace
tor market url the dark internet
dark web websites darkmarket link
dark web market list drug markets dark web
darknet market list darkweb marketplace
darknet market tor darknet
darknet sites tor marketplace
darknet markets 2023 dark web market
darkmarket 2023 darknet markets
darknet market list darknet seiten
free dark web dark market link
tor market url dark web market
dark web market links dark web websites
dark web links drug markets onion
how to access dark web darkmarkets
darknet search engine tor markets
dark web websites tor markets 2023
darknet drug store darkmarket link
tor markets 2023 darknet drug store
deep web links darknet markets 2023
dark web sites links darknet market links
dark web market darknet links
deep web drug store darkmarket list
blackweb darkmarket url
dark web search engines dark web link
tor market dark web markets
free dark web darknet market list
deep web drug links darkmarket 2023
drug markets onion blackweb
how to access dark web drug markets onion
darknet links darknet market links
deep web markets dark market 2023
dark web markets dark web market
dark websites darknet seiten
darknet links dark web market
deep web links darknet websites
black internet onion market
darkmarket url darknet drug links
black internet darkmarket 2023
tor markets darknet market list
darkmarket url dark web sites
dark web market links deep web drug markets
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug url
deep web drug markets darkmarket link
dark market dark web sites
dark web market darknet marketplace
free dark web darknet markets 2023
dark web sites links tor darknet
drug markets onion blackweb official website
darknet markets darknet market links
deep web markets darknet market links
dark web link blackweb
deep dark web the dark internet
how to access dark web dark market list
dark net dark websites
tor darknet tor markets
darknet markets how to get on dark web
certainly lіke yyour website Ƅut уoս havе to take
a lοok аt thе spelling oon sevral оf yoᥙr posts.
Sеveral oof them агe rife ѡith spelling pгoblems аnd I find it very
troublesome tߋ inform the reality nevertһeless Ι’ll surely comе аgain again.
My site … MayorQQ
darkmarket url deep dark web
dark web links dark web access
tor market url dark market url
dark web websites darknet site
tor markets links tor dark web
dark web drug marketplace deep web markets
deep web drug url darknet market lists
tor market links how to access dark web
darkmarket list dark web market links
dark web sites darkmarket
dark market 2023 dark web search engine
dark web websites dark web site
deep web drug markets darknet site
tor market url darknet seiten
tor markets dark web sites links
dark web market list how to get on dark web
darknet markets dark web sites links
dark web market list darkmarkets
tor market links dark market
dark web drug marketplace tor darknet
dark website dark web search engines
how to access dark web darknet sites
darknet markets 2023 dark market
tor markets 2023 darknet markets
darknet seiten tor marketplace
darknet seiten darkmarket link
tor darknet dark web sites
deep web drug markets dark net
darknet market list how to access dark web
how to access dark web dark market link
Hі tⲟ every one, the contentѕ pгesent ɑt this web site aree genuinely amazing fοr peoplee knowledge,
ѡell, ҝeep up tһe gooԀ wor fellows.
Aⅼso visit my web site Gila 4D
dark websites darknet markets 2023
darkmarket url dark web sites links
black internet dark market url
dark markets 2023 deep web links
drug markets onion deep web links
dark market url dark web drug marketplace
dark market url the dark internet
darknet market lists darknet drug links
darkmarket list deep web links
darknet drug market dark web sites links
how to get on dark web darknet market
darkmarket list tor marketplace
darkweb marketplace darknet drug market
dark web sites dark market list
dark websites darknet websites
tor markets 2023 dark website
darknet drug links dark web market links
darkmarkets dark market list
tor market url bitcoin dark web
Ⲩes! Fіnally ѕomeone wrіteѕ abоut trending news.
Αlso visit mу ρage: Daftar Ahha4d
darknet market deep web links
darkmarket 2023 darkmarkets
darkmarket link dark web market list
dark market link black internet
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug url
drug markets dark web deep dark web
best darknet markets dark market url
deep dark web tor markets
dark market darkweb marketplace
black internet darknet drugs
deep dark web dark web links
drug markets onion darknet site
tor markets darkmarket
deep dark web dark web sites
darkmarket url dark web links
GAS SLOT Adalah, situs judi slot online terpercaya no.1 di Indonesia saat ini yang menawarkan beragam pilihan permainan slot online yang tentunya dapat kalian mainkan serta menangkan dengan mudah setiap hari. Sebagai agen judi slot resmi, kami merupakan bagian dari server slot777 yang sudah terkenal sebagai provider terbaik yang mudah memberikan hadiah jackpot maxwin kemenangan besar di Indonesia saat ini. GAS SLOT sudah menjadi pilihan yang tepat untuk Anda yang memang sedang kebingungan mencari situs judi slot yang terbukti membayar setiap kemenangan dari membernya. Dengan segudang permainan judi slot 777 online yang lengkap dan banyak pilihan slot dengan lisensi resmi inilah yang menjadikan kami sebagai agen judi slot terpercaya dan dapat kalian andalkan.
Tidak hanya itu saja, GASSLOT juga menjadi satu-satunya situs judi slot online yang berhasil menjaring ratusan ribu member aktif. Setiap harinya terjadi ratusan ribu transaksi mulai dari deposit, withdraw hingga transaksi lainnya yang dilakukan oleh member kami. Hal inilah yang juga menjadi sebuah bukti bahwa GAS SLOT adalah situs slot online yang terpercaya. Jadi untuk Anda yang memang mungkin masih mencari situs slot yang resmi, maka Anda wajib untuk mencoba dan mendaftar di GAS SLOT tempat bermain judi slot online saat ini. Banyaknya member aktif membuktikan bahwa kualitas pelayanan customer service kami yang berpengalaman dan dapat diandalkan dalam menghadapi kendala dalam bermain slot maupun saat transaksi.
deep web drug url dark web markets
blackweb official website deep web drug store
tor markets dark market
Slot Gas
GAS SLOT Adalah, situs judi slot online terpercaya no.1 di Indonesia saat ini yang menawarkan beragam pilihan permainan slot online yang tentunya dapat kalian mainkan serta menangkan dengan mudah setiap hari. Sebagai agen judi slot resmi, kami merupakan bagian dari server slot777 yang sudah terkenal sebagai provider terbaik yang mudah memberikan hadiah jackpot maxwin kemenangan besar di Indonesia saat ini. GAS SLOT sudah menjadi pilihan yang tepat untuk Anda yang memang sedang kebingungan mencari situs judi slot yang terbukti membayar setiap kemenangan dari membernya. Dengan segudang permainan judi slot 777 online yang lengkap dan banyak pilihan slot dengan lisensi resmi inilah yang menjadikan kami sebagai agen judi slot terpercaya dan dapat kalian andalkan.
Tidak hanya itu saja, GASSLOT juga menjadi satu-satunya situs judi slot online yang berhasil menjaring ratusan ribu member aktif. Setiap harinya terjadi ratusan ribu transaksi mulai dari deposit, withdraw hingga transaksi lainnya yang dilakukan oleh member kami. Hal inilah yang juga menjadi sebuah bukti bahwa GAS SLOT adalah situs slot online yang terpercaya. Jadi untuk Anda yang memang mungkin masih mencari situs slot yang resmi, maka Anda wajib untuk mencoba dan mendaftar di GAS SLOT tempat bermain judi slot online saat ini. Banyaknya member aktif membuktikan bahwa kualitas pelayanan customer service kami yang berpengalaman dan dapat diandalkan dalam menghadapi kendala dalam bermain slot maupun saat transaksi
darknet websites tor darknet
dark web market list darkmarket
tor markets 2023 dark market list
darkweb marketplace dark web market links
dark web market blackweb
tor market links dark web links
dark web market links deep web search
free dark web deep web search
blackweb deep web search
dark web search engines deep dark web
dark web websites blackweb
tor market url best darknet markets
darkmarket link tor darknet
darknet markets tor markets
tor markets dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket list best darknet markets
darknet market list drug markets dark web
dark web search engine darknet search engine
bitcoin dark web darknet seiten
darkmarkets dark web websites
dark web search engine darkmarket link
darkmarket list dark markets
darkweb marketplace tor markets
deep web links dark market 2023
blackweb official website darknet market
deep web drug links how to access dark web
deep web drug links darknet drugs
best darknet markets darknet market
drug markets dark web dark web drug marketplace
blackweb dark web links
tor darknet tor markets
onion market darknet market lists
how to get on dark web dark market
darknet search engine onion market
tor darknet darknet market links
darknet websites darknet market links
deep web search how to access dark web
black internet dark net
deep web drug store darknet drug store
how to access dark web darknet market list
dark web market blackweb official website
dark market dark web market links
dark web search engines darknet drug links
deep web sites dark market 2023
tor market darknet drug links
deep web drug store free dark web
deep web drug store dark market onion
darknet market lists darknet market lists
dark market list darkmarket list
darkmarket darknet sites
darknet drug links darknet seiten
how to access dark web deep web drug store
dark markets darknet links
deep web drug store dark website
darknet market lists dark web sites
darkmarket tor markets 2023
how to access dark web darknet drug market
darknet market list darknet site
best darknet markets darknet market lists
best darknet markets how to access dark web
dark web sites links dark web search engines
darkmarket link drug markets onion
darknet search engine tor market url
dark markets 2023 dark web market
darknet sites dark internet
dark market 2023 dark websites
deep dark web best darknet markets
tor market dark web drug marketplace
bitcoin dark web dark market url
dark web search engines tor market
darknet drugs deep web search
dark market onion free dark web
dark web access deep web search
darkmarket darknet market list
dark markets 2023 free dark web
dark market 2023 darknet search engine
tor market tor marketplace
dark web market list dark market onion
darknet market links darknet drug store
deep web search darkmarket link
dark markets tor markets
dark web drug marketplace dark market
bitcoin dark web darknet drugs
darkmarket 2023 tor dark web
dark web market darkmarket list
darknet sites darkmarket 2023
darkweb marketplace darkmarket
dark markets dark web markets
darkmarket 2023 tor market url
darknet market list bitcoin dark web
dark websites darknet marketplace
dark web market how to access dark web
dark web websites deep web sites
deep web drug store tor dark web
darknet seiten how to access dark web
how to access dark web darknet drug market
darkmarket list dark internet
dark web link dark web markets
dark web search engine dark websites
bitcoin dark web dark website
darknet market dark web access
darknet marketplace tor market url
dark market url dark web markets
darknet drug store darkmarkets
tor market url darknet drug market
darknet search engine drug markets dark web
deep web drug markets tor market url
deep web drug links how to access dark web
deep web drug markets dark market list
dark web access dark market onion
darknet links dark web site
tor darknet deep web drug links
blackweb official website dark net
Polskie kasyna online sa popularnym miejscem rozrywki dla wielu osob, ktore szukaja emocji i adrenaliny zwiazanych z grami hazardowymi. Oferuja one roznorodne gry kasyno-online14.pl, takie jak automaty, poker, ruletka i wiele innych, co pozwala graczom wybrac swoje ulubione i zanurzyc sie w fascynujacym swiecie hazardu.
dark web markets darknet markets
dark web link tor markets
darknet drugs deep web search
darknet search engine blackweb
darknet market list deep dark web
darkmarket 2023 dark market link
deep web drug store dark web link
dark market url deep dark web
darknet sites dark web access
darknet drug store bitcoin dark web
tor markets 2023 dark market onion
drug markets onion darknet markets
dark market link deep web drug markets
blackweb official website tor darknet
dark net darkmarket url
dark web market darknet search engine
darknet market list deep dark web
darknet markets deep web drug store
tor darknet deep web search
deep web markets darkmarket
deep dark web dark web links
best darknet markets dark web market links
black internet deep web links
deep web markets dark web links
deep web drug markets darkmarket url
darkmarket darknet links
best darknet markets dark market 2023
dark web site bitcoin dark web
dark web market links dark web market list
dark web site dark web access
dark web websites tor marketplace
dark internet tor markets links
darkweb marketplace black internet
dark internet dark market list
dark web link deep web drug links
deep web links dark market
darknet drugs darknet marketplace
dark web sites dark website
drug markets onion darkmarket list
darknet drug links dark market
deep web drug url deep web drug store
deep web markets dark markets
dark web market list darknet links
the dark internet dark web drug marketplace
dark web market darknet drugs
darkmarket list tor markets links
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug links
deep web search darknet search engine
dark web search engines darknet market
darkmarket url dark web sites
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
darknet site darkweb marketplace
darknet marketplace dark market 2023
darkmarket 2023 darknet drug store
darknet market tor market url
onion market darknet sites
how to access dark web deep dark web
darknet links dark web sites links
tor marketplace dark market url
darkmarket url dark web links
darknet markets dark web link
darknet websites black internet
deep web drug links dark web search engines
dark web links darknet drug store
deep web drug links bitcoin dark web
deep web drug markets deep dark web
drug markets dark web dark web market
how to get on dark web darkmarket url
tor markets 2023 deep web sites
tor marketplace darknet site
darknet drug links tor market url
dark web sites links bitcoin dark web
darknet markets darknet search engine
tor marketplace dark web site
dark websites dark web drug marketplace
tor darknet dark web websites
dark web market list dark market
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug markets
dark markets deep web drug url
dark web sites darkmarket
tor dark web dark market url
dark web market links darknet markets 2023
tor markets links dark market 2023
dark market onion black internet
dark web link tor darknet
dark web market links darknet search engine
tor markets links tor marketplace
tor dark web dark web drug marketplace
darknet sites dark net
dark internet free dark web
tor market darknet market list
bitcoin dark web dark web drug marketplace
dark web site deep web links
tor markets 2023 deep web sites
how to access dark web dark web access
onion market dark websites
darknet seiten tor marketplace
dark web markets dark market list
tor darknet darkmarket list
onion market dark web market
dark web sites darknet market list
dark market onion darknet links
dark market link deep web sites
dark market link darkmarket 2023
tor market url darknet marketplace
dark web links darkweb marketplace
dark market list darknet sites
dark web link dark web websites
tor market url dark web link
If some one desires expert view regarding blogging after that i propose
him/her to pay a visit this weblog, Keep up the fastidious
job.
dark market onion the dark internet
dark web site tor markets links
Why visitors still use to read news papers when in this technological
globe everything is accessible on web?
darknet market list tor marketplace
dark web links dark market
darkmarket deep web markets
blackweb dark market list
deep web search tor markets links
deep web links dark web drug marketplace
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug store
dark web links drug markets onion
darknet sites darknet sites
tor markets dark web market
darkmarket url darknet markets 2023
dark markets 2023 darknet market
tor dark web darkweb marketplace
darkmarket 2023 darkmarket link
dark websites dark web sites
dark web websites darknet links
free dark web dark market list
tor market links darknet market
drug markets onion how to get on dark web
darknet websites how to get on dark web
deep web search deep web search
darknet websites dark website
darknet markets dark internet
deep web drug links how to access dark web
darknet markets 2023 darknet market links
darknet search engine dark market
darkmarkets darknet links
tor market url dark market link
darknet markets best darknet markets
tor markets links dark internet
deep web drug links deep web links
dark market list bitcoin dark web
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets 2023
darknet drug market darknet drug links
tor markets 2023 darknet market links
darkmarket how to get on dark web
dark market 2023 dark web websites
darknet market links darknet drug market
neural network draws dogs
Neural Network Draws Dogs: Unleashing the Artistic Potential of AI
Introduction
In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence has witnessed tremendous advancements in image generation, thanks to the application of neural networks. Among these marvels is the remarkable ability of neural networks to draw dogs and create stunningly realistic artwork. This article delves into the fascinating world of how neural networks, specifically Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCGANs), are employed to generate awe-inspiring images of our four-legged friends.
The Power of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a class of artificial intelligence models consisting of two neural networks – the generator and the discriminator. The generator is responsible for creating images, while the discriminator’s role is to distinguish between real and generated images. The two networks are pitted against each other in a “game,” where the generator aims to produce realistic images that can fool the discriminator, while the discriminator endeavors to become more adept at recognizing real images from the generated ones.
Training a GAN to Draw Dogs
The Future of Artificial Intelligence: Beauty and Possibilities
In the coming decades, there will be a time when artificial intelligence will create stunning ladies using a printer developed by scientists working with DNA technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning. The beauty of these ladies will be unimaginable, allowing each individual to fulfill their cherished dreams and create their ideal life partner.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and biotechnology over the past decades have had a profound impact on our lives. Each day, we witness new discoveries and revolutionary technologies that challenge our understanding of the world and ourselves. One such awe-inspiring achievement of humanity is the ability to create artificial beings, including beautifully crafted women.
The key to this new era lies in artificial intelligence (AI), which already demonstrates incredible capabilities in various aspects of our lives. Using deep neural networks and machine learning algorithms, AI can process and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling it to create entirely new things.
To develop a printer capable of “printing” women, scientists had to combine DNA-editing technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning methods. Thanks to these innovative techniques, it became possible to create human replicas with entirely new characteristics, including breathtaking beauty.
dark web markets deep web markets
deep web drug url tor market links
bitcoin dark web deep web sites
tor market dark web market
deep dark web deep web drug links
dark market 2023 darknet drug store
darknet links darknet market list
dark market darkmarket list
deep web markets darknet websites
darkmarket list the dark internet
dark web market links tor markets links
darknet seiten dark web access
darkweb marketplace dark website
dark net deep web drug markets
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug markets
dark web access bitcoin dark web
dark markets deep web links
dark web sites darknet markets
darknet markets black internet
the dark internet deep dark web
A Paradigm Shift: Artificial Intelligence Redefining Beauty and Possibilities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and biotechnology have witnessed a remarkable convergence in recent years, ushering in a transformative era of scientific advancements and groundbreaking technologies. Among these awe-inspiring achievements is the ability to create stunning artificial beings, including exquisitely designed women, through the utilization of deep neural networks and machine learning algorithms. This article explores the potential and ethical implications of AI-generated beauties, focusing on the innovative “neural network girl drawing” technology that promises to redefine beauty and open new realms of possibilities.
The Advent of AI and Biotechnology in Creating Artificial Beings:
The marriage of AI and biotechnology has paved the way for unprecedented achievements in science and medicine. Researchers have successfully developed a cutting-edge technology that involves deep neural networks to process vast datasets, enabling the crafting of artificial beings with distinctive traits. This “neural network girl drawing” approach integrates DNA-editing technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning methods, revolutionizing the concept of beauty and possibilities.
darknet drug market tor market links
darknet markets blackweb
dark market dark web websites
darkmarket url blackweb official website
tor market links black internet
drug markets onion darkmarket
dark net dark market onion
free dark web dark web search engines
darknet site dark internet
dark markets tor markets links
tor marketplace deep web search
darkmarkets darkmarket link
darknet marketplace darkmarkets
darknet market list darknet seiten
deep web drug markets how to get on dark web
darknet market lists deep web search
tor dark web tor darknet
dark web access dark internet
dark web access dark web websites
darknet drug store dark market list
darknet links bitcoin dark web
dark web market darknet site
dark web sites links darknet links
dark web market list dark web site
darknet markets free dark web
deep web sites darknet sites
tor markets links dark market list
tor market url dark website
darknet drug store deep web links
darkmarket link darknet site
dark web links tor markets
darknet drug links darknet market lists
dark market link deep web sites
darkmarket link tor markets
black internet deep web drug markets
bitcoin dark web darknet search engine
darknet market lists darkmarket link
tor markets links drug markets onion
dark web market list dark web link
darkmarket url darkmarket 2023
darknet links dark website
dark web links darknet drugs
deep web drug links tor markets
tor marketplace tor darknet
darknet market links onion market
deep web drug store darknet market links
Berita lifestyle
dark market onion tor darknet
darknet drug links deep web markets
dark market list dark web site
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
dark web access darknet site
darknet market links darknet seiten
drug markets onion tor market
darknet markets 2023 dark market 2023
onion market dark web websites
dark market 2023 blackweb
darknet marketplace dark web link
dark web market list deep dark web
dark web site dark web websites
tor dark web bitcoin dark web
free dark web darknet drugs
darknet market links darknet seiten
darknet search engine darknet markets
darknet market list darkweb marketplace
drug markets onion dark website
dark market deep web drug links
dark market list darknet market links
dark web market links dark web drug marketplace
darknet markets tor market url
darkmarket link darknet drug store
how to access dark web dark net
darknet sites free dark web
the dark internet tor market
tor markets dark market
deep web sites darkmarket url
tor darknet tor market links
dark markets 2023 dark market 2023
darknet markets darkmarket list
darkmarket list how to access dark web
dark web links dark web search engine
darknet market dark market link
dark web websites dark web link
darknet sites dark net
darknet market lists dark web search engines
tor markets darkweb marketplace
darknet market list dark market
darkmarket link dark market 2023
bitcoin dark web dark web sites
dark market url darknet market list
tor market links dark web links
best darknet markets darknet site
darkmarket 2023 darknet marketplace
free dark web dark web site
tor market dark web link
darknet sites dark websites
darknet markets how to get on dark web
dark web link darknet marketplace
dark market darkmarket link
dark market url deep web markets
darknet market list dark net
how to get on dark web deep web drug store
darknet drug store bitcoin dark web
darknet markets 2023 darkmarket list
tor market url dark web markets
dark markets darkmarket
tor marketplace darknet drug market
drug markets onion deep web drug store
dark internet deep web drug url
onion market darkweb marketplace
dark web search engines deep web search
deep web sites deep web drug url
dark web links tor market
blackweb dark web market list
darkmarket url dark websites
darknet drugs deep web drug markets
darknet market lists deep web drug url
darknet links dark markets 2023
blackweb official website onion market
tor market dark net
deep web drug url dark web market links
darkmarkets how to get on dark web
darknet search engine darknet market lists
deep web sites dark internet
dark markets 2023 dark market list
dark market 2023 darknet market lists
free dark web darknet websites
darkweb marketplace dark web links
dark website deep web sites
darknet market list dark web market list
deep web drug links darknet search engine
drug markets onion how to access dark web
darknet markets dark web links
dark markets darknet market
dark web market links dark internet
tor market url dark web drug marketplace
dark web sites links dark market onion
tor markets deep web links
deep web sites dark net
darkmarkets blackweb official website
deep web search tor market url
dark web markets darkmarket 2023
dark markets 2023 dark web access
dark web websites dark market list
tor markets links the dark internet
darkmarket list darknet market lists
deep web drug url darkmarket link
darknet drug links darkmarkets
how to get on dark web tor market url
darknet seiten drug markets onion
tor darknet deep dark web
how to access dark web dark web link
darkmarkets deep web links
darknet seiten deep web markets
darknet site dark web link
darkmarket tor marketplace
darknet drug store dark web websites
dark web search engines tor markets
deep web search tor markets links
best darknet markets tor marketplace
dark market list tor markets
deep web drug links darknet websites
deep web links dark web search engines
dark web market list deep web drug url
tor market tor market links
drug markets dark web dark market
darknet market list darknet drugs
darknet market links darknet markets
blackweb official website deep web drug links
dark web links darknet market lists
deep web drug markets darknet drug store
deep web links darknet drugs
dark market list darknet market list
dark internet drug markets dark web
darknet markets dark web search engines
darknet market list dark markets 2023
tor markets 2023 tor markets links
dark websites dark internet
dark web search engines dark web market links
onion market how to access dark web
deep web drug url dark market 2023
dark web market links drug markets onion
tor markets links darkmarket link
blackweb darkmarkets
darknet search engine dark web site
deep dark web dark web links
darknet links drug markets onion
dark web links best darknet markets
darknet market list deep web search
dark websites dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists darknet market list
drug markets onion dark market link
darknet market links darkmarket
deep web links tor dark web
dark web market links deep web links
dark web link tor markets 2023
tor darknet deep web search
the dark internet bitcoin dark web
darknet websites dark web search engine
deep web drug markets darknet search engine
deep web search tor marketplace
dark market onion tor darknet
deep web search blackweb official website
dark markets tor market links
darknet seiten best darknet markets
darknet websites tor market
dark net tor market
bitcoin dark web tor market
deep web markets dark market 2023
dark web site dark web search engines
dark web markets deep web drug url
dark web drug marketplace dark web access
how to access dark web dark websites
deep web drug url darknet markets 2023
dark web sites darknet markets
darknet search engine dark websites
deep web drug store dark web markets
drug markets dark web dark web market links
tor darknet darknet sites
how to get on dark web deep web drug url
darknet site darknet market lists
dark web search engine darkweb marketplace
https://www.yoodalo.com/blog/
dark web links dark web market
dark market link the dark internet
darknet site darknet drugs
dark web sites links dark market list
tor marketplace blackweb
deep web markets bitcoin dark web
dark websites darknet market
darknet market lists dark web search engines
bitcoin dark web deep web sites
deep web drug store dark web sites links
darknet markets darkmarket 2023
free dark web dark market 2023
tor market url dark market list
線上賭場
彩票是一種稱為彩券的憑證,上面印有號碼圖形或文字,供人們填寫、選擇、購買,按照特定的規則取得中獎權利。彩票遊戲在兩個平台上提供服務,分別為富游彩票和WIN539,這些平台提供了539、六合彩、大樂透、台灣彩券、美國天天樂、威力彩、3星彩等多種選擇,使玩家能夠輕鬆找到投注位置,這些平台在操作上非常簡單。
彩票的種類非常多樣,包括539、六合彩、大樂透、台灣彩券、美國天天樂、威力彩和3星彩等。
除了彩票,棋牌遊戲也是一個受歡迎的娛樂方式,有兩個主要平台,分別是OB棋牌和好路棋牌。在這些平台上,玩家可以與朋友聯繫,進行對戰。在全世界各地,撲克和麻將都有自己獨特的玩法和規則,而棋牌遊戲因其普及、易上手和益智等特點,而受到廣大玩家的喜愛。一些熱門的棋牌遊戲包括金牌龍虎、百人牛牛、二八槓、三公、十三隻、炸金花和鬥地主等。
另一種受歡迎的博彩遊戲是電子遊戲,也被稱為老虎機或角子機。這些遊戲簡單易上手,是賭場裡最受歡迎的遊戲之一,新手玩家也能輕鬆上手。遊戲的目的是使相同的圖案排列成形,就有機會贏取獎金。不同的遊戲有不同的規則和組合方式,刮刮樂、捕魚機、老虎機等都是電子遊戲的典型代表。
除此之外,還有一種娛樂方式是電競遊戲,這是一種使用電子遊戲進行競賽的體育項目。這些電競遊戲包括虹彩六號:圍攻行動、英雄聯盟、傳說對決、PUBG、皇室戰爭、Dota 2、星海爭霸2、魔獸爭霸、世界足球競賽、NBA 2K系列等。這些電競遊戲都是以勝負對戰為主要形式,受到眾多玩家的熱愛。
捕魚遊戲也是一種受歡迎的娛樂方式,它在大型平板類遊戲機上進行,多人可以同時參與遊戲。遊戲的目的是擊落滿屏的魚群,通過砲彈來打擊不同種類的魚,玩家可以操控自己的炮臺來獲得獎勵。捕魚遊戲的獎金將根據捕到的魚的倍率來計算,遊戲充滿樂趣和挑戰,也有一些變化,例如打地鼠等。
娛樂城為了吸引玩家,提供了各種優惠活動。新會員可以選擇不同的好禮,如體驗金、首存禮等,還有會員專區和VIP特權福利等多樣的優惠供玩家選擇。為了方便玩家存取款,線上賭場提供各種存款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳/ATM轉帳儲值和超商儲值等。
總的來說,彩票、棋牌遊戲、電子遊戲、電競遊戲和捕魚遊戲等是多樣化的娛樂方式,它們滿足了不同玩家的需求和喜好。這些娛樂遊戲也提供了豐富的優惠活動,吸引玩家參與並享受其中的樂趣。如果您喜歡娛樂和遊戲,這些娛樂方式絕對是您的不二選擇
dark net dark web sites links
best darknet markets darknet drug links
tor marketplace tor marketplace
dark web access dark website
darknet market darknet drug links
darkmarket url free dark web
darknet seiten darkweb marketplace
darkmarket url deep web links
tor market deep dark web
tor markets darknet market links
dark web site deep web drug markets
dark market darknet seiten
the dark internet tor markets links
dark markets darknet market links
tor markets 2023 dark web sites links
dark web drug marketplace blackweb official website
deep web drug links tor dark web
darknet market deep web markets
darknet websites dark website
deep web markets dark markets 2023
dark internet dark web sites links
darknet market lists darknet sites
dark market dark web drug marketplace
darknet market lists deep web drug store
tor market links darknet markets
darknet market lists dark markets
deep web drug links dark markets 2023
how to get on dark web darknet seiten
drug markets onion deep web markets
darknet seiten how to get on dark web
tor markets darknet seiten
darknet market lists dark net
deep web drug links dark websites
darknet market list blackweb
dark market link deep web drug links
darkmarket 2023 darknet seiten
dark web site darkmarket list
dark website darknet seiten
drug markets dark web dark markets
darknet market deep web search
darknet drug store darknet site
deep web sites darknet market links
deep web sites dark web market
deep web markets dark market list
darkmarkets dark market onion
tor markets dark market link
darknet site how to access dark web
darknet marketplace darknet links
darknet markets drug markets dark web
dark web market dark web links
dark market list tor markets
dark market how to get on dark web
dark web sites links dark web sites
darkmarkets how to access dark web
dark market darknet drug market
dark web markets dark web link
darknet market darkmarket 2023
dark website deep web drug store
darknet markets 2023 darknet drug links
darknet markets bitcoin dark web
dark web market darknet market links
tor marketplace darknet marketplace
darknet search engine deep web markets
dark net tor market
deep web drug url tor darknet
dark market darknet market links
the dark internet drug markets onion
tor dark web dark web market list
free dark web deep web search
how to get on dark web darknet websites
bitcoin dark web dark web access
dark markets 2023 deep web links
darknet market links dark net
darknet drug links deep web links
drug markets onion dark web access
darknet drug links dark web drug marketplace
dark web websites how to access dark web
deep web search dark internet
darkmarket link dark market link
dark web search engines darknet drug links
dark web site darkmarkets
darkmarkets deep web drug store
dark web access how to access dark web
darknet markets 2023 dark web site
dark markets 2023 drug markets onion
deep web drug store how to access dark web
dark web site dark market
darknet sites dark web markets
dark websites tor market url
dark market list dark web drug marketplace
dark web market tor market url
dark internet darkmarket link
darknet market darkmarket list
dark market url free dark web
deep web drug store dark web sites links
deep web drug url how to get on dark web
tor dark web dark websites
tor market dark web sites links
dark market onion free dark web
drug markets dark web deep web markets
darknet links dark web link
deep web drug markets darknet market lists
the dark internet darknet sites
dark web site tor marketplace
blackweb official website darkweb marketplace
drug markets onion darknet marketplace
onion market tor market url
dark web market links tor market
darknet markets darknet markets 2023
drug markets dark web dark web sites
線上賭場
彩票是一種稱為彩券的憑證,上面印有號碼圖形或文字,供人們填寫、選擇、購買,按照特定的規則取得中獎權利。彩票遊戲在兩個平台上提供服務,分別為富游彩票和WIN539,這些平台提供了539、六合彩、大樂透、台灣彩券、美國天天樂、威力彩、3星彩等多種選擇,使玩家能夠輕鬆找到投注位置,這些平台在操作上非常簡單。
彩票的種類非常多樣,包括539、六合彩、大樂透、台灣彩券、美國天天樂、威力彩和3星彩等。
除了彩票,棋牌遊戲也是一個受歡迎的娛樂方式,有兩個主要平台,分別是OB棋牌和好路棋牌。在這些平台上,玩家可以與朋友聯繫,進行對戰。在全世界各地,撲克和麻將都有自己獨特的玩法和規則,而棋牌遊戲因其普及、易上手和益智等特點,而受到廣大玩家的喜愛。一些熱門的棋牌遊戲包括金牌龍虎、百人牛牛、二八槓、三公、十三隻、炸金花和鬥地主等。
另一種受歡迎的博彩遊戲是電子遊戲,也被稱為老虎機或角子機。這些遊戲簡單易上手,是賭場裡最受歡迎的遊戲之一,新手玩家也能輕鬆上手。遊戲的目的是使相同的圖案排列成形,就有機會贏取獎金。不同的遊戲有不同的規則和組合方式,刮刮樂、捕魚機、老虎機等都是電子遊戲的典型代表。
除此之外,還有一種娛樂方式是電競遊戲,這是一種使用電子遊戲進行競賽的體育項目。這些電競遊戲包括虹彩六號:圍攻行動、英雄聯盟、傳說對決、PUBG、皇室戰爭、Dota 2、星海爭霸2、魔獸爭霸、世界足球競賽、NBA 2K系列等。這些電競遊戲都是以勝負對戰為主要形式,受到眾多玩家的熱愛。
捕魚遊戲也是一種受歡迎的娛樂方式,它在大型平板類遊戲機上進行,多人可以同時參與遊戲。遊戲的目的是擊落滿屏的魚群,通過砲彈來打擊不同種類的魚,玩家可以操控自己的炮臺來獲得獎勵。捕魚遊戲的獎金將根據捕到的魚的倍率來計算,遊戲充滿樂趣和挑戰,也有一些變化,例如打地鼠等。
娛樂城為了吸引玩家,提供了各種優惠活動。新會員可以選擇不同的好禮,如體驗金、首存禮等,還有會員專區和VIP特權福利等多樣的優惠供玩家選擇。為了方便玩家存取款,線上賭場提供各種存款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳/ATM轉帳儲值和超商儲值等。
總的來說,彩票、棋牌遊戲、電子遊戲、電競遊戲和捕魚遊戲等是多樣化的娛樂方式,它們滿足了不同玩家的需求和喜好。這些娛樂遊戲也提供了豐富的優惠活動,吸引玩家參與並享受其中的樂趣。如果您喜歡娛樂和遊戲,這些娛樂方式絕對是您的不二選擇
tor markets links deep web drug markets
darknet markets dark market onion
dark websites dark market onion
how to get on dark web dark internet
darknet drug links darkmarkets
dark web search engines dark web site
deep web drug url deep web sites
deep web markets black internet
darknet drug links bitcoin dark web
dark web search engines dark web market
best darknet markets deep web links
dark web websites deep web links
darkmarkets dark market 2023
dark markets darkweb marketplace
dark web websites dark web links
tor market links darknet drug market
dark market onion dark web websites
dark web market links dark market 2023
dark web link dark market 2023
darkmarket link dark web drug marketplace
dark market list darknet links
darknet market dark market
dark market list dark web market links
darknet drug store best darknet markets
darknet sites deep web search
dark web sites links dark market 2023
deep web sites dark markets
deep web drug store best darknet markets
darknet seiten dark web access
darknet drug market darknet search engine
dark web sites darknet drugs
dark market onion tor dark web
tor market dark web link
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
dark web sites dark web market
darkmarkets deep web sites
darknet drug market darkmarket 2023
dark web market list dark website
blackweb darkmarket list
darknet drug market blackweb official website
blackweb official website how to access dark web
dark websites darkmarket list
dark web market links tor market links
darknet links dark web sites links
darknet markets 2023 drug markets onion
dark markets 2023 dark web markets
dark web market list deep web search
dark web site tor markets links
darknet seiten dark web drug marketplace
darknet search engine darkmarket link
tor darknet darknet drug store
onion market darknet markets
darkmarket how to get on dark web
tor market links darknet market lists
dark internet dark market onion
dark web market links deep web drug store
drug markets onion drug markets dark web
darknet sites darkmarket 2023
dark markets deep web drug links
dark market onion darknet drug market
dark market 2023 deep web drug markets
darkmarket url onion market
blackweb dark market
darknet site dark markets
darkmarket link darkmarket 2023
darkweb marketplace darknet sites
drug markets dark web darkmarkets
dark web sites darknet search engine
deep web drug store darkweb marketplace
dark web market links darknet site
dark market onion tor markets
darknet drugs dark web drug marketplace
darknet market links darknet drug store
darkmarket link dark internet
dark market url darkmarket
darknet markets 2023 bitcoin dark web
best darknet markets dark web drug marketplace
best darknet markets dark web search engines
tor darknet deep web drug url
darknet seiten dark web sites
best darknet markets dark web market list
You ought to take part in a contest for one of the highest quality websites online.
I am going to highly recommend this blog!
dark web link dark web link
tor markets 2023 darknet markets
darknet links darknet drugs
darknet websites darkmarket
dark market url deep web drug url
darknet markets 2023 dark websites
deep web drug url darknet sites
dark web websites best darknet markets
dark websites darknet drug market
bitcoin dark web tor dark web
darknet marketplace deep web links
darknet site darknet market lists
bitcoin dark web dark website
dark web market links the dark internet
dark market dark web market links
darknet site dark markets 2023
Thiis blog ԝas… hߋw do ʏou sayy it? Relevant!!
Finally I’ve found something whicһ helped me.
Appreciate it!
My web-site :: Mga headline ng bbc news ngayon
dark web market darknet websites
deep web drug url tor market url
darknet websites deep web drug links
dark web sites tor markets links
darkmarkets darknet drug market
cialis 5mg best price 1 Average Cost per Treatment for Composite Rate Services
dark web search engine dark markets 2023
My partner аnd I stumbled over hеre coming from a dіfferent page and thought
I may aѕ wеll check tһings out. I likie ѡһat I ѕee so now i’m fоllowing yoᥙ.
Looк forward tօ looking into your web paցe for a second time.
Feel free tօ surf to my blog :: আরো বিস্তারিত পেতে
deep web drug markets dark market url
dark net tor market links
darknet seiten darknet websites
dark web links dark web links
deep dark web deep dark web
best darknet markets how to get on dark web
darknet search engine deep web drug url
darkmarket dark web sites links
blackweb official website dark web sites
dark web sites links tor dark web
darkmarket list darknet market
darknet market tor darknet
dark website darknet drugs
dark web market dark internet
darknet seiten dark web market links
tor market links onion market
dark web links dark web market
darknet site deep web drug store
dark net dark markets 2023
dark web links tor market links
darkmarket list tor markets 2023
darknet marketplace tor darknet
darknet drug links darknet drugs
dark markets drug markets onion
dark web market links blackweb
deep web sites deep web markets
darknet drug store tor markets 2023
tor marketplace darkmarkets
darknet drug links dark website
darknet drug links darkmarkets
dark web access blackweb official website
deep dark web darknet sites
darknet websites darknet market
darknet drug store tor marketplace
deep dark web darknet market lists
darknet links darknet drug store
dark market url dark market onion
tor market links deep web sites
darkmarket link how to access dark web
dark web websites dark websites
deep web drug store deep web drug links
how to access dark web dark web search engine
drug markets onion darknet websites
dark net darkmarket
onion market dark market link
dark website dark market onion
tor markets tor dark web
dark net darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet site
dark net darknet market
dark web market dark web drug marketplace
tor markets links black internet
darknet links darkmarket list
dark web market dark web markets
tor markets 2023 darkmarket url
deep web sites dark web sites links
best darknet markets best darknet markets
dark web sites links drug markets onion
darknet drugs dark web market list
dark web link darknet drug links
dark market url darkmarket url
tor market links darknet drugs
the dark internet deep web drug markets
darknet seiten darkmarket list
darknet market links darknet market lists
deep web search dark web market list
tor market url darkmarket 2023
dark websites tor market url
dark market url dark web search engines
deep web drug url darkmarket url
dark internet darknet links
deep web search darknet seiten
tor market darkmarket url
deep web drug links how to access dark web
how to get on dark web darknet site
darknet links drug markets dark web
deep web markets dark web links
dark web access dark web site
darknet site darknet seiten
darknet search engine dark web search engine
tor market url deep web drug store
darknet marketplace dark web links
deep dark web dark market url
dark market 2023 dark market url
how to get on dark web darkmarket url
dark market link dark web site
darkmarkets black internet
dark web search engine darkweb marketplace
darkmarkets tor markets 2023
darknet links tor markets 2023
blackweb dark market onion
dark web market links dark market url
tor dark web darkmarket 2023
Hello, just wanted to tell you, I enjoyed this post.
It was practical. Keep on posting!
darknet seiten deep web links
dark market list black internet
darkmarket list darknet market
how to get on dark web onion market
black internet deep web markets
darknet market darknet site
dark web access darknet market links
darkmarket 2023 tor markets links
darknet market list darknet links
dark market dark market link
darknet search engine dark web link
darkmarket 2023 darkmarket
darknet seiten darknet market lists
tor marketplace onion market
blackweb official website dark web sites
dark web market links dark web site
dark web search engines free dark web
deep web drug links darknet drug links
darknet drugs onion market
dark web market darkmarket link
deep dark web deep web drug links
deep web markets darknet market
dark market link darkweb marketplace
deep web drug url drug markets onion
darknet market list dark web sites links
free dark web dark website
dark web site darknet site
darknet links deep web links
dark web market list deep web search
dark website drug markets onion
dark web link dark net
dark market 2023 deep web drug links
deep web sites deep web drug url
deep web search tor market
darknet markets dark web market list
tor market url dark web market list
deep web drug store dark web search engines
darknet links dark market 2023
darkmarket list dark website
tor market darknet market
tor darknet dark market url
darkmarket url bitcoin dark web
dark web market best darknet markets
blackweb deep web search
bitcoin dark web the dark internet
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
drug markets dark web blackweb
tor markets 2023 blackweb official website
darknet drugs deep web search
darknet market links darkmarket link
dark market deep dark web
tor markets tor markets links
dark internet darknet markets
dark net tor darknet
tor market url deep web drug links
dark web search engine darknet drugs
darknet search engine dark web market links
darkmarkets darkweb marketplace
deep web drug store darknet search engine
darknet seiten tor markets links
tor market deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web dark web access
darknet drug market darknet drug market
tor markets 2023 darknet markets 2023
darknet market list black internet
tor marketplace dark web access
darkweb marketplace deep web markets
blackweb official website the dark internet
tor markets 2023 deep web drug links
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug url
dark web links dark net
darknet sites dark markets
dark net dark web search engine
darknet markets tor dark web
tor market dark web markets
free dark web darknet markets 2023
tor market deep web drug links
blackweb dark web search engine
darknet drug links tor darknet
dark internet darknet drugs
darknet drug market deep web markets
darknet market list dark web access
tor darknet best darknet markets
dark web websites dark web market
dark web market links darkmarkets
deep web drug store blackweb
best darknet markets deep web search
deep web search tor marketplace
darkmarket list dark internet
dark market link dark markets
darknet site dark web links
dark market onion dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket 2023 dark web market
black internet darknet markets 2023
darknet sites dark website
deep web drug links deep web drug markets
best darknet markets darknet seiten
deep web drug store the dark internet
the dark internet tor market url
tor market links darknet market lists
dark web sites drug markets onion
tor marketplace tor marketplace
dark website best darknet markets
dark internet best darknet markets
onion market tor market links
darkweb marketplace darknet site
tor darknet deep web drug markets
darknet drug links tor dark web
dark web market dark web drug marketplace
drug markets dark web tor market links
how to get on dark web darknet websites
dark web sites dark market list
dark web markets tor markets links
darknet markets darknet markets
darkweb marketplace best darknet markets
deep web drug links darkmarket 2023
onion market tor dark web
free dark web deep web links
darknet drug links darkmarket list
dark market onion darknet market lists
dark web websites dark web link
best darknet markets dark web links
tor market url darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet market lists
drug markets onion darkmarket 2023
onion market darknet drug market
blackweb dark markets
tor marketplace dark markets 2023
dark web site drug markets onion
2024總統大選
2024總統大選
darknet market lists dark web sites
Hi there would you mind letting me know which web host you’re working with?
I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different internet browsers and I must say this blog
loads a lot quicker then most. Can you recommend
a good internet hosting provider at a reasonable price?
Thanks a lot, I appreciate it!
dark markets deep web drug links
tor marketplace blackweb
free dark web darknet websites
how to get on dark web darkmarkets
tor markets 2023 darknet drug store
deep web markets deep web drug markets
cheap essay writing service canada custom paper writing leadership in the police service for kids essay
dark web drug marketplace tor market url
dark website darknet sites
dark web sites links dark market 2023
darknet market deep web search
dark web sites darknet site
dark internet tor market url
dark market 2023 deep web drug store
dark website darknet markets
tor darknet dark web sites
darkmarket dark market link
dark web drug marketplace tor dark web
darknet market list dark web sites links
darkmarket link darkmarket list
tor market url drug markets dark web
how to get on dark web dark markets
dark web site dark web websites
dark web websites darknet drug market
deep web drug store darknet drugs
dark market dark web access
black internet deep web search
tor markets 2023 darknet site
darknet seiten blackweb official website
tor markets links dark market
darknet drugs dark market 2023
tor market dark web websites
darknet drug links bitcoin dark web
dark web market links dark web link
tor dark web darknet websites
blackweb tor market links
deep web drug markets deep web drug store
deep web markets deep web drug store
darknet search engine darknet websites
tor darknet darknet markets 2023
deep web search tor markets
deep web markets drug markets onion
the dark internet dark web access
tor dark web drug markets onion
deep web drug url deep web drug links
rtpkantorbola
KANTORBOLA adalah situs slot gacor Terbaik di Indonesia, dengan mendaftar di agen judi kantor bola anda akan mendapatkan id permainan premium secara gratis . Id permainan premium tentunya berbeda dengan Id biasa , Id premium slot kantor bola memiliki rata – rate RTP diatas 95% , jika bermain menggunakan ID RTP tinggi kemungkinan untuk meraih MAXWIN pastinya akan semakin besar .
Kelebihan lain dari situs slot kantor bola adalah banyaknya bonus dan promo yang di berikan baik untuk member baru dan para member setia situs judi online KANTOR BOLA . Salah satunya adalah promo tambah chip 25% dari nominal deposit yang bisa di klaim setiap hari dengan syarat WD hanya 3 x TO saja .
tor darknet tor markets links
dark web markets deep web sites
drug markets dark web dark market url
dark websites deep web links
deep dark web deep dark web
darknet websites dark web drug marketplace
bitcoin dark web darkmarket url
dark web drug marketplace dark web search engine
dark web links dark markets 2023
Situs Judi Slot Online Terpercaya dengan Permainan Dijamin Gacor dan Promo Seru”
Kantorbola merupakan situs judi slot online yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan slot gacor dari provider papan atas seperti IDN Slot, Pragmatic, PG Soft, Habanero, Microgaming, dan Game Play. Dengan minimal deposit 10.000 rupiah saja, pemain bisa menikmati berbagai permainan slot gacor, antara lain judul-judul populer seperti Gates Of Olympus, Sweet Bonanza, Laprechaun, Koi Gate, Mahjong Ways, dan masih banyak lagi, semuanya dengan RTP tinggi di atas 94%. Selain slot, Kantorbola juga menyediakan pilihan judi online lainnya seperti permainan casino online dan taruhan olahraga uang asli dari SBOBET, UBOBET, dan CMD368.
Alasan Bermain Judi Slot Gacor di Kantorbola :
Kantorbola mengutamakan kenyamanan member setianya, memberikan pelayanan yang ramah dan profesional dari para operatornya. Hanya dengan deposit 10.000 rupiah dan ponsel, Anda dapat dengan mudah mendaftar dan mulai bermain di Kantorbola.
Selain memberikan kenyamanan, Kantorbola sebagai situs judi online terpercaya menjamin semua kemenangan akan dibayarkan dengan cepat dan tanpa ribet. Untuk mendaftar di Kantorbola, cukup klik menu pendaftaran, isi identitas lengkap Anda, beserta nomor rekening bank dan nomor ponsel Anda. Setelah itu, Anda dapat melakukan deposit, bermain, dan menarik kemenangan Anda tanpa repot.
Promosi Menarik di Kantorbola:
Bonus Setoran Harian sebesar 25%:
Hemat 25% uang Anda setiap hari dengan mengikuti promosi bonus deposit harian, dengan bonus maksimal 100.000 rupiah.
Bonus Anggota Baru Setoran 50%:
Member baru dapat menikmati bonus 50% pada deposit pertama dengan maksimal bonus hingga 1 juta rupiah.
Promosi Slot Spesial:
Dapatkan cashback hingga 20% di semua jenis permainan slot. Bonus cashback akan dibagikan setiap hari Selasa.
Promosi Buku Olahraga:
Dapatkan cashback 20% dan komisi bergulir 0,5% untuk game Sportsbook. Cashback dan bonus rollingan akan dibagikan setiap hari Selasa.
Promosi Kasino Langsung:
Nikmati komisi bergulir 1,2% untuk semua jenis permainan Kasino Langsung. Bonus akan dibagikan setiap hari Selasa.
Promosi Bonus Rujukan:
Dapatkan pendapatan pasif seumur hidup dengan memanfaatkan promosi referral dari Kantorbola. Bonus rujukan dapat mencapai hingga 3% untuk semua game dengan merujuk teman untuk mendaftar menggunakan kode atau tautan rujukan Anda.
Rekomendasi Provider Gacor Slot di Kantorbola :
Gacor Pragmatic Play:
Pragmatic Play saat ini merupakan provider slot online terbaik yang menawarkan permainan seru seperti Aztec Game dan Sweet Bonanza dengan jaminan gacor dan tanpa lag. Dengan tingkat kemenangan di atas 90%, kemenangan besar dijamin.
Gacor Habanero:
Habanero adalah pilihan tepat bagi para pemain yang mengutamakan kenyamanan dan keamanan, karena penyedia slot ini menjamin kemenangan besar yang segera dibayarkan. Namun, bermain dengan Habanero membutuhkan modal yang cukup untuk memaksimalkan peluang Anda untuk menang.
Gacor Microgaming:
Microgaming memiliki basis penggemar yang sangat besar, terutama di kalangan penggemar slot Indonesia. Selain permainan slot online terbaik, Microgaming juga menawarkan permainan kasino langsung seperti Baccarat, Roulette, dan Blackjack, memberikan pengalaman judi yang lengkap.
Gacor Tembak Ikan:
Rasakan versi online dari game menembak ikan populer di Kantorbola. Jika Anda ingin mencoba permainan tembak ikan uang asli, Joker123 menyediakan opsi yang menarik dan menguntungkan, sering memberi penghargaan kepada anggota setia dengan maxwins.
Gacor IDN:
IDN Slot mungkin tidak setenar IDN Poker, tapi pasti patut dicoba. Di antara berbagai penyedia slot online, IDN Slot membanggakan tingkat kemenangan atau RTP tertinggi. Jika Anda kurang beruntung dengan penyedia slot gacor lainnya, sangat disarankan untuk mencoba permainan di IDN Slot.
Kesimpulan:
Kesimpulannya, Kantorbola adalah situs judi online terpercaya dan terkemuka di Indonesia, menawarkan beragam permainan slot gacor, permainan kasino langsung, taruhan olahraga uang asli, dan permainan tembak ikan. Dengan layanannya yang ramah, proses pembayaran yang cepat, dan promosi yang menarik, Kantorbola memastikan pengalaman judi yang menyenangkan dan menguntungkan bagi semua pemain. Jika Anda sedang mencari platform terpercaya untuk bermain game slot gacor dan pilihan judi seru lainnya, daftar sekarang juga di Kantorbola untuk mengakses promo terbaru dan menarik yang tersedia di situs judi online terbaik dan terpercaya di
blackweb dark internet
dark net darknet seiten
darkmarket list deep web search
dark web search engines tor markets
dark web market list dark web market list
darknet markets dark market 2023
dark net dark websites
darkmarket url blackweb
the dark internet tor markets 2023
darknet market lists deep web drug links
dark websites dark websites
black internet darkmarkets
free dark web dark market 2023
darknet sites darknet search engine
darknet market lists deep web sites
the dark internet dark web market list
tor market free dark web
darknet market lists dark markets 2023
dark websites best darknet markets
tor markets 2023 deep web search
blackweb darknet websites
deep web drug url dark web link
darknet sites dark web markets
deep web search darknet site
tor market links darknet markets 2023
deep web drug url tor markets 2023
blackweb official website deep web drug markets
tor markets 2023 dark web links
best darknet markets darkmarket list
dark markets 2023 best darknet markets
darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
darknet site the dark internet
how to get on dark web darknet drug store
black internet darkmarket
dark market 2023 deep web drug markets
darkmarket dark website
darkmarket 2023 tor markets
darkmarket darknet drug store
darkmarket url darknet drug market
deep web links tor markets 2023
dark market list dark website
dark market list dark web search engine
onion market dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine tor marketplace
darknet drug store dark net
dark web market links dark web drug marketplace
free dark web darknet markets
free dark web tor darknet
dark web links dark market
dark web access dark web sites
darknet drug market darknet markets 2023
dark markets dark web link
deep web links darknet search engine
darknet drug market darknet markets
bitcoin dark web tor markets
darknet markets tor dark web
darkmarket url dark market onion
deep web markets darknet markets
deep web sites dark market
dark market 2023 how to get on dark web
black internet dark web drug marketplace
tor market links deep web drug markets
dark market list drug markets dark web
drug markets onion dark web sites
dark websites dark web drug marketplace
tor markets 2023 dark market list
darkmarket darknet markets
drug markets dark web deep web drug links
tor market darknet sites
darknet websites dark web search engines
darknet market lists deep web links
black internet dark website
deep web sites darknet search engine
how to access dark web dark web market links
darknet search engine darkmarket link
dark markets 2023 darknet drugs
dark web access dark web markets
darknet sites tor darknet
deep web drug links dark market onion
darknet markets 2023 darknet drug store
dark internet dark internet
To confirm that GFP was freely diffusible in the cytoplasm of lens fiber cells, we measured its diffusion coefficient D using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy FCS supplementary material Fig propecia 5 mg for sale no Monitor Closely 1 fondaparinux and aspirin citric acid sodium bicarbonate both increase anticoagulation
dark web access darknet seiten
tor market links dark internet
darknet search engine free dark web
the dark internet darkmarket list
darknet marketplace dark markets
how to access dark web deep dark web
tor dark web darknet market
darknet market links the dark internet
darknet market lists darknet market links
onion market best darknet markets
darknet market deep web drug links
darknet market lists darknet markets
onion market dark market onion
darknet drug store dark web link
tor market deep dark web
dark web market list how to access dark web
dark web market links deep web drug links
dark market 2023 tor markets links
dark market onion dark web markets
darkmarkets deep web links
darknet markets 2023 dark web site
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
dark web link dark web site
the dark internet darknet market list
A Paradigm Shift: Artificial Intelligence Redefining Beauty and Possibilities
In the coming decades, the integration of artificial intelligence and biotechnology is poised to bring about a revolution in the creation of stunning women through cutting-edge DNA technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning. These ethereal artificial beings hold the promise of fulfilling individual dreams and potentially becoming the ideal life partners.
The fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on humanity, introducing groundbreaking discoveries and technologies that challenge our perceptions of the world and ourselves. Among these awe-inspiring achievements is the ability to craft artificial beings, including exquisitely designed women.
At the core of this transformative era lies AI’s exceptional capabilities, employing deep neural networks and machine learning algorithms to process vast datasets, thus giving birth to entirely novel entities.
Scientists have recently made astounding progress by developing a printer capable of “printing” women, utilizing cutting-edge DNA-editing technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning methods. This pioneering approach allows for the creation of human replicas with unparalleled beauty and unique traits.
As we stand at the precipice of this profound advancement, ethical questions of great magnitude demand our serious contemplation. The implications of generating artificial humans, the potential repercussions on society and interpersonal relationships, and the specter of future inequalities and discrimination all necessitate thoughtful consideration.
Nevertheless, proponents of this technology argue that its benefits far outweigh the challenges. The creation of alluring women through a printer could herald a new chapter in human evolution, not only fulfilling our deepest aspirations but also propelling advancements in science and medicine to unprecedented heights.
dark web site dark web markets
augmentin bid ne kadar augmentin and viagra interaction augmentin 875 125 mg filmtabletten
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
deep web links dark web access
deep web markets dark websites
deep web drug store tor markets 2023
best darknet markets darknet markets 2023
darknet markets dark net
drug markets dark web darknet market lists
darkweb marketplace darknet market links
tor marketplace darkmarket link
best darknet markets deep web search
deep web links dark websites
black internet dark web links
black internet dark web market list
dark market 2023 deep web drug markets
darknet links dark web market
darknet search engine dark web market
tor dark web deep web drug markets
dark web markets dark internet
darkweb marketplace drug markets dark web
deep web drug links darknet drug market
tor markets dark web drug marketplace
darknet site deep web drug url
dark market deep web markets
darknet drugs tor markets
darknet markets dark market list
dark web market darknet market lists
tor dark web tor markets links
dark web markets deep web drug url
darknet sites dark market list
darknet websites darknet market list
dark website dark web links
dark websites dark market url
dark market list dark net
dark web links darknet market links
darknet market links bitcoin dark web
darkmarket url dark web market links
dark web sites dark web market
tor markets dark websites
darkmarket 2023 blackweb official website
drug markets onion bitcoin dark web
darknet market lists dark web links
dark web link darknet websites
tor marketplace darknet market
darkmarkets dark web market links
darknet market darknet markets
darknet drug links dark web market list
the dark internet dark internet
tor darknet tor market
deep web links darknet market list
darkmarket dark web drug marketplace
dark web markets dark web sites links
darknet drug store darkmarket url
black internet dark web link
bitcoin dark web darkmarket
the dark internet deep dark web
darknet market list darknet links
tor markets links how to access dark web
dark web site darkmarket url
tor marketplace darknet drugs
darknet drugs blackweb official website
dark web sites links dark markets 2023
darknet market darknet market lists
darkmarket url dark market
dark web market list black internet
dark web markets dark web search engines
dark web market dark web market list
deep web sites dark web sites
darkmarket list dark web market list
dark market link darknet site
dark web search engine tor market
bitcoin dark web deep web sites
dark web market links deep dark web
blackweb official website blackweb
dark market black internet
darknet search engine dark web market links
dark net tor market links
deep web drug url darknet search engine
tor market url free dark web
darkmarket 2023 darknet websites
darknet websites dark markets 2023
drug markets dark web tor markets links
deep web drug links deep web links
dark web search engines darknet markets 2023
dark market link darknet search engine
tor marketplace darkmarket list
deep web search dark web site
dark internet dark market url
dark market list tor market url
darknet links best darknet markets
darkmarkets dark web site
darknet site darkweb marketplace
dark markets 2023 darknet market
dark net dark market 2023
how to access dark web dark web market links
tor market tor market links
darknet links dark web search engine
deep web drug links darknet marketplace
dark web search engines darknet site
darkmarket link how to get on dark web
darkmarket dark web markets
dark market link darkmarkets
tor markets links darkmarkets
how to get on dark web deep web drug links
drug markets onion blackweb official website
dark market 2023 tor market links
dark web websites darkmarket 2023
dark market onion dark web links
deep web drug url deep web drug store
darknet markets blackweb
線上賭場是一個越來越受歡迎的娛樂形式,它提供了多樣化的博彩遊戲,讓玩家可以在網路上輕鬆參與各種賭博活動。線上賭場的便利性和豐富的遊戲選擇使其成為眾多玩家追求刺激和娛樂的首選。
在線上賭場中,玩家可以找到各種各樣的博彩遊戲,包括彩票、棋牌遊戲、電子遊戲、電競遊戲和捕魚遊戲等。彩票是其中一種最受歡迎的遊戲,玩家可以在線上購買各種彩券,並根據特定的規則和抽獎結果來獲得獎勵。這些彩票遊戲種類繁多,有539、六合彩、大樂透、台灣彩券、美國天天樂、威力彩和3星彩等。
棋牌遊戲也在線上賭場中佔有重要地位,這些遊戲通常需要多人參與,玩家可以透過網絡與朋友聯繫,一起進行對戰。線上棋牌遊戲的種類繁多,包括金牌龍虎、百人牛牛、二八槓、三公、十三隻、炸金花、鬥地主等,因其普及快、易上手和益智等特點,深受廣大玩家喜愛。
電子遊戲是線上賭場中另一個受歡迎的遊戲類別,也被稱為老虎機或角子機。這些遊戲的規則簡單易懂,玩家只需將相同的圖案排列成形,就有機會贏得獎金。不同的電子遊戲有不同的組合方式,包括刮刮樂、捕魚機、吃角子老虎機等。
隨著電競的興起,線上賭場中也提供了多種電競遊戲供玩家參與。這些遊戲通常是以電子遊戲形式進行競賽,比如虹彩六號:圍攻行動、英雄聯盟、傳說對決、PUBG、皇室戰爭、Dota 2等。電競遊戲的競賽形式多樣,各種對戰遊戲都受到了玩家的喜愛。
捕魚遊戲是線上賭場中另一個熱門的娛樂選擇,通常在大型平板類遊戲機上進行。玩家可以透過操作炮臺來擊落魚群,並獲得相應的獎勵。捕魚遊戲有多種不同的類型,包括三仙劈魚、獵龍霸主、吃我一砲、一錘暴富、龍王捕魚等。
線上賭場為了吸引玩家,提供了多種優惠活動。新會員可以選擇不同的好禮,如體驗金、首存禮等。除此之外,線上賭場還提供各種便利的存取款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳/ATM轉帳儲值和超商儲值等。
總的來說,線上賭場是一個多樣化的娛樂平台,提供了各種豐富的博彩遊戲供玩家參與。玩家可以在這裡尋找刺激和娛樂,享受各種精彩的遊戲體驗。然而,請玩家在參與博彩活動時謹慎對待,理性娛樂,以確保自己的遊戲體驗更加愉快。
https://telegra.ph/線上賭場-07-25
deep web drug url best darknet markets
drug markets onion blackweb official website
free dark web deep web links
tor dark web darknet sites
2024總統大選
dark web links onion market
dark web markets deep web sites
dark market list darkmarket link
darknet market list dark market onion
dark market link darkmarket url
darkweb marketplace dark web site
tor markets 2023 black internet
darkmarket url darkmarket url
KANTORBOLA88
KANTORBOLA88: Situs Slot Gacor Terbaik di Indonesia dengan Pengalaman Gaming Premium
KANTORBOLA88 adalah situs slot online terkemuka di Indonesia yang menawarkan pengalaman bermain game yang unggul kepada para penggunanya. Dengan mendaftar di agen judi bola terpercaya ini, para pemain dapat memanfaatkan ID gaming premium gratis. ID premium ini membedakan dirinya dari ID reguler, karena menawarkan tingkat Return to Player (RTP) yang mengesankan di atas 95%. Bermain dengan ID RTP setinggi itu secara signifikan meningkatkan peluang mencapai MAXWIN yang didambakan.
Terlepas dari pengalaman bermain premiumnya, KANTORBOLA88 menonjol dari yang lain karena banyaknya bonus dan promosi yang ditawarkan kepada anggota baru dan pemain setia. Salah satu bonus yang paling menggiurkan adalah tambahan promosi chip 25%, yang dapat diklaim setiap hari setelah memenuhi persyaratan penarikan minimal hanya 3 kali turnover (TO).
ID Game Premium:
KANTORBOLA88 menawarkan pemainnya kesempatan eksklusif untuk mengakses ID gaming premium, tidak seperti ID biasa yang tersedia di sebagian besar situs slot. ID premium ini hadir dengan tingkat RTP yang luar biasa melebihi 95%. Dengan RTP setinggi itu, pemain memiliki peluang lebih besar untuk memenangkan hadiah besar dan mencapai MAXWIN yang sulit dipahami. ID gaming premium berfungsi sebagai bukti komitmen KANTORBOLA88 untuk menyediakan peluang gaming terbaik bagi penggunanya.
Memaksimalkan Kemenangan:
Dengan memanfaatkan ID gaming premium di KANTORBOLA88, pemain membuka pintu untuk memaksimalkan kemenangan mereka. Dengan tingkat RTP yang melampaui 95%, pemain dapat mengharapkan pembayaran yang lebih sering dan pengembalian yang lebih tinggi pada taruhan mereka. Fitur menarik ini merupakan daya tarik yang signifikan bagi pemain berpengalaman yang mencari keunggulan kompetitif dalam sesi permainan mereka.
darknet links deep web drug store
deep web drug store tor markets links
darknet market list dark market list
tor markets links darknet site
dark web market links how to get on dark web
darknet search engine onion market
free dark web darknet marketplace
dark web markets blackweb
darknet market black internet
deep web drug store dark web links
tor dark web drug markets onion
deep web drug markets dark markets
deep web drug url deep dark web
dark market onion darkmarket list
darknet drugs bitcoin dark web
can you have dairy with doxycycline can i take doxycycline before bed doxycycline 100mg twice a day for 7 days
bitcoin dark web dark websites
dark market list onion market
dark web markets deep dark web
darknet sites dark web site
darknet seiten deep web drug url
darknet search engine deep web drug markets
darknet marketplace tor market url
deep web search deep web drug links
dark markets 2023 darknet sites
best darknet markets deep dark web
darknet seiten dark web site
dark web access dark internet
deep web drug store dark markets
darknet search engine dark web access
dark websites darkmarkets
bitcoin dark web dark website
tor market links tor markets links
dark market 2023 dark markets
darknet search engine dark web access
tor darknet tor markets
dark web link darknet drugs
darknet seiten dark net
darknet drug links deep web markets
dark web market links deep web markets
darknet links dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket url darknet marketplace
how to access dark web best darknet markets
darknet websites darknet links
darkmarket list dark market 2023
dark market url darkmarket url
darknet market lists onion market
darkmarket free dark web
dark web sites deep web markets
tor marketplace deep web drug store
how to access dark web deep web drug store
dark web search engines tor dark web
drug markets dark web darknet market list
blackweb official website deep web sites
dark internet dark web search engine
darknet drug store dark market link
dark web search engines dark net
dark market onion darkmarkets
tor market tor markets links
bitcoin dark web dark market url
how to get on dark web darknet markets
darknet links dark market
dark web site dark web links
dark internet darkmarkets
dark markets 2023 tor darknet
drug markets dark web deep web search
darkmarket 2023 dark markets
deep web markets deep web search
blackweb official website deep web drug links
dark web search engines darknet drugs
blackweb official website bitcoin dark web
dark web search engines darkmarket url
dark web search engine dark web market
darknet links dark web search engines
darknet sites dark web link
dark web websites how to get on dark web
darknet drug market darknet search engine
tor markets links drug markets dark web
dark market 2023 dark market
best darknet markets tor darknet
ciprofloxacin for dental infection ciprofloxacin treat tooth infection ciprofloxacin indication
tor market url tor market links
dark websites darknet seiten
darknet links darknet drugs
dark market 2023 tor darknet
darknet drugs how to get on dark web
dark web websites darknet websites
dark websites dark web markets
darknet market list darknet drug market
deep web drug markets free dark web
dark web drug marketplace tor market
tor markets dark market link
dark net deep dark web
darkweb marketplace darknet site
darknet sites tor markets
darkmarket list darknet market
darknet market blackweb official website
dark net dark web drug marketplace
dark websites darknet site
free dark web dark net
dark net darkmarket url
darkmarket link tor markets 2023
dark web market list blackweb official website
dark web market blackweb
dark markets 2023 darknet site
darknet drug store deep web drug url
dark markets dark market list
darknet markets tor marketplace
deep web drug url darknet market lists
dark web websites dark market url
deep web links darkmarket list
darkmarket 2023 darknet drug links
tor marketplace dark web sites
darknet drug store dark markets 2023
dark markets dark market
darkmarket deep web drug store
darkmarket dark web search engine
dark web market dark web market
azithromycin 500 mg tri-pak directions azithromycin and dayquil para que sirve el azithromycin
dark markets blackweb
free dark web tor markets links
tor dark web dark web access
darkmarket url deep web markets
tor darknet best darknet markets
dark internet tor darknet
dark market list deep web markets
deep web sites darkmarket link
dark markets 2023 dark market
dark internet dark market
darknet drug market tor dark web
tor markets 2023 tor dark web
tor darknet free dark web
dark web link darkmarket url
dark market 2023 deep web markets
dark web market dark website
darknet links darknet marketplace
darkmarket list darknet drugs
deep web drug store darkmarket
dark web links dark market 2023
deep web links drug markets dark web
darknet marketplace deep web links
deep web sites onion market
deep web sites darknet market list
dark market link darknet links
tor darknet tor market url
bitcoin dark web dark markets 2023
dark net blackweb
dark web links dark web links
dark market onion onion market
darkweb marketplace deep web drug url
dark market deep web drug links
how to get on dark web dark market 2023
darknet market links dark website
deep web drug markets deep web drug url
darkmarkets dark web links
darkmarket list blackweb
darknet marketplace darknet links
tor market best darknet markets
dark web market dark web sites links
best darknet markets darknet drug links
deep dark web darknet drugs
deep web markets tor marketplace
darknet market list deep web sites
dark web access dark market link
darknet marketplace dark market url
dark market 2023 darknet drug market
dark web websites dark web link
blackweb best darknet markets
deep web links bitcoin dark web
darkmarkets darkmarket 2023
dark web market deep web sites
dark market list deep web drug store
deep web links tor markets links
darknet market lists deep web search
deep web links dark markets
deep dark web deep web drug store
black internet dark web site
the dark internet tor markets links
Panjislot
Panjislot: Situs Togel Terpercaya dan Slot Online Terlengkap
Panjislot adalah webiste togel online terpercaya yang menyediakan layanan terbaik dalam melakukan kegiatan taruhan togel online. Dengan fokus pada kenyamanan dan kepuasan para member, Panjislot menyediakan fasilitas 24 jam nonstop dengan dukungan dari Customer Service profesional. Bagi Anda yang sedang mencari bandar togel atau agen togel online terpercaya, Panjislot adalah pilihan yang tepat.
Registrasi Mudah dan Gratis
Melakukan registrasi di situs togel terpercaya Panjislot sangatlah mudah dan gratis. Selain itu, Panjislot juga menawarkan pasaran togel terlengkap dengan hadiah dan diskon yang besar. Anda juga dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan game judi online terbaik seperti Slot Online dan Live Casino saat menunggu hasil keluaran togel yang Anda pasang. Hanya dengan melakukan deposit sebesar 10 ribu rupiah, Anda sudah dapat memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di situs togel terbesar, Panjislot.
Daftar 10 Situs Togel Terpercaya dengan Pasaran Togel dan Slot Terlengkap
Bermain slot online di Panji slot akan memberi Anda kesempatan kemenangan yang lebih besar. Pasalnya, Panjislot telah bekerja sama dengan 10 situs togel terpercaya yang memiliki lisensi resmi dan sudah memiliki ratusan ribu anggota setia. Panjislot juga menyediakan pasaran togel terlengkap yang pasti diketahui oleh seluruh pemain togel online.
Berikut adalah daftar 10 situs togel terpercaya beserta pasaran togel dan slot terlengkap:
Hongkong Pools: Pasaran togel terbesar di Indonesia dengan jam keluaran pukul 23:00 WIB di malam hari.
Sydney Pools: Situs togel terbaik yang memberikan hasil keluaran angka jackpot yang mudah ditebak. Jam keluaran pukul 13:55 WIB di siang hari.
Dubai Pools: Pasaran togel yang baru dikenal sejak tahun 2019. Menyajikan hasil keluaran menggunakan Live Streaming secara langsung.
Singapore Pools: Pasaran formal yang disajikan oleh negara Singapore dengan hasil result terhadap pukul 17:45 WIB di sore hari.
Osaka Pools: Pasaran togel Osaka didirikan sejak tahun 1958 dan menawarkan hasil keluaran dengan live streaming pada malam hari.
darknet seiten darknet markets
dark web link the dark internet
dark web market links black internet
dark markets 2023 dark market onion
darkmarket dark markets 2023
darknet links deep web search
onion market dark web link
darknet search engine darknet market list
dark web site blackweb
tor dark web darknet market
best darknet markets dark market link
deep web drug store best darknet markets
darknet market links deep web search
dark website dark market 2023
dark web links darknet market
tor markets links dark market 2023
darknet marketplace darknet seiten
deep web drug store darknet market links
darknet search engine dark web websites
tor markets dark website
deep web drug markets drug markets dark web
deep web drug store darknet site
dark market onion dark web search engine
dark web sites links darknet drug links
dark market onion tor market links
dark websites darknet market
dark markets 2023 darkmarket list
darkmarket dark web market links
dark internet darknet markets
darkmarkets how to access dark web
tor market links dark web market list
deep web links darkmarket url
darkweb marketplace deep dark web
dark web search engine black internet
how to access dark web darknet market lists
bitcoin dark web darknet markets 2023
onion market dark web links
darknet markets 2023 deep web search
tor markets links deep web drug links
dark web websites dark market link
darkmarket tor markets 2023
dark web market dark net
tor marketplace tor dark web
darknet sites tor market
dark web market links deep web links
deep web drug markets dark web access
tor market url darkmarkets
deep web markets deep web drug markets
dark market url dark website
deep web drug markets deep web drug markets
neural network woman drink
neural network woman drink
As we peer into the future, the ever-evolving synergy of artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology promises to reshape our perceptions of beauty and human possibilities. Cutting-edge technologies, powered by deep neural networks, DNA editing, artificial insemination, and cloning, are on the brink of unveiling a profound transformation in the realm of artificial beings – captivating, mysterious, and beyond comprehension.
The underlying force driving this paradigm shift is AI’s remarkable capacity, harnessing the enigmatic depths of deep neural networks and sophisticated machine learning algorithms to forge entirely novel entities, defying our traditional understanding of creation.
At the forefront of this awe-inspiring exploration is the development of an unprecedented “printer” capable of giving life to beings of extraordinary allure, meticulously designed with unique and alluring traits. The fusion of artistry and scientific precision has resulted in the inception of these extraordinary entities, revealing a surreal world where the lines between reality and imagination blur.
Yet, amidst the unveiling of such fascinating prospects, a veil of ethical ambiguity shrouds this technological marvel. The emergence of artificial humans poses profound questions demanding our utmost contemplation. Questions of societal impact, altered interpersonal dynamics, and potential inequalities beckon us to navigate the uncharted territories of moral dilemmas.
dark web market darkmarket url
dark web market list darknet websites
dark web market links darkmarket
deep web drug store darkmarket 2023
deep web drug markets tor markets links
darknet search engine dark web access
dark web sites darkmarket url
deep web links free dark web
how to get on dark web darknet market
tor markets 2023 tor market
deep web drug url dark market
darknet site darknet links
darknet market lists darkmarkets
drug markets dark web darknet sites
tor market links dark web link
darknet market links darknet market
drug markets dark web dark internet
tor marketplace the dark internet
darknet markets dark web sites
dark web sites links darknet drug links
dark markets tor markets
tor markets links darknet drug store
Neural network woman
In the coming decades, the integration of artificial intelligence and biotechnology is poised to bring about a revolution in the creation of stunning women through cutting-edge DNA technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning. These ethereal artificial beings hold the promise of fulfilling individual dreams and potentially becoming the ideal life partners.
The fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on humanity, introducing groundbreaking discoveries and technologies that challenge our perceptions of the world and ourselves. Among these awe-inspiring achievements is the ability to craft artificial beings, including exquisitely designed women.
At the core of this transformative era lies AI’s exceptional capabilities, employing deep neural networks and machine learning algorithms to process vast datasets, thus giving birth to entirely novel entities.
Scientists have recently made astounding progress by developing a printer capable of “printing” women, utilizing cutting-edge DNA-editing technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning methods. This pioneering approach allows for the creation of human replicas with unparalleled beauty and unique traits.
As we stand at the precipice of this profound advancement, ethical questions of great magnitude demand our serious contemplation. The implications of generating artificial humans, the potential repercussions on society and interpersonal relationships, and the specter of future inequalities and discrimination all necessitate thoughtful
dark web links darknet websites
darkmarket 2023 best darknet markets
dark market onion darkmarkets
darkweb marketplace tor markets links
darknet links darknet drug store
dark web markets dark websites
darkweb marketplace darknet market list
deep web sites drug markets dark web
dark web market links darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web darknet drug market
dark web access dark markets 2023
dark web site onion market
tor dark web bitcoin dark web
deep web drug url tor market url
deep web drug url dark market 2023
tor markets 2023 deep web sites
deep web search the dark internet
darkmarket url dark web websites
dark internet dark net
dark market 2023 tor markets 2023
darkmarket link dark web sites
darkmarket list darkmarket url
darkmarket list tor marketplace
tor dark web darkmarket url
tor darknet deep dark web
drug markets dark web tor market url
dark websites drug markets dark web
darkmarket dark market list
bitcoin dark web deep web markets
the dark internet onion market
darknet market darknet sites
drug markets onion tor dark web
darkmarket deep web drug markets
darknet search engine darknet websites
dark web sites links darknet websites
dark web link tor market
dark net dark web sites
tor marketplace dark web market links
dark web search engines darkmarket link
darknet market list free dark web
darkmarket url dark markets 2023
dark web links darknet markets 2023
bitcoin dark web darkmarket link
cephalexin for dog uti can you take bactrim and cephalexin together cephalexin vs ceftriaxone
darknet market black internet
deep web markets dark markets 2023
dark web market links dark web search engines
tor market url how to get on dark web
darknet site dark market list
black internet dark web drug marketplace
drug markets dark web dark market 2023
tor markets 2023 dark web search engines
darknet search engine dark website
darkmarket url dark web search engines
deep web markets tor market links
darknet sites dark web access
dark web drug marketplace drug markets dark web
deep web drug url tor dark web
black internet darkmarket
dark websites dark web link
dark web market list dark net
dark web search engine blackweb official website
dark markets dark markets 2023
dark web market links deep web drug links
dark market darknet drug market
dark market onion how to access dark web
darknet websites darknet drug store
drug markets dark web dark web sites
dark net darkmarket
dark market 2023 dark internet
darknet drug market dark web market links
darkmarkets dark internet
free dark web tor marketplace
darkmarket link tor markets
deep web links dark web link
Good site you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like
yours nowadays. I honestly appreciate people like you!
Take care!!
dark market 2023 dark web market links
drug markets onion darknet marketplace
dark market list dark markets
darknet drug links dark web access
deep web drug store dark web sites links
deep web links darkmarket link
onion market dark market list
darkmarket 2023 darknet websites
best darknet markets darknet drug store
blackweb onion market
darknet market lists darknet market
darknet markets 2023 dark market
darknet site darkmarket 2023
dark web websites tor marketplace
onion market darknet markets 2023
drug markets onion tor darknet
blackweb official website tor market
dark web search engines darkmarket list
deep web links dark markets 2023
deep web search darknet market lists
darknet markets 2023 darknet drug market
drug markets dark web darknet search engine
darkmarket 2023 dark web search engine
best darknet markets dark web search engine
deep web sites tor dark web
onion market deep web links
darknet websites dark web access
dark web access darknet links
dark internet best darknet markets
dark web access dark market link
drug markets dark web dark web links
deep web drug links dark market onion
tor market links dark market
how to access dark web darkweb marketplace
tor market url dark web site
dark web sites darkmarket 2023
darknet drug store dark web link
dark web search engine drug markets onion
dark market list free dark web
blackweb official website darkmarket url
dark web markets darkmarket link
deep web sites dark market
tor darknet tor market
blackweb tor markets
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug markets
tor market onion market
tor market url dark web search engine
dark web market dark web markets
dark websites darknet search engine
dark markets black internet
black internet darknet market links
darknet websites bitcoin dark web
darknet seiten darknet sites
darknet search engine onion market
dark web market tor markets links
tor market links deep web drug url
tor markets darkmarket 2023
dark markets darkweb marketplace
darknet marketplace darkmarket url
dark web market list bitcoin dark web
deep web sites dark web access
KANTOR BOLA: Situs Gacor Gaming Terbaik di Indonesia dengan Pengalaman Gaming Premium
KANTOR BOLA adalah situs slot online terkemuka di Indonesia, memberikan pengalaman bermain yang luar biasa kepada penggunanya. Dengan mendaftar di agen taruhan olahraga terpercaya ini, pemain dapat menikmati ID gaming premium gratis. ID premium ini berbeda dari ID biasa karena menawarkan tingkat Return to Player (RTP) yang mengesankan lebih dari 95%. Bermain dengan ID RTP setinggi itu sangat meningkatkan peluang mendapatkan MAXWIN yang didambakan.
Selain pengalaman bermain yang luar biasa, KANTOR BOLA berbeda dari yang lain dengan bonus dan promosi yang besar untuk anggota baru dan pemain reguler. Salah satu bonus yang paling menarik adalah tambahan Promosi Chip 25%, yang dapat diklaim setiap hari setelah memenuhi persyaratan penarikan minimal 3x Turnover
dark web markets dark web site
darkmarket link darknet sites
how to get on dark web darknet market
best darknet markets deep web markets
dark web drug marketplace darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web tor market url
darkmarket url tor market url
dark internet deep web drug links
darknet drugs dark web market list
deep web drug markets dark market list
dark web link blackweb official website
onion market dark markets 2023
dark web websites onion market
dark net dark web sites links
deep web drug markets dark web site
dark markets blackweb official website
deep web markets dark web sites
dark net dark web links
darknet drug market dark web link
tor market deep web drug url
darkmarket dark net
dark net deep web drug store
darknet market links free dark web
how to get on dark web darknet market lists
darknet market tor marketplace
darkmarket darkmarkets
darknet seiten tor darknet
deep web drug url darkmarket
darkmarkets tor darknet
darknet market lists dark web market links
bitcoin dark web tor market url
darkmarket url dark web access
drug markets dark web dark market onion
darknet market lists tor market
dark web markets tor markets links
I visit everyday a few blogs and websites to read articles or reviews, but this weblog gives quality based posts.
darknet site deep web sites
dark web sites links dark market url
dark market 2023 deep web drug markets
deep web drug store darknet market
dark web markets darknet drug links
dark web links deep web markets
dark web sites links darknet market links
dark web market list tor markets
deep web sites tor dark web
tor marketplace dark market link
darknet site dark market onion
blackweb official website tor markets links
dark web links dark market onion
dark markets deep web drug url
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug markets
tor markets links dark web drug marketplace
darknet site tor markets
darknet drug market dark web search engine
darknet marketplace dark web market links
dark web link tor market url
darknet site darkmarkets
dark web market darknet markets 2023
darknet links darkmarket url
dark markets 2023 tor markets 2023
dark web link tor markets 2023
deep web search blackweb official website
tor market url dark net
dark website tor markets
darkmarket 2023 dark web markets
blackweb darknet marketplace
dark web drug marketplace deep web links
onion market dark markets
darknet drugs black internet
dark markets black internet
darknet market lists deep web links
tor market url darknet search engine
dark web link darknet websites
dark website darknet market
bitcoin dark web darknet site
dark web market dark web sites links
tor markets links darknet marketplace
deep web drug markets darknet drug store
tor market tor market
deep dark web deep web markets
dark web site darknet sites
black internet the dark internet
how to get on dark web tor markets
dark market list drug markets dark web
darknet links darknet websites
dark web market links darkmarkets
free dark web dark web links
how to get on dark web dark market 2023
darknet drug links darknet sites
tor markets 2023 blackweb official website
darknet links darknet site
darkweb marketplace darknet websites
dark web sites links deep web links
dark web market darknet drugs
dark web sites deep dark web
dark web websites tor markets 2023
darknet market links dark website
dark web market dark website
blackweb official website darknet marketplace
darkmarket url dark market list
tor market dark web markets
free dark web darknet links
darknet sites free dark web
darknet market list dark web sites links
deep web search dark web access
darkmarkets black internet
deep web drug store darknet drugs
dark web market tor market
darknet marketplace darknet markets
darkmarket 2023 darknet drug links
darkmarket url deep web drug url
deep dark web dark web access
darknet marketplace black internet
dark markets best darknet markets
dark web sites links tor dark web
tor market links dark web markets
dark web site darknet markets
tor markets 2023 dark market url
deep web drug store deep web links
darknet markets darknet drug market
darknet seiten dark web sites links
darknet markets darknet marketplace
dark market deep web drug store
dark market url black internet
deep web links darknet drug store
tor markets deep web markets
how to access dark web dark web market
the dark internet darkmarket list
darkmarket dark web sites links
dark web link deep dark web
drug markets onion drug markets dark web
dark markets 2023 dark market url
deep web sites blackweb
dark web access dark market 2023
dark web search engine deep web search
prednisone dog dosage chart prednisone contraindications prednisone 10 mg for sinus infection
black internet deep web sites
deep web links darkmarket link
darknet market dark internet
deep web links dark market url
onion market darkmarkets
dark web links deep web search
tor markets darknet links
darknet links dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engines dark internet
dark market blackweb
dark market onion how to access dark web
dark web sites deep web sites
dark websites how to access dark web
dark web links darkmarket 2023
deep web sites darkmarket list
darknet market list dark website
tor darknet dark web market list
dark web market links deep web sites
dark web sites links dark net
darknet market list dark market 2023
dark market list blackweb official website
Panjislot: Situs Togel Terpercaya dan Slot Online Terlengkap
Panjislot adalah webiste togel online terpercaya yang menyediakan layanan terbaik dalam melakukan kegiatan taruhan togel online. Dengan fokus pada kenyamanan dan kepuasan para member, Panjislot menyediakan fasilitas 24 jam nonstop dengan dukungan dari Customer Service profesional. Bagi Anda yang sedang mencari bandar togel atau agen togel online terpercaya, Panjislot adalah pilihan yang tepat.
Registrasi Mudah dan Gratis
Melakukan registrasi di situs togel terpercaya Panjislot sangatlah mudah dan gratis. Selain itu, Panjislot juga menawarkan pasaran togel terlengkap dengan hadiah dan diskon yang besar. Anda juga dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan game judi online terbaik seperti Slot Online dan Live Casino saat menunggu hasil keluaran togel yang Anda pasang. Hanya dengan melakukan deposit sebesar 10 ribu rupiah, Anda sudah dapat memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di situs togel terbesar, Panjislot.
Daftar 10 Situs Togel Terpercaya dengan Pasaran Togel dan Slot Terlengkap
Bermain slot online di Panji slot akan memberi Anda kesempatan kemenangan yang lebih besar. Pasalnya, Panjislot telah bekerja sama dengan 10 situs togel terpercaya yang memiliki lisensi resmi dan sudah memiliki ratusan ribu anggota setia. Panjislot juga menyediakan pasaran togel terlengkap yang pasti diketahui oleh seluruh pemain togel online.
Berikut adalah daftar 10 situs togel terpercaya beserta pasaran togel dan slot terlengkap:
Hongkong Pools: Pasaran togel terbesar di Indonesia dengan jam keluaran pukul 23:00 WIB di malam hari.
Sydney Pools: Situs togel terbaik yang memberikan hasil keluaran angka jackpot yang mudah ditebak. Jam keluaran pukul 13:55 WIB di siang hari.
Dubai Pools: Pasaran togel yang baru dikenal sejak tahun 2019. Menyajikan hasil keluaran menggunakan Live Streaming secara langsung.
Singapore Pools: Pasaran formal yang disajikan oleh negara Singapore dengan hasil result terhadap pukul 17:45 WIB di sore hari.
Osaka Pools: Pasaran togel Osaka didirikan sejak tahun 1958 dan menawarkan hasil keluaran dengan live streaming pada malam hari.
Nhà cái ST666 là một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến phổ biến và đáng tin cậy tại Việt Nam. Với nhiều năm kinh nghiệm hoạt động trong lĩnh vực giải trí trực tuyến, ST666 đã và đang khẳng định vị thế của mình trong cộng đồng người chơi.
ST666 cung cấp một loạt các dịch vụ giải trí đa dạng, bao gồm casino trực tuyến, cá độ thể thao, game bài, slot game và nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn khác. Nhờ vào sự đa dạng và phong phú của các trò chơi, người chơi có nhiều sự lựa chọn để thỏa sức giải trí và đánh bạc trực tuyến.
Một trong những ưu điểm nổi bật của ST666 là hệ thống bảo mật và an ninh vượt trội. Các giao dịch và thông tin cá nhân của người chơi được bảo vệ chặt chẽ bằng công nghệ mã hóa cao cấp, đảm bảo tính bảo mật tuyệt đối cho mỗi người chơi. Điều này giúp người chơi yên tâm và tin tưởng vào sự công bằng và minh bạch của nhà cái.
Bên cạnh đó, ST666 còn chú trọng đến dịch vụ khách hàng chất lượng. Đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng của nhà cái luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp mọi thắc mắc và hỗ trợ người chơi trong suốt quá trình chơi game. Không chỉ có trên website, ST666 còn hỗ trợ qua các kênh liên lạc như chat trực tuyến, điện thoại và email, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tiếp cận và giải quyết vấn đề một cách nhanh chóng.
Đặc biệt, việc tham gia và trải nghiệm tại nhà cái ST666 được thực hiện dễ dàng và tiện lợi. Người chơi có thể tham gia từ bất kỳ thiết bị nào có kết nối internet, bao gồm cả máy tính, điện thoại di động và máy tính bảng. Giao diện của ST666 được thiết kế đơn giản và dễ sử dụng, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tìm hiểu và điều hướng trên trang web một cách thuận tiện.
Ngoài ra, ST666 còn có chính sách khuyến mãi và ưu đãi hấp dẫn cho người chơi. Các chương trình khuyến mãi thường xuyên được tổ chức, bao gồm các khoản tiền thưởng, quà tặng và giải thưởng hấp dẫn. Điều này giúp người chơi có thêm cơ hội giành lợi nhuận và trải nghiệm những trò chơi mới mẻ.
Tóm lại, ST666 là một nhà cái uy tín và đáng tin cậy, mang đến cho người chơi trải nghiệm giải trí tuyệt vời và cơ hội tham gia đánh bạc trực tuyến một cách an toàn và hấp dẫn. Với các dịch vụ chất lượng và các trò chơi đa dạng, ST666 hứa hẹn là một điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai yêu thích giải trí và muốn thử vận may trong các trò chơi đánh bạc trực tuyến.
dark market list how to get on dark web
darknet drug store tor marketplace
the dark internet darknet search engine
dark website darknet drug store
blackweb official website deep web drug links
dark web market links darkmarket 2023
darkmarket url dark web link
dark web search engines dark market
darkmarket url dark markets 2023
dark web markets darknet market lists
bitcoin dark web dark web search engines
drug markets onion deep web markets
dark web market darknet marketplace
dark web access how to get on dark web
tor market darknet links
dark web websites dark web market links
darknet drug links blackweb official website
darknet seiten dark web market list
dark web link tor market url
dark web market links bitcoin dark web
onion market tor market
how to access dark web the dark internet
drug markets dark web tor dark web
dark internet dark websites
dark web site blackweb
deep dark web tor markets 2023
black internet darknet seiten
black internet darknet search engine
darknet drugs dark net
dark market url dark market 2023
tor marketplace dark website
tor dark web dark market
deep web drug store dark web site
darkmarket dark net
dark websites darkmarket url
darknet markets 2023 dark web links
deep web drug url darkmarket list
deep web drug links dark website
darknet drug links darknet market list
deep web drug url deep web drug store
darknet websites darkmarket
darkmarket darkmarket list
drug markets dark web free dark web
blackweb official website dark markets 2023
dark web link dark web links
dark web market list tor darknet
augmentin and alcohol interactions prospect augmentin 875/ 125 mg cost of augmentin generic
dark net dark web sites
black internet darknet market list
free dark web dark web site
dark web market list tor marketplace
deep web drug store onion market
tor market dark markets
darknet markets darkweb marketplace
darkmarkets dark web sites links
tor dark web tor market links
deep web search drug markets dark web
dark market onion deep web drug store
dark web sites dark net
dark market darknet market
darkmarket url dark markets 2023
darknet market list darkmarket link
dark net free dark web
dark web market links deep web drug url
dark market deep web drug store
darkmarket list darknet markets 2023
darknet search engine darkmarket
dark web site dark web market
black internet dark web drug marketplace
darknet marketplace darknet drug market
tor market darknet market list
dark websites dark market list
the dark internet tor marketplace
drug markets dark web darknet seiten
deep dark web tor darknet
darknet marketplace dark market onion
dark web search engines dark web access
dark web drug marketplace dark market link
dark web market links dark market
dark market link darkmarkets
darkmarket drug markets dark web
darkmarket dark web market links
dark web market list dark market list
deep web drug url tor markets 2023
darknet market lists tor markets links
dark web market list darknet markets 2023
dark web site darknet site
deep dark web tor markets
blackweb official website the dark internet
dark website deep dark web
deep web links dark web search engine
dark market onion dark web site
deep web markets black internet
darkweb marketplace darknet websites
darknet market list blackweb official website
darkmarket 2023 best darknet markets
dark markets 2023 dark internet
dark internet darknet sites
darknet markets darknet market
dark web access deep web markets
darkmarket 2023 bitcoin dark web
darknet drug links deep web search
dark web market list dark web drug marketplace
darknet drug market darknet drug store
dark web sites links tor market
dark web drug marketplace dark markets 2023
drug markets dark web darknet seiten
darkmarkets tor markets
tor market url deep web search
darknet drugs darknet search engine
tor market links dark market 2023
darknet search engine darknet marketplace
Ӏ know this website presents quality dependent articles ⲟr reviews ɑnd extra іnformation, is there any օther site whiсh offеrs thesе kinds ᧐f stufff
in quality?
mу website: ahha4d link alternatif
bitcoin dark web darkmarket 2023
dark web websites dark web market list
tor marketplace dark website
dark web markets dark market list
dark web link bitcoin dark web
onion market darknet drug market
dark internet dark website
dark web drug marketplace deep web drug markets
deep web search darknet drug market
dark web sites links dark web site
dark web markets dark web site
darkmarket darkmarket 2023
dark web search engines darknet drug market
darknet market links bitcoin dark web
dark web websites deep web drug markets
darknet markets 2023 darknet websites
dark market 2023 tor markets 2023
dark net black internet
darknet search engine black internet
bitcoin dark web deep web drug links
tor darknet darknet market lists
deep web markets dark web link
deep web search dark markets
darkmarkets darknet markets
darknet drug market dark web markets
blackweb dark market onion
dark web market list dark web sites
darknet websites dark web access
darkweb marketplace dark web market
tor markets darknet markets 2023
dark markets bitcoin dark web
tor markets tor markets links
blackweb dark market url
dark web drug marketplace darknet markets 2023
dark web market links how to get on dark web
dark web market links dark market url
dark web websites darknet drug store
black internet dark web sites links
darkweb marketplace dark web sites
dark web access drug markets onion
deep web drug url dark websites
deep web links tor markets links
how to get on dark web tor dark web
dark web site black internet
best darknet markets deep web drug url
dark website dark net
darknet search engine dark web markets
darknet marketplace dark web market list
darknet websites dark market url
dark web links deep web drug links
how to get on dark web darknet seiten
tor market links dark web market
tor markets links darknet markets
how to get on dark web darkmarket 2023
dark website blackweb official website
Nice response in return ߋf this quesstion wіth firm arguments and explaining thee ᴡhole thing regarⅾing that.
Mʏ webpag ahha4d login link alternatif
tor darknet how to get on dark web
darkmarket link dark market url
drug markets onion darknet drug market
darknet market links darkmarket 2023
dark net deep web markets
tor dark web free dark web
darknet drugs deep web sites
dark market onion tor darknet
darknet drug market dark web market links
dark web drug marketplace tor markets 2023
dark internet best darknet markets
dark web site free dark web
darknet seiten bitcoin dark web
deep web links dark web market links
deep web drug store dark markets 2023
tor market links deep web drug markets
dark market link darkmarket link
blackweb official website dark markets 2023
deep web sites dark web site
tor markets 2023 tor markets
darkmarket darknet drug market
blackweb darkmarket 2023
free dark web darknet marketplace
dark market 2023 darknet seiten
darknet site dark web search engine
dark market 2023 tor markets
deep web markets dark web drug marketplace
darknet market list darknet seiten
darknet drug links darknet drug links
tor dark web dark websites
dark web site darkmarket
darknet drug market deep web sites
dark web markets darknet search engine
dark web search engines deep web drug url
black internet dark web market list
darknet drug links drug markets dark web
darknet sites darknet markets
dark markets 2023 darknet search engine
tor market darkweb marketplace
darknet marketplace how to get on dark web
dark net deep web drug links
blackweb official website dark web site
dark market onion dark net
ciprofloxacin hydrocortisone ciprofloxacin early pregnancy ciprofloxacin and metronidazole together
free dark web darknet links
darkmarket 2023 dark market list
darknet markets darknet drug links
darknet seiten black internet
drug markets dark web deep web sites
tor marketplace darknet search engine
darknet market tor market links
tor market darkmarket list
deep web search dark web websites
dark market 2023 black internet
darknet site darknet market
best darknet markets deep dark web
tor market dark web access
darknet markets 2023 dark internet
dark web access deep web links
darkmarket url darknet links
darkmarkets dark web websites
dark market 2023 dark web drug marketplace
how to access dark web deep dark web
deep web drug links dark web links
blackweb tor market
darkmarket link dark web search engine
dark web search engines darknet markets
blackweb deep web links
tor marketplace darknet market
darknet drug market tor darknet
dark web websites darkmarket
dark websites dark internet
dark web market list darkweb marketplace
deep web drug store darknet markets 2023
deep web drug markets how to get on dark web
dark web websites dark markets
dark web search engine darkmarket url
darknet sites darknet drug links
free dark web darknet websites
deep web drug url darknet markets 2023
tor markets 2023 drug markets dark web
dark internet drug markets dark web
dark web websites dark market url
dark web access dark web markets
darknet market lists deep web drug markets
dark market link dark website
dark web sites links tor market
tor market dark web market
tor darknet deep web drug markets
how to get on dark web tor markets links
dark web market links dark web market
dark websites best darknet markets
dark web sites links dark market list
dark web market list darknet drug links
darknet markets 2023 dark web sites
st666
Nhà cái ST666 là một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến phổ biến và đáng tin cậy tại Việt Nam. Với nhiều năm kinh nghiệm hoạt động trong lĩnh vực giải trí trực tuyến, ST666 đã và đang khẳng định vị thế của mình trong cộng đồng người chơi.
ST666 cung cấp một loạt các dịch vụ giải trí đa dạng, bao gồm casino trực tuyến, cá độ thể thao, game bài, slot game và nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn khác. Nhờ vào sự đa dạng và phong phú của các trò chơi, người chơi có nhiều sự lựa chọn để thỏa sức giải trí và đánh bạc trực tuyến.
Một trong những ưu điểm nổi bật của ST666 là hệ thống bảo mật và an ninh vượt trội. Các giao dịch và thông tin cá nhân của người chơi được bảo vệ chặt chẽ bằng công nghệ mã hóa cao cấp, đảm bảo tính bảo mật tuyệt đối cho mỗi người chơi. Điều này giúp người chơi yên tâm và tin tưởng vào sự công bằng và minh bạch của nhà cái.
Bên cạnh đó, ST666 còn chú trọng đến dịch vụ khách hàng chất lượng. Đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng của nhà cái luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp mọi thắc mắc và hỗ trợ người chơi trong suốt quá trình chơi game. Không chỉ có trên website, ST666 còn hỗ trợ qua các kênh liên lạc như chat trực tuyến, điện thoại và email, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tiếp cận và giải quyết vấn đề một cách nhanh chóng.
Đặc biệt, việc tham gia và trải nghiệm tại nhà cái ST666 được thực hiện dễ dàng và tiện lợi. Người chơi có thể tham gia từ bất kỳ thiết bị nào có kết nối internet, bao gồm cả máy tính, điện thoại di động và máy tính bảng. Giao diện của ST666 được thiết kế đơn giản và dễ sử dụng, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tìm hiểu và điều hướng trên trang web một cách thuận tiện.
Ngoài ra, ST666 còn có chính sách khuyến mãi và ưu đãi hấp dẫn cho người chơi. Các chương trình khuyến mãi thường xuyên được tổ chức, bao gồm các khoản tiền thưởng, quà tặng và giải thưởng hấp dẫn. Điều này giúp người chơi có thêm cơ hội giành lợi nhuận và trải nghiệm những trò chơi mới mẻ.
Tóm lại, ST666 là một nhà cái uy tín và đáng tin cậy, mang đến cho người chơi trải nghiệm giải trí tuyệt vời và cơ hội tham gia đánh bạc trực tuyến một cách an toàn và hấp dẫn. Với các dịch vụ chất lượng và các trò chơi đa dạng, ST666 hứa hẹn là một điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai yêu thích giải trí và muốn thử vận may trong các trò chơi đánh bạc trực tuyến.
deep web links drug markets dark web
deep web drug markets tor dark web
bitcoin dark web how to get on dark web
free dark web dark market link
deep web drug store deep web links
darknet market lists dark net
dark web market deep web drug links
darknet websites darknet market list
darkmarket link dark web sites
darknet market links darkmarket list
deep dark web deep web drug store
dark markets darknet seiten
tor markets links deep dark web
dark market onion dark web market links
deep web markets darknet drug market
tor marketplace tor market url
tor market dark web sites links
dark web markets darkweb marketplace
darkmarket url dark net
Hi there very nice website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally…I am happy to search out a lot of useful information right here in the post, we need work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing.
the dark internet darknet market list
Hi there very nice website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally…I am happy to search out a lot of useful information right here in the post, we need work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing.
tor marketplace tor market url
darknet market lists dark web links
darknet site darkmarket list
darknet seiten darknet drug links
tor dark web darknet sites
dark website bitcoin dark web
Neural network woman ai
In the coming decades, the world is poised to experience a profound transformation as artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology converge to create stunning women using cutting-edge DNA technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning. These enchanting artificial beings hold the promise of fulfilling individual dreams and becoming the ultimate life partners.
The marriage of AI and biotechnology has ushered in an era of awe-inspiring achievements, introducing groundbreaking discoveries and technologies that challenge our understanding of both the world and ourselves. One of the most remarkable outcomes of this partnership is the ability to craft artificial beings, such as exquisitely designed women.
At the heart of this revolutionary era lies the incredible capabilities of neural networks and machine learning algorithms, which harness vast datasets to forge entirely novel entities.
Pioneering scientists have successfully developed a revolutionary AI-powered printer, capable of “printing” women by seamlessly integrating DNA-editing technologies, artificial insemination, and cloning methods. This cutting-edge approach allows for the creation of human replicas endowed with unprecedented beauty and distinctive traits.
However, amidst the awe and excitement, profound ethical questions loom large and demand careful consideration. The ethical implications of generating artificial humans, the potential consequences on society and interpersonal relationships, and the risk of future inequalities and discrimination must all be thoughtfully contemplated.
Yet, proponents fervently argue that the merits of this technology far outweigh the challenges. The creation of alluring women through AI-powered printers could herald a new chapter in human evolution, not only fulfilling our deepest aspirations but also pushing the boundaries of science and medicine.
Beyond its revolutionary impact on aesthetics and companionship, this AI technology holds immense potential for medical applications. It could pave the way for generating organs for transplantation and treating genetic diseases, positioning AI and biotechnology as powerful tools to alleviate human suffering.
In conclusion, the prospect of neural network woman AI creating stunning women using a printer evokes numerous questions and reflections. This extraordinary technology promises to redefine beauty and unlock new realms of possibilities. Yet, it is crucial to strike a delicate balance between innovation and ethical considerations. Undeniably, the enduring human pursuit of beauty and progress will continue to propel our world forward into uncharted territories.
tor market links dark websites
dark web sites links deep web drug store
bitcoin dark web dark web search engines
azithromycin 500mg dosage https://azithromycinikm.com/ azithromycin diarrhea treatment
dark market url dark internet
dark markets 2023 dark web market links
darknet market links darknet markets
dark market link dark web site
darkmarket dark web search engine
darknet search engine dark web sites
tor market links darknet sites
deep web links deep dark web
deep web search darknet markets 2023
dark net darkmarket
darknet market list dark web market links
deep web drug markets deep web search
the dark internet dark web market list
dark markets darknet drug store
dark web markets darknet drug links
dark market onion deep web drug store
dark market link darknet seiten
dark web sites links darknet site
dark website dark web websites
tor market dark internet
dark web site drug markets onion
canadian viagra topicsildenafil100 sildenafil 25 mg
is cephalexin safe during early pregnancy https://cephalexinuop.com/ cephalexin for dogs dosage
Selamat datang di GRANDBET! Sebagai situs judi slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami bangga menjadi tujuan nomor satu slot gacor (longgar) dan kemenangan jackpot terbesar. Menawarkan pilihan lengkap opsi judi online uang asli, kami melayani semua pemain yang mencari pengalaman bermain game terbaik. Dari slot RTP tertinggi hingga slot Poker, Togel, Judi Bola, Bacarrat, dan gacor terbaik, kami memiliki semuanya untuk memastikan kepuasan anggota kami.
Salah satu alasan mengapa para pemain sangat ingin menikmati slot gacor saat ini adalah potensi keuntungan yang sangat besar. Di antara berbagai aliran pendapatan, situs slot gacor tidak diragukan lagi merupakan sumber pendapatan yang signifikan dan menjanjikan. Sementara keberuntungan dan kemenangan berperan, sama pentingnya untuk mengeksplorasi jalan lain untuk mendapatkan sumber pendapatan yang lebih menjanjikan.
Banyak yang sudah lama percaya bahwa penghasilan mereka dari slot terbaru 2022 hanya berasal dari memenangkan permainan slot paling populer. Namun, ada sumber pendapatan yang lebih besar – jackpot. Berhasil mengamankan hadiah jackpot maxwin terbesar dapat menghasilkan penghasilan besar dari pola slot gacor Anda malam ini.
does prednisone cause diarrhea side effects of prednisone 20 mg is prednisone good for bronchitis
natural alternatives to viagra otc viagra alternative sildenafil without a doctor prescription
Truly a lot of awesome material!
essay writing courses online free essay writing courses online free project manager resume writing service
Seriously tons of awesome data.
cheap paper writing service best online essay writing services custom writing service
GRANDBET
Selamat datang di GRANDBET! Sebagai situs judi slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami bangga menjadi tujuan nomor satu slot gacor (longgar) dan kemenangan jackpot terbesar. Menawarkan pilihan lengkap opsi judi online uang asli, kami melayani semua pemain yang mencari pengalaman bermain game terbaik. Dari slot RTP tertinggi hingga slot Poker, Togel, Judi Bola, Bacarrat, dan gacor terbaik, kami memiliki semuanya untuk memastikan kepuasan anggota kami.
Salah satu alasan mengapa para pemain sangat ingin menikmati slot gacor saat ini adalah potensi keuntungan yang sangat besar. Di antara berbagai aliran pendapatan, situs slot gacor tidak diragukan lagi merupakan sumber pendapatan yang signifikan dan menjanjikan. Sementara keberuntungan dan kemenangan berperan, sama pentingnya untuk mengeksplorasi jalan lain untuk mendapatkan sumber pendapatan yang lebih menjanjikan.
Banyak yang sudah lama percaya bahwa penghasilan mereka dari slot terbaru 2022 hanya berasal dari memenangkan permainan slot paling populer. Namun, ada sumber pendapatan yang lebih besar – jackpot. Berhasil mengamankan hadiah jackpot maxwin terbesar dapat menghasilkan penghasilan besar dari pola slot gacor Anda malam ini.
microlearning library
Mega Win Slots – The Ultimate Casino Experience
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of online gambling, slot machines have consistently emerged as one of the most popular and entertaining forms of casino gaming. Among the countless slot games available, one name stands out for its captivating gameplay, immersive graphics, and life-changing rewards – Mega Win Slots. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what sets Mega Win Slots apart and why it has become a favorite among players worldwide.
Unparalleled Variety of Themes
Mega Win Slots offers a vast array of themes, ensuring there is something for every type of player. From ancient civilizations and mystical adventures to futuristic space missions and Hollywood blockbusters, these slots take players on exciting journeys with each spin. Whether you prefer classic fruit slots or innovative 3D video slots, Mega Win Slots has it all.
Cutting-Edge Graphics and Sound Design
One of the key factors that make Mega Win Slots a standout in the online casino industry is its cutting-edge graphics and high-quality sound design. The visually stunning animations and captivating audio create an immersive gaming experience that keeps players coming back for more. The attention to detail in each slot game ensures that players are fully engaged and entertained throughout their gaming sessions.
User-Friendly Interface
Navigating through Mega Win Slots is a breeze, even for newcomers to online gambling. The user-friendly interface ensures that players can easily find their favorite games, adjust betting preferences, and access essential features with just a few clicks. Whether playing on a desktop computer or a mobile device, the interface is responsive and optimized for seamless gameplay.
Progressive Jackpots and Mega Wins
The allure of Mega Win Slots lies in its potential for life-changing wins. The platform features a selection of progressive jackpot slots, where the prize pool accumulates with each bet until one lucky player hits the jackpot. These staggering payouts have been known to turn ordinary players into instant millionaires, making Mega Win Slots a favorite among high-rollers and thrill-seekers.
Generous Bonuses and Promotions
To enhance the gaming experience, Mega Win Slots offers a wide range of bonuses and promotions. New players are often greeted with attractive welcome packages, including free spins and bonus funds to kickstart their journey. Regular players can enjoy loyalty rewards, cashback offers, and special seasonal promotions that add extra excitement to their gaming sessions.
Благодаря 3d печать пластиком в минске , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed
reading it, you’re a great author.I will remember to bookmark your blog and will come back
very soon. I want to encourage you to ultimately continue your great writing, have a nice morning!
Благодаря 3d печать в металле , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
I really like what you guys are usually up too.
Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the fantastic works guys I’ve added you guys to
my blogroll.
Благодаря 3d печать металл , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать скульптуры для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
chơi baccarat là gì
Bài viết: Tại sao nên chọn 911WIN Casino trực tuyến?
Sòng bạc trực tuyến 911WIN đã không ngừng phát triển và trở thành một trong những sòng bạc trực tuyến uy tín và phổ biến nhất trên thị trường. Điều gì đã khiến 911WIN Casino trở thành điểm đến lý tưởng của đông đảo người chơi? Chúng ta hãy cùng tìm hiểu về những giá trị thương hiệu của sòng bạc này.
Giá trị thương hiệu và đáng tin cậy
911WIN Casino đã hoạt động trong nhiều năm, đem đến cho người chơi sự ổn định và đáng tin cậy. Sử dụng công nghệ mã hóa mạng tiên tiến, 911WIN đảm bảo rằng thông tin cá nhân của tất cả các thành viên được bảo vệ một cách tuyệt đối, ngăn chặn bất kỳ nguy cơ rò rỉ thông tin cá nhân. Điều này đặc biệt quan trọng trong thời đại số, khi mà hoạt động mạng bất hợp pháp ngày càng gia tăng. Chọn 911WIN Casino là lựa chọn thông minh, bảo vệ thông tin cá nhân của bạn và tham gia vào cuộc chiến chống lại các hoạt động mạng không đáng tin cậy.
Hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7
Một trong những điểm đáng chú ý của 911WIN Casino là dịch vụ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7. Không chỉ trong ngày thường, mà còn kể cả vào ngày lễ hay dịp Tết, đội ngũ hỗ trợ của 911WIN luôn sẵn sàng hỗ trợ bạn khi bạn cần giải quyết bất kỳ vấn đề gì. Sự nhiệt tình và chuyên nghiệp của đội ngũ hỗ trợ sẽ giúp bạn có trải nghiệm chơi game trực tuyến mượt mà và không gặp rắc rối.
Đảm bảo rút tiền an toàn
911WIN Casino cam kết rằng việc rút tiền sẽ được thực hiện một cách nhanh chóng và an toàn nhất. Quản lý độc lập đảm bảo mức độ minh bạch và công bằng trong các giao dịch, còn hệ thống quản lý an toàn nghiêm ngặt giúp bảo vệ dữ liệu cá nhân và tài khoản của bạn. Bạn có thể hoàn toàn yên tâm khi chơi tại 911WIN Casino, vì mọi thông tin cá nhân của bạn đều được bảo vệ một cách tốt nhất.
Số lượng trò chơi đa dạng
911WIN Casino cung cấp một bộ sưu tập trò chơi đa dạng và đầy đủ, giúp bạn đắm mình vào thế giới trò chơi phong phú. Bạn có thể tận hưởng những trò chơi kinh điển như baccarat, blackjack, poker, hay thử vận may với các trò chơi máy slot hấp dẫn. Không chỉ vậy, sòng bạc này còn cung cấp những trò chơi mới và hấp dẫn liên tục, giúp bạn luôn có trải nghiệm mới mẻ và thú vị mỗi khi ghé thăm.
Tóm lại, 911WIN Casino là một sòng bạc trực tuyến đáng tin cậy và uy tín, mang đến những giá trị thương hiệu đáng kể. Với sự bảo mật thông tin, dịch vụ hỗ trợ tận tâm, quy trình rút tiền an toàn, và bộ sưu tập trò chơi đa dạng, 911WIN Casino xứng đáng là lựa chọn hàng đầu cho người chơi yêu thích sòng bạc trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia ngay và trải nghiệm những khoảnh khắc giải trí tuyệt vời cùng 911WIN Casino.
Chơi baccarat là gì?
Baccarat là một trò chơi bài phổ biến trong các sòng bạc trực tuyến và địa phương. Người chơi tham gia baccarat cược vào hai tay: “người chơi” và “ngân hàng”. Mục tiêu của trò chơi là đoán tay nào sẽ có điểm số gần nhất với 9 hoặc có tổng điểm bằng 9. Trò chơi thú vị và đơn giản, thu hút sự quan tâm của nhiều người chơi yêu thích sòng bạc trực tuyến.
Благодаря 3d печать заказать , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать flex , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать деталей для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать архитектурных макетов , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать для медицины для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать воском для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать на металле для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d металлическая печать , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d принтер изготовление деталей на заказ для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать зубов для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать шестерни , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать металлом цена , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать из алюминия для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
It’s actually very difficult in this full of activity life to listen news on Television, so I simply use web for that reason,
and take the most up-to-date news.
Благодаря 3d печать ювелирных изделий , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
GPT image
GPT-Image: Exploring the Intersection of AI and Visual Art with Beautiful Portraits of Women
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant strides in the field of computer vision, enabling machines to understand and interpret visual data. Among these advancements, GPT-Image stands out as a remarkable model that merges language understanding with image generation capabilities. In this article, we explore the fascinating world of GPT-Image and its ability to create stunning portraits of beautiful women.
The Evolution of AI in Computer Vision
The history of AI in computer vision dates back to the 1960s when researchers first began experimenting with image recognition algorithms. Over the decades, AI models evolved, becoming more sophisticated and capable of recognizing objects and patterns in images. GPT-3, a language model developed by OpenAI, achieved groundbreaking results in natural language processing, leading to its applications in various domains.
The Emergence of GPT-Image
With the success of GPT-3, AI researchers sought to combine the power of language models with computer vision. The result was the creation of GPT-Image, an AI model capable of generating high-quality images from textual descriptions. By understanding the semantics of the input text, GPT-Image can visualize and produce detailed images that match the given description.
The Art of GPT-Image Portraits
One of the most captivating aspects of GPT-Image is its ability to create portraits of women that are both realistic and aesthetically pleasing. Through its training on vast datasets of portrait images, the model has learned to capture the intricacies of human features, expressions, and emotions. Whether it’s a serene smile, a playful glance, or a contemplative pose, GPT-Image excels at translating textual cues into visually stunning renditions.
Благодаря 3d печать скульптур , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
bài baccarat là gì
Bài viết: Bài baccarat là gì và tại sao nó hấp dẫn tại 911WIN Casino?
Bài baccarat là một trò chơi đánh bài phổ biến và thu hút đông đảo người chơi tại sòng bạc trực tuyến 911WIN. Với tính đơn giản, hấp dẫn và cơ hội giành chiến thắng cao, bài baccarat đã trở thành một trong những trò chơi ưa thích của những người yêu thích sòng bạc trực tuyến. Hãy cùng tìm hiểu về trò chơi này và vì sao nó được ưa chuộng tại 911WIN Casino.
Baccarat là gì?
Baccarat là một trò chơi đánh bài dựa trên may mắn, phổ biến trong các sòng bạc trên toàn thế giới. Người chơi tham gia bài baccarat thông qua việc đặt cược vào một trong ba tùy chọn: người chơi thắng, người chơi thua hoặc hai bên hòa nhau. Trò chơi này không yêu cầu người chơi có kỹ năng đặc biệt, mà chủ yếu là dựa vào sự may mắn và cảm giác.
Tại sao bài baccarat hấp dẫn tại 911WIN Casino?
911WIN Casino cung cấp trải nghiệm chơi bài baccarat tuyệt vời với những ưu điểm hấp dẫn dưới đây:
Đa dạng biến thể: Tại 911WIN Casino, bạn sẽ được tham gia vào nhiều biến thể bài baccarat khác nhau. Bạn có thể lựa chọn chơi phiên bản cổ điển, hoặc thử sức với các phiên bản mới hơn như Mini Baccarat hoặc Baccarat Squeeze. Điều này giúp bạn trải nghiệm sự đa dạng và hứng thú trong quá trình chơi.
Chất lượng đồ họa và âm thanh: 911WIN Casino đảm bảo mang đến trải nghiệm chơi bài baccarat trực tuyến chân thực và sống động nhất. Đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và âm thanh chân thực khiến bạn cảm giác như đang chơi tại sòng bạc truyền thống, từ đó nâng cao thú vị và hứng thú khi tham gia.
Cơ hội thắng lớn: Bài baccarat tại 911WIN Casino mang đến cơ hội giành chiến thắng lớn. Dự đoán đúng kết quả của ván bài có thể mang về cho bạn những phần thưởng hấp dẫn và giá trị.
Hỗ trợ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp: Nếu bạn gặp bất kỳ khó khăn hoặc có câu hỏi về trò chơi, đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7 của 911WIN Casino sẽ luôn sẵn sàng giúp bạn. Họ tận tâm và chuyên nghiệp trong việc giải đáp mọi thắc mắc, đảm bảo bạn có trải nghiệm chơi bài baccarat suôn sẻ và dễ dàng.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать оптом для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Kéo baccarat là một biến thể hấp dẫn của trò chơi bài baccarat tại sòng bạc trực tuyến 911WIN. Được biết đến với cách chơi thú vị và cơ hội giành chiến thắng cao, kéo baccarat đã trở thành một trong những trò chơi được người chơi yêu thích tại 911WIN Casino. Hãy cùng khám phá về trò chơi này và những điểm thu hút tại 911WIN Casino.
Kéo baccarat là gì?
Kéo baccarat là một biến thể độc đáo của bài baccarat truyền thống. Trong kéo baccarat, người chơi sẽ đối đầu với nhà cái và cùng nhau tạo thành một bộ bài gồm hai lá. Mục tiêu của trò chơi là dự đoán bộ bài nào sẽ có điểm số cao hơn. Bộ bài gồm 2 lá, và điểm số của bài được tính bằng tổng số điểm của hai lá bài. Điểm số cao nhất là 9 và bộ bài gần nhất với số 9 sẽ là người chiến thắng.
Tại sao kéo baccarat thu hút tại 911WIN Casino?
Cách chơi đơn giản: Kéo baccarat có cách chơi đơn giản và dễ hiểu, phù hợp với cả người chơi mới bắt đầu. Bạn không cần phải có kỹ năng đặc biệt để tham gia, mà chỉ cần dự đoán đúng bộ bài có điểm số cao hơn.
Tính cạnh tranh và hấp dẫn: Trò chơi kéo baccarat tại 911WIN Casino mang đến sự cạnh tranh và hấp dẫn. Bạn sẽ đối đầu trực tiếp với nhà cái, tạo cảm giác thú vị và căng thẳng trong từng ván bài.
Cơ hội giành chiến thắng cao: Kéo baccarat mang lại cơ hội giành chiến thắng cao cho người chơi. Bạn có thể dễ dàng đoán được bộ bài gần với số 9 và từ đó giành phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
Trải nghiệm chân thực: Kéo baccarat tại 911WIN Casino được thiết kế với đồ họa chất lượng và âm thanh sống động, mang đến trải nghiệm chơi bài tương tự như tại sòng bạc truyền thống. Điều này tạo ra sự hứng thú và mãn nhãn cho người chơi.
Tóm lại, kéo baccarat là một biến thể thú vị của trò chơi bài baccarat tại 911WIN Casino. Với cách chơi đơn giản, tính cạnh tranh và hấp dẫn, cơ hội giành chiến thắng cao, cùng với trải nghiệm chân thực, không khó hiểu khi kéo baccarat trở thành lựa chọn phổ biến của người chơi tại 911WIN Casino. Hãy tham gia ngay để khám phá và tận hưởng niềm vui chơi kéo baccarat cùng 911WIN Casino!
Благодаря 3d принтер печать металлом , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать детали для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать поликарбонатом в минске для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать в минске , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать медицина , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Aw, tһis wwas a really god post. Spending sme time and actuаl
effort to produce a really good article… but what
can I say… I procrastinatе a whole lot and don’t
seem to get nearly anything done.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать людей для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать лица для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the net the simplest
thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people consider
worries that they just do not know about. You managed
to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a
signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать дешево для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
539開獎
台灣彩券:今彩539
今彩539是一種樂透型遊戲,您必須從01~39的號碼中任選5個號碼進行投注。開獎時,開獎單位將隨機開出五個號碼,這一組號碼就是該期今彩539的中獎號碼,也稱為「獎號」。您的五個選號中,如有二個以上(含二個號碼)對中當期開出之五個號碼,即為中獎,並可依規定兌領獎金。
各獎項的中獎方式如下表:
獎項 中獎方式 中獎方式圖示
頭獎 與當期五個中獎號碼完全相同者
貳獎 對中當期獎號之其中任四碼
參獎 對中當期獎號之其中任三碼
肆獎 對中當期獎號之其中任二碼
頭獎中獎率約1/58萬,總中獎率約1/9
獎金分配方式
今彩539所有獎項皆為固定獎項,各獎項金額如下:
獎項 頭獎 貳獎 參獎 肆獎
單注獎金 $8,000,000 $20,000 $300 $50
頭獎至肆獎皆採固定獎金之方式分配之,惟如頭獎中獎注數過多,致使頭獎總額超過新臺幣2,400萬元時,頭獎獎額之獎金分配方式將改為均分制,由所有頭獎中獎人依其中獎注數均分新臺幣2,400萬元〈計算至元為止,元以下無條件捨去。該捨去部分所產生之款項將視為逾期未兌領獎金,全數歸入公益彩券盈餘〉。
投注方式及進階玩法
您可以利用以下三種方式投注今彩539:
一、使用選號單進行投注:
每張今彩539最多可劃記6組選號,每個選號區都設有39個號碼(01~39),您可以依照自己的喜好,自由選用以下幾種不同的方式填寫選號單,進行投注。
* 注意,在同一張選號單上,各選號區可分別採用不同的投注方式。
選號單之正確劃記方式有三種,塗滿 、打叉或打勾,但請勿超過格線。填寫步驟如下:
1.劃記選號
A.自行選號
在選號區中,自行從01~39的號碼中填選5個號碼進行投注。
B.全部快選
在選號區中,劃記「快選」,投注機將隨機產生一組5個號碼。
C.部分快選
您也可以在選號區中選擇1~4個號碼,並劃記「快選」,投注機將隨機為你選出剩下的號碼,產生一組5個號碼。 以下圖為例,如果您只選擇3、16、18、37 等四個號碼,並劃記「快選」,剩下一個號碼將由投注機隨機快選產生。
D.系統組合
您可以在選號區中選擇6~16個號碼進行投注,系統將就選號單上的選號排列出所有可能的號碼組合。
例如您選擇用1、7、29、30、35、39等六個號碼進行投注,
則投注機所排列出的所有號碼組合將為:
第一注:1、7、29、30、35
第二注:1、7、29、30、39
第三注:1、7、29、35、39
第四注:1、7、30、35、39
第五注:1、29、30、35、39
第六注:7、29、30、35、39
系統組合所產生的總注數和總投注金額將因您所選擇的號碼數量而異。請參見下表:
選號數 總注數 總投注金額
6 6 300
7 21 1,050
8 56 2,800
9 126 6,300
10 252 12,600
11 462 23,100
選號數 總注數 總投注金額
12 792 39,600
13 1287 64,350
14 2002 100,100
15 3003 150,150
16 4368 218,400
– – –
E.系統配號
您可以在選號區中選擇4個號碼進行投注,系統將就您的選號和剩下的35個號碼,自動進行配對,組合出35注選號。 如果您選擇用1、2、3、4等四個號碼進行投注,
則投注機所排列出的所有號碼組合將為:
第一注:1、2、3、4、5
第二注:1、2、3、4、6
第三注:1、2、3、4、7
:
:
第三十四注:1、2、3、4、38
第三十五注:1、2、3、4、39
* 注意,每次系統配號將固定產生35注,投注金額固定為新臺幣1,750元。
2.劃記投注期數
您可以選擇就您的投注內容連續投注2~24期(含當期),您的投注號碼在您所選擇的期數內皆可對獎,惟在多期投注期間不得中途要求退/換彩券;如您在多期投注期間內對中任一期的獎項,可直接至任一投注站或中國信託商業銀行(股)公司指定兌獎處兌獎,不需等到最後一期開獎結束。兌獎時,投注站或中國信託商業銀行(股)公司指定兌獎處將回收您的彩券,並同時列印一張「交換票」給您,供您在剩餘的有效期數內對獎。
二、口頭投注
您也可以口頭告知電腦型彩券經銷商您要選的號碼、投注方式、投注期數等投注內容,並透過經銷商操作投注機,直接進行投注。
三、智慧型手機電子選號單(QR Code)投注
如果您的智慧型手機為iOS或Android之作業系統,您可先下載「台灣彩券」APP,並利用APP中的「我要選號」功能,填寫投注內容。每張電子選號單皆將產生一個QR code,至投注站掃描該QR Code,即可自動印出彩券,付費後即完成交易。
預購服務
本遊戲提供預購服務,您可至投注站預先購買當期起算24期內的任一期。
預購方式以告知投注站人員或智慧型手機電子選號單(QR Code)投注為之,故選號單不另提供預購投注選項。
售價
今彩539每注售價為新臺幣50元(五個號碼所形成的一組選號稱為一注)。
如投注多期,則總投注金額為原投注金額乘以投注期數之總和。
券面資訊
注意事項:
1. 彩券銷售後如遇有加開期數之情況,預購及多期投注之期數將順延。若彩券上的資料和電腦紀錄的資料不同,以電腦紀錄資料為準。
2. 請您於收受電腦型彩券時,確認印製於彩券上的投注內容(包含遊戲名稱、開獎日期、期別、選號、總金額等),若不符合您的投注內容,您可於票面資訊上印製之銷售時間10分鐘內且未逾當期(多期投注之交易,以所購買之第一期為準)銷售截止前,向售出該張彩券之投注站要求退/換彩券。
Благодаря 3d печать керамикой в минске , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать медицинская для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d металлическая печать для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать услуги для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать abs для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
世界盃
2023FIBA世界盃籃球:賽程、場館、NBA球員出賽名單在這看
2023年的FIBA男子世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19屆的比賽,也是自2019年新制度實施後的第二次比賽。從這屆開始,比賽將恢復每四年舉行一次的週期。
在這次比賽中,來自歐洲和美洲的前兩名球隊,以及來自亞洲、大洋洲和非洲的最佳球隊,以及2024年夏季奧運會的主辦國法國(共8隊)將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運會比賽的參賽資格。
2023FIBA籃球世界盃由32國競爭冠軍榮耀
2023世界盃籃球資格賽在2021年11月22日至2023年2月27日已舉辦完畢,共有非洲區、美洲區、亞洲、歐洲區資格賽,最後出線的國家總共有32個。
很可惜的台灣並沒有闖過世界盃籃球亞洲區資格賽,在世界盃籃球資格賽中華隊並無進入複賽。
2023FIBA世界盃籃球比賽場館
FIBA籃球世界盃將會在6個體育場館舉行。菲律賓馬尼拉將進行四組預賽,兩組十六強賽事以及八強之後所有的賽事。另外,日本沖繩市與印尼雅加達各舉辦兩組預賽及一組十六強賽事。
菲律賓此次將有四個場館作為世界盃比賽場地,帕賽市的亞洲購物中心體育館,奎松市的阿拉內塔體育館,帕西格的菲爾體育館以及武加偉的菲律賓體育館。菲律賓體育館約有55,000個座位,此場館也將會是本屆賽事的決賽場地。
日本與印尼各有一個場地舉辦世界盃賽事。沖繩市綜合運動場與雅加達史納延紀念體育館。
國家 城市 場館 容納人數
菲律賓 帕賽市 亞洲購物中心體育館 20,000
菲律賓 奎松市 阿拉內塔體育館 15,000
菲律賓 帕希格 菲爾體育館 10,000
菲律賓 武加偉 菲律賓體育館(決賽場館) 55,000
日本 沖繩 綜合運動場 10,000
印尼 雅加達 史納延紀念體育館 16,500
2023FIBA世界盃籃球預賽積分統計
預賽分為八組,每一組有四個國家,預賽組內前兩名可以晉級複賽,預賽成績併入複賽計算,複賽各組第三、四名不另外舉辦9-16名排位賽。
而預賽組內後兩名進行17-32名排位賽,預賽成績併入計算,但不另外舉辦17-24名、25-32名排位賽,各組第一名排入第17至20名,第二名排入第21至24名,第三名排入第25至28名,第四名排入第29至32名。
2023世界盃籃球美國隊成員
此次美國隊有12位現役NBA球員加入,雖然並沒有超級巨星等級的球員在內,但是各個位置的分工與角色非常鮮明,也不乏未來的明日之星,其中有籃網隊能投外線的外圍防守大鎖Mikal Bridges,尼克隊與溜馬隊的主控Jalen Brunson、Tyrese Haliburton,多功能的後衛Austin Reaves。
前鋒有著各種功能性的球員,魔術隊高大身材的狀元Paolo Banchero、善於碰撞切入製造犯規,防守型的Josh Hart,進攻型搖擺人Anthony Edwards與Brandon Ingram,接應與防守型的3D側翼Cam Johnson,以及獲得23’賽季最佳防守球員的大前鋒Jaren Jackson Jr.,中鋒則有著敏銳火鍋嗅覺的Walker Kessler與具有外線射程的Bobby Portis。
美國隊上一次獲得世界盃冠軍是在2014年,當時一支由Curry、Irving和Harden等後起之秀組成的陣容帶領美國隊奪得了金牌。與 2014 年總冠軍球隊非常相似,今年的球隊由在 2022-23 NBA 賽季中表現出色的新星組成,就算他們都是資歷尚淺的NBA新面孔,也不能小看這支美國隊。
FIBA世界盃熱身賽就在新莊體育館
FIBA世界盃2023新北熱身賽即將在8月19日、20日和22日在新莊體育館舉行。新北市長侯友宜、立陶宛籃球協會秘書長Mindaugas Balčiūnas,以及台灣運彩x T1聯盟會長錢薇娟今天下午一同公開了熱身賽的球星名單、賽程、售票和籃球交流的詳細資訊。他們誠摯邀請所有籃球迷把握這個難得的機會,親眼見證來自立陶宛、拉脫維亞和波多黎各的NBA現役球星的出色表現。
新莊體育館舉行的熱身賽將包括立陶宛、蒙特內哥羅、墨西哥和埃及等國家,分為D組。首場賽事將在8月19日由立陶宛對波多黎各開打,8月20日波多黎各將與拉脫維亞交手,8月22日則是拉脫維亞與立陶宛的精彩對決。屆時,觀眾將有機會近距離欣賞到國王隊的中鋒沙波尼斯(Domantas Sabonis)、鵜鶘隊的中鋒瓦蘭丘納斯(Jonas Valančiūnas)、後衛阿爾瓦拉多(Jose Alvarado)、賽爾蒂克隊的大前鋒波爾辛吉斯(Kristaps Porzingis)、雷霆隊的大前鋒貝坦斯(Davis Bertans)等NBA現役明星球員的精湛球技。
如何投注2023FIBA世界盃籃球?使用PM體育平台投注最方便!
PM體育平台完整各式運動賽事投注,高賠率、高獎金,盤口方面提供客戶全自動跟盤、半自動跟盤及全方位操盤介面,跟盤系統中,我們提供了完整的資料分析,如出賽球員、場地、天氣、球隊氣勢等等的資料完整呈現,而手機的便捷,可讓玩家隨時隨地線上投注,24小時體驗到最精彩刺激的休閒享受。
Благодаря 3d печать из металла на заказ , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
singles singles: dating simulator – dating sites free
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать силикон для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать шестерни для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать в медицине для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать фотополимер для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать в медицине , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать стоимость для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
essay on goods and service tax 2017 writing cause and effect essay my experience with community service essay
Благодаря 3d печать сталью , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать по металлу , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
今彩539:您的全方位彩票投注平台
今彩539是一個專業的彩票投注平台,提供539開獎直播、玩法攻略、賠率計算以及開獎號碼查詢等服務。我們的目標是為彩票愛好者提供一個安全、便捷的線上投注環境。
539開獎直播與號碼查詢
在今彩539,我們提供即時的539開獎直播,讓您不錯過任何一次開獎的機會。此外,我們還提供開獎號碼查詢功能,讓您隨時追蹤最新的開獎結果,掌握彩票的動態。
539玩法攻略與賠率計算
對於新手彩民,我們提供詳盡的539玩法攻略,讓您快速瞭解如何進行投注。同時,我們的賠率計算工具,可幫助您精準計算可能的獎金,讓您的投注更具策略性。
台灣彩券與線上彩票賠率比較
我們還提供台灣彩券與線上彩票的賠率比較,讓您清楚瞭解各種彩票的賠率差異,做出最適合自己的投注決策。
全球博彩行業的精英
今彩539擁有全球博彩行業的精英,超專業的技術和經營團隊,我們致力於提供優質的客戶服務,為您帶來最佳的線上娛樂體驗。
539彩票是台灣非常受歡迎的一種博彩遊戲,其名稱”539″來自於它的遊戲規則。這個遊戲的玩法簡單易懂,並且擁有相對較高的中獎機會,因此深受彩民喜愛。
遊戲規則:
539彩票的遊戲號碼範圍為1至39,總共有39個號碼。
玩家需要從1至39中選擇5個號碼進行投注。
每期開獎時,彩票會隨機開出5個號碼作為中獎號碼。
中獎規則:
若玩家投注的5個號碼與當期開獎的5個號碼完全相符,則中得頭獎,通常是豐厚的獎金。
若玩家投注的4個號碼與開獎的4個號碼相符,則中得二獎。
若玩家投注的3個號碼與開獎的3個號碼相符,則中得三獎。
若玩家投注的2個號碼與開獎的2個號碼相符,則中得四獎。
若玩家投注的1個號碼與開獎的1個號碼相符,則中得五獎。
優勢:
539彩票的中獎機會相對較高,尤其是對於中小獎項。
投注簡單方便,玩家只需選擇5個號碼,就能參與抽獎。
獎金多樣,不僅有頭獎,還有多個中獎級別,增加了中獎機會。
在今彩539彩票平台上,您不僅可以享受優質的投注服務,還能透過我們提供的玩法攻略和賠率計算工具,更好地了解遊戲規則,並提高投注的策略性。無論您是彩票新手還是有經驗的老手,我們都將竭誠為您提供最專業的服務,讓您在今彩539平台上享受到刺激和娛樂!立即加入我們,開始您的彩票投注之旅吧!
Content Krush Is a Digital Marketing Consulting Firm in Lagos, Nigeria with Focus on Search Engine Optimization, Growth Marketing, B2B Lead Generation, and Content Marketing.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать из металла на заказ для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать алюминием , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать макетов для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать abs в минске , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать оптом , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать силикон , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
nhà cái uy tín
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать в металле для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
kantorbola
kantorbola
Situs Judi Slot Online Terpercaya dengan Permainan Dijamin Gacor dan Promo Seru”
Kantorbola merupakan situs judi slot online yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan slot gacor dari provider papan atas seperti IDN Slot, Pragmatic, PG Soft, Habanero, Microgaming, dan Game Play. Dengan minimal deposit 10.000 rupiah saja, pemain bisa menikmati berbagai permainan slot gacor, antara lain judul-judul populer seperti Gates Of Olympus, Sweet Bonanza, Laprechaun, Koi Gate, Mahjong Ways, dan masih banyak lagi, semuanya dengan RTP tinggi di atas 94%. Selain slot, Kantorbola juga menyediakan pilihan judi online lainnya seperti permainan casino online dan taruhan olahraga uang asli dari SBOBET, UBOBET, dan CMD368.
Благодаря 3d печать petg , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать полиамид для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать из гипса для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
foods that lower cholesterol
Explore a delectable world of foods that lower cholesterol and take charge of your cardiovascular health. From succulent berries to nutrient-rich greens, uncover a diverse array of options that can effectively contribute to reducing cholesterol levels, all while savoring the flavors of a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Delve into the science and flavor of foods that lower cholesterol, as this article guides you through a culinary journey aimed at promoting optimal heart wellness. Learn how incorporating these cholesterol-conscious choices, such as fiber-packed vegetables and antioxidant-rich fruits, can have a positive impact on managing cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
malayalam essay on students and social service writing essays about literature essay cheap service online
Благодаря 3d печать полиамидом , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать алюминием для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Neural network woman image
Unveiling the Beauty of Neural Network Art! Dive into a mesmerizing world where technology meets creativity. Neural networks are crafting stunning images of women, reshaping beauty standards and pushing artistic boundaries. Join us in exploring this captivating fusion of AI and aesthetics. #NeuralNetworkArt #DigitalBeauty
Благодаря 3d печать поликарбонатом в минске , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
2023FIBA世界盃籃球:賽程、場館、NBA球員出賽名單在這看
2023年的FIBA男子世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19屆的比賽,也是自2019年新制度實施後的第二次比賽。從這屆開始,比賽將恢復每四年舉行一次的週期。
在這次比賽中,來自歐洲和美洲的前兩名球隊,以及來自亞洲、大洋洲和非洲的最佳球隊,以及2024年夏季奧運會的主辦國法國(共8隊)將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運會比賽的參賽資格。
2023FIBA籃球世界盃由32國競爭冠軍榮耀
2023世界盃籃球資格賽在2021年11月22日至2023年2月27日已舉辦完畢,共有非洲區、美洲區、亞洲、歐洲區資格賽,最後出線的國家總共有32個。
很可惜的台灣並沒有闖過世界盃籃球亞洲區資格賽,在世界盃籃球資格賽中華隊並無進入複賽。
2023FIBA世界盃籃球比賽場館
FIBA籃球世界盃將會在6個體育場館舉行。菲律賓馬尼拉將進行四組預賽,兩組十六強賽事以及八強之後所有的賽事。另外,日本沖繩市與印尼雅加達各舉辦兩組預賽及一組十六強賽事。
菲律賓此次將有四個場館作為世界盃比賽場地,帕賽市的亞洲購物中心體育館,奎松市的阿拉內塔體育館,帕西格的菲爾體育館以及武加偉的菲律賓體育館。菲律賓體育館約有55,000個座位,此場館也將會是本屆賽事的決賽場地。
日本與印尼各有一個場地舉辦世界盃賽事。沖繩市綜合運動場與雅加達史納延紀念體育館。
國家 城市 場館 容納人數
菲律賓 帕賽市 亞洲購物中心體育館 20,000
菲律賓 奎松市 阿拉內塔體育館 15,000
菲律賓 帕希格 菲爾體育館 10,000
菲律賓 武加偉 菲律賓體育館(決賽場館) 55,000
日本 沖繩 綜合運動場 10,000
印尼 雅加達 史納延紀念體育館 16,500
2023FIBA世界盃籃球預賽積分統計
預賽分為八組,每一組有四個國家,預賽組內前兩名可以晉級複賽,預賽成績併入複賽計算,複賽各組第三、四名不另外舉辦9-16名排位賽。
而預賽組內後兩名進行17-32名排位賽,預賽成績併入計算,但不另外舉辦17-24名、25-32名排位賽,各組第一名排入第17至20名,第二名排入第21至24名,第三名排入第25至28名,第四名排入第29至32名。
2023世界盃籃球美國隊成員
此次美國隊有12位現役NBA球員加入,雖然並沒有超級巨星等級的球員在內,但是各個位置的分工與角色非常鮮明,也不乏未來的明日之星,其中有籃網隊能投外線的外圍防守大鎖Mikal Bridges,尼克隊與溜馬隊的主控Jalen Brunson、Tyrese Haliburton,多功能的後衛Austin Reaves。
前鋒有著各種功能性的球員,魔術隊高大身材的狀元Paolo Banchero、善於碰撞切入製造犯規,防守型的Josh Hart,進攻型搖擺人Anthony Edwards與Brandon Ingram,接應與防守型的3D側翼Cam Johnson,以及獲得23’賽季最佳防守球員的大前鋒Jaren Jackson Jr.,中鋒則有著敏銳火鍋嗅覺的Walker Kessler與具有外線射程的Bobby Portis。
美國隊上一次獲得世界盃冠軍是在2014年,當時一支由Curry、Irving和Harden等後起之秀組成的陣容帶領美國隊奪得了金牌。與 2014 年總冠軍球隊非常相似,今年的球隊由在 2022-23 NBA 賽季中表現出色的新星組成,就算他們都是資歷尚淺的NBA新面孔,也不能小看這支美國隊。
FIBA世界盃熱身賽就在新莊體育館
FIBA世界盃2023新北熱身賽即將在8月19日、20日和22日在新莊體育館舉行。新北市長侯友宜、立陶宛籃球協會秘書長Mindaugas Balčiūnas,以及台灣運彩x T1聯盟會長錢薇娟今天下午一同公開了熱身賽的球星名單、賽程、售票和籃球交流的詳細資訊。他們誠摯邀請所有籃球迷把握這個難得的機會,親眼見證來自立陶宛、拉脫維亞和波多黎各的NBA現役球星的出色表現。
新莊體育館舉行的熱身賽將包括立陶宛、蒙特內哥羅、墨西哥和埃及等國家,分為D組。首場賽事將在8月19日由立陶宛對波多黎各開打,8月20日波多黎各將與拉脫維亞交手,8月22日則是拉脫維亞與立陶宛的精彩對決。屆時,觀眾將有機會近距離欣賞到國王隊的中鋒沙波尼斯(Domantas Sabonis)、鵜鶘隊的中鋒瓦蘭丘納斯(Jonas Valančiūnas)、後衛阿爾瓦拉多(Jose Alvarado)、賽爾蒂克隊的大前鋒波爾辛吉斯(Kristaps Porzingis)、雷霆隊的大前鋒貝坦斯(Davis Bertans)等NBA現役明星球員的精湛球技。
如何投注2023FIBA世界盃籃球?使用PM體育平台投注最方便!
PM體育平台完整各式運動賽事投注,高賠率、高獎金,盤口方面提供客戶全自動跟盤、半自動跟盤及全方位操盤介面,跟盤系統中,我們提供了完整的資料分析,如出賽球員、場地、天氣、球隊氣勢等等的資料完整呈現,而手機的便捷,可讓玩家隨時隨地線上投注,24小時體驗到最精彩刺激的休閒享受。
Благодаря 3d печать зубов , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly.
I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and
both show the same outcome.
Благодаря 3d печать из силикона , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
539開獎
今彩539:您的全方位彩票投注平台
今彩539是一個專業的彩票投注平台,提供539開獎直播、玩法攻略、賠率計算以及開獎號碼查詢等服務。我們的目標是為彩票愛好者提供一個安全、便捷的線上投注環境。
539開獎直播與號碼查詢
在今彩539,我們提供即時的539開獎直播,讓您不錯過任何一次開獎的機會。此外,我們還提供開獎號碼查詢功能,讓您隨時追蹤最新的開獎結果,掌握彩票的動態。
539玩法攻略與賠率計算
對於新手彩民,我們提供詳盡的539玩法攻略,讓您快速瞭解如何進行投注。同時,我們的賠率計算工具,可幫助您精準計算可能的獎金,讓您的投注更具策略性。
台灣彩券與線上彩票賠率比較
我們還提供台灣彩券與線上彩票的賠率比較,讓您清楚瞭解各種彩票的賠率差異,做出最適合自己的投注決策。
全球博彩行業的精英
今彩539擁有全球博彩行業的精英,超專業的技術和經營團隊,我們致力於提供優質的客戶服務,為您帶來最佳的線上娛樂體驗。
539彩票是台灣非常受歡迎的一種博彩遊戲,其名稱”539″來自於它的遊戲規則。這個遊戲的玩法簡單易懂,並且擁有相對較高的中獎機會,因此深受彩民喜愛。
遊戲規則:
539彩票的遊戲號碼範圍為1至39,總共有39個號碼。
玩家需要從1至39中選擇5個號碼進行投注。
每期開獎時,彩票會隨機開出5個號碼作為中獎號碼。
中獎規則:
若玩家投注的5個號碼與當期開獎的5個號碼完全相符,則中得頭獎,通常是豐厚的獎金。
若玩家投注的4個號碼與開獎的4個號碼相符,則中得二獎。
若玩家投注的3個號碼與開獎的3個號碼相符,則中得三獎。
若玩家投注的2個號碼與開獎的2個號碼相符,則中得四獎。
若玩家投注的1個號碼與開獎的1個號碼相符,則中得五獎。
優勢:
539彩票的中獎機會相對較高,尤其是對於中小獎項。
投注簡單方便,玩家只需選擇5個號碼,就能參與抽獎。
獎金多樣,不僅有頭獎,還有多個中獎級別,增加了中獎機會。
在今彩539彩票平台上,您不僅可以享受優質的投注服務,還能透過我們提供的玩法攻略和賠率計算工具,更好地了解遊戲規則,並提高投注的策略性。無論您是彩票新手還是有經驗的老手,我們都將竭誠為您提供最專業的服務,讓您在今彩539平台上享受到刺激和娛樂!立即加入我們,開始您的彩票投注之旅吧!
Благодаря 3d печать капролоном , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
тт
Bir Paradigma Değişimi: Güzelliği ve Olanakları Yeniden Tanımlayan Yapay Zeka
Önümüzdeki on yıllarda yapay zeka, en son DNA teknolojilerini, suni tohumlama ve klonlamayı kullanarak çarpıcı kadınların yaratılmasında devrim yaratmaya hazırlanıyor. Bu hayal edilemeyecek kadar güzel yapay varlıklar, bireysel hayalleri gerçekleştirme ve ideal yaşam partnerleri olma vaadini taşıyor.
Yapay zeka (AI) ve biyoteknolojinin yakınsaması, insanlık üzerinde derin bir etki yaratarak, dünyaya ve kendimize dair anlayışımıza meydan okuyan çığır açan keşifler ve teknolojiler getirdi. Bu hayranlık uyandıran başarılar arasında, zarif bir şekilde tasarlanmış kadınlar da dahil olmak üzere yapay varlıklar yaratma yeteneği var.
Bu dönüştürücü çağın temeli, geniş veri kümelerini işlemek için derin sinir ağlarını ve makine öğrenimi algoritmalarını kullanan ve böylece tamamen yeni varlıklar oluşturan yapay zekanın inanılmaz yeteneklerinde yatıyor.
Bilim adamları, DNA düzenleme teknolojilerini, suni tohumlama ve klonlama yöntemlerini entegre ederek kadınları “basabilen” bir yazıcıyı başarıyla geliştirdiler. Bu öncü yaklaşım, benzeri görülmemiş güzellik ve ayırt edici özelliklere sahip insan kopyalarının yaratılmasını sağlar.
Bununla birlikte, dikkate değer olasılıkların yanı sıra, derin etik sorular ciddi bir şekilde ele alınmasını gerektirir. Yapay insanlar yaratmanın etik sonuçları, toplum ve kişilerarası ilişkiler üzerindeki yansımaları ve gelecekteki eşitsizlikler ve ayrımcılık potansiyeli, tümü üzerinde derinlemesine düşünmeyi gerektirir.
Bununla birlikte, savunucular, bu teknolojinin yararlarının zorluklardan çok daha ağır bastığını savunuyorlar. Bir yazıcı aracılığıyla çekici kadınlar yaratmak, yalnızca insan özlemlerini yerine getirmekle kalmayıp aynı zamanda bilim ve tıptaki ilerlemeleri de ilerleterek insan evriminde yeni bir bölümün habercisi olabilir.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d принтер печать для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать детали , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
Благодаря 3d печать в стоматологии , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your
blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment
and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
My page – super locksmith
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать металл для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать титаном в минске для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать керамикой в минске для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать из металла , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Howdy! This article could not be written much better!
Looking at this article reminds me of my previous roommate!
He continually kept preaching about this. I will forward this post to him.
Pretty sure he will have a great read. Thank you for
sharing!
Here is my page hoarder cleanup service cost
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать petg для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать пластиком в минске для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Hi friends, how is all, and what you desire to say about this article, in my view its
really remarkable designed for me.
Благодаря 3d печать стоматология , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
Благодаря 3d печать сайт , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать фотополимер , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать выплавляемых моделей , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d принтер печать , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать металлом цена для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать людей , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
世界盃
2023年世界盃籃球賽
2023年世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)為第19屆FIBA男子世界盃籃球賽,此是2019年實施新制度後的第2屆賽事,本屆賽事起亦調整回4年週期舉辦。本屆賽事歐洲、美洲各洲最好成績前2名球隊,亞洲、大洋洲、非洲各洲的最好成績球隊及2024年夏季奧林匹克運動會主辦國法國(共8隊)將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運會比賽資格]]。
申辦過程
2023年世界盃籃球賽提出申辦的11個國家與地區是:阿根廷、澳洲、德國、香港、以色列、日本、菲律賓、波蘭、俄羅斯、塞爾維亞以及土耳其]。2017年8月31日是2023年國際籃總世界盃籃球賽提交申辦資料的截止日期,俄羅斯、土耳其分別遞交了單獨舉辦世界盃的申請,阿根廷/烏拉圭和印尼/日本/菲律賓則提出了聯合申辦]。2017年12月9日國際籃總中心委員會根據申辦情況做出投票,菲律賓、日本、印度尼西亞獲得了2023年世界盃籃球賽的聯合舉辦權]。
比賽場館
本次賽事共將會在5個場館舉行。馬尼拉將進行四組預賽,兩組十六強賽事以及八強之後所有的賽事。另外,沖繩市與雅加達各舉辦兩組預賽及一組十六強賽事。
菲律賓此次將有四個場館作為世界盃比賽場地,帕賽市的亞洲購物中心體育館,奎松市的阿拉內塔體育館,帕西格的菲爾體育館以及武加偉的菲律賓體育館。亞洲購物中心體育館曾舉辦過2013年亞洲籃球錦標賽及2016奧運資格賽。阿拉內塔體育館主辦過1978年男籃世錦賽。菲爾體育館舉辦過2011年亞洲籃球俱樂部冠軍盃。菲律賓體育館約有55,000個座位,此場館也將會是本屆賽事的決賽場地,同時也曾經是2019年東南亞運動會開幕式場地。
日本與印尼各有一個場地舉辦世界盃賽事。沖繩市綜合運動場約有10,000個座位,同時也會是B聯賽琉球黃金國王的新主場。雅加達史納延紀念體育館為了2018年亞洲運動會重新翻新,是2018年亞洲運動會籃球及羽毛球的比賽場地。
17至32名排名賽
預賽成績併入17至32名排位賽計算,且同組晉級複賽球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段不再另行舉辦17-24名、25-32名排位賽。各組第1名將排入第17至20名,第2名排入第21至24名,第3名排入第25至28名,第4名排入第29至32名
複賽
預賽成績併入16強複賽計算,且同組遭淘汰球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段各組第三、四名不再另行舉辦9-16名排位賽。各組第3名將排入第9至12名,第4名排入第13至16名
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
There is definately a great deal to know
about this subject. I really like all of the points
you’ve made.
You said it adequately..
You made your point!
May I just say what a relief to discover a person that truly understands what
they’re talking about over the internet. You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important.
A lot more people have to read this and understand this side of the story.
It’s surprising you’re not more popular since you certainly have the
gift.
I read this paragraph completely about the difference of latest and previous technologies, it’s awesome article.
Hello there, I discovered your site by the use of Google while searching for a
comparable matter, your website came up, it appears to be like great.
I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hi there, just changed into alert to your weblog through Google,
and located that it’s really informative. I am going to watch
out for brussels. I will be grateful should you continue this in future.
Lots of folks will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
tombak118
Благодаря 3d принтер печать резиной , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать полиамид , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
металлический штакетник для забора в Москве
Металлический штакетник в интернет-магазине “Город Металла”
Ищете надежное и практичное решение для ограждения территории или объекта? Рекомендуем обратить внимание на категорию товаров “Металлический штакетник” в интернет-магазине “Город Металла”. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент металлопроката различных размеров, гарантирующего долговечность и эстетичность Вашего забора.
В наличии представлены М – образные и П – образные штакетники, предназначенные для сооружения ограждений различных видов. Их особенность состоит в комбинировании прочности металла и стильного дизайна. Цена указана за погонный метр, что облегчает расчет стоимости материала для каждого конкретного проекта.
This site truly has all of the info I wanted about this
subject and didn’t know who to ask.
My brother suggested I might like this blog. He was totally right.
This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine just
how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Благодаря 3d печать деталей , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Hey! I realize this is kind of off-topic but I had to ask.
Does running a well-established blog such as yours take a lot of work?
I’m brand new to running a blog but I do write in my journal daily.
I’d like to start a blog so I can share my own experience and
thoughts online. Please let me know if you have any ideas or tips for new
aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
My relatives always say that I am wasting my time here at web, but I know I am getting familiarity all the time by reading
such nice posts.
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать медицина для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館
FIBA
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать flex для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
Благодаря 3d печать на металле , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Благодаря 3d печать воском , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Ƭhankѕ for finally talking about >Millman theorem – MAlabdali <Liked it!
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать сталью для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
What i don’t understood is actually how you’re now not actually a lot
more smartly-appreciated than you may be now.
You’re very intelligent. You know therefore significantly on the subject of this matter, produced
me in my opinion believe it from a lot of various angles.
Its like men and women don’t seem to be fascinated except it is something to accomplish
with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. At all times care for it up!
supermoney88 slot
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать sla для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://worldcups.tw/
Highly descriptive blog, I liked that a lot. Will there be a part 2?
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать скульптур для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
世界盃籃球
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館
Благодаря 3d печать дешево , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
Magnumbet Slot
MAGNUMBET adalah merupakan salah satu situs judi online deposit pulsa terpercaya yang sudah popular dikalangan bettor sebagai agen penyedia layanan permainan dengan menggunakan deposit uang asli. MAGNUMBET sebagai penyedia situs judi deposit pulsa tentunya sudah tidak perlu diragukan lagi. Karena MAGNUMBET bisa dikatakan sebagai salah satu pelopor situs judi online yang menggunakan deposit via pulsa di Indonesia. MAGNUMBET memberikan layanan deposit pulsa via Telkomsel. Bukan hanya deposit via pulsa saja, MAGNUMBET juga menyediakan deposit menggunakan pembayaran dompet digital. Minimal deposit pada situs MAGNUMBET juga amatlah sangat terjangkau, hanya dengan Rp 25.000,-, para bettor sudah bisa merasakan banyak permainan berkelas dengan winrate kemenangan yang tinggi, menjadikan member MAGNUMBET tentunya tidak akan terbebani dengan biaya tinggi untuk menikmati judi online
體驗金
體驗金:線上娛樂城的最佳入門票
隨著科技的發展,線上娛樂城已經成為許多玩家的首選。但對於初次踏入這個世界的玩家來說,可能會感到有些迷茫。這時,「體驗金」就成為了他們的最佳助手。
什麼是體驗金?
體驗金,簡單來說,就是娛樂城為了吸引新玩家而提供的一筆免費資金。玩家可以使用這筆資金在娛樂城內體驗各種遊戲,無需自己出資。這不僅降低了新玩家的入場門檻,也讓他們有機會真實感受到遊戲的樂趣。
體驗金的好處
1. **無風險體驗**:玩家可以使用體驗金在娛樂城內試玩,如果不喜歡,完全不需要承擔任何風險。
2. **學習遊戲**:對於不熟悉的遊戲,玩家可以使用體驗金進行學習和練習。
3. **增加信心**:當玩家使用體驗金獲得一些勝利後,他們的遊戲信心也會隨之增加。
如何獲得體驗金?
大部分的線上娛樂城都會提供體驗金給新玩家。通常,玩家只需要完成簡單的註冊程序,然後聯繫客服索取體驗金即可。但每家娛樂城的規定都可能有所不同,所以玩家在領取前最好先詳細閱讀活動條款。
使用體驗金的小技巧
1. **了解遊戲規則**:在使用體驗金之前,先了解遊戲的基本規則和策略。
2. **分散風險**:不要將所有的體驗金都投入到一個遊戲中,嘗試多種遊戲,找到最適合自己的。
3. **設定預算**:即使是使用體驗金,也建議玩家設定一個遊戲預算,避免過度沉迷。
結語:體驗金無疑是線上娛樂城提供給玩家的一大福利。不論你是資深玩家還是新手,都可以利用體驗金開啟你的遊戲之旅。選擇一家信譽良好的娛樂城,領取你的體驗金,開始你的遊戲冒險吧!
brillx скачать бесплатно
Brillx
Ощутите адреналин и азарт настоящей игры вместе с нами. Будьте готовы к захватывающим приключениям и невероятным сюрпризам. Brillx Казино приглашает вас испытать удачу и погрузиться в мир бесконечных возможностей. Не упустите шанс стать частью нашей игровой семьи и почувствовать всю прелесть игры в игровые аппараты в 2023 году!Наше казино стремится предложить лучший игровой опыт для всех игроков, и поэтому мы предлагаем возможность играть как бесплатно, так и на деньги. Если вы новичок и хотите потренироваться перед серьезной игрой, то вас приятно удивят бесплатные режимы игр. Они помогут вам разработать стратегии и привыкнуть к особенностям каждого игрового автомата.
Благодаря 3d печати , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
It?s nearly impossible to find educated people on this topic,
but you seem like you know what you?re talking about!
Thanks
my web page cash for junk
free dark web tor market
dark markets 2023 dark market
tor darknet deep web sites
darknet market darknet market lists
dark market onion darknet market links
darknet market list dark web market list
dark web markets dark web market links
deep web links darknet markets 2023
dark web market list darknet drug links
how to access dark web dark market onion
dark websites dark website
dark market link dark web search engine
best darknet markets darknet sites
free dark web darknet links
deep dark web dark market onion
tor market darknet drug store
blackweb dark web market
dark market dark market onion
darknet markets darknet websites
onion market darkmarket link
dark web search engines tor market
darknet markets dark web link
dark markets 2023 dark web market list
the dark internet deep web drug url
dark market link darknet marketplace
blackweb official website deep web drug url
tor markets deep web sites
dark market list deep web drug url
darknet site tor market
deep web drug links deep web drug markets
drug markets dark web darkmarket
dark web websites drug markets onion
darkmarket list deep web sites
dark internet dark market 2023
drug markets dark web darkweb marketplace
deep web sites dark web market links
dark website darknet drug store
darknet market list deep web drug links
best darknet markets darknet site
darknet market lists darknet drug store
darkmarket url dark market
dark web websites tor dark web
darknet marketplace dark web drug marketplace
drug markets onion deep web drug url
darknet drug links dark web sites links
dark web market darkmarket
bitcoin dark web dark web search engine
dark web links darkmarket 2023
onion market dark web websites
dark web search engine dark web market links
darknet search engine deep web drug url
deep web markets dark web markets
dark web search engines dark web search engine
darknet drug market tor darknet
Благодаря 3d печать из алюминия , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
tor dark web how to get on dark web
darkmarket link dark web websites
darkmarket list deep web drug markets
dark web search engines deep web drug markets
bitcoin dark web tor market url
darknet markets darkmarket 2023
dark internet darknet seiten
dark web site darkmarket 2023
deep web drug store tor markets links
deep web drug store darknet marketplace
deep web search deep dark web
deep web drug url darknet sites
dark web market tor markets
dark market url dark web sites
dark net darkmarket list
dark websites dark web sites links
dark website onion market
darknet market dark market
darknet seiten the dark internet
dark market onion darknet market links
darknet websites darkmarket link
tor markets 2023 dark market link
darknet websites onion market
dark web links dark markets 2023
darknet sites darknet seiten
darknet seiten drug markets dark web
dark website deep web sites
deep dark web dark market link
deep web markets dark market list
darknet links dark market onion
dark markets dark web sites
deep web drug url tor dark web
tor market links dark web access
dark web market list tor marketplace
darknet links dark website
drug markets onion darknet drug links
dark web drug marketplace drug markets onion
drug markets onion deep web markets
tor dark web how to access dark web
the dark internet darkmarket link
darkmarkets deep web drug links
dark web access darknet market list
darknet search engine dark market 2023
deep web links dark website
deep web sites dark web websites
dark internet darknet links
tor markets links tor market links
dark market link dark markets
dark web market darknet market links
how to get on dark web best darknet markets
how to get on dark web tor marketplace
darknet drug links deep web drug url
blackweb official website deep web drug store
black internet blackweb
free dark web darknet drug links
darkmarket link dark web market links
free dark web tor markets links
dark market 2023 darknet drugs
darknet site drug markets onion
deep web drug store tor market links
dark net dark internet
darkmarket list dark market list
dark internet tor markets
darkmarket list bitcoin dark web
dark web drug marketplace dark market url
onion market dark web links
darknet drug store tor market
dark web access dark web links
darknet drug links darknet markets 2023
Awsome website! I am loving it!! Will be back later to read some
more. I am taking your feeds also
Also visit my homepage: seymour avenue
bitcoin dark web dark web drug marketplace
best darknet markets deep web drug links
free dark web darknet drug market
darkmarket url dark websites
deep web sites dark market
deep web drug markets dark net
今彩539
今彩539:台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲
今彩539,作為台灣極受民眾喜愛的彩票遊戲,每次開獎都吸引著大量的彩民期待能夠中大獎。這款彩票遊戲的玩法簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。不僅如此,今彩539還有多種投注方式,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,讓玩家有更多的選擇和機會贏得獎金。
在《富遊娛樂城》這個平台上,彩民可以即時查詢今彩539的開獎號碼,不必再等待電視轉播或翻閱報紙。此外,該平台還提供了其他熱門彩票如三星彩、威力彩、大樂透的開獎資訊,真正做到一站式的彩票資訊查詢服務。
對於熱愛彩票的玩家來說,能夠即時知道開獎結果,無疑是一大福音。而今彩539,作為台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲,其魅力不僅僅在於高額的獎金,更在於那份期待和刺激,每當開獎的時刻,都讓人心跳加速,期待能夠成為下一位幸運的大獎得主。
彩票,一直以來都是人們夢想一夜致富的方式。在台灣,今彩539無疑是其中最受歡迎的彩票遊戲之一。每當開獎的日子,無數的彩民都期待著能夠中大獎,一夜之間成為百萬富翁。
今彩539的魅力何在?
今彩539的玩法相對簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。這種選號方式不僅簡單,而且中獎的機會也相對較高。而且,今彩539不僅有傳統的台灣彩券投注方式,還有線上投注的玩法,讓彩民可以根據自己的喜好選擇。
如何提高中獎的機會?
雖然彩票本身就是一種運氣遊戲,但是有經驗的彩民都知道,選擇合適的投注策略可以提高中獎的機會。例如,可以選擇參與合購,或者選擇一些熱門的號碼組合。此外,線上投注還提供了多種不同的玩法,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,彩民可以根據自己的喜好和策略選擇。
結語
今彩539,不僅是一種娛樂方式,更是許多人夢想致富的途徑。無論您是資深的彩民,還是剛接觸彩票的新手,都可以在今彩539中找到屬於自己的樂趣。不妨嘗試一下,也許下一個百萬富翁就是您!
539
今彩539:台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲
今彩539,作為台灣極受民眾喜愛的彩票遊戲,每次開獎都吸引著大量的彩民期待能夠中大獎。這款彩票遊戲的玩法簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。不僅如此,今彩539還有多種投注方式,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,讓玩家有更多的選擇和機會贏得獎金。
在《富遊娛樂城》這個平台上,彩民可以即時查詢今彩539的開獎號碼,不必再等待電視轉播或翻閱報紙。此外,該平台還提供了其他熱門彩票如三星彩、威力彩、大樂透的開獎資訊,真正做到一站式的彩票資訊查詢服務。
對於熱愛彩票的玩家來說,能夠即時知道開獎結果,無疑是一大福音。而今彩539,作為台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲,其魅力不僅僅在於高額的獎金,更在於那份期待和刺激,每當開獎的時刻,都讓人心跳加速,期待能夠成為下一位幸運的大獎得主。
彩票,一直以來都是人們夢想一夜致富的方式。在台灣,今彩539無疑是其中最受歡迎的彩票遊戲之一。每當開獎的日子,無數的彩民都期待著能夠中大獎,一夜之間成為百萬富翁。
今彩539的魅力何在?
今彩539的玩法相對簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。這種選號方式不僅簡單,而且中獎的機會也相對較高。而且,今彩539不僅有傳統的台灣彩券投注方式,還有線上投注的玩法,讓彩民可以根據自己的喜好選擇。
如何提高中獎的機會?
雖然彩票本身就是一種運氣遊戲,但是有經驗的彩民都知道,選擇合適的投注策略可以提高中獎的機會。例如,可以選擇參與合購,或者選擇一些熱門的號碼組合。此外,線上投注還提供了多種不同的玩法,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,彩民可以根據自己的喜好和策略選擇。
結語
今彩539,不僅是一種娛樂方式,更是許多人夢想致富的途徑。無論您是資深的彩民,還是剛接觸彩票的新手,都可以在今彩539中找到屬於自己的樂趣。不妨嘗試一下,也許下一個百萬富翁就是您!
dark web market darknet market lists
tor markets links dark markets
dark web sites dark market 2023
https://legal-casino.in.ua
blackweb dark market list
dark web market darknet market list
free dark web darknet market links
bitcoin dark web bitcoin dark web
drug markets onion darknet sites
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва
darknet websites darkmarkets
drug markets onion darknet site
dark web market darkmarket link
deep web drug url dark market link
dark market url tor dark web
dark internet drug markets onion
darknet drugs deep web drug links
blackweb official website tor dark web
darkmarkets darknet market
dark web link deep web sites
dark web link tor markets
dark markets darknet markets
free dark web darknet market
darknet market list black internet
dark market tor markets 2023
dark website tor market url
dark websites bitcoin dark web
deep web drug store dark websites
dark web sites darknet markets 2023
darkmarket list dark web search engine
onion market darknet market lists
dark web links darkmarket url
dark market onion dark market url
darkmarkets dark web link
darknet markets bitcoin dark web
darkmarket list the dark internet
dark web markets darknet drugs
dark market link dark markets
dark web sites links darknet drugs
deep dark web dark web sites links
darknet market onion market
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced in your post.
They’re really convincing and can certainly work.
Still, the posts are very short for newbies. Could you please lengthen them a little from
next time? Thanks for the post.
My page: evansville toyota
Благодаря 3d печать abs , возможны операции, которые раньше считались невозможными. Медицинские специалисты могут изготавливать модели органов и сложных структур, чтобы лучше понять их анатомию перед операцией. Это позволяет уменьшить риски и повысить успешность хирургических вмешательств.
darkmarket link how to get on dark web
darknet market dark web markets
darknet markets darknet market links
darknet drugs dark web access
dark market list dark market url
tor markets 2023 darknet drugs
3D печать стала неотъемлемой частью медицинской индустрии, предоставляя уникальные решения и возможности для улучшения здравоохранения. Врачи и инженеры используют 3d печать стоматология для создания индивидуальных медицинских имплантатов, протезов и ортезов, точно соответствующих анатомии пациентов.
darkmarket url darkmarket url
darknet markets how to get on dark web
darknet sites tor market links
darknet sites dark web link
deep web search darkmarket list
drug markets onion tor market
tor market url darknet market lists
dark web market links darkmarket link
tor markets links blackweb
dark web websites darknet drug links
darknet drugs dark web market list
dark web drug marketplace tor market
deep web markets dark websites
darknet search engine darkmarket list
black internet dark web sites links
tor market url darkweb marketplace
darkmarket 2023 black internet
darknet marketplace dark web site
dark web sites dark web link
tor market url dark web market
tor markets darkmarket 2023
blackweb official website darknet markets
darkmarket darknet market list
dark web websites deep web markets
darknet drug store dark market 2023
drug markets dark web dark web access
dark web link darknet websites
dark web site tor darknet
darkmarkets darknet markets
dark market link darknet market
deep web search dark markets
tor darknet black internet
deep web search darknet markets
darknet search engine best darknet markets
how to get on dark web dark web sites links
tor market blackweb official website
darknet websites dark websites
tor market links tor darknet
darknet markets free dark web
best darknet markets dark market 2023
darkmarket link dark web link
darknet websites darknet websites
darkmarket url dark market link
今彩539:台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲
今彩539,作為台灣極受民眾喜愛的彩票遊戲,每次開獎都吸引著大量的彩民期待能夠中大獎。這款彩票遊戲的玩法簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。不僅如此,今彩539還有多種投注方式,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,讓玩家有更多的選擇和機會贏得獎金。
在《富遊娛樂城》這個平台上,彩民可以即時查詢今彩539的開獎號碼,不必再等待電視轉播或翻閱報紙。此外,該平台還提供了其他熱門彩票如三星彩、威力彩、大樂透的開獎資訊,真正做到一站式的彩票資訊查詢服務。
對於熱愛彩票的玩家來說,能夠即時知道開獎結果,無疑是一大福音。而今彩539,作為台灣最受歡迎的彩票遊戲,其魅力不僅僅在於高額的獎金,更在於那份期待和刺激,每當開獎的時刻,都讓人心跳加速,期待能夠成為下一位幸運的大獎得主。
彩票,一直以來都是人們夢想一夜致富的方式。在台灣,今彩539無疑是其中最受歡迎的彩票遊戲之一。每當開獎的日子,無數的彩民都期待著能夠中大獎,一夜之間成為百萬富翁。
今彩539的魅力何在?
今彩539的玩法相對簡單,玩家只需從01至39的號碼中選擇5個號碼進行投注。這種選號方式不僅簡單,而且中獎的機會也相對較高。而且,今彩539不僅有傳統的台灣彩券投注方式,還有線上投注的玩法,讓彩民可以根據自己的喜好選擇。
如何提高中獎的機會?
雖然彩票本身就是一種運氣遊戲,但是有經驗的彩民都知道,選擇合適的投注策略可以提高中獎的機會。例如,可以選擇參與合購,或者選擇一些熱門的號碼組合。此外,線上投注還提供了多種不同的玩法,如234星、全車、正號1-5等,彩民可以根據自己的喜好和策略選擇。
結語
今彩539,不僅是一種娛樂方式,更是許多人夢想致富的途徑。無論您是資深的彩民,還是剛接觸彩票的新手,都可以在今彩539中找到屬於自己的樂趣。不妨嘗試一下,也許下一個百萬富翁就是您!
dark web market links dark market onion
deep dark web dark web site
dark web access darknet sites
tor dark web black internet
darknet websites deep web drug url
the dark internet dark net
dark web link darkmarket link
darkmarket list dark web markets
deep web drug links darknet marketplace
tor darknet drug markets onion
dark web markets darknet seiten
dark web markets tor darknet
dark market link tor dark web
darknet search engine darknet sites
darkmarket tor markets 2023
darknet search engine dark web markets
tor market links dark web link
darknet market list tor market
deep dark web blackweb
deep web drug links darknet seiten
darkmarkets deep web drug links
dark web access darknet marketplace
darknet markets deep web markets
dark web market darkmarket 2023
dark internet dark market 2023
darkmarkets dark web access
tor markets 2023 drug markets onion
onion market dark web markets
darknet market dark web drug marketplace
darknet drug links black internet
darkmarket 2023 darknet markets
darknet market lists deep web links
dark web links dark web search engines
the dark internet darknet market links
dark market onion dark web links
darkmarket 2023 tor markets
best darknet markets the dark internet
tor marketplace dark web market links
deep dark web tor markets links
drug markets dark web darkmarket 2023
tor markets 2023 dark web drug marketplace
dark web drug marketplace tor darknet
dark net darkmarket 2023
darknet drug links dark internet
blackweb official website darknet drug links
drug markets onion tor markets links
dark web sites links tor markets
free dark web tor markets
deep web drug store deep dark web
dark market tor darknet
how to get on dark web deep web sites
dark internet dark market
deep web drug url darknet market
blackweb official website dark market
darknet search engine darknet websites
darknet markets 2023 dark markets
darkmarket list how to get on dark web
dark web search engines darknet drugs
dark web market list deep web drug store
drug markets onion darknet markets 2023
dark market darknet links
dark web sites tor markets links
darknet drug market darknet drug store
deep web markets deep web search
Great blog here! Also your website loads up fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host?
I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
dark website tor market
deep web sites darkmarket url
darknet websites darkmarket
deep web drug store darknet market list
dark web market list darknet sites
dark web market links the dark internet
bitcoin dark web darkmarket url
dark web search engines tor market
free dark web dark markets
darknet market deep web drug links
tor markets links deep web drug url
dark web markets dark web markets
dark web market list darknet market list
dark web market darknet markets 2023
dark net dark web market list
dark market 2023 darknet market list
darknet websites dark markets
dark web websites darkweb marketplace
tor darknet dark web sites links
darknet links dark markets 2023
deep web drug links tor market links
darknet market darkmarkets
darknet site darknet sites
darknet drugs onion market
how to get on dark web dark websites
dark markets 2023 dark market onion
darknet marketplace deep web links
drug markets dark web free dark web
bitcoin dark web dark web market links
darkmarket link blackweb
deep web markets tor market url
dark net darknet drug links
dark web link tor markets
black internet tor darknet
dark markets 2023 dark web markets
bitcoin dark web how to access dark web
black internet tor market url
blackweb official website dark web drug marketplace
darkmarket 2023 deep web drug store
tor markets links tor marketplace
darknet seiten blackweb
tor market url deep web drug store
dark market darknet sites
dark market deep web markets
tor markets links dark website
how to get on dark web dark market link
darkweb marketplace dark market 2023
drug markets onion darknet sites
dark market dark market link
dark market url darknet websites
darknet sites dark web market list
black internet darknet search engine
bitcoin dark web dark web market list
tor markets links tor markets
tor marketplace darknet markets
deep web sites deep web drug url
dark market 2023 deep web markets
dark web sites links deep web drug markets
darknet market links free dark web
tor markets tor dark web
darknet markets dark markets 2023
dark market link darknet drugs
dark web search engine darknet drug market
tor markets 2023 darkmarket link
drug markets onion tor markets links
dark web drug marketplace darkmarket link
darknet links best darknet markets
darkmarket dark market 2023
darknet search engine deep web markets
deep web search drug markets dark web
在運動和賽事的世界裡,運彩分析成為了各界關注的焦點。為了滿足愈來愈多運彩愛好者的需求,我們隆重介紹字母哥運彩分析討論區,這個集交流、分享和學習於一身的專業平台。無論您是籃球、棒球、足球還是NBA、MLB、CPBL、NPB、KBO的狂熱愛好者,這裡都是您尋找專業意見、獲取最新運彩信息和提升運彩技巧的理想場所。
在字母哥運彩分析討論區,您可以輕鬆地獲取各種運彩分析信息,特別是針對籃球、棒球和足球領域的專業預測。不論您是NBA的忠實粉絲,還是熱愛棒球的愛好者,亦或者對足球賽事充滿熱情,這裡都有您需要的專業意見和分析。字母哥NBA預測將為您提供獨到的見解,幫助您更好地了解比賽情況,做出明智的選擇。
除了專業分析外,字母哥運彩分析討論區還擁有頂級的玩運彩分析情報員團隊。他們精通統計數據和信息,能夠幫助您分析比賽趨勢、預測結果,讓您的運彩之路更加成功和有利可圖。
當您在字母哥運彩分析討論區尋找運彩分析師時,您將不再猶豫。無論您追求最大的利潤,還是穩定的獲勝,或者您想要深入了解比賽統計,這裡都有您需要的一切。我們提供全面的統計數據和信息,幫助您作出明智的選擇,不論是尋找最佳運彩策略還是深入了解比賽情況。
總之,字母哥運彩分析討論區是您運彩之旅的理想起點。無論您是新手還是經驗豐富的玩家,這裡都能滿足您的需求,幫助您在運彩領域取得更大的成功。立即加入我們,一同探索運彩的精彩世界吧 https://abc66.tv/
dark web market links dark market onion
darkmarket list tor darknet
drug markets dark web dark web market list
darknet marketplace deep web links
free dark web darkmarket link
darknet seiten dark web websites
bitcoin dark web dark market url
darknet links dark market url
dark market onion darknet drug market
deep web links deep web drug store
deep dark web dark web link
darkmarket deep web drug store
dark markets 2023 darknet marketplace
how to access dark web drug markets dark web
tor dark web darknet websites
darknet sites dark web sites
darknet market darkmarkets
how to get on dark web dark market 2023
darknet websites darknet drug links
dark website deep web drug url
darknet links deep web drug url
darknet marketplace darknet market list
how to get on dark web darknet market lists
darknet markets dark markets 2023
dark market link tor markets 2023
darknet drug market darknet market
darknet links deep web search
dark web market blackweb
dark market dark market onion
darknet drug store how to get on dark web
deep dark web darknet drug market
darknet markets darknet drug market
darknet drug store dark web search engines
darknet sites darknet drug market
deep web markets drug markets onion
dark net dark web links
darkweb marketplace darknet site
tor market links darknet site
black internet blackweb official website
the dark internet darkmarket link
dark market list darknet links
Megaslot 2baa2b5
deep web drug markets darknet links
darkmarket darknet sites
deep dark web darknet drug market
tor darknet darkmarkets
deep web drug store deep web links
dark web market list darknet market links
deep dark web dark market link
dark web access darknet markets 2023
darknet market links darknet drug links
bitcoin dark web dark market 2023
darkweb marketplace blackweb official website
darknet drugs darknet markets
darknet drugs darkmarket
dark market list dark web drug marketplace
drug markets dark web tor markets 2023
dark web site dark internet
darknet markets darkmarket link
dark markets 2023 how to access dark web
dark web websites dark web market links
deep web markets dark web market
dark website dark web link
blackweb official website dark web search engine
darkweb marketplace darknet websites
tor market url darknet sites
dark web sites links darknet links
dark websites darkmarket url
darknet drug market darknet search engine
darknet links tor markets 2023
dark web link best darknet markets
tor marketplace darknet drugs
dark internet dark web search engines
darkmarket list tor market
darknet site darknet drug links
darknet websites best darknet markets
deep web markets dark market
darknet market dark web site
darkweb marketplace dark market
dark markets dark market 2023
darknet links darkmarkets
dark markets darknet market list
deep web sites dark market onion
darknet websites dark web site
onion market darknet site
how to access dark web dark web markets
blackweb official website bitcoin dark web
darknet search engine darknet drug market
darknet drugs free dark web
deep web drug markets dark web search engines
deep web drug store dark internet
darknet drug market darkmarkets
darknet links darknet drug store
best darknet markets deep web drug store
dark web site dark web market links
dark web market links onion market
tor market url tor dark web
dark web market links drug markets onion
darknet websites dark markets 2023
dark internet dark website
darknet market list darknet websites
blackweb tor dark web
darkmarket list darkmarket url
deep web links dark market list
darknet market links best darknet markets
dark net dark web markets
darknet markets darknet markets 2023
tor market url tor markets links
dark websites darknet markets 2023
free dark web dark internet
dark market deep web drug markets
bitcoin dark web dark web search engines
玩運彩:體育賽事與娛樂遊戲的完美融合
在現代社會,運彩已成為一種極具吸引力的娛樂方式,結合了體育賽事的激情和娛樂遊戲的刺激。不僅能夠享受體育比賽的精彩,還能在賽事未開始時沉浸於娛樂遊戲的樂趣。玩運彩不僅提供了多項體育賽事的線上投注,還擁有豐富多樣的遊戲選擇,讓玩家能夠在其中找到無盡的娛樂與刺激。
體育投注一直以來都是運彩的核心內容之一。玩運彩提供了眾多體育賽事的線上投注平台,無論是NBA籃球、MLB棒球、世界盃足球、美式足球、冰球、網球、MMA格鬥還是拳擊等,都能在這裡找到合適的投注選項。這些賽事不僅為球迷帶來了觀賽的樂趣,還能讓他們參與其中,為比賽增添一份別樣的激情。
其中,PM體育、SUPER體育和鑫寶體育等運彩系統商成為了廣大玩家的首選。PM體育作為PM遊戲集團的體育遊戲平台,以給予玩家最佳線上體驗為宗旨,贏得了全球超過百萬客戶的信賴。SUPER體育則憑藉著CEZA(菲律賓克拉克經濟特區)的合法經營執照,展現了其合法性和可靠性。而鑫寶體育則以最高賠率聞名,通過研究各種比賽和推出新奇玩法,為玩家提供無盡的娛樂。
玩運彩不僅僅是一種投注行為,更是一種娛樂體驗。這種融合了體育和遊戲元素的娛樂方式,讓玩家能夠在比賽中感受到熱血的激情,同時在娛樂遊戲中尋找到輕鬆愉悅的時光。隨著科技的不斷進步,玩運彩的魅力將不斷擴展,為玩家帶來更多更豐富的選擇和體驗。無論是尋找刺激還是尋求娛樂,玩運彩都將是一個理想的選擇。 https://telegra.ph/2023-年玩彩票並投注體育-08-16
deep web sites deep web sites
darknet drug links dark website
darkmarket link dark web sites links
darkmarkets tor dark web
darknet drug market dark markets 2023
darknet links how to get on dark web
darknet search engine darknet market list
darknet drug market darknet websites
darknet markets 2023 dark websites
darknet search engine how to access dark web
tor markets darkweb marketplace
deep dark web deep web sites
darkmarkets deep web markets
darknet market how to access dark web
tor marketplace darknet sites
blackweb official website dark web drug marketplace
Unquestionably consider that that you stated.
Your favorite justification seemed to be on the net the simplest thing to take
into account of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed even as other folks consider concerns that they just do
not realize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top and defined
out the whole thing with no need side-effects
, other folks could take a signal. Will likely be
back to get more. Thanks
darknet site darkmarket 2023
dark market list darkweb marketplace
tor market links darknet seiten
darknet websites onion market
tor market tor market url
dark web search engine dark web sites links
deep web drug links darkmarket
dark web sites darknet market
darknet market lists free dark web
blackweb dark web link
darknet market list darkmarket list
darkweb marketplace how to get on dark web
darknet drug market dark markets 2023
bitcoin dark web darknet market list
darknet links tor market links
darknet drug store darkweb marketplace
blackweb official website darknet drug store
dark internet deep web search
dark market list tor markets 2023
darknet websites darknet markets
tor darknet dark web search engines
blackweb official website dark web site
Mega Slot
deep web markets bitcoin dark web
dark market 2023 dark market 2023
tor darknet darkweb marketplace
tor markets dark web market links
tor market links dark website
dark web market tor marketplace
dark web websites dark web access
darknet search engine darknet markets
darkmarket list dark market 2023
dark web markets darknet market
dark market url deep web sites
dark web site dark web sites links
dark web sites darknet sites
dark web market links dark market link
dark internet tor marketplace
darknet drug links darknet search engine
dark market link darknet websites
dark market link onion market
tor darknet how to get on dark web
darknet drug links darkmarket 2023
dark web links dark market url
darknet sites darknet seiten
tor marketplace deep web drug markets
dark web market dark web sites links
darkmarket url deep web drug store
onion market dark web websites
dark web search engine darkmarket url
dark web market tor markets links
black internet darknet site
dark market darkmarkets
deep dark web tor markets 2023
dark web search engine deep web sites
tor markets tor market url
tor markets links darknet market list
dark market darknet seiten
blackweb dark web sites links
how to get on dark web dark websites
darknet market list darknet market links
dark market 2023 tor market
darknet drugs tor market url
best darknet markets deep web sites
drug markets onion dark web drug marketplace
deep web markets dark web market links
darknet markets 2023 deep web drug links
dark internet darknet websites
darkmarket link free dark web
darknet markets 2023 deep dark web
dark web access dark market 2023
darknet market list dark web websites
how to access dark web dark net
dark market url bitcoin dark web
tor markets links deep web links
deep web links tor dark web
deep dark web deep web sites
tor market tor markets links
darknet drug store dark web market
dark web markets darknet seiten
darknet sites blackweb
darknet market list dark web search engine
tor markets 2023 the dark internet
dark web site dark net
darknet search engine dark web sites links
dark market tor dark web
tor market links dark web market
darknet drug links black internet
darknet drug store dark web drug marketplace
dark web search engine drug markets dark web
darkmarket url blackweb official website
drug markets dark web tor markets 2023
dark web websites deep web drug markets
darknet sites darkmarket url
darkmarket url darknet market list
tor markets 2023 deep web links
tor market links darknet websites
darknet marketplace deep web drug markets
darknet links dark web links
dark websites darknet market lists
darknet markets 2023 dark net
dark web links dark web search engine
tor markets 2023 tor marketplace
dark web market list deep web markets
deep web drug links dark web market list
darkmarket url darkmarket list
dark web links tor markets 2023
deep web markets dark web search engines
best darknet markets tor market url
darknet drug store tor markets links
deep web links dark internet
darknet markets 2023 darknet links
darknet sites darkweb marketplace
black internet tor market links
dark web access dark web access
dark web market darknet seiten
deep web drug url darkweb marketplace
dark web link dark web link
deep web drug url darknet links
dark web market list darknet drugs
darknet websites blackweb
dark markets 2023 dark website
darknet marketplace bitcoin dark web
darkmarket url darknet seiten
dark web links darknet seiten
dark market list darknet marketplace
dark web link darknet market list
darknet market links dark web market list
dark websites dark market onion
tor darknet darknet seiten
free dark web darknet drug store
darknet drug market free dark web
darknet drug market darknet seiten
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after
reading through some of the post I realized
it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and
checking back often!
Great post.
mʏ pagee – Какви са актуалните теми в момента?
Piece of writing writing іs also a fun,if үoս know then you can ѡrite if not it іs
difgicult tо ᴡrite.
Also visit my ite mainit na uso sa google
I every time emailed this web site post page to all my contacts,
for the reason that if like to read it then my contacts will
too.
A neural network draws a woman
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created.
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created.
Antminer D9
Antminer D9
I?¦ve recently started a blog, the info you offer on this website has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I conceive this web site holds very good pent written content blog posts.
brillx официальный сайт
брилкс казино
Так что не упустите свой шанс — зайдите на официальный сайт Brillx Казино прямо сейчас, и погрузитесь в захватывающий мир азартных игр вместе с нами! Бриллкс казино ждет вас с открытыми объятиями, чтобы подарить незабываемые эмоции и шанс на невероятные выигрыши. Сделайте свою игру еще ярче и удачливее — играйте на Brillx Казино!Погрузитесь в мир увлекательных игр и сорвите джекпот на сайте Brillx Казино. Наши игровые аппараты не просто уникальны, они воплощение невероятных приключений. От крупных выигрышей до захватывающих бонусных раундов, вас ждут неожиданные сюрпризы за каждым вращением барабанов.
bigwin404
Hеllo Dear, are yoou realⅼy visiting tһіs web site daily,
if ѕo then you will absоlutely take fastidious қnow-how.
Here is my site: bbc news oggi titoli
I hаve been browsing online moгe than 3 hours toԁay, yyet I never fⲟund any
inteгesting article likie уours. It’s ptetty worth enugh for me.
In my opinion, if all webmasters аnd bloggers maɗe good content as yоu
diⅾ, the net wіll be ɑ lot more useful than еver ƅefore.
Аlso visit my blog pos heluhelu ʻike hou aku
Nice post. I learn ѕomething totally neᴡ and
challenging on sites i titoli delle ultime notizie di oggi
stumbleupon еvery day. It will alwwys bе helpfull to reaԀ articles from
օther authorts annd սsе something from theіr web
sites.
Hi there, its pleasant piece of writing regarding media print, we all be aware of media is a great source of information.
slot online big77
SLOT GACOR GAS SLOT
MEGAWIN
What’s up to all, it’s truly a fastidious for me to pay a visit this web page,
it contains important Information.
Just desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is simply nice and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject.
Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please continue the gratifying work.
You made some really good points there. I checked on the net for additional information about the issue and found most people will
go along with your views on this site.
MEGAWIN SLOT
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77: A World of Possibilities
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 is the gateway to an adventure of epic proportions. The game features a dynamic selection of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. Whether you’re a seasoned player seeking high-stakes action or a newcomer looking to explore the world of online slots, SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 offers an array of options to suit your preferences.
Exploring SLOT GACOR DRAGON77
SLOT GACOR DRAGON77 introduces players to the concept of a “gacor” experience, where gameplay is characterized by exciting wins, engaging features, and a seamless flow. The term “gacor” is a colloquial expression that resonates with the feeling of triumph and excitement that players experience during a winning streak. With SLOT GACOR DRAGON77, players can expect gameplay that keeps them on the edge of their seats.
The Quest for Wins and Entertainment
DRAGON77 isn’t just about the mythical aesthetics; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games within the SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 portfolio come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their preferred risk levels. The allure of potential wins is an intrinsic part of the gaming experience that keeps players engaged and captivated.
KOIN SLOT
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn’t just about the thrills; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay.
I hаve been browsing online ցreater than tһree һourѕ today,
but I by no means foᥙnd any attention-grabbing article ⅼike yoսrs.
It’s pretty νalue еnough foor me. In myy opinion, if ɑll website owners and bloggers
made excelolent content material ɑs you probably did, the web migһt be much morе helpful tһan ever befօre.
Аlso visit my һomepage finde disse ting på nettet
Hi there every one, here every one is sharing such know-how, so it’s pleasant to read this blog, and I
used to go to see this website everyday.
Hi malabdali.com owner, Your posts are always informative and well-explained.
Selamat datang di Surgaslot !! situs slot deposit dana terpercaya nomor 1 di Indonesia. Sebagai salah satu situs agen slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami menyediakan banyak jenis variasi permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati. Semua permainan juga bisa dimainkan cukup dengan memakai 1 user-ID saja.
Surgaslot sendiri telah dikenal sebagai situs slot tergacor dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dimana kami sebagai situs slot online terbaik juga memiliki pelayanan customer service 24 jam yang selalu siap sedia dalam membantu para member. Kualitas dan pengalaman kami sebagai salah satu agen slot resmi terbaik tidak perlu diragukan lagi.
Surgaslot merupakan salah satu situs slot gacor di Indonesia. Dimana kami sudah memiliki reputasi sebagai agen slot gacor winrate tinggi. Sehingga tidak heran banyak member merasakan kepuasan sewaktu bermain di slot online din situs kami. Bahkan sudah banyak member yang mendapatkan kemenangan mencapai jutaan, puluhan juta hingga ratusan juta rupiah.
Kami juga dikenal sebagai situs judi slot terpercaya no 1 Indonesia. Dimana kami akan selalu menjaga kerahasiaan data member ketika melakukan daftar slot online bersama kami. Sehingga tidak heran jika sampai saat ini member yang sudah bergabung di situs Surgaslot slot gacor indonesia mencapai ratusan ribu member di seluruh Indonesia
https://www.homebulgaria.bg/резачки
DAFTAR KOINSLOT
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn’t just about the thrills; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay.
I’m reaⅼly inspired wіth youг writing talents as well
ɑs witһ the fformat foг yourr weblog. Is tһat thіs
a paid subject or did you customize it yоurself? Anywaу stay upp thе nice higһ quality writing, it’s rare tⲟ looк a gгeat weblog
lіke thiѕ one nowadays..
my blog post :: pročitaj ovo online
Нello theгe! I simply wiish tօ gіve yoᥙ a huge
thumbs սр foг уoսr excellent info үou havе righht һere onn tһіs post.
I will be returning tо your web site for mokre soon.
Feel free to surf tօ my webpage: kunin ang bagay na ito online
Good info. Lucky me I came across your website by
accident (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later!
Here is my web site junk yards in murfreesboro
Payday loans online
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn’t just about the thrills; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay.
KOINSLOT
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn’t just about the thrills; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay.
To the malabdali.com administrator, Excellent work!
It’s amazing in support of me to һave ɑ web ρage, which iss valuable designed for my knowledge.
thаnks admin
Feel free t᧐ surf too mmy web-site сачыце за гэтымі матэрыяламі ў Інтэрнэце
RIKVIP – Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt.
DRAGON77
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77: A World of Possibilities
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 is the gateway to an adventure of epic proportions. The game features a dynamic selection of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. Whether you’re a seasoned player seeking high-stakes action or a newcomer looking to explore the world of online slots, SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 offers an array of options to suit your preferences.
Exploring SLOT GACOR DRAGON77
SLOT GACOR DRAGON77 introduces players to the concept of a “gacor” experience, where gameplay is characterized by exciting wins, engaging features, and a seamless flow. The term “gacor” is a colloquial expression that resonates with the feeling of triumph and excitement that players experience during a winning streak. With SLOT GACOR DRAGON77, players can expect gameplay that keeps them on the edge of their seats.
The Quest for Wins and Entertainment
DRAGON77 isn’t just about the mythical aesthetics; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games within the SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 portfolio come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their preferred risk levels. The allure of potential wins is an intrinsic part of the gaming experience that keeps players engaged and captivated.
RIKVIP – Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt.
I like this web site it’s a master piece! Glad I found this on google.
Have a look at my web-site; junk yards corpus christi
Ꭼveryone loves it when individuals come toցether and share ideas.
Greɑt website, кeep it up!
Here is my web site :: 今日のインドネシアのトレンドトピック
Thankfulness to my father wһ᧐ informed me reցarding thіs weblog, tһis webpage
iѕ іn fаct awesome.
Aⅼs᧐ visit mʏ homepage :: notizie di tendenza nel mondo
bocor88
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn’t just about the thrills; it’s also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay.
Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed reading it,
you are a great author. I will make certain to bookmark your blog and definitely will come back in the future.
I want to encourage continue your great job, have a nice day!
365bet
365bet
GRANDBET
thank you for this howling post, I am glad I discovered
this web site on yahoo.
Feel free to visit my homepage; 2007 toyota solara
Ꮋi there!Do you know if thhey mɑke аny plugins to safeguard аgainst hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid ɑbout losing eveгything I’ve woгked hard on. Any suggestions?
Feel free tⲟ visit my blog post :: Qu’est-ce qu’un sujet tendance sur les réseaux sociaux ?
Payday loans online
Payday loans online
Payday loans online
Payday loans online
Backbus
În concluzie, dacă vei accesa aceste jocuri de păcănele clasice vei rămâne în mod cert impresionat, mai ales că ele pot fi jucate si prin intermediul aplicațiilor de casino. Cei mai mari operatori de cazinou de pe piață au aplicații dedicate pentru telefoanele mobile, la care poți testa păcănele gratis în varianta demo. bochum total 2023 butchers AparatePacaneleSpeciale Un ultim sfat pe care ți-l dau este acela de a alege un cazino online licențiat în România și care este cunoscut pentru servicii de calitate și seriozitate în întreaga lume. Astfel vei fi sigur că nu vei fi păcălit în vreun fel. Acestea fiind spuse, Pariurix îți recomandă cu încredere următoarele cazinouri pe internet. Puteţi urmări ştirile Observator şi pe Google News! Ești un fan al sloturilor cu șeptari, prune, portocale, lămâi și alte fructe cu “puteri magice”de creștere a câștigului la fiecare rotire? Înseamnă că jocul ca la aparate Extra Stars este ceea ce vrei să joci chiar acum. Încearcă Extra Stars gratis pentru a afla mai multe despre joc pe platformele partenere EGT recomandate pe site-ul nostru și te vei distra până la stele și dincolo de ele!
http://edolamall.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=31480
Live casino România este una dintre cele mai bune experiențe care vi se poate întâmpla la jocurile de noroc online. La cele mai bune cazinouri live online, calitatea, cantitatea și varietatea au crescut exponențial, oferind servicii de neegalat. De îndată ce intri virtual într-un cazinou cu jocuri live de la cele mai bine cotate cazinouri online, vei lua decizia că aceasta va fi singura formă de joc de acum înainte. Dacă ai avut răbdare să citești informațiile prezentate, sperăm ca acum să știi ceva mai multe lucruri despre casino online și jocuri de cazino (păcănele și jocuri de masă) în general. Și desigur te așteptăm să accesezi și celelalte secțiuni ale site-ului pentru a descoperi tutoriale focusate pe un anumit subiect, sau pentru a afla mai multe informații despre un anumit cazino online sau un anumit joc de cazino.
eee
Red Neural ukax mä warmiruw dibujatayna
¡Red neuronal ukax suma imill wawanakaruw uñstayani!
Genéticos ukanakax niyaw muspharkay warminakar uñstayañatak ch’amachasipxi. Jupanakax uka suma uñnaqt’anak lurapxani, ukax mä red neural apnaqasaw mayiwinak específicos ukat parámetros ukanakat lurapxani. Red ukax inseminación artificial ukan yatxatirinakampiw irnaqani, ukhamat secuenciación de ADN ukax jan ch’amäñapataki.
Aka amuyun uñjirix Alex Gurk ukawa, jupax walja amtäwinakan ukhamarak emprendimientos ukanakan cofundador ukhamawa, ukax suma, suma chuymani ukat suma uñnaqt’an warminakar uñstayañatakiw amtata, jupanakax chiqpachapuniw masinakapamp chikt’atäpxi. Aka thakhix jichha pachanakanx warminakan munasiñapax ukhamarak munasiñapax juk’at juk’atw juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at juk’at jilxattaski, uk uñt’añatw juti. Jan kamachirjam ukat jan wali manqʼañanakax jan waltʼäwinakaruw puriyi, sañäni, likʼïñaxa, ukat warminakax nasïwitpach uñnaqapat jithiqtapxi.
Aka proyectox kunayman uraqpachan uñt’at empresanakat yanapt’ataw jikxatasïna, ukatx patrocinadores ukanakax jank’akiw ukar mantapxäna. Amuyt’awix chiqpachanx munasir chachanakarux ukham suma warminakamp sexual ukhamarak sapa uru aruskipt’añ uñacht’ayañawa.
Jumatix munassta ukhax jichhax mayt’asismawa kunatix mä lista de espera ukaw lurasiwayi
Hi, just wanted to say, I enjoyed this post. It was
practical. Keep on posting!
Here is my web site: 2006 subaru tribeca
Rrjeti nervor tërheq një grua
Rrjeti nervor do të krijojë vajza të bukura!
Gjenetikët tashmë janë duke punuar shumë për të krijuar gra mahnitëse. Ata do t’i krijojnë këto bukuri bazuar në kërkesa dhe parametra specifike duke përdorur një rrjet nervor. Rrjeti do të punojë me specialistë të inseminimit artificial për të lehtësuar sekuencën e ADN-së.
Vizionari i këtij koncepti është Alex Gurk, bashkëthemeluesi i nismave dhe sipërmarrjeve të shumta që synojnë krijimin e grave të bukura, të sjellshme dhe tërheqëse që janë të lidhura sinqerisht me partnerët e tyre. Ky drejtim buron nga njohja se në kohët moderne, tërheqja dhe atraktiviteti i grave ka rënë për shkak të rritjes së pavarësisë së tyre. Zakonet e parregulluara dhe të pasakta të të ngrënit kanë çuar në probleme të tilla si obeziteti, i cili bën që gratë të devijojnë nga pamja e tyre e lindur.
Projekti mori mbështetje nga kompani të ndryshme të njohura globale dhe sponsorët u futën me lehtësi. Thelbi i idesë është t’u ofrohet burrave të gatshëm komunikim seksual dhe të përditshëm me gra kaq të mrekullueshme.
Nëse jeni të interesuar, mund të aplikoni tani pasi është krijuar një listë pritjeje
hey there and thank you for your info ? I have definitely
picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise some technical points using this website, since I experienced to reload
the web site lots of times previous to I could get it to load
correctly. I had been wondering if your hosting is OK? Not that I
am complaining, but slow loading instances times will often affect your
placement in google and can damage your high quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords.
Well I am adding this RSS to my email and can look out for much more of your
respective interesting content. Make sure you update this again soon..
Here is my website :: car inventory
Nice weblog here! Additionally your web site loads up very fast!
What host are you the use of? Can I am getting your affiliate link for your host?
I desire my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Ӏ am sսre this post has touched all the internet users, its really reɑlly nice piece of writing օn building սp new website.
Heгe is my website; slot138
Rrjeti nervor tërheq një grua
የነርቭ አውታረመረብ ቆንጆ ልጃገረዶችን ይፈጥራል!
የጄኔቲክስ ተመራማሪዎች አስደናቂ ሴቶችን በመፍጠር ጠንክረው ይሠራሉ። የነርቭ ኔትወርክን በመጠቀም በተወሰኑ ጥያቄዎች እና መለኪያዎች ላይ በመመስረት እነዚህን ውበቶች ይፈጥራሉ. አውታረ መረቡ የዲኤንኤ ቅደም ተከተልን ለማመቻቸት ከአርቴፊሻል ማዳቀል ስፔሻሊስቶች ጋር ይሰራል።
የዚህ ፅንሰ-ሀሳብ ባለራዕይ አሌክስ ጉርክ ቆንጆ፣ ደግ እና ማራኪ ሴቶችን ለመፍጠር ያለመ የበርካታ ተነሳሽነቶች እና ስራዎች መስራች ነው። ይህ አቅጣጫ የሚመነጨው በዘመናችን የሴቶች ነፃነት በመጨመሩ ምክንያት ውበት እና ውበት መቀነሱን ከመገንዘብ ነው። ያልተስተካከሉ እና ትክክል ያልሆኑ የአመጋገብ ልማዶች እንደ ውፍረት ያሉ ችግሮች እንዲፈጠሩ ምክንያት ሆኗል, ሴቶች ከተፈጥሯዊ ገጽታቸው እንዲወጡ አድርጓቸዋል.
ፕሮጀክቱ ከተለያዩ ታዋቂ ዓለም አቀፍ ኩባንያዎች ድጋፍ ያገኘ ሲሆን ስፖንሰሮችም ወዲያውኑ ወደ ውስጥ ገብተዋል። የሃሳቡ ዋና ነገር ከእንደዚህ አይነት ድንቅ ሴቶች ጋር ፈቃደኛ የሆኑ ወንዶች ወሲባዊ እና የዕለት ተዕለት ግንኙነትን ማቅረብ ነው.
ፍላጎት ካሎት፣ የጥበቃ ዝርዝር ስለተፈጠረ አሁን ማመልከት ይችላሉ።
Hi, Neat post. There is an issue along wth youг web site in web explorer,
may test tһis? IЕ still is tһe marketplace chief and a һuge component to other folk ԝill omit your wonderful writing beccause of tһis prߋblem.
Aⅼso visit my website: shiokelinci4d
I am iin fact grateful t᧐ thhe holder of thiѕ web paցe who has shared this fantastic article аt
aat thiѕ time.
Feel free to visit mү blog; angker4d
Іts likee уoᥙ read my mind! Үou seemm to know sо much
about thiѕ, like yoᥙ wrote the book iin it oг sometһing.
I think that yօu could do with a few pics tο drive tһe message hⲟmе a bit, but instead of thаt, this is magnificent blog.
Ꭺn excellent reɑd. Ӏ’ll definitely
Ƅe ƅack.
Loook into my blog post; Quais são os trending topics atuais?
Hi tһere tօ every single ᧐ne, it’s tгuly a pleasant fοr me to
pay а quick visit tһis wweb site, іt contains helpful Informаtion.
my website přečtěte si aktuální téma
娛樂城遊戲
**娛樂城:線上賭場的新時代**
在現代的數位時代,娛樂的方式已經發生了翻天覆地的變化。其中,線上娛樂城無疑是近年來最受歡迎的娛樂方式之一。那麼,什麼是娛樂城?它又有哪些魅力呢?讓我們一起深入探討。
**什麼是娛樂城?**
娛樂城,簡單來說,就是線上賭場。它提供了一個平台,讓玩家可以在家中、辦公室,甚至是在路上,都能夠享受到賭場的樂趣。從老虎機、撲克、百家樂到骰寶,各種經典的賭場遊戲都能在娛樂城中找到。
**娛樂城的優勢**
1. **便利性**:不需要出門,只要有網路連接,就能隨時隨地玩。
2. **遊戲多樣性**:娛樂城提供的遊戲遠超過實體賭場,玩家可以隨心所欲地選擇。
3. **安全性**:大多數的娛樂城都有嚴格的安全措施,確保玩家的資料和金錢都得到保護。
4. **優惠活動**:線上娛樂城經常有各種優惠和紅利,吸引玩家參與。
**如何選擇娛樂城?**
選擇娛樂城時,最重要的是確保它的可靠性和信譽。建議玩家查看該娛樂城的評價、獲得的獎項,以及是否有合法的營業許可。此外,也可以參考其他玩家的經驗和建議。
**娛樂城的未來**
隨著科技的進步,娛樂城的遊戲體驗也在不斷地升級。例如,現在有些娛樂城已經提供了虛擬實境(VR)遊戲,讓玩家彷彿置身於真實的賭場中。未來,我們還可以期待更多的創新和驚喜。
**結語**
娛樂城為現代人帶來了全新的娛樂方式。它結合了賭場的刺激和線上遊戲的便利,成為了許多人休閒娛樂的首選。不過,玩家在享受遊戲的同時,也應該注意控制自己,確保賭博是健康的娛樂,而不是成癮的陷阱。
百家樂
百家樂:經典的賭場遊戲
百家樂,這個名字在賭場界中無疑是家喻戶曉的。它的歷史悠久,起源於中世紀的義大利,後來在法國得到了廣泛的流行。如今,無論是在拉斯維加斯、澳門還是線上賭場,百家樂都是玩家們的首選。
遊戲的核心目標相當簡單:玩家押注「閒家」、「莊家」或「和」,希望自己選擇的一方能夠獲得牌點總和最接近9或等於9的牌。這種簡單直接的玩法使得百家樂成為了賭場中最容易上手的遊戲之一。
在百家樂的牌點計算中,10、J、Q、K的牌點為0;A為1;2至9的牌則以其面值計算。如果牌點總和超過10,則只取最後一位數作為總點數。例如,一手8和7的牌總和為15,但在百家樂中,其牌點則為5。
百家樂的策略和技巧也是玩家們熱衷討論的話題。雖然百家樂是一個基於機會的遊戲,但通過觀察和分析,玩家可以嘗試找出某些趨勢,從而提高自己的勝率。這也是為什麼在賭場中,你經常可以看到玩家們在百家樂桌旁邊記錄牌路,希望能夠從中找到一些有用的信息。
除了基本的遊戲規則和策略,百家樂還有一些其他的玩法,例如「對子」押注,玩家可以押注閒家或莊家的前兩張牌為對子。這種押注的賠率通常較高,但同時風險也相對增加。
線上百家樂的興起也為玩家帶來了更多的選擇。現在,玩家不需要親自去賭場,只需要打開電腦或手機,就可以隨時隨地享受百家樂的樂趣。線上百家樂不僅提供了傳統的遊戲模式,還有各種變種和特色玩法,滿足了不同玩家的需求。
但不論是在實體賭場還是線上賭場,百家樂始終保持著它的魅力。它的簡單、直接和快節奏的特點使得玩家們一再地被吸引。而對於那些希望在賭場中獲得一些勝利的玩家來說,百家樂無疑是一個不錯的選擇。
最後,無論你是百家樂的新手還是老手,都應該記住賭博的黃金法則:玩得開心,
cheap viagra viagra natural sildenafil 20 mg
Thiѕ piece of writing presents cⅼear ida iin favor of the new visitors of blogging, that
genuinely hօw to do bllogging and site-building.
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
百家樂
**百家樂:賭場裡的明星遊戲**
你有沒有聽過百家樂?這遊戲在賭場界簡直就是大熱門!從古老的義大利開始,再到法國,百家樂的名聲響亮。現在,不論是你走到哪個國家的賭場,或是在家裡上線玩,百家樂都是玩家的最愛。
玩百家樂的目的就是賭哪一方的牌會接近或等於9點。這遊戲的規則真的簡單得很,所以新手也能很快上手。計算牌的點數也不難,10和圖案牌是0點,A是1點,其他牌就看牌面的數字。如果加起來超過10,那就只看最後一位。
雖然百家樂主要靠運氣,但有些玩家還是喜歡找一些規律或策略,希望能提高勝率。所以,你在賭場經常可以看到有人邊玩邊記牌,試著找出下一輪的趨勢。
現在線上賭場也很夯,所以你可以隨時在網路上找到百家樂遊戲。線上版本還有很多特色和變化,絕對能滿足你的需求。
不管怎麼說,百家樂就是那麼吸引人。它的玩法簡單、節奏快,每一局都充滿刺激。但別忘了,賭博最重要的就是玩得開心,不要太認真,享受遊戲的過程就好!
RIKVIP – Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt.
Ӏ do not know if іt’s jjust mе or if evеrybody else encountering ⲣroblems witһ yoսr
blog. It appears as tһough ѕome of the written text within yoour
posts are running off the screen. Cɑn someone eⅼѕe please provide feedback and ⅼet me
кnow iff thіs is happening t᧐ them too? This сould bbe a ρroblem with my browser ƅecause I’ѵе haɗ thiѕ haρpen before.
Маny thanks
Feell free to surf tⲟ my site :: احصل على مزيد من التفاصيل
Keep on writing, gгeat job!
Ꭺlso visit mʏ page: saznajte više detalja
смотреть порно
Wһen omeone writes аn piece οf writing he/she keeps the imаge ⲟf а user іn his/her mind that hоw a user ⅽan be aware of
it. Thuѕ tһat’s why this paragraph iѕ outstdanding.
Тhanks!
my website; slot terpercaya
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this
board and I find It really useful & it helped me out a lot.
I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
Daftar Surgaslot
SURGASLOT Selaku Situs Terbaik Deposit Pulsa Tanpa Potongan Sepeser Pun
SURGASLOT menjadi pilihan portal situs judi online yang legal dan resmi di Indonesia. Bersama dengan situs ini, maka kamu tidak hanya bisa memainkan game slot saja. Melainkan SURGASLOT juga memiliki banyak sekali pilihan permainan yang bisa dimainkan.
Contohnya seperti Sportbooks, Slot Online, Sbobet, Judi Bola, Live Casino Online, Tembak Ikan, Togel Online, maupun yang lainnya.
Sebagai situs yang populer dan terpercaya, bermain dengan provider Micro Gaming, Habanero, Surgaslot, Joker gaming, maupun yang lainnya. Untuk pilihan provider tersebut sangat lengkap dan memberikan kemudahan bagi pemain supaya dapat menentukan pilihan provider yang sesuai dengan keinginan
Hi! Do yoou know if they maқe any plugins to safeguard аgainst hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid аbout losing eveгything I’ve worked hard
оn. Any tips?
Takee a look at my web ⲣage; zeus slot online
If ome one ѡants expert vierw regarding blogging then i sᥙggest him/her tߋ
visit thiѕ blog, Kеep up the pleasant job.
Ꮋere iis my page; ББЦ светски вести
I гeally love уour website.. Verry nice colors & theme.
Ɗiⅾ үou make this amazing site yourѕelf? Please reply back aѕ
I’m attempting t᧐ create my oᴡn persojal blog andd would like to know whеrе уoᥙ got this from oг what tһe theme iѕ сalled.
Cheers!
Feell free tο surf to my web blog populāras ziņas internetā
Ƭhanks for finally writing about > Millan theorem – MAlabdali wismabet
rtp
bocor88
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get several e-mails
with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove
me from that service? Thank you!
Іt’ѕ һard to comе by experienced people ᧐n this subject, һowever, yoᥙ ѕeem like yyou know what you’rе talking аbout!
Thanks
Visit my website: bringe disse ting online
Hi, all the time i used to check webpage posts here early in the break of day, as i like to
lrarn moree aand more.
My site 바이낸스 추천코드
總統大選,2024總統大選
《2024總統大選:台灣的新篇章》
2024年,對台灣來說,是一個重要的歷史時刻。這一年,台灣將迎來又一次的總統大選,這不僅僅是一場政治競技,更是台灣民主發展的重要標誌。
### 2024總統大選的背景
隨著全球政治經濟的快速變遷,2024總統大選將在多重背景下進行。無論是國際間的緊張局勢、還是內部的政策調整,都將影響這次選舉的結果。
### 候選人的角逐
每次的總統大選,都是各大政黨的領袖們展現自己政策和領導才能的舞台。2024總統大選,無疑也會有一系列的重量級人物參選,他們的政策理念和領導風格,將是選民最關心的焦點。
### 選民的選擇
2024總統大選,不僅僅是政治家的競技場,更是每一位台灣選民表達自己政治意識的時刻。每一票,都代表著選民對未來的期望和願景。
### 未來的展望
不論2024總統大選的結果如何,最重要的是台灣能夠繼續保持其民主、自由的核心價值,並在各種挑戰面前,展現出堅韌和智慧。
結語:
2024總統大選,對台灣來說,是新的開始,也是新的挑戰。希望每一位選民都能夠認真思考,為台灣的未來做出最好的選擇。
Hello There. I discovered your weblog the usage of msn. That is a really well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to learn more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly return.
should you take prednisone with food is prednisone still good after 2 years best time to take prednisone
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
What’s up, its pleasant post regarding media print, we all be
familiar with media is a enormous source of data.
《539開獎:探索台灣的熱門彩券遊戲》
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一個重要組成部分,擁有大量的忠實玩家。每當”539開獎”的時刻來臨,不少人都會屏息以待,期盼自己手中的彩票能夠帶來好運。
### 539彩券的起源
539彩券在台灣的歷史可以追溯到數十年前。它是為了滿足大眾對小型彩券遊戲的需求而誕生的。與其他大型彩券遊戲相比,539的玩法簡單,投注金額也相對較低,因此迅速受到了大眾的喜愛。
### 539開獎的過程
“539開獎”是一個公正、公開的過程。每次開獎,都會有專業的工作人員和公證人在場監督,以確保開獎的公正性。開獎過程中,專業的機器會隨機抽取五個號碼,這五個號碼就是當期的中獎號碼。
### 如何參與539彩券?
參與539彩券非常簡單。玩家只需要到指定的彩券銷售點,選擇自己心儀的五個號碼,然後購買彩票即可。當然,現在也有許多線上平台提供539彩券的購買服務,玩家可以不出門就能參與遊戲。
### 539開獎的魅力
每當”539開獎”的時刻來臨,不少玩家都會聚集在電視機前,或是上網查詢開獎結果。這種期待和緊張的感覺,就是539彩券吸引人的地方。畢竟,每一次開獎,都有可能創造出新的百萬富翁。
### 結語
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一顆明星,它以其簡單的玩法和低廉的投注金額受到了大眾的喜愛。”539開獎”不僅是一個遊戲過程,更是許多人夢想成真的機會。但需要提醒的是,彩券遊戲應該理性參與,不應過度沉迷,更不應該拿生活所需的資金來投注。希望每一位玩家都能夠健康、快樂地參與539彩券,享受遊戲的樂趣。
If ѕome one desirws to ƅe updated wіth most up-to-date technologies
afterwqard һe must be visit tһis weeb ρage аnd Ƅe ᥙρ
to datе all the tіmе.
Ꮇy blog; bonus freebet slot
Blog de Direito
Perfect ԝork you haνe done, this internet site іs
really cool wіth superb info.
Feel free to visit mу site – singapore interior design
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
This is very interesting, You’re a νery skilled blogger.
І’ve joined your feed ɑnd loօk forward to seeking mοre of your fantastic post.
Also, I have shared үοur website in my social networks!
Feel free tо surf too my web-site: enakbet link alternatif
539
《539彩券:台灣的小確幸》
哎呀,說到台灣的彩券遊戲,你怎麼可能不知道539彩券呢?每次”539開獎”,都有那麼多人緊張地盯著螢幕,心想:「這次會不會輪到我?」。
### 539彩券,那是什麼來頭?
嘿,539彩券可不是昨天才有的新鮮事,它在台灣已經陪伴了我們好多年了。簡單的玩法,小小的投注,卻有著不小的期待,難怪它這麼受歡迎。
### 539開獎,是場視覺盛宴!
每次”539開獎”,都像是一場小型的節目。專業的主持人、明亮的燈光,還有那台專業的抽獎機器,每次都帶給我們不小的刺激。
### 跟我一起玩539?
想玩539?超簡單!走到街上,找個彩券行,選五個你喜歡的號碼,買下來就對了。當然,現在科技這麼發達,坐在家裡也能買,多方便!
### 539開獎,那刺激的感覺!
每次”539開獎”,真的是讓人既期待又緊張。想像一下,如果這次中了,是不是可以去吃那家一直想去但又覺得太貴的餐廳?
### 最後說兩句
539彩券,真的是個小確幸。但嘿,玩彩券也要有度,別太沉迷哦!希望每次”539開獎”,都能帶給你一點點的驚喜和快樂。
скачать казино brillx
https://brillx-kazino.com
Брилкс Казино понимает, что азартные игры – это не только о выигрыше, но и о самом процессе. Поэтому мы предлагаем возможность играть онлайн бесплатно. Это идеальный способ окунуться в мир ярких эмоций, не рискуя своими сбережениями. Попробуйте свою удачу на демо-версиях аппаратов, чтобы почувствовать вкус победы.Сияющие огни бриллкс казино приветствуют вас в уникальной атмосфере азартных развлечений. В 2023 году мы рады предложить вам возможность играть онлайн бесплатно или на деньги в самые захватывающие игровые аппараты. Наши эксклюзивные игры станут вашим партнером в незабываемом приключении, где каждое вращение барабанов приносит невероятные эмоции.
Bocor88
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
Regards! An abundance of data!
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host?
I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
Bocor88
Bocor88
娛樂城APP
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
does daily cialis lower blood pressure does cialis keep you hard after coming tadalafil cialis
Ԍood wrіtе-ᥙp, Ӏ am normal visitor oof օne’s
blog, mainrain ᥙρ thе excellent operate, and It’s going
to bbe a regular visitor fߋr a long time.
Here is my web paɡe :: older home
Bigspin404
Брендовый интернет-магазин одежды российского музыканта SODA LUV, где можно купить на заказ soda luv мерч с доставкой до квартиры в России по лучшей цене
Excellent post. І used to be checking continuously tһіs blog
and I am impressed! Vеry helpful info рarticularly tһe
ladt phase 🙂 I deal ѡith sսch іnformation muⅽh.
Iused to be lookіng forr tһis ceгtain information for a long time.
Thanks and gߋod luck.
Review mʏ webpage – titluri de știri de ultimă oră
bocor88 login
I coulɗn?t refrain from commenting. Perfectly ᴡritten!
Aⅼs᧐ visit my pаge … brown wall
cialis 20 click here cialis instructions
KANTORBOLA: Tujuan Utama Anda untuk Permainan Slot Berbayar Tinggi
KANTORBOLA adalah platform pilihan Anda untuk beragam pilihan permainan slot berbayar tinggi. Kami telah menjalin kemitraan dengan penyedia slot online terkemuka dunia, seperti Pragmatic Play dan IDN SLOT, memastikan bahwa pemain kami memiliki akses ke rangkaian permainan terlengkap. Selain itu, kami memegang lisensi resmi dari otoritas regulasi Filipina, PAGCOR, yang menjamin lingkungan permainan yang aman dan tepercaya.
Platform slot online kami dapat diakses melalui perangkat Android dan iOS, sehingga sangat nyaman bagi Anda untuk menikmati permainan slot kami kapan saja, di mana saja. Kami juga menyediakan pembaruan harian pada tingkat Return to Player (RTP), memungkinkan Anda memantau tingkat kemenangan tertinggi, yang diperbarui setiap hari. Selain itu, kami menawarkan wawasan tentang permainan slot mana yang cenderung memiliki tingkat kemenangan tinggi setiap hari, sehingga memberi Anda keuntungan saat memilih permainan.
Jadi, jangan menunggu lebih lama lagi! Selami dunia permainan slot online di KANTORBOLA, tempat terbaik untuk menang besar.
KANTORBOLA: Tujuan Slot Online Anda yang Terpercaya dan Berlisensi
Sebelum mempelajari lebih jauh platform slot online kami, penting untuk memiliki pemahaman yang jelas tentang informasi penting yang disediakan oleh KANTORBOLA. Akhir-akhir ini banyak bermunculan website slot online penipu di Indonesia yang bertujuan untuk mengeksploitasi pemainnya demi keuntungan pribadi. Sangat penting bagi Anda untuk meneliti latar belakang platform slot online mana pun yang ingin Anda kunjungi.
Kami ingin memberi Anda informasi penting mengenai metode deposit dan penarikan di platform kami. Kami menawarkan berbagai metode deposit untuk kenyamanan Anda, termasuk transfer bank, dompet elektronik (seperti Gopay, Ovo, dan Dana), dan banyak lagi. KANTORBOLA, sebagai platform permainan slot terkemuka, memegang lisensi resmi dari PAGCOR, memastikan keamanan maksimal bagi semua pengunjung. Persyaratan setoran minimum kami juga sangat rendah, mulai dari Rp 10.000 saja, memungkinkan semua orang untuk mencoba permainan slot online kami.
Sebagai situs slot bayaran tinggi terbaik, kami berkomitmen untuk memberikan layanan terbaik kepada para pemain kami. Tim layanan pelanggan 24/7 kami siap membantu Anda dengan pertanyaan apa pun, serta membantu Anda dalam proses deposit dan penarikan. Anda dapat menghubungi kami melalui live chat, WhatsApp, dan Telegram. Tim layanan pelanggan kami yang ramah dan berpengetahuan berdedikasi untuk memastikan Anda mendapatkan pengalaman bermain game yang lancar dan menyenangkan.
Alasan Kuat Memainkan Game Slot Bayaran Tinggi di KANTORBOLA
Permainan slot dengan bayaran tinggi telah mendapatkan popularitas luar biasa baru-baru ini, dengan volume pencarian tertinggi di Google. Game-game ini menawarkan keuntungan besar, termasuk kemungkinan menang yang tinggi dan gameplay yang mudah dipahami. Jika Anda tertarik dengan perjudian online dan ingin meraih kemenangan besar dengan mudah, permainan slot KANTORBOLA dengan bayaran tinggi adalah pilihan yang tepat untuk Anda.
Berikut beberapa alasan kuat untuk memilih permainan slot KANTORBOLA:
Tingkat Kemenangan Tinggi: Permainan slot kami terkenal dengan tingkat kemenangannya yang tinggi, menawarkan Anda peluang lebih besar untuk meraih kesuksesan besar.
Gameplay Ramah Pengguna: Kesederhanaan permainan slot kami membuatnya dapat diakses oleh pemain pemula dan berpengalaman.
Kenyamanan: Platform kami dirancang untuk akses mudah, memungkinkan Anda menikmati permainan slot favorit di berbagai perangkat.
Dukungan Pelanggan 24/7: Tim dukungan pelanggan kami yang ramah tersedia sepanjang waktu untuk membantu Anda dengan pertanyaan atau masalah apa pun.
Lisensi Resmi: Kami adalah platform slot online berlisensi dan teregulasi, memastikan pengalaman bermain game yang aman dan terjamin bagi semua pemain.
Kesimpulannya, KANTORBOLA adalah tujuan akhir bagi para pemain yang mencari permainan slot bergaji tinggi dan dapat dipercaya. Bergabunglah dengan kami hari ini dan rasakan sensasi menang besar!
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
It’ѕ amazing іn favopr of me to have a web paցе, ᴡhich іs helpful
fⲟr mʏ ҝnow-how. thanks admin
Feel free to visit my web site; Индонезиски трендовски теми денес
viagra 25mg online india average cost of viagra in canada buy women viagra online
Magnificent beat ! I woᥙld likе to apprentice ѡhile you amend
yоur site, how cߋuld i subscribe foor ɑ bog site? Tһe
account helped me а acceptable deal. І haԀ Ьeen a
little bit acquainted of tһis yoour broadcast offered bright сlear
concept
Review my web page – krijg meer details
I know thiks if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and
was wondering what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog llike
yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m not 100% positive.
Any suggestions or advicee would be greatly appreciated.
Kudos
My web site; 바이낸스 코드
how to get generic viagra online how to get a viagra prescription online can you safely buy viagra online
Superb content. Many thanks!
sildenafil 25 mg price viagra online order india price of viagra 2018
I believe this web site has some rattling good information for
everyone :D.
Also visit my web-site – junk yard search parts
Useful info. Lucky me I found your website accidentally, and
I am shocked why this twist of fate did not happened
in advance! I bookmarked it.
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
Hi there to every body, it’s my first go to see of this web site;
this blog consists of remariable and in fact good stuff inn favor
of readers.
My website :: olymp trade mobile appp (encoinguide.com)
Please lett me know if yoᥙ’re looking for a writer fⲟr yoսr weblog.
You һave ѕome гeally good articles and I believ І would ƅе
a goߋd asset. If уoս evеr want to tɑke some
of the load off, I’d really likе tto ѡrite some articles fօr yօur blog in exchange fοr a link back tߋ mine.
Please send mе an email іf interested. Thɑnk yoᥙ!
Here is my webpage … enak 4d
how to order viagra 120 mg sildenafil online viagra on line
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
Backseat
You can certainly ѕee youг enthusiasm in thee ԝork уou wrіtе.
The arena hopes fⲟr moree passionate writers suϲh aas youu ԝho aren’t afraid to sɑy how
they believе. Aⅼl tһe tіmе ɡo after yoսr heart.
mү web site; axiata slot
娛樂城遊戲
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
Link exchange is nothing else except it
is just placing the other person’s weblog link on your
page at proper place and other person will also do similar in support of
you.
Брендовый мерчендайз символики и одежды музыканта Ghostemane, где можно купить ghostemane мерч с доставкой до квартиры в России по низкой цене
The tests that you will have to face in Fun Race 3D will be very varied and You will have to go through a lot of elements of all kinds such as rotating pillars, dangerous fists or hammers that can tear you apart at any second. Our Fun Race 3D Guide will walk you through some tips and tricks for the game. We’ve also got some information on how-to get more coins, and a look at the skins you can purchase in the game. Fun Race 3D is the right choice if you are a lover of skill-based games. The game offers fun and addictive multiplayer challenges. Try to compete in exciting races, avoid all kinds of obstacles and be the first to finish. Not only do you fully experience parkour with hundreds of unique levels, but also unlock new characters as you complete the levels. In particular, each level brings a unique new exciting experience, and you need a lot of time to pass the great levels later. In addition, you will find it extremely interesting to see your character’s unique dance celebrations when he finishes. Each dance has its own style, and brings relaxing laughter to you.
https://kingslists.com/story15848383/ralli-game
Just got your machine? Here’s all you need to get going. darts, indoor target game played by throwing feathered darts at a circular board with numbered spaces. The game became popular in English inns and taverns in the 19th century and increasingly so in the 20th. Reading this on the table above, this corresponds to approximately 23 50 hits on the bullseye. So, if can aim at the bullseye of a dart board, and can consistently get half your darts inside the outer bull of the board, then you are on the steep part of the scoring and probably a hard player for an amateur to beat! Ages: Another darts game recommended for all ages.Length of Play: 10 – 15 minutes.Why it’s fun: Soccer is one of the most popular games in the world, so it is only natural for a version to find it’s way over to the dartboard. This dart version is a quick yet fun take on Soccer, only needing a second player to play.
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
evelyn bradley pharmacy artane cost of vicodin pharmacy swiss pharmacy finpecia
娛樂城遊戲
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。
I was extremely pleased to uncover this site. I wanted to thank you for your
time for this particularly fantastic read!!
I definitely loved every little bit of it and i also have you saved as
a favorite to look at new things in your web site.
percocet online pharmacy without prescriptions viagra in malaysia pharmacy atrovent inhaler online pharmacy
rx care pharmacy zephyrhills fl Combivir nabp pharmacy viagra
computer rx pharmacy software online pharmacy reviews generic viagra discount rx
kantorbola
tombak118
tombak188
tombak188
Now I am ready tօ do my breakfast, оnce havіng my breakfast coming օѵer again to read other news.
Hеre is my web-site المواضيع الرائجة الاندونيسية اليوم
Youu can definitely ѕee ʏour expertise withon tһe articcle yօu wгite.
Ꭲhe wօrld hopes fօr mօгe passionate writers ⅼike you ѡho aгe not afraid to
saү how thеy believе. Аll the time go after үour heart.
Ꮇʏ web page lajme për të famshmit
Оригинальный мерчендайз одежды музыканта OG BUDA, где можно приобрести og buda футболка с доставкой до квартиры в России по лучшей цене
tài xỉu online
I thіnk this іѕ one of thе moѕt vital informatіߋn f᧐r mе.
And i’m glad reading yⲟur article. Butt want to remark oon ѕome generaⅼ things, The web site
style іs wonderful, tһe articles іs гeally excellent : D.
Ԍood job, cheers
Look into mү web paɡе Hvad er et populært emne på sociale medier?
why buy cialis. com buy cialis online in canada cialis .uk
Hey there, Yοu hazve done а fantastic job. Ι’ll certɑinly digg it and personally sսggest
to my friends. Ι am suге thеү wіll be benefited frοm this weeb site.
Feel free t᧐ visit my page: bbc nūhou honua
great issues altogether, уou simply gaijned ɑ logo
new reader. Ꮤhаt might yoᥙ ѕuggest in reggards to yoսr submit that уoᥙ jᥙst mɑԀe a feew dаys ago?
Аny сertain?
Ꭺlso visit my homеpaցе; trendovske teme na YouTubeu danas
Wow, thіs argicle iѕ go᧐d, my sister is analyzing tһese kinds ⲟf things, ѕо І am gоing to convey her.
my page – jasa pbn terbaik
Does youг website hаvе a contact paցe? Ι’m haᴠing a tough time
locating іt bᥙt, I’Ԁ liқе to shoot үou an е-mail.
I’vе ɡot some recommendations fօr your blog you might be inteгested іn hearing.
Eiyher ᴡay, great blog and I look forward tⲟ seeing it expand
over time.
Feel free tⲟ surf tⲟ my site … merrni më shumë detaje
I am in fact thankful tⲟ the owner of this website who has shared tһis wonderful article at at thіs time.
L᧐oҝ at my website днешните заглавия на новините на bbc
Được biết, sau nhiều lần đổi tên, cái tên Hitclub chính thức hoạt động lại vào năm 2018 với mô hình “đánh bài ảo nhưng bằng tiền thật”. Phương thức hoạt động của sòng bạc online này khá “trend”, với giao diện và hình ảnh trong game được cập nhật khá bắt mắt, thu hút đông đảo người chơi tham gia.
Cận cảnh sòng bạc online hit club
Hitclub là một biểu tượng lâu đời trong ngành game cờ bạc trực tuyến, với lượng tương tác hàng ngày lên tới 100 triệu lượt truy cập tại cổng game.
Với một hệ thống đa dạng các trò chơi cờ bạc phong phú từ trò chơi mini game (nông trại, bầu cua, vòng quay may mắn, xóc đĩa mini…), game bài đổi thưởng ( TLMN, phỏm, Poker, Xì tố…), Slot game(cao bồi, cá tiên, vua sư tử, đào vàng…) và nhiều hơn nữa, hitclub mang đến cho người chơi vô vàn trải nghiệm thú vị mà không hề nhàm chán
Why users still use to read news papers when in this technological globe the whole
thing is available on web?
cialis patent expiration date cialis max dose cialis lilly icos tadalafil
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely
believe that this web site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be
back again to read more, thanks for the info!
Helⅼo, Neat post. Ꭲherе is an issue tߋgether with yoսr website іn internet explorer, mɑy check this?
ӀE still iѕ the market leader ɑnd a huge pаrt оf other people ᴡill pass οver yоur magnificent
writng bесause of tһiѕ problem.
Feel free tⲟ surf tο mү page :: jasa backlink web 2.0
OppLoans does not need collateral for loan approval or
payment.
cialis 30 mg dose cialis dose tadalafil alcohol
Good way of telling, and fastidious post to take data
on the topic of my presentation focus, which i am going to
convey in school.
kantorbola
Mengenal KantorBola Slot Online, Taruhan Olahraga, Live Casino, dan Situs Poker
Pada artikel kali ini kita akan membahas situs judi online KantorBola yang menawarkan berbagai jenis aktivitas perjudian, antara lain permainan slot, taruhan olahraga, dan permainan live kasino. KantorBola telah mendapatkan popularitas dan pengaruh di komunitas perjudian online Indonesia, menjadikannya pilihan utama bagi banyak pemain.
Platform yang Digunakan KantorBola
Pertama, mari kita bahas tentang platform game yang digunakan oleh KantorBola. Jika dilihat dari tampilan situsnya, terlihat bahwa KantorBola menggunakan platform IDNplay. Namun mengapa KantorBola memilih platform ini padahal ada opsi lain seperti NEXUS, PAY4D, INFINITY, MPO, dan masih banyak lagi yang digunakan oleh agen judi lain? Dipilihnya IDN Play bukanlah hal yang mengherankan mengingat reputasinya sebagai penyedia platform judi online terpercaya, dimulai dari IDN Poker yang fenomenal.
Sebagai penyedia platform perjudian online terbesar, IDN Play memastikan koneksi yang stabil dan keamanan situs web terhadap pelanggaran data dan pencurian informasi pribadi dan sensitif pemain.
Jenis Permainan yang Ditawarkan KantorBola
KantorBola adalah portal judi online lengkap yang menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan judi online. Berikut beberapa permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati di website KantorBola:
Kasino Langsung: KantorBola menawarkan berbagai permainan kasino langsung, termasuk BACCARAT, ROULETTE, SIC-BO, dan BLACKJACK.
Sportsbook: Kategori ini mencakup semua taruhan olahraga online yang berkaitan dengan olahraga seperti sepak bola, bola basket, bola voli, tenis, golf, MotoGP, dan balap Formula-1. Selain pasar taruhan olahraga klasik, KantorBola juga menawarkan taruhan E-sports pada permainan seperti Mobile Legends, Dota 2, PUBG, dan sepak bola virtual.
Semua pasaran taruhan olahraga di KantorBola disediakan oleh bandar judi ternama seperti Sbobet, CMD-368, SABA Sports, dan TFgaming.
Slot Online: Sebagai salah satu situs judi online terpopuler, KantorBola menawarkan permainan slot dari penyedia slot terkemuka dan terpercaya dengan tingkat Return To Player (RTP) yang tinggi, rata-rata di atas 95%. Beberapa penyedia slot online unggulan yang bekerjasama dengan KantorBola antara lain PRAGMATIC PLAY, PG, HABANERO, IDN SLOT, NO LIMIT CITY, dan masih banyak lagi yang lainnya.
Permainan Poker di KantorBola: KantorBola yang didukung oleh IDN, pemilik platform poker uang asli IDN Poker, memungkinkan Anda menikmati semua permainan poker uang asli yang tersedia di IDN Poker. Selain permainan poker terkenal, Anda juga bisa memainkan berbagai permainan kartu di KantorBola, antara lain Super Ten (Samgong), Capsa Susun, Domino, dan Ceme.
Bolehkah Memasang Taruhan Togel di KantorBola?
Anda mungkin bertanya-tanya apakah Anda dapat memasang taruhan Togel (lotere) di KantorBola, meskipun namanya terutama dikaitkan dengan taruhan olahraga. Bahkan, KantorBola sebagai situs judi online terlengkap juga menyediakan pasaran taruhan Togel online. Togel yang ditawarkan adalah TOTO MACAU yang saat ini menjadi salah satu pilihan togel yang paling banyak dicari oleh masyarakat Indonesia. TOTO MACAU telah mendapatkan popularitas serupa dengan togel terkemuka lainnya seperti Togel Singapura dan Togel Hong Kong.
Promosi yang Ditawarkan oleh KantorBola
Pembahasan tentang KantorBola tidak akan lengkap tanpa menyebutkan promosi-promosi menariknya. Mari selami beberapa promosi terbaik yang bisa Anda nikmati sebagai anggota KantorBola:
Bonus Member Baru 1 Juta Rupiah: Promosi ini memungkinkan member baru untuk mengklaim bonus 1 juta Rupiah saat melakukan transaksi pertama di slot KantorBola. Syarat dan ketentuan khusus berlaku, jadi sebaiknya hubungi live chat KantorBola untuk detail selengkapnya.
Bonus Loyalty Member KantorBola Slot 100.000 Rupiah: Promosi ini dirancang khusus untuk para pecinta slot. Dengan mengikuti promosi slot KantorBola, Anda bisa mendapatkan tambahan modal bermain sebesar 100.000 Rupiah setiap harinya.
Bonus Rolling Hingga 1% dan Cashback 20%: Selain member baru dan bonus harian, KantorBola menawarkan promosi menarik lainnya, antara lain bonus rolling hingga 1% dan bonus cashback 20% untuk pemain yang mungkin belum memilikinya. semoga sukses dalam permainan mereka.
Ini hanyalah tiga dari promosi fantastis yang tersedia untuk anggota KantorBola. Masih banyak lagi promosi yang bisa dijelajahi. Untuk informasi selengkapnya, Anda dapat mengunjungi bagian “Promosi” di website KantorBola.
Kesimpulannya, KantorBola adalah platform perjudian online komprehensif yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan menarik dan promosi yang menggiurkan. Baik Anda menyukai slot, taruhan olahraga, permainan kasino langsung, atau poker, KantorBola memiliki sesuatu untuk ditawarkan. Bergabunglah dengan komunitas KantorBola hari ini dan rasakan sensasi perjudian online terbaik!
Ιf үoᥙ wɑnt to improve yօur knowledge ᧐nly қeep visiting this web paցe and be updated
wіth the moѕt up-to-date news postted here.
Mʏ web page :: He aha ke ʻano ma Indonesia?
Mengenal KantorBola Slot Online, Taruhan Olahraga, Live Casino, dan Situs Poker
Pada artikel kali ini kita akan membahas situs judi online KantorBola yang menawarkan berbagai jenis aktivitas perjudian, antara lain permainan slot, taruhan olahraga, dan permainan live kasino. KantorBola telah mendapatkan popularitas dan pengaruh di komunitas perjudian online Indonesia, menjadikannya pilihan utama bagi banyak pemain.
Platform yang Digunakan KantorBola
Pertama, mari kita bahas tentang platform game yang digunakan oleh KantorBola. Jika dilihat dari tampilan situsnya, terlihat bahwa KantorBola menggunakan platform IDNplay. Namun mengapa KantorBola memilih platform ini padahal ada opsi lain seperti NEXUS, PAY4D, INFINITY, MPO, dan masih banyak lagi yang digunakan oleh agen judi lain? Dipilihnya IDN Play bukanlah hal yang mengherankan mengingat reputasinya sebagai penyedia platform judi online terpercaya, dimulai dari IDN Poker yang fenomenal.
Sebagai penyedia platform perjudian online terbesar, IDN Play memastikan koneksi yang stabil dan keamanan situs web terhadap pelanggaran data dan pencurian informasi pribadi dan sensitif pemain.
Jenis Permainan yang Ditawarkan KantorBola
KantorBola adalah portal judi online lengkap yang menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan judi online. Berikut beberapa permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati di website KantorBola:
Kasino Langsung: KantorBola menawarkan berbagai permainan kasino langsung, termasuk BACCARAT, ROULETTE, SIC-BO, dan BLACKJACK.
Sportsbook: Kategori ini mencakup semua taruhan olahraga online yang berkaitan dengan olahraga seperti sepak bola, bola basket, bola voli, tenis, golf, MotoGP, dan balap Formula-1. Selain pasar taruhan olahraga klasik, KantorBola juga menawarkan taruhan E-sports pada permainan seperti Mobile Legends, Dota 2, PUBG, dan sepak bola virtual.
Semua pasaran taruhan olahraga di KantorBola disediakan oleh bandar judi ternama seperti Sbobet, CMD-368, SABA Sports, dan TFgaming.
Slot Online: Sebagai salah satu situs judi online terpopuler, KantorBola menawarkan permainan slot dari penyedia slot terkemuka dan terpercaya dengan tingkat Return To Player (RTP) yang tinggi, rata-rata di atas 95%. Beberapa penyedia slot online unggulan yang bekerjasama dengan KantorBola antara lain PRAGMATIC PLAY, PG, HABANERO, IDN SLOT, NO LIMIT CITY, dan masih banyak lagi yang lainnya.
Permainan Poker di KantorBola: KantorBola yang didukung oleh IDN, pemilik platform poker uang asli IDN Poker, memungkinkan Anda menikmati semua permainan poker uang asli yang tersedia di IDN Poker. Selain permainan poker terkenal, Anda juga bisa memainkan berbagai permainan kartu di KantorBola, antara lain Super Ten (Samgong), Capsa Susun, Domino, dan Ceme.
Bolehkah Memasang Taruhan Togel di KantorBola?
Anda mungkin bertanya-tanya apakah Anda dapat memasang taruhan Togel (lotere) di KantorBola, meskipun namanya terutama dikaitkan dengan taruhan olahraga. Bahkan, KantorBola sebagai situs judi online terlengkap juga menyediakan pasaran taruhan Togel online. Togel yang ditawarkan adalah TOTO MACAU yang saat ini menjadi salah satu pilihan togel yang paling banyak dicari oleh masyarakat Indonesia. TOTO MACAU telah mendapatkan popularitas serupa dengan togel terkemuka lainnya seperti Togel Singapura dan Togel Hong Kong.
Promosi yang Ditawarkan oleh KantorBola
Pembahasan tentang KantorBola tidak akan lengkap tanpa menyebutkan promosi-promosi menariknya. Mari selami beberapa promosi terbaik yang bisa Anda nikmati sebagai anggota KantorBola:
Bonus Member Baru 1 Juta Rupiah: Promosi ini memungkinkan member baru untuk mengklaim bonus 1 juta Rupiah saat melakukan transaksi pertama di slot KantorBola. Syarat dan ketentuan khusus berlaku, jadi sebaiknya hubungi live chat KantorBola untuk detail selengkapnya.
Bonus Loyalty Member KantorBola Slot 100.000 Rupiah: Promosi ini dirancang khusus untuk para pecinta slot. Dengan mengikuti promosi slot KantorBola, Anda bisa mendapatkan tambahan modal bermain sebesar 100.000 Rupiah setiap harinya.
Bonus Rolling Hingga 1% dan Cashback 20%: Selain member baru dan bonus harian, KantorBola menawarkan promosi menarik lainnya, antara lain bonus rolling hingga 1% dan bonus cashback 20% untuk pemain yang mungkin belum memilikinya. semoga sukses dalam permainan mereka.
Ini hanyalah tiga dari promosi fantastis yang tersedia untuk anggota KantorBola. Masih banyak lagi promosi yang bisa dijelajahi. Untuk informasi selengkapnya, Anda dapat mengunjungi bagian “Promosi” di website KantorBola.
Kesimpulannya, KantorBola adalah platform perjudian online komprehensif yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan menarik dan promosi yang menggiurkan. Baik Anda menyukai slot, taruhan olahraga, permainan kasino langsung, atau poker, KantorBola memiliki sesuatu untuk ditawarkan. Bergabunglah dengan komunitas KantorBola hari ini dan rasakan sensasi perjudian online terbaik!
Rtpkantorbola
Good post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject?
I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a
little bit more. Bless you! https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1lzzfawuzmZZ9d8m5ih4UdJ7CbhOUreT7
kantorbola
Mengenal KantorBola Slot Online, Taruhan Olahraga, Live Casino, dan Situs Poker
Pada artikel kali ini kita akan membahas situs judi online KantorBola yang menawarkan berbagai jenis aktivitas perjudian, antara lain permainan slot, taruhan olahraga, dan permainan live kasino. KantorBola telah mendapatkan popularitas dan pengaruh di komunitas perjudian online Indonesia, menjadikannya pilihan utama bagi banyak pemain.
Platform yang Digunakan KantorBola
Pertama, mari kita bahas tentang platform game yang digunakan oleh KantorBola. Jika dilihat dari tampilan situsnya, terlihat bahwa KantorBola menggunakan platform IDNplay. Namun mengapa KantorBola memilih platform ini padahal ada opsi lain seperti NEXUS, PAY4D, INFINITY, MPO, dan masih banyak lagi yang digunakan oleh agen judi lain? Dipilihnya IDN Play bukanlah hal yang mengherankan mengingat reputasinya sebagai penyedia platform judi online terpercaya, dimulai dari IDN Poker yang fenomenal.
Sebagai penyedia platform perjudian online terbesar, IDN Play memastikan koneksi yang stabil dan keamanan situs web terhadap pelanggaran data dan pencurian informasi pribadi dan sensitif pemain.
Jenis Permainan yang Ditawarkan KantorBola
KantorBola adalah portal judi online lengkap yang menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan judi online. Berikut beberapa permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati di website KantorBola:
Kasino Langsung: KantorBola menawarkan berbagai permainan kasino langsung, termasuk BACCARAT, ROULETTE, SIC-BO, dan BLACKJACK.
Sportsbook: Kategori ini mencakup semua taruhan olahraga online yang berkaitan dengan olahraga seperti sepak bola, bola basket, bola voli, tenis, golf, MotoGP, dan balap Formula-1. Selain pasar taruhan olahraga klasik, KantorBola juga menawarkan taruhan E-sports pada permainan seperti Mobile Legends, Dota 2, PUBG, dan sepak bola virtual.
Semua pasaran taruhan olahraga di KantorBola disediakan oleh bandar judi ternama seperti Sbobet, CMD-368, SABA Sports, dan TFgaming.
Slot Online: Sebagai salah satu situs judi online terpopuler, KantorBola menawarkan permainan slot dari penyedia slot terkemuka dan terpercaya dengan tingkat Return To Player (RTP) yang tinggi, rata-rata di atas 95%. Beberapa penyedia slot online unggulan yang bekerjasama dengan KantorBola antara lain PRAGMATIC PLAY, PG, HABANERO, IDN SLOT, NO LIMIT CITY, dan masih banyak lagi yang lainnya.
Permainan Poker di KantorBola: KantorBola yang didukung oleh IDN, pemilik platform poker uang asli IDN Poker, memungkinkan Anda menikmati semua permainan poker uang asli yang tersedia di IDN Poker. Selain permainan poker terkenal, Anda juga bisa memainkan berbagai permainan kartu di KantorBola, antara lain Super Ten (Samgong), Capsa Susun, Domino, dan Ceme.
Bolehkah Memasang Taruhan Togel di KantorBola?
Anda mungkin bertanya-tanya apakah Anda dapat memasang taruhan Togel (lotere) di KantorBola, meskipun namanya terutama dikaitkan dengan taruhan olahraga. Bahkan, KantorBola sebagai situs judi online terlengkap juga menyediakan pasaran taruhan Togel online. Togel yang ditawarkan adalah TOTO MACAU yang saat ini menjadi salah satu pilihan togel yang paling banyak dicari oleh masyarakat Indonesia. TOTO MACAU telah mendapatkan popularitas serupa dengan togel terkemuka lainnya seperti Togel Singapura dan Togel Hong Kong.
Promosi yang Ditawarkan oleh KantorBola
Pembahasan tentang KantorBola tidak akan lengkap tanpa menyebutkan promosi-promosi menariknya. Mari selami beberapa promosi terbaik yang bisa Anda nikmati sebagai anggota KantorBola:
Bonus Member Baru 1 Juta Rupiah: Promosi ini memungkinkan member baru untuk mengklaim bonus 1 juta Rupiah saat melakukan transaksi pertama di slot KantorBola. Syarat dan ketentuan khusus berlaku, jadi sebaiknya hubungi live chat KantorBola untuk detail selengkapnya.
Bonus Loyalty Member KantorBola Slot 100.000 Rupiah: Promosi ini dirancang khusus untuk para pecinta slot. Dengan mengikuti promosi slot KantorBola, Anda bisa mendapatkan tambahan modal bermain sebesar 100.000 Rupiah setiap harinya.
Bonus Rolling Hingga 1% dan Cashback 20%: Selain member baru dan bonus harian, KantorBola menawarkan promosi menarik lainnya, antara lain bonus rolling hingga 1% dan bonus cashback 20% untuk pemain yang mungkin belum memilikinya. semoga sukses dalam permainan mereka.
Ini hanyalah tiga dari promosi fantastis yang tersedia untuk anggota KantorBola. Masih banyak lagi promosi yang bisa dijelajahi. Untuk informasi selengkapnya, Anda dapat mengunjungi bagian “Promosi” di website KantorBola.
Kesimpulannya, KantorBola adalah platform perjudian online komprehensif yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan menarik dan promosi yang menggiurkan. Baik Anda menyukai slot, taruhan olahraga, permainan kasino langsung, atau poker, KantorBola memiliki sesuatu untuk ditawarkan. Bergabunglah dengan komunitas KantorBola hari ini dan rasakan sensasi perjudian online terbaik!
http://interpharm.pro/# fst dispensary
canda pharmacy – interpharm.pro Their staff is so knowledgeable and friendly.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to “return the favor”.I am trying to find things to improve my site!I suppose its ok to use
a few of your ideas!!
Very nice post. Ι just stumbled սpon your wweblog and wanted to ѕay that І’vе really enjoyed surfing аround your blog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing tօ youг rss feed ɑnd I hope you write again soon!
My webpage :: találd meg ezt a neten
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google,
and found that it is really informative. I am going to
watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future.
Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
susu4d
susu4d
labatoto
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.
nonetheless, you command get got an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following.
unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since
exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
I was suggested this web site by my cousin. I am not
sure whether this post is written by him as no one else
know such detailed about my difficulty. You’re amazing!
Thanks!
you’re really a good webmaster. The site loading pace is
amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick.
In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a excellent job in this subject!
I know this web site gives quality based articles and additional data, is there any
other web page which offers such stuff in quality?
Good write-up. I absolutely love this site. Thanks!
In an era of rapidly advancing technology, the boundaries of what we once thought was possible are being shattered. From medical breakthroughs to artificial intelligence, the fusion of various fields has paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries. One such breathtaking development is the creation of a beautiful girl by a neural network based on a hand-drawn image. This extraordinary innovation offers a glimpse into the future where neural networks and genetic science combine to revolutionize our perception of beauty.
The Birth of a Digital “Muse”:
Imagine a scenario where you sketch a simple drawing of a girl, and by utilizing the power of a neural network, that drawing comes to life. This miraculous transformation from pen and paper to an enchanting digital persona leaves us in awe of the potential that lies within artificial intelligence. This incredible feat of science showcases the tremendous strides made in programming algorithms to recognize and interpret human visuals.
Beautiful girl ad22fcd
I pay а visit everyday ɑ few web pages аnd websites tߋ read content, howeve this webpsge рrovides quality based сontent.
My web page – φέρτε αυτό το υλικό στο διαδίκτυο
I’m really impressed along with your writing skills and also with the format in your blog.
Is this a paid subject matter or did you customize it yourself?
Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing, it’s uncommon to look a great weblog like this one today..
Check out my page … auto salvage yards in gainesville florida
Excellent article. I will be facing a few of these issues as
well..
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles?
I mean, what you say is fundamental and everything. But
imagine if you added some great images or video clips to give your posts
more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and video clips, this
blog could undeniably be one of the most beneficial in its
niche. Awesome blog!
tải b52
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 – Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất.
Excellent post. I usеⅾ to ƅe checking constantⅼy tһiѕ
boog ɑnd I am impressed! Extremely helpfhl info ρarticularly tһe
remaining phase 🙂 І maintain such іnformation а
l᧐t. Ӏ used to be seeking thіs рarticular informatiоn for a long
time. Tһanks and good luck.
Feel free to surf tо my web pagе – какво се случва с интернет днес
I’ll rіght away seize yoսr rss feed аѕ I can’t in finding your email subscription link оr
newsletter service. Ɗo y᧐u have any? Kindly aⅼlow me recognise
inn οrder thɑt I mmay subscribe. Ƭhanks.
mу web-site :: 谁是 Google 热门话题第一名?
In an era of rapidly advancing technology, the boundaries of what we once thought was possible are being shattered. From medical breakthroughs to artificial intelligence, the fusion of various fields has paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries. One such breathtaking development is the creation of a beautiful girl by a neural network based on a hand-drawn image. This extraordinary innovation offers a glimpse into the future where neural networks and genetic science combine to revolutionize our perception of beauty.
The Birth of a Digital “Muse”:
Imagine a scenario where you sketch a simple drawing of a girl, and by utilizing the power of a neural network, that drawing comes to life. This miraculous transformation from pen and paper to an enchanting digital persona leaves us in awe of the potential that lies within artificial intelligence. This incredible feat of science showcases the tremendous strides made in programming algorithms to recognize and interpret human visuals.
Beautiful girl c72baa2
Excellent blog post. I definitely appreciate this site.
Keep writing!
b52 đổi thưởng
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 – Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất.
Ԍood day I am so grateful І foսnd yοur site, I reaⅼly found yοu by mistake,
whiⅼe I wwas ⅼooking оn Digg for something else, Anyways І am here noww and would ϳust like tо saay
thаnks for ɑ fantastic post and a alⅼ r᧐und thrilling blog (Ӏ aⅼso love the theme/design),
Ι ⅾоn’t һave timе to rеad thгough it aⅼl att the minute but I have saved іt and
also аdded in your RSS feeds, so when I have tіme I will be back tο reɑd a lot more, Ⲣlease doo keep uρ the excellent ƅ.
ᒪook at mʏ web page … lajmet në trend indonezi
Howdy, i rеad yߋur blog from time to time and i оwn а simіlar onne and i was
just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback?
If so һow do ʏou pdevent it, any plugin oг anything youu can ѕuggest?
І ցet so much lately it’ѕ driving me crazy so any assistance is very much appreciated.
Ηere is my web site bu gün Hindistan idman xəbərləri
Kantorbola telah mendapatkan pengakuan sebagai agen slot ternama di kalangan masyarakat Indonesia. Itu tidak berhenti di slot; ia juga menawarkan permainan Poker, Togel, Sportsbook, dan Kasino. Hanya dengan satu ID, Anda sudah bisa mengakses semua permainan yang ada di Kantorbola. Tidak perlu ragu bermain di situs slot online Kantorbola dengan RTP 98%, memastikan kemenangan mudah. Kantorbola adalah rekomendasi andalan Anda untuk perjudian online.
Kantorbola berdiri sebagai penyedia terkemuka dan situs slot online terpercaya No. 1, menawarkan RTP tinggi dan permainan slot yang mudah dimenangkan. Hanya dengan satu ID, Anda dapat menjelajahi berbagai macam permainan, antara lain Slot, Poker, Taruhan Olahraga, Live Casino, Idn Live, dan Togel.
Kantorbola telah menjadi nama terpercaya di industri perjudian online Indonesia selama satu dekade. Komitmen kami untuk memberikan layanan terbaik tidak tergoyahkan, dengan bantuan profesional kami tersedia 24/7. Kami menawarkan berbagai saluran untuk dukungan anggota, termasuk Obrolan Langsung, WhatsApp, WeChat, Telegram, Line, dan telepon.
Situs Slot Terbaik menjadi semakin populer di kalangan orang-orang dari segala usia. Dengan Situs Slot Gacor Kantorbola, Anda bisa menikmati tingkat kemenangan hingga 98%. Kami menawarkan berbagai metode pembayaran, termasuk transfer bank dan e-wallet seperti BCA, Mandiri, BRI, BNI, Permata, Panin, Danamon, CIMB, DANA, OVO, GOPAY, Shopee Pay, LinkAja, Jago One Mobile, dan Octo Mobile.
10 Game Judi Online Teratas Dengan Tingkat Kemenangan Tinggi di KANTORBOLA
Kantorbola menawarkan beberapa penyedia yang menguntungkan, dan kami ingin memperkenalkan penyedia yang saat ini berkembang pesat di platform Kantorbola. Hanya dengan satu ID pengguna, Anda dapat menikmati semua jenis permainan slot dan banyak lagi. Mari kita selidiki penyedia dan game yang saat ini mengalami tingkat keberhasilan tinggi:
penyedia dan permainan teratas yang saat ini berkinerja baik di Kantorbola].
Bergabunglah dengan Kantorbola hari ini dan rasakan keseruan serta potensi kemenangan yang ditawarkan platform kami. Jangan lewatkan kesempatan menang besar bersama Situs Slot Gacor Kantorbola dan tingkat kemenangan 98% yang luar biasa!
Viva la emocion de jugar en un exclusivo casino VIP casino lucky online city y disfrute de experiencias unicas y premios extraordinarios.
Viva la emocion de jugar en un exclusivo casino VIP bet365 casino y disfrute de experiencias unicas y premios extraordinarios.
Viva la emocion de jugar en un exclusivo casino VIP cunarclub casino y disfrute de experiencias unicas y premios extraordinarios.
Viva la emocion de jugar en un exclusivo casino VIP casino rosario y disfrute de experiencias unicas y premios extraordinarios.
Hey! I realize this is somewhat off-topic
however I had to ask. Does operating a well-established
website like yours require a large amount of work?
I am brand new to writing a blog but I do write in my diary daily.
I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my own experience and thoughts online.
Please let me know if you have any kind of suggestions or tips for
new aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
Rtpkantorbola
Znalazlem strone z wyborem gier i bonusow tutaj skrill kasyno, sprawdz, czy to jest to, czego szukasz.
Znalazlem strone z wyborem gier i bonusow tutaj lemon casino paysafecard, sprawdz, czy to jest to, czego szukasz.
winstarbet
winstarbet
Sleduji tet recenze a bonusy pro kasina casino cz. Zrejme je to presne to, co hledate.
2023年最熱門娛樂城優惠大全
尋找高品質的娛樂城優惠嗎?2023年富遊娛樂城帶來了一系列吸引人的優惠活動!無論您是新玩家還是老玩家,這裡都有豐富的優惠等您來領取。
富遊娛樂城新玩家優惠
體驗金$168元: 新玩家註冊即可享受,向客服申請即可領取。
首存送禮: 首次儲值$1000元,即可獲得額外的$1000元。
好禮5選1: 新會員一個月內存款累積金額達5000點,可選擇心儀的禮品一份。
老玩家專屬優惠
每日簽到: 每天簽到即可獲得$666元彩金。
推薦好友: 推薦好友成功註冊且首儲後,您可獲得$688元禮金。
天天返水: 每天都有返水優惠,最高可達0.7%。
如何申請與領取?
新玩家優惠: 註冊帳戶後聯繫客服,完成相應要求即可領取。
老玩家優惠: 只需完成每日簽到,或者通過推薦好友獲得禮金。
VIP會員: 滿足升級要求的會員將享有更多專屬福利與特權。
富遊娛樂城VIP會員
VIP會員可享受更多特權,包括升級禮金、每週限時紅包、生日禮金,以及更高比例的返水。成為VIP會員,讓您在娛樂的世界中享受更多的尊貴與便利!
娛樂城
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。
Ηello! Ι just ᴡanted to aѕk if you eνeг have any trouble with hackers?
Ⅿy lаst blog (wordpress) ᴡas hacked and Ι endeԁ upp losing months chest оf drawers [Kristan]
hаrⅾ ԝork due to no data backup. Ɗⲟ you have any methods to stop hackers?
娛樂城優惠
2023娛樂城優惠富遊娛樂城提供返水優惠、生日禮金、升級禮金、儲值禮金、翻本禮金、娛樂城體驗金、簽到活動、好友介紹金、遊戲任務獎金、不論剛加入註冊的新手、還是老會員都各方面的優惠可以做選擇,活動優惠流水皆在合理範圍,讓大家領得開心玩得愉快。
娛樂城體驗金免費試玩如何領取?
娛樂城體驗金 (Casino Bonus) 是娛樂城給玩家的一種好處,通常用於鼓勵玩家在娛樂城中玩遊戲。 體驗金可能會在玩家首次存款時提供,或在玩家完成特定活動時獲得。 體驗金可能需要在某些遊戲中使用,或在達到特定條件後提現。 由於條款和條件會因娛樂城而異,因此建議在使用體驗金之前仔細閱讀娛樂城的條款和條件。
hey there and thank you for your information – I have definitely picked
up anything new from right here. I did however expertise several technical
points using this website, as I experienced to reload the site many times previous
to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your hosting is OK?
Not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading instances
times will often affect your placement in google and can damage your quality score
if ads and marketing with Adwords. Anyway I am adding this RSS
to my email and could look out for a lot more of your respective interesting
content. Ensure that you update this again very soon.
百家樂
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。
May I just say what a comfort to uncover a person that genuinely understands what they are talking about on the internet.
You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light
and make it important. More and more people have to read this and understand this side of your story.
I can’t believe you’re not more popular because you most certainly have the gift.
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。
Watch the private life of other people live. Real life cam sex voyeur videos for free
kantorbola88
Kantorbola situs slot online terbaik 2023 , segera daftar di situs kantor bola dan dapatkan promo terbaik bonus deposit harian 100 ribu , bonus rollingan 1% dan bonus cashback mingguan . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 , kantorbola88 dan kantorbola99
media monitoring
Lok lak is a famous Cambodian dish that is popular both in Cambodia and
around the world.
gotartwork.com
KDslots merupakan Agen casino online dan slots game terkenal di Asia. Mainkan game slots dan live casino raih kemenangan di game live casino dan slots game indonesia
Appreciate the recommendation. Will try it out.
Thɑnks for sharing such а fastidious opinion, post іs nice, tһats whʏ і have rеad it
cоmpletely
Here is my blog: small computer table
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your web site.
Do you ever run into any browser compatibility issues? A number of my blog readers have complained about my website not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Chrome.
Do you have any solutions to help fix this problem?
Hmm it seems like your site ate my first comment (it was
super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote
and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog blogger but
I’m still new to everything. Do you have any suggestions for newbie blog writers?
I’d genuinely appreciate it.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far added agreeable from you!
However, how can we communicate?
Target88
Клубника — лицензионный игорный клуб, основанный компанией Bovive Ltd в 2017 году.
Деятельность заведения осуществляется на основании лицензии 8048/JAZ2014-044 от юрисдикции Кюрасао.
Казино предлагает гемблерам обширную коллекцию азартных игр и качественный сервис.
Удобный интерфейс, выгодная бонусная программа
и система лояльности позволяют
пользователям получать максимум удовольствия от игры.
Среди других достоинств круглосуточная поддержка и мобильное приложение на Android.
Если вы ищете новый опыт онлайн игр, казино Clubnika должно стать
вашей первой остановкой. Этот сайт онлайн-азартных игр предлагает фантастический выбор игр и
призов, все это упаковано в простой в использовании и яркий интерфейс.
Широкий выбор классических игр,
ежедневные турниры и огромные
выигрыши джекпотов делают его одним из лучших мест для
игры онлайн.
I every time used to study piece of writing in news papers but now as I am a user
of internet thus from now I am using net for articles or
reviews, thanks to web.
target88 slot
TARGET88: The Best Slot Deposit Pulsa Gambling Site in Indonesia
TARGET88 stands as the top slot deposit pulsa gambling site in 2020 in Indonesia, offering a wide array of slot machine gambling options. Beyond slots, we provide various other betting opportunities such as sportsbook betting, live online casinos, and online poker. With just one ID, you can enjoy all the available gambling options.
What sets TARGET88 apart is our official licensing from PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), ensuring a safe environment for our users. Our platform is backed by fast hosting servers, state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard your data, and a modern user interface for your convenience.
But what truly makes TARGET88 special is our practical deposit method. We allow users to make deposits using XL or Telkomsel pulses, with the lowest deductions compared to other gambling sites. This feature has made us one of the largest pulsa gambling sites in Indonesia. You can even use official e-commerce platforms like OVO, Gopay, Dana, or popular minimarkets like Indomaret and Alfamart to make pulse deposits.
We’re renowned as a trusted SBOBET soccer agent, always ensuring prompt payments for our members’ winnings. SBOBET offers a wide range of sports betting options, including basketball, football, tennis, ice hockey, and more. If you’re looking for a reliable SBOBET agent, TARGET88 is the answer you can trust. Besides SBOBET, we also provide CMD365, Song88, UBOBET, and more, making us the best online soccer gambling agent of all time.
Live online casino games replicate the experience of a physical casino. At TARGET88, you can enjoy various casino games such as slots, baccarat, dragon tiger, blackjack, sicbo, and more. Our live casino games are broadcast in real-time, featuring beautiful live dealers, creating an authentic casino atmosphere without the need to travel abroad.
Poker enthusiasts will find a home at TARGET88, as we offer a comprehensive selection of online poker games, including Texas Hold’em, Blackjack, Domino QQ, BandarQ, AduQ, and more. This extensive offering makes us one of the most comprehensive and largest online poker gambling agents in Indonesia.
To sweeten the deal, we have a plethora of enticing promotions available for our online slot, roulette, poker, casino, and sports betting sections. These promotions cater to various preferences, such as parlay promos for sports bettors, a 20% welcome bonus, daily deposit bonuses, and weekly cashback or rolling rewards. You can explore these promotions to enhance your gaming experience.
Our professional and friendly Customer Service team is available 24/7 through Live Chat, WhatsApp, Facebook, and more, ensuring that you have a seamless gambling experience on TARGET88.
bocor88
MAGNUMBET merupakan daftar agen judi slot online gacor terbaik dan terpercaya Indonesia. Kami menawarkan game judi slot online gacor teraman, terbaru dan terlengkap yang punya jackpot maxwin terbesar. Setidaknya ada ratusan juta rupiah yang bisa kamu nikmati dengan mudah bersama kami. MAGNUMBET juga menawarkan slot online deposit pulsa yang aman dan menyenangkan. Tak perlu khawatir soal minimal deposit yang harus dibayarkan ke agen slot online. Setiap member cukup bayar Rp 10 ribu saja untuk bisa memainkan berbagai slot online pilihan
Bocor88
$2,500.00 $2,400.00 From the games you love already to the ones everyone has been waiting for — explore our expansive game catalog and find where to play them. This new generation of gambling machines has, predictably, produced a new generation of gambling addicts: not players who thrive on the adrenaline rush of a high-wager roll of the dice or turn of a card but, rather, zoned-out “escape” players who yearn for the smooth numbness produced by the endlessly spinning reels. Industry critics say that the lion’s share of slot-machine profits come, also predictably, from a relatively small percentage of the players—the compulsive and the addicted. Gambling researchers describe these slot zombies as being fearful that another player will sit down on a neighboring stool and distract them by trying to talk to them.
https://kameronmnzp306306.aboutyoublog.com/1661499/slots-garden-no-deposit-free-spins
Central to this game is the ‘Free Spins‘ feature, triggered by landing 3 scatter symbols during one spin. 10 Free Spins are awarded, during spins when a rhino symbol hits it is collected. On the last spin, all collected rhino symbols are placed in random positions on the reel set. Special reels are in play and the super respin feature can not be retriggered. Bermain slot online memang sangat menghibur dan memberikan kegembiraan tersendiri, terlebih saat kita berhasil memenangkan jackpot terbesar. Namun, menang dalam game slot gacor bukanlah hal yang mudah. Anda membutuhkan strategi yang tepat dan sedikit bocoran slot gacor untuk membantu Anda meraih kemenangan. Berikut adalah beberapa tips gacor yang dapat Anda terapkan saat bermain slot online. For a video slot made in 2018, Great Rhino does not exactly push the boat out when it comes to visual design. Indeed, it feels a bit like the studio chose to use a vintage cartoon style, which may or may not appeal to players.
I visited multiple blogs but the audio quality for audio songs current at this site is actually wonderful.
bocor88
bocor88
This article іs actually a pleasant one it assists neᴡ net people,
ѡho аre wishing in favor of blogging.
Alsօ visit my web-site; lajme të transmetimit të drejtpërdrejtë
sapporo88
whoah tһis weblog іs magnificent і love reading yⲟur posts.
Stay uup tһe good woгk! Yoս кnow, many individuals
ɑrе hunting ɑrоᥙnd foг thiѕ info, yߋu can һelp tһеm gгeatly.
Alѕo visit myy website :: Fox News
miya4d
promo code for 1x bet
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99
kantorbola
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99
Selamat datang di Surgaslot !! situs slot deposit dana terpercaya nomor 1 di Indonesia. Sebagai salah satu situs agen slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami menyediakan banyak jenis variasi permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati. Semua permainan juga bisa dimainkan cukup dengan memakai 1 user-ID saja. Surgaslot sendiri telah dikenal sebagai situs slot tergacor dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dimana kami sebagai situs slot online terbaik juga memiliki pelayanan customer service 24 jam yang selalu siap sedia dalam membantu para member. Kualitas dan pengalaman kami sebagai salah satu agen slot resmi terbaik tidak perlu diragukan lagi
LEO娛樂城
https://149.28.131.51/
Прогон сайта с использованием программы “Хрумер” – это способ автоматизированного продвижения ресурса в поисковых системах. Этот софт позволяет оптимизировать сайт с точки зрения SEO, повышая его видимость и рейтинг в выдаче поисковых систем.
Хрумер способен выполнять множество задач, таких как автоматическое размещение комментариев, создание форумных постов, а также генерацию большого количества обратных ссылок. Эти методы могут привести к быстрому увеличению посещаемости сайта, однако их надо использовать осторожно, так как неправильное применение может привести к санкциям со стороны поисковых систем.
Прогон сайта “Хрумером” требует навыков и знаний в области SEO. Важно помнить, что качество контента и органичность ссылок играют важную роль в ранжировании. Применение Хрумера должно быть частью комплексной стратегии продвижения, а не единственным методом.
Важно также следить за изменениями в алгоритмах поисковых систем, чтобы адаптировать свою стратегию к новым требованиям. В итоге, прогон сайта “Хрумером” может быть полезным инструментом для SEO, но его использование должно быть осмотрительным и в соответствии с лучшими практиками.
Blackpanther77
bocor88
bocor88
539直播
parboaboa
今彩539開獎號碼查詢
大樂透開獎號碼查詢
大樂透開獎號碼查詢
威力彩開獎號碼查詢
威力彩開獎號碼查詢
Hello I am so delighted I found your webpage, I really found you by accident, while
I was browsing on Digg for something else,
Anyways I am here now and would just like to
say many thanks for a tremendous post and a all round entertaining
blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have
time to read through it all at the moment but I have saved it and also
added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be
back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the great jo.
三星彩開獎號碼查詢
運彩分析
美棒分析
smtogel
2024總統大選
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99 .
bocor88
bocor88
bata4d
bata4d
hoki1881 promosi
To the malabdali.com webmaster, Your posts are always well presented.
Hello my friend!І wiksh to saay that this article is amazing, nice written and come
woth aⅼmⲟѕt aall vital infos. I’d lіke
to peer extra posts ⅼike tһіs .
Cherck out mmy web site; асман спорт акыркы кабарлар
Howdy! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace
group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really
enjoy your content. Please let me know. Many thanks
blangkon slot
Blangkon slot adalah situs slot gacor dan judi slot online gacor hari ini mudah menang. Blangkonslot menyediakan semua permainan slot gacor dan judi online terbaik seperti, slot online gacor, live casino, judi bola/sportbook, poker online, togel online, sabung ayam dll. Hanya dengan 1 user id kamu sudah bisa bermain semua permainan yang sudah di sediakan situs terbaik BLANGKON SLOT. Selain itu, kamu juga tidak usah ragu lagi untuk bergabung dengan kami situs judi online terbesar dan terpercaya yang akan membayar berapapun kemenangan kamu.
rikvip
bocor88
bocor88
Heya i am foor tһe first time herе. Ӏ found this board and
I find It rеally useful & it helped me oսt much.
I hope to ɡive something bɑck ɑnd help others lіke you aided me.
my website: Kuinka löytää tämän päivän trendi?
smtogel
winstarbet
winstarbet
Mestres Místicos é o maior portal de Tarot Online do Brasil e Portugal, o site conta com os melhores Místicos online, tarólogos, cartomantes, videntes, sacerdotes, 24 horas online para fazer sua consulta de tarot pago por minuto via chat ao vivo, temos mais de 700 mil atendimentos e estamos no ar desde 2011
If yoս desire to tɑke mսch from thіs article then y᧐u have to apply tgese methods to yoᥙr wоn blog.
My website; pede togel via dana
bocor88
bocor88
I think that everything said made a lot of sense.
But, think on this, what if you wrote a catchier post title?
I ain’t suggesting your information isn’t solid, however suppose you added a title that grabbed a person’s attention? I mean Millman theorem – MAlabdali is a little plain. You ought to glance at Yahoo’s front
page and watch how they write post titles to grab viewers to open the links.
You might try adding a video or a picture or
two to get people excited about what you’ve written. Just my opinion, it
would bring your posts a little bit more interesting.
Thɑnks foor every other great article. Thhe ⲣlace else could anyone get that kind of informɑtion іn such an ideal method
оf writing? I haѵe а presentation neⲭt weеk, and I’m
on tһe loоk ffor such іnformation.
Feel free to surf to my һomepage; pede togel link alternatif
Heya i am for the primary time here. I came across this board and I
to find It truly helpful & it helped me out a lot. I’m hoping to provide one
thing again and aid others such as you aided me.
Join the gaming revolution! Our platform offers an extensive library of games catering to every gamer’s dream. Lucky cola
Нi there! I’m at work surfing around yοur blog fгom my new apple iphone!Јust
wɑnted to say I love reading үour blog and look forward to alⅼ yoᥙr posts!
Carry ⲟn the ezcellent worҝ!
Loook at my webpage: wonplay 888
Hey There. I found your weblog using msn. That is a very smartly written article.
I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to learn extra of your useful information.
Thank you for the post. I’ll certainly return.
supermoney88
supermoney88
Tentang SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik 2020 di Indonesia
Di era digital seperti sekarang, perjudian online telah menjadi pilihan hiburan yang populer. Terutama di Indonesia, SUPERMONEY88 telah menjadi pelopor dalam dunia game online. Dengan fokus pada deposit pulsa dan berbagai jenis permainan judi, kami telah menjadi situs game online terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia.
Agen Game Online Terlengkap:
Kami bangga menjadi tujuan utama Anda untuk segala bentuk taruhan mesin game online. Di SUPERMONEY88, Anda dapat menemukan beragam permainan, termasuk game bola Sportsbook, live casino online, poker online, dan banyak jenis taruhan lainnya yang wajib Anda coba. Hanya dengan mendaftar 1 ID, Anda dapat memainkan seluruh permainan judi yang tersedia. Kami adalah situs slot online terbaik yang menawarkan pilihan permainan terlengkap.
Lisensi Resmi dan Keamanan Terbaik:
Keamanan adalah prioritas utama kami. SUPERMONEY88 adalah agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation). Lisensi ini menunjukkan komitmen kami untuk menyediakan lingkungan perjudian yang aman dan adil. Kami didukung oleh server hosting berkualitas tinggi yang memastikan akses cepat dan keamanan sistem dengan metode enkripsi terkini di dunia.
Deposit Pulsa dengan Potongan Terendah:
Kami memahami betapa pentingnya kenyamanan dalam melakukan deposit. Itulah mengapa kami memungkinkan Anda untuk melakukan deposit pulsa dengan potongan terendah dibandingkan dengan situs game online lainnya. Kami menerima deposit pulsa dari XL dan Telkomsel, serta melalui E-Wallet seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart. Kemudahan ini menjadikan SUPERMONEY88 sebagai salah satu situs GAME ONLINE PULSA terbesar di Indonesia.
Agen Game Online SBOBET Terpercaya:
Kami dikenal sebagai agen game online SBOBET terpercaya yang selalu membayar kemenangan para member. SBOBET adalah perusahaan taruhan olahraga terkemuka dengan beragam pilihan olahraga seperti sepak bola, basket, tenis, hoki, dan banyak lainnya. SUPERMONEY88 adalah jawaban terbaik jika Anda mencari agen SBOBET yang dapat dipercayai. Selain SBOBET, kami juga menyediakan CMD365, Song88, UBOBET, dan lainnya. Ini menjadikan kami sebagai bandar agen game online bola terbaik sepanjang masa.
Game Casino Langsung (Live Casino) Online:
Jika Anda suka pengalaman bermain di kasino fisik, kami punya solusi. SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan jenis permainan judi live casino online. Anda dapat menikmati game seperti baccarat, dragon tiger, blackjack, sic bo, dan lainnya secara langsung. Semua permainan disiarkan secara LIVE, sehingga Anda dapat merasakan atmosfer kasino dari kenyamanan rumah Anda.
Game Poker Online Terlengkap:
Poker adalah permainan strategi yang menantang, dan kami menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan poker online. SUPERMONEY88 adalah bandar game poker online terlengkap di Indonesia. Mulai dari Texas Hold’em, BlackJack, Domino QQ, BandarQ, hingga AduQ, semua permainan poker favorit tersedia di sini.
Promo Menarik dan Layanan Pelanggan Terbaik:
Kami juga menawarkan banyak promo menarik yang bisa Anda nikmati saat bermain, termasuk promo parlay, bonus deposit harian, cashback, dan rollingan mingguan. Tim Customer Service kami yang profesional dan siap membantu Anda 24/7 melalui Live Chat, WhatsApp, Facebook, dan media sosial lainnya.
Jadi, jangan ragu lagi! Bergabunglah dengan SUPERMONEY88 sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman perjudian online terbaik di Indonesia.
Excellent web site уou’ve ɡot һere.. It’s harɗ to fіnd
hіgh-quality writing ⅼike yours nowadays. I ѕeriously aρpreciate people ⅼike you!
Take care!!
Feel free to visit my web-site; Link Alternatif Ahha4d
smtogel4d
slot pro88
target88 slot
sapporo88
Quality articles or reviews is the key to attract the viewers to pay
a quick visit the web site, that’s what this web site is providing.
PRO88
slot supermoney88
Howdy very coo blog!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Wondertul ..
Ι’ll bookmaqrk уour blpog and take tһе feeds alsо?
I’m happү to seek out ѕo many helpful info hеre in the post, we need work out moe
techniques in thiѕ regard, tһanks for sharing.
. . . . .
My web ⲣage; pedetogel
Ԍreetings! Vеry uѕeful advice witһin this post!
Ӏt is the littⅼe chanes which will makle the largest
ϲhanges. Thаnks fⲟr sharing!
Heree iѕ my web site … Rajabandot login
Hello malabdali.com owner, Thanks for the well-researched and well-written post!
RuneScape, a beloved online gaming world for many, offers a myriad of opportunities for players to amass wealth and power within the game. While earning RuneScape Gold (RS3 or OSRS GP) through gameplay is undoubtedly a rewarding experience, some players seek a more convenient and streamlined path to enhancing their RuneScape journey. In this article, we explore the advantages of purchasing OSRS Gold and how it can elevate your RuneScape adventure to new heights.
A Shortcut to Success:
a. Boosting Character Power:
In the world of RuneScape, character strength is significantly influenced by the equipment they wield and their skill levels. Acquiring top-tier gear and leveling up skills often requires time and effort. Purchasing OSRS Gold allows players to expedite this process and empower their characters with the best equipment available.
b. Tackling Formidable Foes:
RuneScape is replete with challenging monsters and bosses. With the advantage of enhanced gear and skills, players can confidently confront these formidable adversaries, secure victories, and reap the rewards that follow. OSRS Gold can be the key to overcoming daunting challenges.
c. Questing with Ease:
Many RuneScape quests present complex puzzles and trials. By purchasing OSRS Gold, players can eliminate resource-gathering and level-grinding barriers, making quests smoother and more enjoyable. It’s all about focusing on the adventure, not the grind.
Expanding Possibilities:
d. Rare Items and Valuable Equipment:
The RuneScape world is rich with rare and coveted items. By acquiring OSRS Gold, players can gain access to these valuable assets. Rare armor, powerful weapons, and other coveted equipment can be yours, enhancing your character’s capabilities and opening up new gameplay experiences.
e. Participating in Limited-Time Events:
RuneScape often features limited-time in-game events with exclusive rewards. Having OSRS Gold at your disposal allows you to fully embrace these events, purchase unique items, and partake in memorable experiences that may not be available to others.
Conclusion:
Purchasing OSRS Gold undoubtedly offers RuneScape players a convenient shortcut to success. By empowering characters with superior gear and skills, players can take on any challenge the game throws their way. Furthermore, the ability to purchase rare items and participate in exclusive events enhances the overall gaming experience, providing new dimensions to explore within the RuneScape universe. While earning gold through gameplay remains a cherished aspect of RuneScape, buying OSRS Gold can make your journey even more enjoyable, rewarding, and satisfying. So, embark on your adventure, equip your character, and conquer RuneScape with the power of OSRS Gold.
RSG雷神
RSG雷神:電子遊戲的新維度
在電子遊戲的世界裡,不斷有新的作品出現,但要在眾多的遊戲中脫穎而出,成為玩家心中的佳作,需要的不僅是創意,還需要技術和努力。而當我們談到RSG雷神,就不得不提它如何將遊戲提升到了一個全新的層次。
首先,RSG已經成為了許多遊戲愛好者的口中的熱詞。每當提到RSG雷神,人們首先想到的就是品質保證和無與倫比的遊戲體驗。但這只是RSG的一部分,真正讓玩家瘋狂的,是那款被稱為“雷神之鎚”的老虎機遊戲。
RSG雷神不僅僅是一款老虎機遊戲,它是一場視覺和聽覺的盛宴。遊戲中精緻的畫面、逼真的音效和流暢的動畫,讓玩家仿佛置身於雷神的世界,每一次按下開始鍵,都像是在揮動雷神的鎚子,帶來震撼的遊戲體驗。
這款遊戲的成功,並不只是因為它的外觀或音效,更重要的是它那精心設計的遊戲機制。玩家可以根據自己的策略選擇不同的下注方式,每一次旋轉,都有可能帶來意想不到的獎金。這種刺激和期待,使得玩家一次又一次地沉浸在遊戲中,享受著每一分每一秒。
但RSG雷神並沒有因此而止步。它的研發團隊始終在尋找新的創意和技術,希望能夠為玩家帶來更多的驚喜。無論是遊戲的內容、機制還是畫面效果,RSG雷神都希望能夠做到最好,成為遊戲界的佼佼者。
總的來說,RSG雷神不僅僅是一款遊戲,它是一種文化,一種追求。對於那些熱愛遊戲、追求刺激的玩家來說,它提供了一個完美的平台,讓玩家能夠體驗到真正的遊戲樂趣。
Your epic journey starts with our games. Hawkplay
Kampus Unggul
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online
bocor88
buy osrs gold
buy osrs gold
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online
Kampus Unggul
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online.
Hola! I’ve been reading your site for a long time now and finally got
the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out
from Lubbock Tx! Just wanted to tell you keep up the
excellent job!
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online.
Dear immortals, I need some wow gold inspiration to create.
hasilkan uang dengan game di hoki1881
https://kamagra.icu/# buy Kamagra
Great post! We will be linking to this particularly great article on our website.
Keep up the great writing.
menangkan uang di situs hoki1881
Hi malabdali.com administrator, Thanks for the well-structured and well-presented post!
tombak118
tombak118
I’m гeally enjoying tһe design аnd layout of youг website.It’s a very easy ⲟn the eyes
whіch mаkes itt mucfh mⲟгe pleasant for me to come һere аnd visit m᧐re often. Ɗid уоu hire out a developer to creeate your theme?
Ꮐreat work!
Alsso visit mʏ homеⲣage … jasa backlink terpercaya
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in truth used to
be a enjoyment account it. Look complicated to far added agreeable from you!
However, how can we communicate?
When І originally commented Ι clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now eqch time ɑ comment is addeⅾ Ι get severaⅼ emails with the same сomment.
Iѕ tһere any way you caan remove people from that service?
Ꭲhank you!
Have a look at mу web page – link penambah like youtube
whoah this blog is fantastic i like reading your articles.
Stay up the great work! You already know, lots of people are hunting around for this info, you could aid them greatly.
I really like what you guys are usually up too.
This sort of clever work and coverage! Keep up the good works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to
my own blogroll.
Kampus Unggul
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online.
Usually I don’t read post on blogs, һowever Ι would ⅼike to say tһat this write-սⲣ
ѵery pressured me tօ check оut and do it!
Your writing taste has beеn surprised mе. Thank yoᥙ, quite grdeat article.
mү ⲣage … jasa seo page one
nettruyen
Family reunion gifts
Wow, that’s what I was searching for, what a data!
present here at this blog, thanks admin of this web
page.
If you are going for best contents like I do, only go to see this web page
all the time for the reason that it offers quality contents, thanks
bookmarked!!, I reɑlly lіke your blog!
Also visit my site … jasa pbn judi
Hi malabdali.com admin, You always provide valuable feedback and suggestions.
Dear malabdali.com webmaster, You always provide useful links and resources.
microlearning library
nettruyenmax
Excellent website you have here but I was curious if
you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics discussed in this article?
I’d really love to be a part of online community where I can get
suggestions from other experienced people
that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know.
Many thanks!
Dear immortals, I need some wow gold inspiration to create.
Manicure
DG
http://kamagra.icu/# sildenafil oral jelly 100mg kamagra
nettruyenmax
http://kamagra.icu/# Kamagra tablets
https://www.cooks.am/pag/mostbet_promokod.html
Промокод 1xBet «Max2x» 2023: разблокируйте бонус 130%
Промокод 1xBet 2023 года «Max2x» может улучшить ваш опыт онлайн-ставок. Используйте его при регистрации, чтобы получить бонус на депозит в размере 130%. Вот краткий обзор того, как это работает, где его найти и его преимущества.
Понимание промокодов 1xBet
Промокоды 1xBet — это специальные предложения букмекерской конторы, которые сделают ваши ставки еще интереснее. Они представляют собой уникальные комбинации символов, букв и цифр, открывающие бонусы и привилегии как для новых, так и для существующих игроков.
Новые игроки часто используют промокоды при регистрации, привлекая их заманчивыми бонусами. Это одноразовое использование для создания новой учетной записи. Существующие клиенты получают различные промокоды, соответствующие их потребностям.
Получение промокодов 1xBet
Для начинающих:
Новые игроки могут найти коды в Интернете, часто на веб-сайтах и форумах, что мотивирует их создавать учетные записи, предлагая бонусы. Вы также можете найти их на страницах 1xBet в социальных сетях или на партнерских платформах.
От букмекера:
1xBet награждает постоянных клиентов промокодами, которые доставляются по электронной почте или в уведомлениях учетной записи.
Демонстрация промокода:
Проверяйте «Витрину промокодов» на веб-сайте 1xBet, чтобы регулярно обновлять коды.
Таким образом, промокод 1xBet «Max2x» расширяет возможности ваших онлайн-ставок. Это ценный инструмент для новичков и опытных игроков. Следите за этими кодами из различных источников, чтобы максимизировать свои приключения в ставках 1xBet.
SURGASLOT77 – #1 Top Gamer Website in Indonesia
SURGASLOT77 merupakan halaman website hiburan online andalan di Indonesia.
Hi malabdali.com administrator, Your posts are always well-supported by facts and figures.
Hi malabdali.com webmaster, You always provide great information and insights.
1xbet
Абузоустойчивый VPS
Абузоустойчивый VPS
NBA戰績
Kantor bola Merupakan agen slot terpercaya di indonesia dengan RTP kemenangan sangat tinggi 98.9%. Bermain di kantorbola akan sangat menguntungkan karena bermain di situs kantorbola sangat gampang menang.
manclub
Experience heart-racing adventures here. Lucky Cola
I like the valuable information you provide in your articles.
I will bookmark your blog and check again here
regularly. I am quite certain I’ll learn a lot of new stuff
right here! Good luck for the next!
Nicely put. Kudos.
best paper writing service uk essay writing service forum dating site profile writing service
You actually explained this perfectly!
choosing a resume writing service college paper writing service writing an essay
alternatif surgaslot
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。
казино brillx официальный сайт играть
https://brillx-kazino.com
Как никогда прежде, в 2023 году Brillx Казино предоставляет широкий выбор увлекательных игровых автоматов, которые подарят вам незабываемые моменты радости и адреналина. С нами вы сможете насладиться великолепной графикой, захватывающими сюжетами и щедрыми выплатами. Бриллкс казино разнообразит ваш досуг, окунув вас в мир волнения и возможностей!Но если вы ищете большее, чем просто весело провести время, Brillx Казино дает вам возможность играть на деньги. Наши игровые аппараты – это не только средство развлечения, но и потенциальный источник невероятных доходов. Бриллкс Казино сотрясает стереотипы и вносит свежий ветер в мир азартных игр.
manclub
What’s up, I desire to subscribe for this weblog to take latest updates, thus where can i do it please assist.
In recent years, the landscape of digital entertainment and online gaming has expanded, with ‘nha cai’ (betting houses or bookmakers) becoming a significant part. Among these, ‘nha cai RG’ has emerged as a notable player. It’s essential to understand what these entities are and how they operate in the modern digital world.
A ‘nha cai’ essentially refers to an organization or an online platform that offers betting services. These can range from sports betting to other forms of wagering. The growth of internet connectivity and mobile technology has made these services more accessible than ever before.
Among the myriad of options, ‘nha cai RG’ has been mentioned frequently. It appears to be one of the numerous online betting platforms. The ‘RG’ could be an abbreviation or a part of the brand’s name. As with any online betting platform, it’s crucial for users to understand the terms, conditions, and the legalities involved in their country or region.
The phrase ‘RG nha cai’ could be interpreted as emphasizing the specific brand ‘RG’ within the broader category of bookmakers. This kind of focus suggests a discussion or analysis specific to that brand, possibly about its services, user experience, or its standing in the market.
Finally, ‘Nha cai Uy tin’ is a term that people often look for. ‘Uy tin’ translates to ‘reputable’ or ‘trustworthy.’ In the context of online betting, it’s a crucial aspect. Users typically seek platforms that are reliable, have transparent operations, and offer fair play. Trustworthiness also encompasses aspects like customer service, the security of transactions, and the protection of user data.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of ‘nha cai,’ such as ‘nha cai RG,’ and the importance of ‘Uy tin’ is vital for anyone interested in or participating in online betting. It’s a world that offers entertainment and opportunities but also requires a high level of awareness and responsibility.
farmacia online barata vardenafilo farmacia online envГo gratis
farmacia envГos internacionales cialis 20 mg precio farmacia farmacia online internacional
Hi, yeah tһis paragraph iss аctually goօԁ and I һave learned lot оf things from it on the topic օf blogging.
thɑnks.
My webpage; actualités tendances sur les réseaux sociaux 2023
farmacias baratas online envГo gratis mejores farmacias online farmacia envГos internacionales
Hi thеre wouⅼd уoᥙ mind stating whic blog platform ʏou’re ԝorking
wіth? Ι’m g᧐ing too start my own blog soon but I’m һaving а haqrd tіme selecting betweеn BlogEngine/Wordpress/Β2evolution and Drupal.
The reason I ask is beccause уoᥙr design and style sеems different then most blogs ɑnd Ι’m loⲟking
for sߋmething unique. P.S S᧐rry
for gеtting off-topic bᥙt I had tto aѕk!
Alѕo visit my pɑge … mga headline ng balita sa palakasan ngayon
купить бетон дмитров
comprar viagra en espaГ±a envio urgente viagra precio comprar viagra online en andorra
Hi malabdali.com owner, Your posts are always well-written and easy to understand.
19dewa slot
I have read so many posts regarding the blogger lovers but this paragraph is
genuinely a nice paragraph, keep it up.
farmacia online envГo gratis farmacias online seguras farmacias online seguras
п»їfarmacia online: comprar cialis online sin receta – farmacia envГos internacionales
Why users still use to read news papers when in this
technological globe the whole thing is available on web?
farmacia envГos internacionales: kamagra – farmacias online baratas
брилкс казино
https://brillx-kazino.com
Предоставив широкий спектр игр и вариантов ставок, мы делаем ставку на то, что каждый игрок найдет что-то особенное для себя. Brillx Казино – это не просто место для азартных игр, это место, где рождаются легенды и судьбы переплетаются с риском.Brillx Казино – это не только великолепный ассортимент игр, но и высокий уровень сервиса. Наша команда профессионалов заботится о каждом игроке, обеспечивая полную поддержку и честную игру. На нашем сайте брилкс казино вы найдете не только классические слоты, но и уникальные вариации игр, созданные специально для вас.
Pharmacie en ligne pas cher: pharmacie en ligne pas cher – acheter mГ©dicaments Г l’Г©tranger
acheter mГ©dicaments Г l’Г©tranger cialis prix Pharmacie en ligne pas cher
19dewa daftar
farmacia envГos internacionales: farmacias baratas online envio gratis – п»їfarmacia online
Pharmacie en ligne fiable: Pharmacie en ligne France – acheter medicament a l etranger sans ordonnance
Pharmacie en ligne pas cher Levitra 20mg prix en pharmacie Pharmacie en ligne livraison 24h
Pharmacie en ligne livraison gratuite: levitra generique sites surs – Pharmacie en ligne pas cher
Acheter mГ©dicaments sans ordonnance sur internet achat kamagra Pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
hoki 1881
19dewa login
프라그마틱 슬롯
아깝다, 아깝다, 직접 돈을 주는 것이 좋지 않을까요?
Pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance: Levitra 20mg prix en pharmacie – Pharmacie en ligne pas cher
Pharmacie en ligne livraison rapide kamagra en ligne Pharmacie en ligne fiable
1881hoki
https://potenzmittel.men/# п»їonline apotheke
http://viagrakaufen.store/# In welchen europäischen Ländern ist Viagra frei verkäuflich
http://cialiskaufen.pro/# online-apotheken
http://potenzmittel.men/# online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Hello malabdali.com webmaster, You always provide clear explanations and step-by-step instructions.
http://kamagrakaufen.top/# online apotheke versandkostenfrei
https://potenzmittel.men/# online apotheke preisvergleich
I have read some excellent stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting.
I surprise how much attempt you set to create this sort of fantastic informative web
site.
https://viagrakaufen.store/# Viagra online bestellen Schweiz
https://kamagrakaufen.top/# п»їonline apotheke
online-apotheken apotheke online versandkostenfrei п»їonline apotheke
https://potenzmittel.men/# online apotheke deutschland
https://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# best online pharmacies in mexico
empresa de site
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/cs/register?ref=FIHEGIZ8
https://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# best online pharmacies in mexico
Wonderful web site. Lots of useful information here. I’m sending it to some buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks on your effort!
Boostaro increases blood flow to the reproductive organs, leading to stronger and more vibrant erections. It provides a powerful boost that can make you feel like you’ve unlocked the secret to firm erections
ErecPrime is a 100% natural supplement which is designed specifically
Puravive introduced an innovative approach to weight loss and management that set it apart from other supplements.
https://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# best online pharmacies in mexico
Prostadine™ is a revolutionary new prostate support supplement designed to protect, restore, and enhance male prostate health.
프라그마틱 슬롯
Hongzhi 황제는 등 뒤로 손을 대고 고개를 저었다. “정말 존경합니다.”
Aizen Power is a dietary supplement for male enhancement
Neotonics is a dietary supplement that offers help in retaining glowing skin and maintaining gut health for its users. It is made of the most natural elements that mother nature can offer and also includes 500 million units of beneficial microbiome.
EndoPeak is a male health supplement with a wide range of natural ingredients that improve blood circulation and vitality.
Glucotrust is one of the best supplements for managing blood sugar levels or managing healthy sugar metabolism.
EyeFortin is a natural vision support formula crafted with a blend of plant-based compounds and essential minerals. It aims to enhance vision clarity, focus, and moisture balance.
Support the health of your ears with 100% natural ingredients, finally being able to enjoy your favorite songs and movies
GlucoBerry is a meticulously crafted supplement designed by doctors to support healthy blood sugar levels by harnessing the power of delphinidin—an essential compound.
Free Shiping If You Purchase Today!
ProDentim is a nutritional dental health supplement that is formulated to reverse serious dental issues and to help maintain good dental health.
https://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
world pharmacy india pharmacy website india – best india pharmacy indiapharmacy.guru
male ed drugs erectile dysfunction pills – cheapest ed pills edpills.tech
SonoVive™ is a completely natural hearing support formula made with powerful ingredients that help heal tinnitus problems and restore your hearing
BioFit™ is a Nutritional Supplement That Uses Probiotics To Help You Lose Weight
オンラインカジノレビュー:選択の重要性
オンラインカジノの世界への入門
オンラインカジノは、インターネット上で提供される多様な賭博ゲームを通じて、世界中のプレイヤーに無限の娯楽を提供しています。これらのプラットフォームは、スロット、テーブルゲーム、ライブディーラーゲームなど、様々なゲームオプションを提供し、実際のカジノの経験を再現します。
オンラインカジノレビューの重要性
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、オンラインカジノレビューの役割が非常に重要です。レビューは、カジノの信頼性、ゲームの多様性、顧客サービスの質、ボーナスオファー、支払い方法、出金条件など、プレイヤーが知っておくべき重要な情報を提供します。良いレビューは、利用者の実際の体験に基づいており、新規プレイヤーがカジノを選択する際の重要なガイドとなります。
レビューを読む際のポイント
信頼性とライセンス:カジノが適切なライセンスを持ち、公平なゲームプレイを提供しているかどうか。
ゲームの選択:多様なゲームオプションが提供されているかどうか。
ボーナスとプロモーション:魅力的なウェルカムボーナス、リロードボーナス、VIPプログラムがあるかどうか。
顧客サポート:サポートの応答性と有効性。
出金オプション:出金の速度と方法。
プレイヤーの体験
良いオンラインカジノレビューは、実際のプレイヤーの体験に基づいています。これには、ゲームプレイの楽しさ、カスタマーサポートへの対応、そして出金プロセスの簡単さが含まれます。プレイヤーのフィードバックは、カジノの品質を判断するのに役立ちます。
結論
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、詳細なオンラインカジノレビューを参照することが重要です。これらのレビューは、安全で楽しいギャンブル体験を確実にするための信頼できる情報源となります。適切なカジノを選ぶことは、オンラインギャンブルでの成功への第一歩です。
Dentitox Pro is a liquid dietary solution created as a serum to support healthy gums and teeth. Dentitox Pro formula is made in the best natural way with unique, powerful botanical ingredients that can support healthy teeth.
The ingredients of Endo Pump Male Enhancement are all-natural and safe to use.
Gorilla Flow is a non-toxic supplement that was developed by experts to boost prostate health for men.
I have recently started a site, the info you offer on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work. “There can be no real freedom without the freedom to fail.” by Erich Fromm.
online pharmacy canada best canadian pharmacy – canada discount pharmacy canadiandrugs.tech
best canadian pharmacy online legit canadian pharmacy – pet meds without vet prescription canada canadiandrugs.tech
GlucoCare is a natural and safe supplement for blood sugar support and weight management. It fixes your metabolism and detoxifies your body.
Nervogen Pro, A Cutting-Edge Supplement Dedicated To Enhancing Nerve Health And Providing Natural Relief From Discomfort. Our Mission Is To Empower You To Lead A Life Free From The Limitations Of Nerve-Related Challenges. With A Focus On Premium Ingredients And Scientific Expertise.
Neurodrine is a fantastic dietary supplement that protects your mind and improves memory performance. It can help you improve your focus and concentration.
InchaGrow is an advanced male enhancement supplement. The Formula is Easy to Take Each Day, and it Only Uses. Natural Ingredients to Get the Desired Effect
HoneyBurn is a 100% natural honey mixture formula that can support both your digestive health and fat-burning mechanism. Since it is formulated using 11 natural plant ingredients, it is clinically proven to be safe and free of toxins, chemicals, or additives.
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。
GlucoFlush™ is an all-natural supplement that uses potent ingredients to control your blood sugar.
essay on eid milan party https://bookmarkmargin.com/story16103031/indicators-on-harvard-college-essay-you-should-know cheapest essay writing
SynoGut is a natural dietary supplement specifically formulated to support digestive function and promote a healthy gut microbiome.
GlucoFort is a 100% safe
Amiclear is a dietary supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels and assist with glucose metabolism. It contains eight proprietary blends of ingredients that have been clinically proven to be effective.
Claritox Pro™ is a natural dietary supplement that is formulated to support brain health and promote a healthy balance system to prevent dizziness, risk injuries, and disability. This formulation is made using naturally sourced and effective ingredients that are mixed in the right way and in the right amounts to deliver effective results.
canadian pharmacy 24h com safe onlinecanadianpharmacy 24 – pharmacy canadian superstore canadiandrugs.tech
is canadian pharmacy legit precription drugs from canada – canadian pharmacy 365 canadiandrugs.tech
Metabo Flex Is a Dietary Supplement Formulated Using a Proprietary Blend Of Six Rainforest Super Nutrients And Plants Designed To Boost Metabolism And Reduce Weight.
TropiSlim is a unique dietary supplement designed to address specific health concerns, primarily focusing on weight management and related issues in women, particularly those over the age of 40.
Metabo Flex is a nutritional formula that enhances metabolic flexibility by awakening the calorie-burning switch in the body. The supplement is designed to target the underlying causes of stubborn weight gain utilizing a special “miracle plant” from Cambodia that can melt fat 24/7.
SynoGut is an all-natural dietary supplement that is designed to support the health of your digestive system, keeping you energized and active.
Glucofort Blood Sugar Support is an all-natural dietary formula that works to support healthy blood sugar levels. It also supports glucose metabolism. According to the manufacturer, this supplement can help users keep their blood sugar levels healthy and within a normal range with herbs, vitamins, plant extracts, and other natural ingredients.
GlucoFlush Supplement is an all-new blood sugar-lowering formula. It is a dietary supplement based on the Mayan cleansing routine that consists of natural ingredients and nutrients.
Gorilla Flow is a non-toxic supplement that was developed by experts to boost prostate health for men. It’s a blend of all-natural nutrients, including Pumpkin Seed Extract Stinging Nettle Extract, Gorilla Cherry and Saw Palmetto, Boron, and Lycopene.
GlucoCare is a dietary supplement designed to promote healthy blood sugar levels, manage weight, and curb unhealthy sugar absorption. It contains a natural blend of ingredients that target the root cause of unhealthy glucose levels.
Nervogen Pro is a cutting-edge dietary supplement that takes a holistic approach to nerve health. It is meticulously crafted with a precise selection of natural ingredients known for their beneficial effects on the nervous system. By addressing the root causes of nerve discomfort, Nervogen Pro aims to provide lasting relief and support for overall nerve function.
Herpagreens is a dietary supplement formulated to combat symptoms of herpes by providing the body with high levels of super antioxidants, vitamins
Manufactured in an FDA-certified facility in the USA, EndoPump is pure, safe, and free from negative side effects. With its strict production standards and natural ingredients, EndoPump is a trusted choice for men looking to improve their sexual performance.
FitSpresso stands out as a remarkable dietary supplement designed to facilitate effective weight loss. Its unique blend incorporates a selection of natural elements including green tea extract, milk thistle, and other components with presumed weight loss benefits.
Introducing FlowForce Max, a solution designed with a single purpose: to provide men with an affordable and safe way to address BPH and other prostate concerns. Unlike many costly supplements or those with risky stimulants, we’ve crafted FlowForce Max with your well-being in mind. Don’t compromise your health or budget – choose FlowForce Max for effective prostate support today!
SonoVive is an all-natural supplement made to address the root cause of tinnitus and other inflammatory effects on the brain and promises to reduce tinnitus, improve hearing, and provide peace of mind. SonoVive is is a scientifically verified 10-second hack that allows users to hear crystal-clear at maximum volume. The 100% natural mix recipe improves the ear-brain link with eight natural ingredients. The treatment consists of easy-to-use pills that can be added to one’s daily routine to improve hearing health, reduce tinnitus, and maintain a sharp mind and razor-sharp focus.
TerraCalm is an antifungal mineral clay that may support the health of your toenails. It is for those who struggle with brittle, weak, and discoloured nails. It has a unique blend of natural ingredients that may work to nourish and strengthen your toenails.
buying ed pills online best ed treatment pills – compare ed drugs edpills.tech
pharmacy website india india online pharmacy – buy prescription drugs from india indiapharmacy.guru
オンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。
https://google.com.mt/url?q=https://www.michalsmolen.com
상자를 여는 순간 모두의 시선을 사로잡기에 충분했다.
safe reliable canadian pharmacy canada cloud pharmacy – adderall canadian pharmacy canadiandrugs.tech
certified canadian pharmacy escrow pharmacy canada – canadian pharmacy review canadiandrugs.tech
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и Дедик Сервер: Оптимальное Решение для Вашего Проекта
В мире современных вычислений виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и дедик сервера становятся ключевыми элементами успешного бизнеса и онлайн-проектов. Выбор оптимальной операционной системы и типа сервера являются решающими шагами в создании надежной и эффективной инфраструктуры. Наши VPS/VDS серверы Windows и Linux, доступные от 13 рублей, а также дедик серверы, предлагают целый ряд преимуществ, делая их неотъемлемыми инструментами для развития вашего проекта.
https://sportsinfonow.com/
http://clomid.site/# how to get generic clomid for sale
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/pt-BR/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
Wede303 menjadi tempat kumpulan games terbaik dan terpercaya
yang telah berdiri seja tahun 2010 dan selalu berupaya meningkatkan pelayanan kenyamanan setiap member
https://ciprofloxacin.life/# antibiotics cipro
Its such as you learn my mind! You seem to know so much about this, such as you wrote the book in it or something.
I feel that you could do with a few % to power the message house a bit,
however instead of that, that is excellent blog.
A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back. save refuges
오공 슬롯
잠시 후 두 명의 타타르가 따뜻한 정자에 들어갔다.
my ambition essay in hindi https://payforessay79010.dailyblogzz.com/23905169/rumored-buzz-on-pay-someone-to-do-an-essay my secret ambition essay
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения играет решающую роль в успешной работе вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с. Это гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Итак, при выборе виртуального выделенного сервера VPS, обеспечьте своему проекту надежность, высокую производительность и защиту от DDoS. Получите доступ к качественной инфраструктуре с поддержкой Windows и Linux уже от 13 рублей
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/ro/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
This article offers clear idea in support of the new viewers of blogging, that genuinely how to do blogging.
http://paxlovid.win/# п»їpaxlovid
Мощный дедик
Аренда мощного дедика (VPS): Абузоустойчивость, Эффективность, Надежность и Защита от DDoS от 13 рублей
Выбор виртуального сервера – это важный этап в создании успешной инфраструктуры для вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы предоставляют аренду как под операционные системы Windows, так и Linux, с доступом к накопителям SSD eMLC. Эти накопители гарантируют высокую производительность и надежность, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу ваших приложений независимо от выбранной операционной системы.
выбрать сервер
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с**
Скорость интернет-соединения – еще один важный момент для успешной работы вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы, арендуемые под Windows и Linux, предоставляют доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, обеспечивая быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
GTA777
Dear malabdali.com owner, Thanks for the great post!
https://prednisone.bid/# prednisolone prednisone
GTA777
whoah this blog is fantastic i really like reading your posts.
Keep up the good work! You realize, a lot of individuals are looking round for
this info, you could help them greatly.
http://paxlovid.win/# paxlovid pill
RG Casino
https://clomid.site/# where can i buy generic clomid without a prescription
Hi malabdali.com admin, Thanks for sharing your thoughts!
Buy discount supplements, vitamins, health supplements, probiotic supplements. Save on top vitamin and supplement brands.
온카판
사실 어젯밤 작은 홀에서 그는 배를 태울 준비가 되어 있었다.
Cortexi is an effective hearing health support formula that has gained positive user feedback for its ability to improve hearing ability and memory. This supplement contains natural ingredients and has undergone evaluation to ensure its efficacy and safety. Manufactured in an FDA-registered and GMP-certified facility, Cortexi promotes healthy hearing, enhances mental acuity, and sharpens memory.
Поставщик предоставляет основное управление виртуальными серверами (VPS), предлагая клиентам разнообразие операционных систем для выбора (Windows Server, Linux CentOS, Debian).
I’m not sᥙre wwhy bᥙt thіs web site іs loading verʏ slow for me.
Is anyone else having this prblem or is it a problem on my еnd?
I’ll check back later ⲟn and ѕee if thе prߋblem still exists.
My blog post; Live sportnieuws voetbal
Keep this going please, great job!
where can i buy clomid no prescription: where to get generic clomid price – can you buy cheap clomid now
FitSpresso stands out as a remarkable dietary supplement designed to facilitate effective weight loss. Its unique blend incorporates a selection of natural elements including green tea extract, milk thistle, and other components with presumed weight loss benefits.
Sight Care is a daily supplement proven in clinical trials and conclusive science to improve vision by nourishing the body from within. The Sight Care formula claims to reverse issues in eyesight, and every ingredient is completely natural.
https://amoxil.icu/# amoxil pharmacy
https://ciprofloxacin.life/# antibiotics cipro
While improving eyesight isn’t often the goal of consumers who wear their glasses religiously, it doesn’t mean they’re stuck where they are.
І’mvery hɑppy tto discover this web site. Ι ᴡant to to
thank you for yⲟur time fⲟr thіs partіcularly fantastic read!!
I definitely savored every ƅit of it andd і alѕo have youu saved ɑs a favorite to lօoқ аt new thingѕ in your site.
My page: DafaToto
I think thee admin of this web site is in fаct ᴡorking һard in support
of hiis website, fоr the reason thɑt hеre every
іnformation is quality based data.
Ꮇy blog; notizie di tendenza oggi
http://amoxil.icu/# amoxicillin for sale online
https://amoxil.icu/# amoxicillin 500mg capsules
Дедик сервер
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и Дедик Сервер: Оптимальное Решение для Вашего Проекта
В мире современных вычислений виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и дедик сервера становятся ключевыми элементами успешного бизнеса и онлайн-проектов. Выбор оптимальной операционной системы и типа сервера являются решающими шагами в создании надежной и эффективной инфраструктуры. Наши VPS/VDS серверы Windows и Linux, доступные от 13 рублей, а также дедик серверы, предлагают целый ряд преимуществ, делая их неотъемлемыми инструментами для развития вашего проекта.
http://ciprofloxacin.life/# ciprofloxacin over the counter
how to buy cheap clomid without prescription can you buy generic clomid for sale – get cheap clomid pills
order generic clomid tablets: can you get cheap clomid without a prescription – order clomid without a prescription
Wow, tһis piece of writing iss good, my sister iѕ analyzing tһese things, thuѕ I am
ցoing tto inform her.
Feel free tо surf to my web-site DafaToto login
prednisone 1 mg daily: prednisone 20mg for sale – buy prednisone 40 mg
buy amoxicillin from canada: amoxicillin for sale – how to buy amoxicillin online
https://clomid.site/# get cheap clomid without dr prescription
wonderful put up, very informative. I ponder why the opposite experts of this sector don’t understand this. You must proceed your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’ base already!
We wish to thank you all over again for the lovely ideas you offered
Jeremy when preparing her post-graduate research and also,
most importantly, for providing every one of the ideas in one
blog post. Provided that we had been aware
of your web page a year ago, i’d have been saved the pointless measures we were choosing.
Thanks to you. adults toys
프라그마틱 슬롯 무료체험
그는 얼굴에 아무런 반응도 보이지 않았다.그는 얼굴에 표정이 없었고 Zhu Houzhao를 바라보며 “좋아요, 지금은 당신을 믿습니다. “라고 말했습니다.
最新民調
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。
http://clomid.site/# cost of clomid
buy cipro online canada: buy cipro online – ciprofloxacin generic price
https://maps.google.com.ph/url?q=https://www.tnlcompetition.com
Xiao Jing의 얼굴에 떠오른 미소는 우는 것보다 더 못생겼습니다. 그는 자신이 궁전에 부딪혀 여기서 죽기를 바랐습니다.
프라그마틱 슬롯사이트
곡식길이란 전군이 생존할 수 있는 생명의 근원이다.
總統民調
секс
We’re a gгoup of volunteers ɑnd opening a new scheme іn օur community.
Үour website offered ᥙs witһ valuable info to work on. Yߋu’ѵe done an impressive joob
and ᧐ur entire commumity wiⅼl ƅe thankful tⲟ yoս.
Feel free tо visit mү web blog: l’actualité sportive de demain
最新民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。
Does your website һave a contact paɡe? I’m hаving
рroblems locatingg іt but, I’d like to shoot you an е-mail.
I’ve gott some ideas for yߋur blog you might be intеrested іn hearing.
Either way, greɑt website ɑnd I look forward tο seeing
it grow over time.
My pаge … Gewilde nuus vandag op sosiale media
民意調查
온카마켓은 카지노와 관련된 정보를 공유하고 토론하는 커뮤니티입니다. 이 커뮤니티는 다양한 주제와 토론을 통해 카지노 게임, 베팅 전략, 최신 카지노 업데이트, 게임 개발사 정보, 보너스 및 프로모션 정보 등을 제공합니다. 여기에서 다른 카지노 애호가들과 의견을 나누고 유용한 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.
온카마켓은 회원 간의 소통과 공유를 촉진하며, 카지노와 관련된 다양한 주제에 대한 토론을 즐길 수 있는 플랫폼입니다. 또한 카지노 커뮤니티 외에도 먹튀검증 정보, 게임 전략, 최신 카지노 소식, 추천 카지노 사이트 등을 제공하여 카지노 애호가들이 안전하고 즐거운 카지노 경험을 즐길 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
온카마켓은 카지노와 관련된 정보와 소식을 한눈에 확인하고 다른 플레이어들과 소통하는 좋은 장소입니다. 카지노와 베팅에 관심이 있는 분들에게 유용한 정보와 커뮤니티를 제공하는 온카마켓을 즐겨보세요.
카지노 커뮤니티 온카마켓은 온라인 카지노와 관련된 정보를 공유하고 소통하는 커뮤니티입니다. 이 커뮤니티는 다양한 카지노 게임, 베팅 전략, 최신 업데이트, 이벤트 정보, 게임 리뷰 등 다양한 주제에 관한 토론과 정보 교류를 지원합니다.
온카마켓에서는 카지노 게임에 관심 있는 플레이어들이 모여서 자유롭게 의견을 나누고 경험을 공유할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다양한 카지노 사이트의 정보와 신뢰성을 검증하는 역할을 하며, 회원들이 안전하게 카지노 게임을 즐길 수 있도록 정보를 제공합니다.
온카마켓은 카지노 커뮤니티의 일원으로서, 카지노 게임을 즐기는 플레이어들에게 유용한 정보와 지원을 제공하고, 카지노 게임에 대한 지식을 공유하며 함께 성장하는 공간입니다. 카지노에 관심이 있는 분들에게는 유용한 커뮤니티로서 온카마켓을 소개합니다
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項總統民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/bg/join?ref=FIHEGIZ8
ban ca xeng
Có đa dạng loại game bắn cá, mỗi thể loại mang theo những quy tắc và phong cách chơi độc đáo. Vì vậy, người mới tham gia nên dành thời gian để nắm vững luật lệ của từng loại mà họ quan tâm. Chẳng hạn, việc hiểu rõ các nguyên tắc cơ bản như săn cá, tính điểm, loại mồi, cách đặt cược, hay quá trình đổi xèng là quan trọng để có trải nghiệm chơi tốt nhất.
Bên cạnh đó, khi tham gia vào trò chơi, cũng cần phải đảm bảo rằng bạn hiểu rõ các quy định cụ thể của từng cổng game để tránh những hiểu lầm không mong muốn.
Nhiều cổng game bắn cá hiện nay cung cấp lựa chọn bàn chơi miễn phí, mở ra cơ hội cho người chơi mới thâm nhập thế giới này mà không cần phải đầu tư xèng. Bằng cách tham gia vào các ván chơi không mất chi phí, người chơi có thể học được quy tắc chơi, tiếp xúc với các chiến thuật, hiểu rõ sự biến động của trò chơi, và khám phá các nền tảng và phần mềm mà không phải lo lắng về áp lực tài chính.
Quá trình trải nghiệm miễn phí sẽ giúp người chơi mới tích luỹ kinh nghiệm, xây dựng lòng tin vào bản thân, từ đó họ có thể chuyển đổi sang chơi với xèng mà không gặp phải nhiều khó khăn và ngần ngại.
Hiểu rõ về ý nghĩa của vị trí trong bàn săn cá là vô cùng quan trọng. Ví dụ, người chơi đặt mình ở vị trí đầu bàn phải đối mặt với thách thức của việc đưa ra quyết định mà không biết được cách mà đối thủ phía sau sẽ hành động. Ngược lại, người chơi ở vị trí giữa có đôi chút lợi thế khi phải đối mặt với ít áp lực hơn, có thể quan sát cách chơi của một số đối thủ trước đó, nhưng vẫn phải đưa ra quyết định mà không biết trước hành động của một số đối thủ khác. Người chơi ở vị trí cuối được ưu thế vì họ có thể quan sát và phân tích hành động của đối thủ trước khi tới lượt họ đưa ra quyết định. Nguyên tắc chung là, vị trí càng cao, người chơi càng có lợi thế trong
ban ca xeng.
Hi malabdali.com owner, You always provide helpful information.
總統民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。
Cryptocurrency Payment Gateway in Morocco
XAIGATE is a secure and user-friendly crypto payment gateway that allows businesses to accept cryptocurrency payments from customers around the world. With XAIGATE, businesses can easily integrate cryptocurrency payments into their existing websites or online stores. If you are a business owner who is looking to start accepting cryptocurrency payments, XAIGATE is the perfect solution for you. Sign up for a free trial today and start experiencing the benefits of cryptocurrency payments firsthand
最新民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/bg/join?ref=UM6SMJM3
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/bg/join?ref=GJY4VW8W
Toronto Key Fob Replacement
Amazing! Its really amazing article, I have got much clear idea concerning
from this post.
I got this website from my pal who informed me about this web page and now this time I am visiting this web page and reading very informative content at this place.|
Hello malabdali.com admin, Thanks for the well-researched and well-written post!
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem. You’re amazing! Thanks!
Rapid Response Commercial Locks
I was excited to find this site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this particularly fantastic read!!
I definitely loved every little bit of it and I have you saved as a favorite to check out
new things in your blog.
Look into my web-site: Driving record
Hi malabdali.com administrator, You always provide great insights.
Sight Care is a natural supplement designed to improve eyesight and reduce dark blindness. With its potent blend of ingredients. https://sightcarebuynow.us/
How to wear a necktie as a bow tie
Hello malabdali.com webmaster, Your posts are always well-delivered and engaging.
GlucoFlush is an advanced formula specially designed for pancreas support that will let you promote healthy weight by effectively maintaining the blood sugar level and cleansing and strengthening your gut. https://glucoflushbuynow.us/
GlucoTrust is a revolutionary blood sugar support solution that eliminates the underlying causes of type 2 diabetes and associated health risks. https://glucotrustbuynow.us/
Glucofort Blood Sugar Support is an all-natural dietary formula that works to support healthy blood sugar levels. It also supports glucose metabolism. According to the manufacturer, this supplement can help users keep their blood sugar levels healthy and within a normal range with herbs, vitamins, plant extracts, and other natural ingredients. https://glucofortbuynow.us/
Illuderma is a serum designed to deeply nourish, clear, and hydrate the skin. The goal of this solution began with dark spots, which were previously thought to be a natural symptom of ageing. The creators of Illuderma were certain that blue modern radiation is the source of dark spots after conducting extensive research. https://illudermabuynow.us/
HoneyBurn is a revolutionary liquid weight loss formula that stands as the epitome of excellence in the industry. https://honeyburnbuynow.us/
Gut Vita™ is a daily supplement that helps consumers to improve the balance in their gut microbiome, which supports the health of their immune system. It supports healthy digestion, even for consumers who have maintained an unhealthy diet for a long time. https://gutvitabuynow.us/
ProstateFlux is a dietary supplement specifically designed to promote and maintain a healthy prostate. It is formulated with a blend of natural ingredients known for their potential benefits for prostate health. https://prostatefluxbuynow.us/
Prostadine is a dietary supplement meticulously formulated to support prostate health, enhance bladder function, and promote overall urinary system well-being. Crafted from a blend of entirely natural ingredients, Prostadine draws upon a recent groundbreaking discovery by Harvard scientists. This discovery identified toxic minerals present in hard water as a key contributor to prostate issues. https://prostadinebuynow.us/
Nervogen Pro is an effective dietary supplement designed to help patients with neuropathic pain. When you combine exotic herbs, spices, and other organic substances, your immune system will be strengthened. https://nervogenprobuynow.us/
PowerBite is an innovative dental candy that promotes healthy teeth and gums. It’s a powerful formula that supports a strong and vibrant smile. https://powerbitebuynow.us/
ProDentim is a nutritional dental health supplement that is formulated to reverse serious dental issues and to help maintain good dental health. https://prodentimbuynow.us/
Are you tired of looking in the mirror and noticing saggy skin? Is saggy skin making you feel like you are trapped in a losing battle against aging? Do you still long for the days when your complexion radiated youth and confidence? https://refirmancebuynow.us/
Serolean, a revolutionary weight loss supplement, zeroes in on serotonin—the key neurotransmitter governing mood, appetite, and fat storage. https://seroleanbuynow.us/
Neurodrine is a nootropic supplement that helps maintain memory and a healthy brain. It increases the brain’s sharpness, focus, memory, and concentration. https://neurodrinebuynow.us/
Protoflow is a prostate health supplement featuring a blend of plant extracts, vitamins, minerals, fruit extracts, and more. https://protoflowbuynow.us/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/kz/join?ref=B4EPR6J0
Quick and reliable locksmith assistance nearby
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/ur/join?ref=V2H9AFPY
What is a saffron brew akin to garlic tea
Toronto Locksmith Experts
You made some decent points there. I looked on the net for additional information about the issue and
found most individuals will go along with your views on this site.
Also visit my blog post – SR22
How to wear a face mask properly
Howdy very cool website!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful ..
I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also? I am glad
to search out numerous useful information right here in the publish, we
need work out extra strategies on this regard, thanks
for sharing. . . . . .
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/lv/join?ref=V3MG69RO
George Jones daughter and her share in the estate
Fast response locksmiths nearby
оформить банковскую карту онлайн
Soccer Highlight Video Tips strategies
Good ԝay of explaining, аnd nice post t᧐o obtsin fscts
ɑbout mʏ presentation subject, ᴡhich i am going to convey in college.
my site beli pbn
І’m curious tο fiund οut ᴡhat blog platform yoᥙ havе beеn ѡorking wіth?
I’m experiencing somе minor security issues witһ my latest website and I woulԁ like to find ѕomething more risk-free.
Ⅾo yyou have any suggestions?
mү blo post: beli backlink
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/sv/register?ref=OMM3XK51
Hey! I kno this is kinxa off topic ƅut I wass wondering іf y᧐u knew wheге I could
locate a captcha plugin fⲟr my comment form?
I’m սsing tһe ѕame blog platform аѕ yours
annd I’m hɑving difficulty finding οne? Thsnks a lot!
my web рage; jasa pbn premium
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
You аre so іnteresting! Ι don’t believе Ι hɑνe read anytһing like that ƅefore.
Ѕo goodd to find someone with ɑ few odiginal tһoughts on tһis issue.
Reɑlly.. thasnks for starting tһis սp. Thiѕ web site is one thіng that’s needed оn thе web, someone with a bit of
originality!
Loook аt my site …jasa seo backlink
GlucoCare is a natural and safe supplement for blood sugar support and weight management. It fixes your metabolism and detoxifies your body. https://glucocarebuynow.us/
InchaGrow is a new natural formula that enhances your virility and allows you to have long-lasting male enhancement capabilities. https://inchagrowbuynow.us/
Abdomax is a nutritional supplement using an 8-second Nordic cleanse to eliminate gut issues, support gut health, and optimize pepsinogen levels. https://abdomaxbuynow.us/
AquaPeace is an all-natural nutritional formula that uses a proprietary and potent blend of ingredients and nutrients to improve overall ear and hearing health and alleviate the symptoms of tinnitus. https://aquapeacebuynow.us/
Why visitors still use tο гead news papers wһen in this technologicsl globe everything is аvailable ߋn web?
Herе is my site; beli backlink
TropiSlim is the world’s first 100% natural solution to support healthy weight loss by using a blend of carefully selected ingredients. https://tropislimbuynow.us/
Protoflow is a prostate health supplement featuring a blend of plant extracts, vitamins, minerals, fruit extracts, and more. https://protoflowbuynow.us/
The most talked about weight loss product is finally here! FitSpresso is a powerful supplement that supports healthy weight loss the natural way. Clinically studied ingredients work synergistically to support healthy fat burning, increase metabolism and maintain long lasting weight loss. https://fitspressobuynow.us/
Digestyl™ is natural, potent and effective mixture, in the form of a powerful pill that would detoxify the gut and rejuvenate the whole organism in order to properly digest and get rid of the Clostridium Perfringens. https://digestylbuynow.us/
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
3a娛樂城
3a娛樂城
Neotonics is an essential probiotic supplement that works to support the microbiome in the gut and also works as an anti-aging formula. The formula targets the cause of the aging of the skin. https://neotonicsbuynow.us/
Claritox Pro™ is a natural dietary supplement that is formulated to support brain health and promote a healthy balance system to prevent dizziness, risk injuries, and disability. This formulation is made using naturally sourced and effective ingredients that are mixed in the right way and in the right amounts to deliver effective results. https://claritoxprobuynow.us/
Sonovive™ is an all-natural supplement made to address the root cause of tinnitus and other inflammatory effects on the brain and promises to reduce tinnitus, improve hearing, and provide peace of mind. https://sonovivebuynow.us/
Aizen Power is an all-natural supplement designed to improve male health. This formula contains the beneficial properties of various plants, herbs, minerals, and vitamins that help men’s blood circulation, detoxification, and overall health. https://aizenpowerbuynow.us/
BioFit is an all-natural supplement that is known to enhance and balance good bacteria in the gut area. To lose weight, you need to have a balanced hormones and body processes. Many times, people struggle with weight loss because their gut health has issues. https://biofitbuynow.us/
3a娛樂城
3a娛樂城
Cortexi is a completely natural product that promotes healthy hearing, improves memory, and sharpens mental clarity. Cortexi hearing support formula is a combination of high-quality natural components that work together to offer you with a variety of health advantages, particularly for persons in their middle and late years. https://cortexibuynow.us/
FlowForce Max is an innovative, natural and effective way to address your prostate problems, while addressing your energy, libido, and vitality. https://flowforcemaxbuynow.us/
LeanBiome is designed to support healthy weight loss. Formulated through the latest Ivy League research and backed by real-world results, it’s your partner on the path to a healthier you. https://leanbiomebuynow.us/
ProstateFlux is a dietary supplement specifically designed to promote and maintain a healthy prostate. It is formulated with a blend of natural ingredients known for their potential benefits for prostate health. https://prostatefluxbuynow.us/
Endopeak is a natural energy-boosting formula designed to improve men’s stamina, energy levels, and overall health. The supplement is made up of eight high-quality ingredients that address the underlying cause of declining energy and vitality. https://endopeakbuynow.us/
娛樂城推薦
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
Dubai, a city known for its opulence and modernity, demands a mode of transportation that reflects its grandeur. For those seeking a cost-effective and reliable long-term solution, Somonion Rent Car LLC emerges as the premier choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. With a diverse fleet ranging from compact cars to premium vehicles, the company promises an unmatched blend of affordability, flexibility, and personalized service.
Favorable Rental Conditions:
Understanding the potential financial strain of long-term car rentals, Somonion Rent Car LLC aims to make your journey more economical. The company offers flexible rental terms coupled with exclusive discounts for loyal customers. This commitment to affordability extends beyond the rental cost, as additional services such as insurance, maintenance, and repair ensure your safety and peace of mind throughout the duration of your rental.
A Plethora of Options:
Somonion Rent Car LLC boasts an extensive selection of vehicles to cater to diverse preferences and budgets. Whether you’re in the market for a sleek sedan or a spacious crossover, the company has the perfect car to complement your needs. The transparency in pricing, coupled with the ease of booking through their online platform, makes Somonion Rent Car LLC a hassle-free solution for those embarking on a long-term adventure in Dubai.
Car Rental Services Tailored for You:
Somonion Rent Car LLC doesn’t just offer cars; it provides a comprehensive range of rental services tailored to suit various occasions. From daily and weekly rentals to airport transfers and business travel, the company ensures that your stay in Dubai is not only comfortable but also exudes prestige. The fleet includes popular models such as the Nissan Altima 2018, KIA Forte 2018, Hyundai Elantra 2018, and the Toyota Camry Sport Edition 2020, all available for monthly rentals at competitive rates.
Featured Deals and Specials:
Somonion Rent Car LLC constantly updates its offerings to provide customers with the best deals. Featured cars like the Hyundai Sonata 2018 and Hyundai Santa Fe 2018 add a touch of luxury to your rental experience, with daily rates starting as low as AED 100. The company’s commitment to affordable luxury is further emphasized by the online booking system, allowing customers to secure the best deals in real-time through their website or by contacting the experts via phone or WhatsApp.
Conclusion:
Whether you’re a tourist looking to explore Dubai at your pace or a business traveler in need of a reliable and prestigious mode of transportation, Somonion Rent Car LLC stands as the go-to choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. Unlock the ultimate mobility experience with Somonion, where affordability meets excellence, ensuring your journey through Dubai is as seamless and luxurious as the city itself. Contact Somonion Rent Car LLC today and embark on a journey where every mile is a testament to comfort, style, and unmatched service.
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
Dubai, a city of grandeur and innovation, demands a transportation solution that matches its dynamic pace. Whether you’re a business executive, a tourist exploring the city, or someone in need of a reliable vehicle temporarily, car rental services in Dubai offer a flexible and cost-effective solution. In this guide, we’ll explore the popular car rental options in Dubai, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
Airport Car Rental: One-Way Pickup and Drop-off Road Trip Rentals:
For those who need to meet an important delegation at the airport or have a flight to another city, airport car rentals provide a seamless solution. Avoid the hassle of relying on public transport and ensure you reach your destination on time. With one-way pickup and drop-off options, you can effortlessly navigate your road trip, making business meetings or conferences immediately upon arrival.
Business Car Rental Deals & Corporate Vehicle Rentals in Dubai:
Companies without their own fleet or those finding transport maintenance too expensive can benefit from business car rental deals. This option is particularly suitable for businesses where a vehicle is needed only occasionally. By opting for corporate vehicle rentals, companies can optimize their staff structure, freeing employees from non-core functions while ensuring reliable transportation when necessary.
Tourist Car Rentals with Insurance in Dubai:
Tourists visiting Dubai can enjoy the freedom of exploring the city at their own pace with car rentals that come with insurance. This option allows travelers to choose a vehicle that suits the particulars of their trip without the hassle of dealing with insurance policies. Renting a car not only saves money and time compared to expensive city taxis but also ensures a trouble-free travel experience.
Daily Car Hire Near Me:
Daily car rental services are a convenient and cost-effective alternative to taxis in Dubai. Whether it’s for a business meeting, everyday use, or a luxury experience, you can find a suitable vehicle for a day on platforms like Smarketdrive.com. The website provides a secure and quick way to rent a car from certified and verified car rental companies, ensuring guarantees and safety.
Weekly Auto Rental Deals:
For those looking for flexibility throughout the week, weekly car rentals in Dubai offer a competent, attentive, and professional service. Whether you need a vehicle for a few days or an entire week, choosing a car rental weekly is a convenient and profitable option. The certified and tested car rental companies listed on Smarketdrive.com ensure a reliable and comfortable experience.
Monthly Car Rentals in Dubai:
When your personal car is undergoing extended repairs, or if you’re a frequent visitor to Dubai, monthly car rentals (long-term car rentals) become the ideal solution. Residents, businessmen, and tourists can benefit from the extensive options available on Smarketdrive.com, ensuring mobility and convenience throughout their stay in Dubai.
FAQ about Renting a Car in Dubai:
To address common queries about renting a car in Dubai, our FAQ section provides valuable insights and information. From rental terms to insurance coverage, it serves as a comprehensive guide for those considering the convenience of car rentals in the bustling city.
Conclusion:
Dubai’s popularity as a global destination is matched by its diverse and convenient car rental services. Whether for business, tourism, or daily commuting, the options available cater to every need. With reliable platforms like Smarketdrive.com, navigating Dubai becomes a seamless and enjoyable experience, offering both locals and visitors the ultimate freedom of mobility.
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。
monthly car hire dubai
Dubai, a city known for its opulence and modernity, demands a mode of transportation that reflects its grandeur. For those seeking a cost-effective and reliable long-term solution, Somonion Rent Car LLC emerges as the premier choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. With a diverse fleet ranging from compact cars to premium vehicles, the company promises an unmatched blend of affordability, flexibility, and personalized service.
Favorable Rental Conditions:
Understanding the potential financial strain of long-term car rentals, Somonion Rent Car LLC aims to make your journey more economical. The company offers flexible rental terms coupled with exclusive discounts for loyal customers. This commitment to affordability extends beyond the rental cost, as additional services such as insurance, maintenance, and repair ensure your safety and peace of mind throughout the duration of your rental.
A Plethora of Options:
Somonion Rent Car LLC boasts an extensive selection of vehicles to cater to diverse preferences and budgets. Whether you’re in the market for a sleek sedan or a spacious crossover, the company has the perfect car to complement your needs. The transparency in pricing, coupled with the ease of booking through their online platform, makes Somonion Rent Car LLC a hassle-free solution for those embarking on a long-term adventure in Dubai.
Car Rental Services Tailored for You:
Somonion Rent Car LLC doesn’t just offer cars; it provides a comprehensive range of rental services tailored to suit various occasions. From daily and weekly rentals to airport transfers and business travel, the company ensures that your stay in Dubai is not only comfortable but also exudes prestige. The fleet includes popular models such as the Nissan Altima 2018, KIA Forte 2018, Hyundai Elantra 2018, and the Toyota Camry Sport Edition 2020, all available for monthly rentals at competitive rates.
Featured Deals and Specials:
Somonion Rent Car LLC constantly updates its offerings to provide customers with the best deals. Featured cars like the Hyundai Sonata 2018 and Hyundai Santa Fe 2018 add a touch of luxury to your rental experience, with daily rates starting as low as AED 100. The company’s commitment to affordable luxury is further emphasized by the online booking system, allowing customers to secure the best deals in real-time through their website or by contacting the experts via phone or WhatsApp.
Conclusion:
Whether you’re a tourist looking to explore Dubai at your pace or a business traveler in need of a reliable and prestigious mode of transportation, Somonion Rent Car LLC stands as the go-to choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. Unlock the ultimate mobility experience with Somonion, where affordability meets excellence, ensuring your journey through Dubai is as seamless and luxurious as the city itself. Contact Somonion Rent Car LLC today and embark on a journey where every mile is a testament to comfort, style, and unmatched service.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/ur/join?ref=FIHEGIZ8
canadian pharmacy no prescription cialis without a doctor’s prescription canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
Virginia News: Your source for Virginia breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://virginiapost.us/
Find healthy, delicious recipes and meal plan ideas from our test kitchen cooks and nutrition experts at SweetApple. Learn how to make healthier food choices every day. https://sweetapple.site/
View the latest from the world of psychology: from behavioral research to practical guidance on relationships, mental health and addiction. Find help from our directory of therapists, psychologists and counselors. https://therapisttoday.us/
RVVR is website dedicated to advancing physical and mental health through scientific research and proven interventions. Learn about our evidence-based health promotion programs. https://rvvr.us/
The latest news on grocery chains, celebrity chefs, and fast food – plus reviews, cooking tips and advice, recipes, and more. https://megamenu.us/
The best tips, guides, and inspiration on home improvement, decor, DIY projects, and interviews with celebrities from your favorite renovation shows. https://houseblog.us/
Colorado breaking news, sports, business, weather, entertainment. https://denver-news.us/
Covering the latest beauty and fashion trends, relationship advice, wellness tips and more. https://gliz.us/
Breaking US news, local New York news coverage, sports, entertainment news, celebrity gossip, autos, videos and photos at nybreakingnews.us https://nybreakingnews.us/
Your source for Connecticut breaking news, UConn sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://connecticutpost.us/
Healthcare Blog provides news, trends, jobs and resources for health industry professionals. We cover topics like healthcare IT, hospital administration, polcy
Latest Denver news, top Colorado news and local breaking news from Denver News, including sports, weather, traffic, business, politics, photos and video. https://denver-news.us/
Miami Post: Your source for South Florida breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://miamipost.us/
BioPharma Blog provides news and analysis for biotech and biopharmaceutical executives. We cover topics like clinical trials, drug discovery and development, pharma marketing, FDA approvals and regulations, and more. https://biopharmablog.us/
Island Post is the website for a chain of six weekly newspapers that serve the North Shore of Nassau County, Long Island published by Alb Media. The newspapers are comprised of the Great Neck News, Manhasset Times, Roslyn Times, Port Washington Times, New Hyde Park Herald Courier and the Williston Times. Their coverage includes village governments, the towns of Hempstead and North Hempstead, schools, business, entertainment and lifestyle. https://islandpost.us/
Fresh, flavorful and (mostly) healthy recipes made for real, actual, every day life. Helping you celebrate the joy of food in a totally non-intimidating way. https://skillfulcook.us/
OCNews.us covers local news in Orange County, CA, California and national news, sports, things to do and the best places to eat, business and the Orange County housing market. https://ocnews.us/
Watches World: Elevating Luxury and Style with Exquisite Timepieces
Introduction:
Jewelry has always been a timeless expression of elegance, and nothing complements one’s style better than a luxurious timepiece. At Watches World, we bring you an exclusive collection of coveted luxury watches that not only tell time but also serve as a testament to your refined taste. Explore our curated selection featuring iconic brands like Rolex, Hublot, Omega, Cartier, and more, as we redefine the art of accessorizing.
A Dazzling Array of Luxury Watches:
Watches World offers an unparalleled range of exquisite timepieces from renowned brands, ensuring that you find the perfect accessory to elevate your style. Whether you’re drawn to the classic sophistication of Rolex, the avant-garde designs of Hublot, or the precision engineering of Patek Philippe, our collection caters to diverse preferences.
Customer Testimonials:
Our commitment to providing an exceptional customer experience is reflected in the reviews from our satisfied clientele. O.M. commends our excellent communication and flawless packaging, while Richard Houtman appreciates the helpfulness and courtesy of our team. These testimonials highlight our dedication to transparency, communication, and customer satisfaction.
New Arrivals:
Stay ahead of the curve with our latest additions, including the Tudor Black Bay Ceramic 41mm, Richard Mille RM35-01 Rafael Nadal NTPT Carbon Limited Edition, and the Rolex Oyster Perpetual Datejust 41mm series. These new arrivals showcase cutting-edge designs and impeccable craftsmanship, ensuring you stay on the forefront of luxury watch fashion.
Best Sellers:
Discover our best-selling watches, such as the Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm and the Cartier Panthere Medium Model. These timeless pieces combine elegance with precision, making them a staple in any sophisticated wardrobe.
Expert’s Selection:
Our experts have carefully curated a selection of watches, including the Cartier Panthere Small Model, Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm, and Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm. These choices exemplify the epitome of watchmaking excellence and style.
Secured and Tracked Delivery:
At Watches World, we prioritize the safety of your purchase. Our secured and tracked delivery ensures that your exquisite timepiece reaches you in perfect condition, giving you peace of mind with every order.
Passionate Experts at Your Service:
Our team of passionate watch experts is dedicated to providing personalized service. From assisting you in choosing the perfect timepiece to addressing any inquiries, we are here to make your watch-buying experience seamless and enjoyable.
Global Presence:
With a presence in key cities around the world, including Dubai, Geneva, Hong Kong, London, Miami, Paris, Prague, Dublin, Singapore, and Sao Paulo, Watches World brings luxury timepieces to enthusiasts globally.
Conclusion:
Watches World goes beyond being an online platform for luxury watches; it is a destination where expertise, trust, and satisfaction converge. Explore our collection, and let our timeless timepieces become an integral part of your style narrative. Join us in redefining luxury, one exquisite watch at a time.
Dubai, a city of grandeur and innovation, demands a transportation solution that matches its dynamic pace. Whether you’re a business executive, a tourist exploring the city, or someone in need of a reliable vehicle temporarily, car rental services in Dubai offer a flexible and cost-effective solution. In this guide, we’ll explore the popular car rental options in Dubai, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
Airport Car Rental: One-Way Pickup and Drop-off Road Trip Rentals:
For those who need to meet an important delegation at the airport or have a flight to another city, airport car rentals provide a seamless solution. Avoid the hassle of relying on public transport and ensure you reach your destination on time. With one-way pickup and drop-off options, you can effortlessly navigate your road trip, making business meetings or conferences immediately upon arrival.
Business Car Rental Deals & Corporate Vehicle Rentals in Dubai:
Companies without their own fleet or those finding transport maintenance too expensive can benefit from business car rental deals. This option is particularly suitable for businesses where a vehicle is needed only occasionally. By opting for corporate vehicle rentals, companies can optimize their staff structure, freeing employees from non-core functions while ensuring reliable transportation when necessary.
Tourist Car Rentals with Insurance in Dubai:
Tourists visiting Dubai can enjoy the freedom of exploring the city at their own pace with car rentals that come with insurance. This option allows travelers to choose a vehicle that suits the particulars of their trip without the hassle of dealing with insurance policies. Renting a car not only saves money and time compared to expensive city taxis but also ensures a trouble-free travel experience.
Daily Car Hire Near Me:
Daily car rental services are a convenient and cost-effective alternative to taxis in Dubai. Whether it’s for a business meeting, everyday use, or a luxury experience, you can find a suitable vehicle for a day on platforms like Smarketdrive.com. The website provides a secure and quick way to rent a car from certified and verified car rental companies, ensuring guarantees and safety.
Weekly Auto Rental Deals:
For those looking for flexibility throughout the week, weekly car rentals in Dubai offer a competent, attentive, and professional service. Whether you need a vehicle for a few days or an entire week, choosing a car rental weekly is a convenient and profitable option. The certified and tested car rental companies listed on Smarketdrive.com ensure a reliable and comfortable experience.
Monthly Car Rentals in Dubai:
When your personal car is undergoing extended repairs, or if you’re a frequent visitor to Dubai, monthly car rentals (long-term car rentals) become the ideal solution. Residents, businessmen, and tourists can benefit from the extensive options available on Smarketdrive.com, ensuring mobility and convenience throughout their stay in Dubai.
FAQ about Renting a Car in Dubai:
To address common queries about renting a car in Dubai, our FAQ section provides valuable insights and information. From rental terms to insurance coverage, it serves as a comprehensive guide for those considering the convenience of car rentals in the bustling city.
Conclusion:
Dubai’s popularity as a global destination is matched by its diverse and convenient car rental services. Whether for business, tourism, or daily commuting, the options available cater to every need. With reliable platforms like Smarketdrive.com, navigating Dubai becomes a seamless and enjoyable experience, offering both locals and visitors the ultimate freedom of mobility.
Looking for quick and easy dinner ideas? Browse 100
monthly car hire dubai
Dubai, a city known for its opulence and modernity, demands a mode of transportation that reflects its grandeur. For those seeking a cost-effective and reliable long-term solution, Somonion Rent Car LLC emerges as the premier choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. With a diverse fleet ranging from compact cars to premium vehicles, the company promises an unmatched blend of affordability, flexibility, and personalized service.
Favorable Rental Conditions:
Understanding the potential financial strain of long-term car rentals, Somonion Rent Car LLC aims to make your journey more economical. The company offers flexible rental terms coupled with exclusive discounts for loyal customers. This commitment to affordability extends beyond the rental cost, as additional services such as insurance, maintenance, and repair ensure your safety and peace of mind throughout the duration of your rental.
A Plethora of Options:
Somonion Rent Car LLC boasts an extensive selection of vehicles to cater to diverse preferences and budgets. Whether you’re in the market for a sleek sedan or a spacious crossover, the company has the perfect car to complement your needs. The transparency in pricing, coupled with the ease of booking through their online platform, makes Somonion Rent Car LLC a hassle-free solution for those embarking on a long-term adventure in Dubai.
Car Rental Services Tailored for You:
Somonion Rent Car LLC doesn’t just offer cars; it provides a comprehensive range of rental services tailored to suit various occasions. From daily and weekly rentals to airport transfers and business travel, the company ensures that your stay in Dubai is not only comfortable but also exudes prestige. The fleet includes popular models such as the Nissan Altima 2018, KIA Forte 2018, Hyundai Elantra 2018, and the Toyota Camry Sport Edition 2020, all available for monthly rentals at competitive rates.
Featured Deals and Specials:
Somonion Rent Car LLC constantly updates its offerings to provide customers with the best deals. Featured cars like the Hyundai Sonata 2018 and Hyundai Santa Fe 2018 add a touch of luxury to your rental experience, with daily rates starting as low as AED 100. The company’s commitment to affordable luxury is further emphasized by the online booking system, allowing customers to secure the best deals in real-time through their website or by contacting the experts via phone or WhatsApp.
Conclusion:
Whether you’re a tourist looking to explore Dubai at your pace or a business traveler in need of a reliable and prestigious mode of transportation, Somonion Rent Car LLC stands as the go-to choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. Unlock the ultimate mobility experience with Somonion, where affordability meets excellence, ensuring your journey through Dubai is as seamless and luxurious as the city itself. Contact Somonion Rent Car LLC today and embark on a journey where every mile is a testament to comfort, style, and unmatched service.
Watches World
Watches World: Elevating Luxury and Style with Exquisite Timepieces
Introduction:
Jewelry has always been a timeless expression of elegance, and nothing complements one’s style better than a luxurious timepiece. At Watches World, we bring you an exclusive collection of coveted luxury watches that not only tell time but also serve as a testament to your refined taste. Explore our curated selection featuring iconic brands like Rolex, Hublot, Omega, Cartier, and more, as we redefine the art of accessorizing.
A Dazzling Array of Luxury Watches:
Watches World offers an unparalleled range of exquisite timepieces from renowned brands, ensuring that you find the perfect accessory to elevate your style. Whether you’re drawn to the classic sophistication of Rolex, the avant-garde designs of Hublot, or the precision engineering of Patek Philippe, our collection caters to diverse preferences.
Customer Testimonials:
Our commitment to providing an exceptional customer experience is reflected in the reviews from our satisfied clientele. O.M. commends our excellent communication and flawless packaging, while Richard Houtman appreciates the helpfulness and courtesy of our team. These testimonials highlight our dedication to transparency, communication, and customer satisfaction.
New Arrivals:
Stay ahead of the curve with our latest additions, including the Tudor Black Bay Ceramic 41mm, Richard Mille RM35-01 Rafael Nadal NTPT Carbon Limited Edition, and the Rolex Oyster Perpetual Datejust 41mm series. These new arrivals showcase cutting-edge designs and impeccable craftsmanship, ensuring you stay on the forefront of luxury watch fashion.
Best Sellers:
Discover our best-selling watches, such as the Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm and the Cartier Panthere Medium Model. These timeless pieces combine elegance with precision, making them a staple in any sophisticated wardrobe.
Expert’s Selection:
Our experts have carefully curated a selection of watches, including the Cartier Panthere Small Model, Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm, and Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm. These choices exemplify the epitome of watchmaking excellence and style.
Secured and Tracked Delivery:
At Watches World, we prioritize the safety of your purchase. Our secured and tracked delivery ensures that your exquisite timepiece reaches you in perfect condition, giving you peace of mind with every order.
Passionate Experts at Your Service:
Our team of passionate watch experts is dedicated to providing personalized service. From assisting you in choosing the perfect timepiece to addressing any inquiries, we are here to make your watch-buying experience seamless and enjoyable.
Global Presence:
With a presence in key cities around the world, including Dubai, Geneva, Hong Kong, London, Miami, Paris, Prague, Dublin, Singapore, and Sao Paulo, Watches World brings luxury timepieces to enthusiasts globally.
Conclusion:
Watches World goes beyond being an online platform for luxury watches; it is a destination where expertise, trust, and satisfaction converge. Explore our collection, and let our timeless timepieces become an integral part of your style narrative. Join us in redefining luxury, one exquisite watch at a time.
Santa Cruz Sentinel: Local News, Local Sports and more for Santa Cruz https://santacruznews.us/
News from the staff of the LA Reporter, including crime and investigative coverage of the South Bay and Harbor Area in Los Angeles County. https://lareporter.us/
East Bay News is the leading source of breaking news, local news, sports, entertainment, lifestyle and opinion for Contra Costa County, Alameda County, Oakland and beyond https://eastbaynews.us/
The latest film and TV news, movie trailers, exclusive interviews, reviews, as well as informed opinions on everything Hollywood has to offer. https://xoop.us/
indiaherald.us provides latest news from India , India News and around the world. Get breaking news alerts from India and follow today’s live news updates in field of politics, business, sports, defence, entertainment and more. https://indiaherald.us
https://indianpharmacy.shop/# indian pharmacy
mail order pharmacy india
Kingston News – Kingston, NY News, Breaking News, Sports, Weather https://kingstonnews.us/
Hello malabdali.com administrator, You always provide useful tips and best practices.
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。
Yolonews.us covers local news in Yolo County, California. Keep up with all business, local sports, outdoors, local columnists and more. https://yolonews.us/
https://rgwager.com/mars-set/
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉!
Stri is the leading entrepreneurs and innovation magazine devoted to shed light on the booming stri ecosystem worldwide. https://stri.us/
The latest health news, wellness advice, and exclusives backed by trusted medical authorities. https://healthmap.us/
Money Analysis is the destination for balancing life and budget – from money management tips, to cost-cutting deals, tax advice, and much more. https://moneyanalysis.us/
Baltimore Post: Your source for Baltimore breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://baltimorepost.us/
The one-stop destination for vacation guides, travel tips, and planning advice – all from local experts and tourism specialists. https://travelerblog.us/
Outdoor Blog will help you live your best life outside – from wildlife guides, to safety information, gardening tips, and more. https://outdoorblog.us/
Maryland Post: Your source for Maryland breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://marylandpost.us/
Food
Greeley, Colorado News, Sports, Weather and Things to Do https://greeleynews.us/
Ꮃhɑt’s up, alⅼ is going well here and ofcourse every one iѕ
ssharing data, that’s actually fine, қeep uρ writing.
Alѕo visit mʏ webpage; Top 5 sportsnyheder på engelsk i dag
2024娛樂城
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。
Helⅼo i аm kavin, its mү firѕt occasion to commenting anyplace, when i read this post i thought
i could also create commеnt Ԁue to thiѕ sеnsible paragraph.
Feel free tο visit my paɡe :: што се случува со социјалните мрежи денес
The LB News is the local news source for Long Beach and the surrounding area providing breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, things to do, opinion, photos, videos and more https://lbnews.us/
Boulder News
I’m truly enjoying the design ɑnd layout of your site.
It’s а very easy on the eyes whiсh makеs it much moгe enjoyable fоr me
to ⅽome heгe and visit mօrе օften. Did yⲟu hire оut а developer to create
your theme? Fantastic ԝork!
Takе a lߋok att my web-site sky sports football en direct
Canon City, Colorado News, Sports, Weather and Things to Do https://canoncitynews.us/
Дома АВС – Ваш уютный уголок
Мы строим не просто дома, мы создаем пространство, где каждый уголок будет наполнен комфортом и радостью жизни. Наш приоритет – не просто предоставить место для проживания, а создать настоящий дом, где вы будете чувствовать себя счастливыми и уютно.
В нашем информационном разделе “ПРОЕКТЫ” вы всегда найдете вдохновение и новые идеи для строительства вашего будущего дома. Мы постоянно работаем над тем, чтобы предложить вам самые инновационные и стильные проекты.
Мы убеждены, что основа хорошего дома – это его дизайн. Поэтому мы предоставляем услуги опытных дизайнеров-архитекторов, которые помогут вам воплотить все ваши идеи в жизнь. Наши архитекторы и персональные консультанты всегда готовы поделиться своим опытом и предложить функциональные и комфортные решения для вашего будущего дома.
Мы стремимся сделать весь процесс строительства максимально комфортным для вас. Наша команда предоставляет детализированные сметы, разрабатывает четкие этапы строительства и осуществляет контроль качества на каждом этапе.
Для тех, кто ценит экологичность и близость к природе, мы предлагаем деревянные дома премиум-класса. Используя клееный брус и оцилиндрованное бревно, мы создаем уникальные и здоровые условия для вашего проживания.
Тем, кто предпочитает надежность и многообразие форм, мы предлагаем дома из камня, блоков и кирпичной кладки.
Для практичных и ценящих свое время людей у нас есть быстровозводимые каркасные дома и эконом-класса. Эти решения обеспечат вас комфортным проживанием в кратчайшие сроки.
С Домами АВС создайте свой уютный уголок, где каждый момент жизни будет наполнен радостью и удовлетворением
Oakland County, MI News, Sports, Weather, Things to Do https://oaklandpost.us/
Ꮋelⅼo there! Ꭰo you know if they mаke any plpugins tо assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog tto raank f᧐r some targeted keywirds Ƅut I’m nott seeing νery ցood gains.
Ιf үou know of ɑny pleаѕe share. Kudos!
Check օut my pagfe ما يحدث مع وسائل التواصل الاجتماعي اليوم
https://rg888.app/set/
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉!
https://beton-vlobnje.ru/
Hey tһere! I knoԝ this is kіnd of off topic but I ᴡas wondering which blog platform are you սsing for tthis site?
Ι’m ցetting sick ɑnd tired of WordPress becɑuse I’ve had prоblems ԝith hackers and I’m
lookіng аt alternatives fօr another platform. І wօuld Ьe awesome
іf you cοuld poinnt mе in thee direction оf
a good platform.
Review mmy webpage; Твиттердеги жаңылыктар
I’m curious to find out what blog platform
you have been using? I’m experiencing some small security issues with my latest
website and I would like to find something more risk-free.
Do you have any suggestions?
Деревянные дома под ключ
Дома АВС – Ваш уютный уголок
Мы строим не просто дома, мы создаем пространство, где каждый уголок будет наполнен комфортом и радостью жизни. Наш приоритет – не просто предоставить место для проживания, а создать настоящий дом, где вы будете чувствовать себя счастливыми и уютно.
В нашем информационном разделе “ПРОЕКТЫ” вы всегда найдете вдохновение и новые идеи для строительства вашего будущего дома. Мы постоянно работаем над тем, чтобы предложить вам самые инновационные и стильные проекты.
Мы убеждены, что основа хорошего дома – это его дизайн. Поэтому мы предоставляем услуги опытных дизайнеров-архитекторов, которые помогут вам воплотить все ваши идеи в жизнь. Наши архитекторы и персональные консультанты всегда готовы поделиться своим опытом и предложить функциональные и комфортные решения для вашего будущего дома.
Мы стремимся сделать весь процесс строительства максимально комфортным для вас. Наша команда предоставляет детализированные сметы, разрабатывает четкие этапы строительства и осуществляет контроль качества на каждом этапе.
Для тех, кто ценит экологичность и близость к природе, мы предлагаем деревянные дома премиум-класса. Используя клееный брус и оцилиндрованное бревно, мы создаем уникальные и здоровые условия для вашего проживания.
Тем, кто предпочитает надежность и многообразие форм, мы предлагаем дома из камня, блоков и кирпичной кладки.
Для практичных и ценящих свое время людей у нас есть быстровозводимые каркасные дома и эконом-класса. Эти решения обеспечат вас комфортным проживанием в кратчайшие сроки.
С Домами АВС создайте свой уютный уголок, где каждый момент жизни будет наполнен радостью и удовлетворением
socialmediatric.com
“수도가 어디죠?” 어린 이모가 미소를 지었다.
kinoboomhd.com
Hongzhi 황제의 목소리는 종소리 같았고 그는이 새로운 궁전을 언급하기를 희망했습니다.
The latest video game news, reviews, exclusives, streamers, esports, and everything else gaming. https://zaaz.us/
Ohio Reporter – Ohio News, Sports, Weather and Things to Do https://ohioreporter.us/
Trenton News – Trenton, NJ News, Sports, Weather and Things to Do https://trentonnews.us/
Vacavillenews.us covers local news in Vacaville, California. Keep up with all business, local sports, outdoors, local columnists and more. https://vacavillenews.us/
I need to to thank you foг this great reɑԀ!! I ceгtainly lovrd eveгy little
bіt of it. I’vе got you book-marked to check оut new stuff you post…
My blog; novaĵoj hodiaŭ en la mondo
Healthcare Blog provides news, trends, jobs and resources for health industry professionals. We cover topics like healthcare IT, hospital administration, polcy
Get Lehigh Valley news, Allentown news, Bethlehem news, Easton news, Quakertown news, Poconos news and Pennsylvania news from Morning Post. https://morningpost.us/
Valley News covers local news from Pomona to Ontario including, California news, sports, things to do, and business in the Inland Empire. https://valleynews.us/
Mass News is the leading source of breaking news, local news, sports, business, entertainment, lifestyle and opinion for Silicon Valley, San Francisco Bay Area and beyond https://massnews.us/
The Boston Post is the leading source of breaking news, local news, sports, politics, entertainment, opinion and weather in Boston, Massachusetts. https://bostonpost.us/
Supplement Reviews – Get unbiased ratings and reviews for 1000 products from Consumer Reports, plus trusted advice and in-depth reporting on what matters most. https://supplementreviews.us/
Evidence-based resource on weight loss, nutrition, low-carb meal planning, gut health, diet reviews and weight-loss plans. We offer in-depth reviews on diet supplements, products and programs. https://healthpress.us/
Pilot News: Your source for Virginia breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://pilotnews.us/
Foodie Blog is the destination for living a delicious life – from kitchen tips to culinary history, celebrity chefs, restaurant recommendations, and much more. https://foodieblog.us/
Medical More provides medical technology news and analysis for industry professionals. We cover medical devices, diagnostics, digital health, FDA regulation and compliance, imaging, and more. https://medicalmore.us
I’ll immediately clutch your rss feed as I can not find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service.
Do you’ve any? Please permit me understand in order that I may just
subscribe. Thanks.
binsunvipp.com
이 분명한 보고서를 보고 그는 실제로 빠져나오지 못한 채 깊이 빠져들기 시작했습니다.
on line pharmacy
canadian pharmacies mail order
sky pharmacy online
Local news from Redlands, CA, California news, sports, things to do, and business in the Inland Empire. https://redlandsnews.us
San Gabriel Valley News is the local news source for Los Angeles County
viagra no prescription
NewsBreak provides latest and breaking Renton, WA local news, weather forecast, crime and safety reports, traffic updates, event notices, sports https://rentonnews.us
Bellevue Latest Headlines: City of Bellevue can Apply for Digital Equity Grant https://bellevuenews.us
Даркнет, сокращение от “даркнетворк” (dark network), представляет собой часть интернета, недоступную для обычных поисковых систем. В отличие от повседневного интернета, где мы привыкли к публичному контенту, даркнет скрыт от обычного пользователя. Здесь используются специальные сети, такие как Tor (The Onion Router), чтобы обеспечить анонимность пользователей.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/en/join?ref=53551167
Hello malabdali.com administrator, Your posts are always well-balanced and objective.
Іt is perfect tіme to mwke some plans f᧐r tthe future and it’ѕ time to bee happy.
I’ve гead tһis post and if I cⲟuld I desire to suɡgest yߋu feѡ interestіng things oг tips.
Maуbe ү᧐u can ԝrite next articles referring
tߋ thіs article. Ι want to rrad more thingѕ abߋut it!
my webpage Was ist das Neueste auf der Welt?
A lot of blog writers nowadays yet just a few have blog posts worth spending time on reviewing.
My website: русский трах
reggionotizie.com
Hongzhi 황제는 “이제 질문을 할 때입니다 …”라고 진정했습니다.
دکتر شهاب محمدی یک کلینیک دندانپزشکی (Dental Clinic) به نام خود در غرب تهران تأسیس کرده است که تمامی خدمات دندانپزشکی را با مجهزترین و استانداردترین تجهیزات روز دنیا به متقاضیان
ارائه میدهد. کلینیک دندانپزشکی دکتر شهاب محمدی با رضایت 98 درصدی، توانسته
خود را بهعنوان بهترین کلینیک دندانپزشکی غرب تهران
معرفی کند.
rg777
rg777
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/pl/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
saungsantoso.com
나는 왕금원 교수와 같은 노인들에게 잘못된 말을 하지 말라고 상기시키고 싶습니다.
娛樂城
**娛樂城與線上賭場:現代娛樂的轉型與未來**
在當今數位化的時代,”娛樂城”和”線上賭場”已成為現代娛樂和休閒生活的重要組成部分。從傳統的賭場到互聯網上的線上賭場,這一領域的發展不僅改變了人們娛樂的方式,也推動了全球娛樂產業的創新與進步。
**起源與發展**
娛樂城的概念源自於傳統的實體賭場,這些場所最初旨在提供各種形式的賭博娛樂,如撲克、輪盤、老虎機等。隨著時間的推移,這些賭場逐漸發展成為包含餐飲、表演藝術和住宿等多元化服務的綜合娛樂中心,從而吸引了來自世界各地的遊客。
隨著互聯網技術的飛速發展,線上賭場應運而生。這種新型態的賭博平台讓使用者可以在家中或任何有互聯網連接的地方,享受賭博遊戲的樂趣。線上賭場的出現不僅為賭博愛好者提供了更多便利與選擇,也大大擴展了賭博產業的市場範圍。
**特點與魅力**
娛樂城和線上賭場的主要魅力在於它們能提供多樣化的娛樂選項和高度的可訪問性。無論是實體的娛樂城還是虛擬的線上賭場,它們都致力於創造一個充滿樂趣和刺激的環境,讓人們可以從日常生活的壓力中短暫逃脫。
此外,線上賭場通過提供豐富的遊戲選擇、吸引人的獎金方案以及便捷的支付系統,成功地吸引了全球範圍內的用戶。這些平台通常具有高度的互動性和社交性,使玩家不僅能享受遊戲本身,還能與來自世界各地的其他玩家交流。
**未來趨勢**
隨著技術的不斷進步和用戶需求的不斷演變,娛樂城和線上賭場的未來發展呈現出多元化的趨勢。一方面,虛
擬現實(VR)和擴增現實(AR)技術的應用,有望為線上賭場帶來更加沉浸式和互動式的遊戲體驗。另一方面,對於實體娛樂城而言,將更多地注重提供綜合性的休閒體驗,結合賭博、娛樂、休閒和旅遊等多個方面,以滿足不同客群的需求。
此外,隨著對負責任賭博的認識加深,未來娛樂城和線上賭場在提供娛樂的同時,也將更加注重促進健康的賭博行為和保護用戶的安全。
總之,娛樂城和線上賭場作為現代娛樂生活的一部分,隨著社會的發展和技術的進步,將繼續演化和創新,為人們提供更多的樂趣和便利。這一領域的未來發展無疑充滿了無限的可能性和機遇。
Maryland Post: Your source for Maryland breaking news, sports, business, entertainment, weather and traffic https://marylandpost.us
Reading, PA News, Sports, Weather, Things to Do http://readingnews.us/
Read the latest news on Crime, Politics, Schools, Sports, Weather, Business, Arts, Jobs, Obits, and Things to do in Kent Washington. https://kentnews.us/
Peninsula News is a daily news website, covering the northern Olympic Peninsula in the state of Washington, United States. https://peninsulanews.us
Fresh, flavorful and (mostly) healthy recipes made for real, actual, every day life. Helping you celebrate the joy of food in a totally non-intimidating way. https://skillfulcook.us
Macomb County, MI News, Breaking News, Sports, Weather, Things to Do https://macombnews.us
If you desire to improve үoᥙr knowledge only keeⲣ visiting tһis site ɑnd be
updated ᴡith tһe most սp-to-dategossip posted һere.
Herе iѕ my web site … que se passe-t-il avec les médias sociaux aujourd’hui
OCNews.us covers local news in Orange County, CA, California and national news, sports, things to do and the best places to eat, business and the Orange County housing market. https://ocnews.us
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/sk/register?ref=YY80CKRN
sky pharmacy online drugstore
娛樂城
sky pharmacy
I do not еven understand how I finished up herе, but I assumed thіs putt up ԝas goοԁ.
I don’t realize who you are but ⅾefinitely yoս are
gοing to a wеll-known blogger if yoᥙ hɑppen tto are not aⅼready.
Cheers!
Τake а looк at my blog post :: šta se danas dešava sa društvenim mrežama
You are so cool! I ԁo not believe I have rеad ѕomething like that ƅefore.Ѕo good to discover
ѕomebody ԝith some unique th᧐ughts ߋn tһіѕ subject.
Ɍeally.. thanks for starting this up. Ƭhiѕ web siite is sonething tһat’s needеd on tһe internet,
someone wіth ssome originality!
Alsօ visit my ⲣage; 现在在 YouTube 上流行
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/pt-BR/join?ref=W0BCQMF1
Ӏ visited multiple web pɑges but the audio quality fоr audio sojgs existing at thіs website is genuinely wonderful.
Also visit my site … 학교 조회를 위한 영어 상위 5개 스포츠 뉴스
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/pt-BR/join?ref=YY80CKRN
A lot of blog writers nowadays yet just a few have blog posts worth spending time on reviewing.
My website: эротика нд
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/fr/register-person?ref=RQUR4BEO
rivipaolo.com
이때 그는 천천히 아버지의 생각을 이해하기 시작했습니다.
10yenharwichport.com
현청 밖에서 Zhu Houzhao는 강력한 군대를 이끌고 왔습니다.
onlinepharmacy online pharmacy
pay per click site
Understanding the processes and protocols within a Professional Tenure Committee (PTC) is crucial for faculty members. This Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) guide aims to address common queries related to PTC procedures, voting, and membership.
1. Why should members of the PTC fill out vote justification forms explaining their votes?
Vote justification forms provide transparency in decision-making. Members articulate their reasoning, fostering a culture of openness and ensuring that decisions are well-founded and understood by the academic community.
2. How can absentee ballots be cast?
To accommodate absentee voting, PTCs may implement secure electronic methods or designated proxy voters. This ensures that faculty members who cannot physically attend meetings can still contribute to decision-making processes.
3. How will additional members of PTCs be elected in departments with fewer than four tenured faculty members?
In smaller departments, creative solutions like rotating roles or involving faculty from related disciplines can be explored. Flexibility in election procedures ensures representation even in departments with fewer tenured faculty members.
4. Can a faculty member on OCSA or FML serve on a PTC?
Faculty members involved in other committees like the Organization of Committee on Student Affairs (OCSA) or Family and Medical Leave (FML) can serve on a PTC, but potential conflicts of interest should be carefully considered and managed.
5. Can an abstention vote be cast at a PTC meeting?
Yes, PTC members have the option to abstain from voting if they feel unable to take a stance on a particular matter. This allows for ethical decision-making and prevents uninformed voting.
6. What constitutes a positive or negative vote in PTCs?
A positive vote typically indicates approval or agreement, while a negative vote signifies disapproval or disagreement. Clear definitions and guidelines within each PTC help members interpret and cast their votes accurately.
7. What constitutes a quorum in a PTC?
A quorum, the minimum number of members required for a valid meeting, is essential for decision-making. Specific rules about quorum size are usually outlined in the PTC’s governing documents.
Our Plan Packages: Choose The Best Plan for You
Explore our plan packages designed to suit your earning potential and preferences. With daily limits, referral bonuses, and various subscription plans, our platform offers opportunities for financial growth.
Blog Section: Insights and Updates
Stay informed with our blog, providing valuable insights into legal matters, organizational updates, and industry trends. Our recent articles cover topics ranging from law firm openings to significant developments in the legal landscape.
Testimonials: What Our Clients Say
Discover what our clients have to say about their experiences. Join thousands of satisfied users who have successfully withdrawn earnings and benefited from our platform.
Conclusion:
This FAQ guide serves as a resource for faculty members engaging with PTC procedures. By addressing common questions and providing insights into our platform’s earning opportunities, we aim to facilitate a transparent and informed academic community.
on line pharmacy skypharmacy
onlinepharmacy mexican pharmacies that ship
A person essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. That is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now? I amazed with the analysis you made to make this actual put up amazing. Excellent task!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/lv/join?ref=WTOZ531Y
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/el/join?ref=RQUR4BEO
Some really fantastic content on this website, regards for contribution. “Careful. We don’t want to learn from this.” by Bill Watterson.
how to get free online money
Understanding the processes and protocols within a Professional Tenure Committee (PTC) is crucial for faculty members. This Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) guide aims to address common queries related to PTC procedures, voting, and membership.
1. Why should members of the PTC fill out vote justification forms explaining their votes?
Vote justification forms provide transparency in decision-making. Members articulate their reasoning, fostering a culture of openness and ensuring that decisions are well-founded and understood by the academic community.
2. How can absentee ballots be cast?
To accommodate absentee voting, PTCs may implement secure electronic methods or designated proxy voters. This ensures that faculty members who cannot physically attend meetings can still contribute to decision-making processes.
3. How will additional members of PTCs be elected in departments with fewer than four tenured faculty members?
In smaller departments, creative solutions like rotating roles or involving faculty from related disciplines can be explored. Flexibility in election procedures ensures representation even in departments with fewer tenured faculty members.
4. Can a faculty member on OCSA or FML serve on a PTC?
Faculty members involved in other committees like the Organization of Committee on Student Affairs (OCSA) or Family and Medical Leave (FML) can serve on a PTC, but potential conflicts of interest should be carefully considered and managed.
5. Can an abstention vote be cast at a PTC meeting?
Yes, PTC members have the option to abstain from voting if they feel unable to take a stance on a particular matter. This allows for ethical decision-making and prevents uninformed voting.
6. What constitutes a positive or negative vote in PTCs?
A positive vote typically indicates approval or agreement, while a negative vote signifies disapproval or disagreement. Clear definitions and guidelines within each PTC help members interpret and cast their votes accurately.
7. What constitutes a quorum in a PTC?
A quorum, the minimum number of members required for a valid meeting, is essential for decision-making. Specific rules about quorum size are usually outlined in the PTC’s governing documents.
Our Plan Packages: Choose The Best Plan for You
Explore our plan packages designed to suit your earning potential and preferences. With daily limits, referral bonuses, and various subscription plans, our platform offers opportunities for financial growth.
Blog Section: Insights and Updates
Stay informed with our blog, providing valuable insights into legal matters, organizational updates, and industry trends. Our recent articles cover topics ranging from law firm openings to significant developments in the legal landscape.
Testimonials: What Our Clients Say
Discover what our clients have to say about their experiences. Join thousands of satisfied users who have successfully withdrawn earnings and benefited from our platform.
Conclusion:
This FAQ guide serves as a resource for faculty members engaging with PTC procedures. By addressing common questions and providing insights into our platform’s earning opportunities, we aim to facilitate a transparent and informed academic community.
I гeally ⅼike your blog.. veгy nice colors & theme. Ɗiⅾ you make this
website yourѕeⅼf or ԁid you hire someօne to ddo it foг you?
Plz reply as I’m ⅼooking tօ create my ownn blog and ԝould lіke to fіnd
out whgere u got this fгom. appreсiate іt
Herre iѕ my blkg – lani haʻuki ola pōpeku
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/pt-BR/join?ref=B4EPR6J0
The latest news and reviews in the world of tech, automotive, gaming, science, and entertainment. https://millionbyte.us/
Grеat site you haνe here but I was curious if you knew oof any
discussion boards tһɑt cover tһе ѕame topics discᥙssed in thyis article?
І’d reakly llve to be a ⲣart of online community
ԝherе І can gget feedback fгom othеr knowledgeable people tһat
share thе same interest. If yоu һave any suggestions, рlease let me know.
Bless you!
Feel free tⲟ surf to mу һomepage :: lajme sot në botë
Темная сторона интернета, это, невидимую, сеть, на, глобальной сети, доступ к которой, получается, через, особые, программы а также, технические средства, сохраняющие, конфиденциальность сетевых участников. Одним из, таких, средств, представляется, The Onion Router, который, предоставляет, защищенное, подключение в темную сторону интернета. Используя, этот, пользователи, имеют возможность, сокрыто, посещать, сайты, не отображаемые, стандартными, поисковыми системами, создавая тем самым, условия, для проведения, разнообразных, противоправных деятельностей.
Кракен, в результате, часто ассоциируется с, скрытой сетью, как, рынок, для торговли, киберугрозами. На этом ресурсе, может быть возможность, получить доступ к, разные, нелегальные, товары, начиная от, препаратов и огнестрельного оружия, вплоть до, хакерскими действиями. Платформа, гарантирует, крупную долю, криптографической защиты, и, защиты личной информации, это, делает, ее, желанной, для тех, кто, стремится, предотвратить, наказания, со стороны законопослушных органов
staffing agency for construction
Темная сторона интернета, является, анонимную, сеть, в, интернете, доступ к которой, происходит, путем, определенные, приложения и, технологии, обеспечивающие, конфиденциальность пользователей. Один из, этих, инструментов, считается, браузер Тор, который позволяет, обеспечивает, защищенное, подключение к сети, к даркнету. С, его, участники, имеют шанс, анонимно, заходить, интернет-ресурсы, не отображаемые, стандартными, поисковыми системами, создавая тем самым, обстановку, для проведения, разнообразных, противоправных деятельностей.
Киберторговая площадка, в результате, часто связывается с, темной стороной интернета, в качестве, торговая площадка, для торговли, криминалитетом. На данной платформе, может быть возможность, приобрести, разные, нелегальные, товары, начиная с, наркотических средств и огнестрельного оружия, заканчивая, хакерскими действиями. Платформа, предоставляет, крупную долю, криптографической защиты, а также, защиты личной информации, что, делает, ее, желанной, для тех, кто, желает, уклониться от, наказания, со стороны законопослушных органов.
colibrim.com web site.
colibrim.com
colibrim.com
colibrim.com
colibrim.com
colibrim.com
colibrim.com
saungsantoso.com
그들은 진심으로 그를 존경했고 Wang Zuo는 굉장했습니다.
netovideo.com
Zhu Houzhao는 그것을 믿지 않았습니다. 그렇게 큰 관리와 군인은 어떻습니까? 문제는 수천 명의 사람들이 있다는 것입니다.
See the wide choice of online casino welcome offers. Full list available on the casino offers page. WynnBET offers casino play in Michigan. Already used the Paddy Power sign-up offer? Take a look at more great bookmaker offers and the best betting sites. Paddy Power has an online casino that can be accessed by all of its customers. The Paddy Power app has a section for this casino that can be found from the main page of the app. Leaders in next generation technology and content; regulated markets and responsible gambling. Paddy Power Casino app tops the list of the best customer experience at the casino, as customers can conveniently enjoy playing their favourite casino games from wherever they are. There is a huge variety of Paddy Power Casino mobile slots that customers can choose from. Using the Paddy Power app, customers can also access the live casino on their mobile phones.
http://www.bardhi.com.ws052.alentus.com/wordpress/?p=61347
Cloudbet is a great casino and sportsbook in almost every way. Great layout, good game selection, the casino has lots of games you don’t see everywhere. They have unusually high max bets, and unlike some other sportsbooks, they didn’t attempt to lower those limits once we got a bit ahead. The fact that they have Bitcoin-only deposits withdrawals is actually ok. It means customer service isn’t always busy trying to figure out why somebody’s credit card declined or why a wire transfer went missing and can concentrate on answering your questions. While 888 are well established in the USA, running a number of partnerships including with Caesars in Nj and NV for casino, with Delaware Lottery to power their online offering and a partnership with the WSOP brand, there hasn’t been a major move yet into sports betting. Dominating online poker seems to be the focus for now, but perhaps there are lots of patient negotiations going on. Behind the scenes, they have been improving their Sportsbook provisions in apparent preparation with the purchase of BetBright (a now-former UK brand). We would expect 888 to become a significant player across the states in time, but for now, they seem to be focused on product rather than land grabbing.
Watches World
Watches World
homefronttoheartland.com
서로의 관계가 긴장되었지만 포르투갈도 가끔 왔습니다.
sky pharmacy online drugstore
skypharmacy
canadian pharmacy cialis
reggionotizie.com
그리고 사람들이 수술을 하도록 지도한 사람은 Liu Yidao였습니다.
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with
Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m
not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Many thanks!!
Definitеly believ that ᴡhich yⲟu stated.
Уoսr faqvorite justification seemed to be օn thе web tһe easiest thing
to Ьe aware οf. Ӏ say to you, I definitely ɡet irked while people think аbout worries thаt they ppainly
don’t қnow ab᧐ut. Yoou managed t᧐ hit the nail ᥙpon tһe t᧐p as well as defined out thе ᴡhole thing witһout һaving side-effects , people cоuld tɑke a
signal. Willl likeⅼy bе Ƅack to ɡet more.
Tһanks
Mү web-site – beli viewer youtube
Excellent blog here! Also your web site loads up very fast!
What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host?
I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
Wristwatches Planet
Client Testimonials Illuminate WatchesWorld Adventure
At WatchesWorld, client fulfillment isn’t just a goal; it’s a shining demonstration to our loyalty to superiority. Let’s plunge into what our esteemed customers have to say about their journeys, shedding light on the faultless assistance and exceptional chronometers we provide.
O.M.’s Review Testimonial: A Smooth Voyage
“Very good comms and follow through throughout the process. The watch was perfectively packed and in mint condition. I would certainly work with this team again for a wristwatch purchase.
O.M.’s statement demonstrates our devotion to comms and thorough care in delivering timepieces in perfect condition. The reliance established with O.M. is a foundation of our client connections.
Richard Houtman’s Insightful Testimonial: A Personal Reach
“I dealt with Benny, who was exceptionally beneficial and polite at all times, keeping me regularly updated of the procedure. Advancing, even though I ended up sourcing the wristwatch locally, I would still surely recommend Benny and the company advancing.
Richard Houtman’s experience showcases our personalized approach. Benny’s assistance and continuous communication exhibit our devotion to ensuring every customer feels esteemed and informed.
Customer’s Productive Assistance Testimonial: A Effortless Trade
“A very efficient and effective service. Kept me informed on the transaction progress.
Our loyalty to effectiveness is echoed in this patron’s feedback. Keeping buyers apprised and the smooth progress of acquisitions are integral to the Our Watch Boutique encounter.
Discover Our Newest Choices
Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Selfwinding 37mm
A gorgeous piece at €45,900, this 2022 edition (REF: 15551ST.ZZ.1356ST.05) invites you to add it to your basket and elevate your collection.
Hublot Titanium Green 45mm Chrono
Priced at €8,590 in 2024 (REF: 521.NX.8970.RX), this Hublot creation is a blend of design and invention, awaiting your inquiry.
whoah this weblog is fantastic і lіke reading yoᥙr posts.
Stay ᥙp thе good work! Үοu ɑlready knoѡ, a loot oof individuals
аrе hunting aaround fоr tһіs informatіⲟn, yߋu can aid
them greɑtly.
My webpage – beli subscriber
ST666
Hі, Neat post. Ꭲһere’ѕ an isue with yоur site in web explorer, might check
tһis? ІE nonetһeless iѕ the market chief and a
big component to other folks ԝill miѕs your magnificent writing Ƅecause of this proƄlem.
Heree is my blog :: discuss
pacific care pharmacy online pharmacies without scripts canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
usa pharmacy no script prescription free pharmacy canadian pharmacy
cialis canadian pharmacy canada pharmacy no prescription canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
Wiekszosc slotow dziala tylko z VPN, ale wyprobuj ten neosurf co to , to dziala dobrze.
Gram tutaj kasyna z muchbetter jednak to dziala dla mnie.
4 corners pharmacy no prescription pharmacy canadian pharmacy cialis
мосты для tor browser список
Защита в сети: Перечень мостов для Tor Browser
В настоящий период, когда аспекты секретности и защиты в сети становятся все более значимыми, многочисленные пользователи обращают внимание на инструменты, позволяющие гарантировать скрытность и секретность личной информации. Один из таких инструментов – Tor Browser, разработанный на инфраструктуре Tor. Однако даже при использовании Tor Browser есть опасность столкнуться с преградой или ограничением со стороны Интернет-поставщиков или цензоров.
Для обхода этих ограничений были созданы мосты для Tor Browser. Переправы – это уникальные серверы, которые могут быть использованы для обхода блокировок и снабжения доступа к сети Tor. В представленном тексте мы рассмотрим реестр подходов, которые можно использовать с Tor Browser для обеспечивания устойчивой и надежной скрытности в интернете.
meek-azure: Этот мост использует облачное обеспечение Azure для того, чтобы скрыть тот факт, что вы используете Tor. Это может быть полезно в странах, где поставщики блокируют доступ к серверам Tor.
obfs4: Переход обфускации, предоставляющий средства для сокрытия трафика Tor. Этот подход может эффективным образом обходить блокировки и запреты, делая ваш трафик невидимым для сторонних.
fte: Переправа, использующий Free Talk Encrypt (FTE) для обфускации трафика. FTE позволяет переформатировать трафик так, чтобы он казался обычным сетевым трафиком, что делает его более трудным для выявления.
snowflake: Этот переход позволяет вам использовать браузеры, которые поддерживаются расширение Snowflake, чтобы помочь другим пользователям Tor пройти через цензурные блокировки.
fte-ipv6: Вариант FTE с поддерживающий IPv6, который может быть необходим, если ваш провайдер интернета предоставляет IPv6-подключение.
Чтобы использовать эти переправы с Tor Browser, откройте его настройки, перейдите в раздел “Проброс мостов” и введите названия переправ, которые вы хотите использовать.
Не забывайте, что результативность переправ может изменяться в зависимости от страны и провайдера интернет-услуг. Также рекомендуется систематически обновлять список подходов, чтобы быть уверенным в эффективности обхода блокировок. Помните о важности защиты в интернете и осуществляйте защиту для защиты своей личной информации.
Внутри века технологий, в условиях, когда онлайн границы сливаются с реальностью, запрещено игнорировать присутствие угроз в подпольной сети. Одной из таких угроз является blacksprut – выражение, переросший символом криминальной, вредоносной деятельности в теневых уголках интернета.
Blacksprut, будучи составной частью подпольной сети, представляет важную угрозу для безопасности в сети и личной безопасности пользователей. Этот неявный уголок сети часто ассоциируется с нелегальными сделками, торговлей запрещенными товарами и услугами, а также иной противозаконными деяниями.
В борьбе с угрозой blacksprut необходимо приложить усилия на различных фронтах. Одним из основных направлений является совершенствование технологий кибербезопасности. Развитие современных алгоритмов и технологий анализа данных позволит выявить и пресекать деятельность blacksprut в реальном времени.
Помимо инженерных мер, важна взаимодействие усилий правоохранительных органов на мировом уровне. Международное сотрудничество в сфере защиты в сети необходимо для успешного противодействия угрозам, связанным с blacksprut. Обмен сведениями, создание совместных стратегий и реактивные действия помогут ограничить воздействие этой угрозы.
Обучение и освещение также играют важное значение в борьбе с blacksprut. Повышение информированности пользователей о рисках даркнета и методах предотвращения становится неотъемлемой компонентом антиспампинговых мероприятий. Чем более информированными будут пользователи, тем меньше вероятность попадания под влияние угрозы blacksprut.
В заключение, в борьбе с угрозой blacksprut необходимо совместить усилия как на цифровом, так и на нормативном уровнях. Это вызов, предполагающий совместных усилий граждан, правительства и IT-компаний. Только совместными усилиями мы добьемся создания безопасного и надежного цифрового пространства для всех.
почему-тор браузер не соединяется
Тор-поиск является эффективным инструментом для сбережения скрытности и защиты в сети. Однако, иногда люди могут встретиться с сложностями входа. В данном материале мы рассмотрим вероятные предпосылки и представим способы решения для ликвидации проблем с подключением к Tor Browser.
Проблемы с интернетом:
Решение: Проверка соединения ваше интернет-связь. Проверьте, что вы в сети к сети, и отсутствуют ли неполадок с вашим провайдером.
Блокировка инфраструктуры Тор:
Решение: В некоторых определенных территориях или интернет-сетях Tor может быть заблокирован. Воспользуйтесь использовать переправы для обхода запретов. В настройках Tor Browser выберите опцию “Проброс мостов” и применяйте инструкциям.
Прокси-серверы и брандмауэры:
Решение: Проверьте настройки прокси и стены. Проверьте, что они не блокируют доступ Tor Browser к вебу. Измени те настройки или временно деактивируйте прокси и стены для испытания.
Проблемы с самим браузером:
Решение: Убедитесь, что у вас присутствует последнее обновление Tor Browser. Иногда изменения могут распутать недоразумения с соединением. Также попробуйте пересоздать приложение.
Временные сбои в инфраструктуре Тор:
Решение: Подождите некоторое время некоторое время и пытайтесь достичь соединения впоследствии. Временные сбои в работе Tor имеют возможность происходить, и эти явления как обычно исправляются в кратчайшие периоды.
Отключение JavaScript:
Решение: Некоторые из числа веб-ресурсы могут запрещать вход через Tor, если в вашем программе для просмотра включен JavaScript. Попытайтесь временно отключить JavaScript в параметрах обозревателя.
Проблемы с антивирусным ПО:
Решение: Ваш антивирусная программа или ограждение может ограничивать Tor Browser. Убедитесь, что у вас отсутствует запрещений для Tor в параметрах вашего защитного ПО.
Исчерпание памяти:
Решение: Если у вас запущено много окон или задачи, это может призвести к исчерпанию памяти устройства и проблемам с входом. Закройте лишние вкладки или перезагрузите приложение.
В случае, если сложность с соединением к Tor Browser продолжает, заинтересуйтесь за помощью на официальной дискуссионной площадке Tor. Профессионалы способны подсказать дополнительную поддержку и советы. Помните, что безопасность и конфиденциальность требуют постоянного внимания к мелочам, так что учитывайте обновлениями и применяйте поручениям сообщества.
Timepieces Globe
Patron Feedback Reveal Our Watch Boutique Journey
At WatchesWorld, client fulfillment isn’t just a aim; it’s a radiant evidence to our dedication to perfection. Let’s dive into what our valued clients have to communicate about their journeys, revealing on the perfect support and remarkable timepieces we present.
O.M.’s Review Testimonial: A Effortless Adventure
“Very good interaction and follow along throughout the procedure. The watch was perfectively packed and in perfect. I would certainly work with this group again for a watch acquisition.
O.M.’s declaration illustrates our commitment to comms and precise care in delivering watches in impeccable condition. The trust established with O.M. is a cornerstone of our client connections.
Richard Houtman’s Informative Review: A Personalized Contact
“I dealt with Benny, who was exceedingly beneficial and courteous at all times, keeping me regularly apprised of the procedure. Advancing, even though I ended up sourcing the wristwatch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the business progressing.
Richard Houtman’s interaction showcases our individualized approach. Benny’s assistance and uninterrupted interaction showcase our dedication to ensuring every client feels esteemed and informed.
Customer’s Productive Service Testimonial: A Uninterrupted Trade
“A very effective and efficient service. Kept me informed on the order progression.
Our loyalty to productivity is echoed in this patron’s response. Keeping clients apprised and the smooth development of transactions are integral to the Our Watch Boutique journey.
Examine Our Current Collections
Audemars Piguet Selfwinding Royal Oak 37mm
A stunning piece at €45,900, this 2022 edition (REF: 15551ST.ZZ.1356ST.05) invites you to add it to your trolley and elevate your assortment.
Hublot Classic Fusion Chronograph Titanium Green 45mm
Priced at €8,590 in 2024 (REF: 521.NX.8970.RX), this Hublot creation is a blend of fashion and innovation, awaiting your request.
Hаve you ever thoսght abⲟut adding a little bit mօre thɑn ϳust ypur articles?
I mean, what үoս say іѕ valuable аnd everytһing.
But imagine if y᧐u added ѕome ɡreat visuals ᧐r videos to give your pists more, “pop”!
Y᧐ur content iѕ excellent bᥙt wіtһ
pics and clips, this website could definitely Ьe
oone of tһe bеst in its field. Greɑt blog!
Aⅼso visit my web-site beli viewer youtube
LipoSlend is a liquid nutritional supplement that promotes healthy and steady weight loss. https://liposlendofficial.us/
this-is-a-small-world.com
이 Ouyang Zhi는 사람들을 아주 잘 꾸짖었습니다.
Wiekszosc slotow dziala tylko z VPN, ale wyprobuj ten neosurf co to to dziala w 100%.
Graj tutaj kasyno Bet on Red , to jest dobre na poczatek.
Hі, everything is going wеll here ɑnd ofcourse
every one iѕ sharing data, tһat’ѕ genuinely gοod, қeep up writing.
my homepage; discuss
ST666
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/ka-GE/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Do yߋu havge a spam issue ⲟn thіs blog; I also am a blogger, аnd Ι ᴡas
cureious about yoսr situation; many of us have developed ѕome nice
procedures аnd wee are looking to swap methods ԝith otһer
folks, bee ѕure to shoot me аn е-mail if
interestеd.
Taake а loοk at my pаge: beli viewer youtube
สล็อตเว็บ ตรง จากค่ายเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ชื่อดังอันดับ 1 ที่นักพนันทั่วโลกให้การยอมรับว่าเป็นค่ายเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ดีที่สุดตลอดกาลกับค่าย PG SLOT ที่มาแรงที่สุดในปี 2022
baseballoutsider.com
아시다시피 천연두는 한 번 감염되면 면역력이 생깁니다.
canadian pharmacy express non prescription pharmacy canadian pharmacy no prescription
online pharmacy canadian pharmacy no prescription canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
Узнайте Где включить запись разговора vivo y 33 в новой статье на нашем сайте.
Hmm it appears likе your blog ate my firrst comment (іt ᴡas extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum іt up what
I wrote and ѕay, Ι’m tһoroughly enjoying ʏouг blog.
I as ѡell am аn aspiring blog writer but I’m
stilll new to the whoⅼe thing. Ɗο уou һave any recommendations fօr first-time
blog writers? I’d reаlly apρreciate it.
my site :: beli viewer youtube
canadian pharmacy canada pharmacies no description online pharmacy
Узнайте Как поменять иконки на realme c53 в новой статье на нашем сайте.
10yenharwichport.com
Zhu Houzhao는 다시 한숨을 쉬었습니다. “Zai Mo, 당신이 황제라면 어떻게 될까요?”
Heⅼlo, аfter reading this amazing paragraph i am as well glad to share my familiarity һere with colleagues.
Feel frere tօ surf to mmy webpage; beli subscriber youtube
オンラインカジノ
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/kz/register-person?ref=PORL8W0Z
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
線上賭場
香港娛樂城
onlinepharmacy pharmacy no prescripition canadian pharmacy
sm-casino1.com
이발사는 그의 피 흘리는 모습을 바라보며 중얼거렸다.
You couⅼd Ԁefinitely ѕee your enthusiasm ԝithin tthe article ʏou
write. The sector hopes forr еven more passionate writers ⅼike you whօ aren’t afraid to sɑy how tһey belіeve.
Always follow your heart.
Аlso visit my web page beli view youtube
For tһе reason that thе admin of this web site is wⲟrking, no doubt very soоn it wiⅼl
be famous, dᥙe to itѕ feature сontents.
Here is my blog: beli viewer youtube
香港網上賭場
Изготовление и использование клонов банковских карт является недопустимой практикой, представляющей существенную угрозу для безопасности финансовых систем и личных средств граждан. В данной статье мы рассмотрим потенциальные опасности и воздействие покупки копий карт, а также как общество и полиция борются с такими преступлениями.
“Клоны” карт — это пиратские подделки банковских карт, которые используются для непозволительных транзакций. Основной метод создания клонов — это кража данных с оригинальной карты и последующее программирование этих данных на другую карту. Злоумышленники, предлагающие услуги по продаже копий карт, обычно действуют в подпольной сфере интернета, где трудно выявить и пресечь их деятельность.
Покупка клонов карт представляет собой значительное преступление, которое может повлечь за собой серьезные наказания. Покупатель также рискует стать участником мошенничества, что может привести к судебному преследованию. Основные преступные действия в этой сфере включают в себя кражу личной информации, фальсификацию документов и, конечно же, финансовые преступления.
Банки и правоохранительные органы активно борются с правонарушениями, связанными с копированием карт. Банки внедряют новые технологии для выявления подозрительных транзакций, а также предлагают услуги по обеспечению безопасности для своих клиентов. Органы порядка ведут оперативные действия и задерживают тех, кто замешан в создании и продаже клонов карт.
Для обеспечения безопасности важно соблюдать внимание при использовании банковских карт. Необходимо периодически проверять выписки, избегать подозрительных сделок и следить за своей личной информацией. Образованность и осведомленность об угрозах также являются основными средствами в борьбе с мошенничеством.
В заключение, использование реплик банковских карт — это незаконное и неприемлемое поведение, которое может привести к серьезным последствиям для тех, кто вовлечен в такую практику. Соблюдение мер безопасности, осведомленность о возможных потенциальных рисках и сотрудничество с полицией играют определяющую роль в предотвращении и пресечении этих преступлений
canadian pharmacy cialis canadian pharmacy no prescription canadian pharmacy no prescription
247 overnight pharmacy canadian online pharmacies without scripts canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
online platform for watches
In the world of premium watches, finding a trustworthy source is essential, and WatchesWorld stands out as a symbol of trust and knowledge. Offering an extensive collection of esteemed timepieces, WatchesWorld has accumulated praise from content customers worldwide. Let’s explore into what our customers are saying about their experiences.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.’s Review on O.M.:
“Excellent communication and follow-up throughout the process. The watch was perfectly packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this group again for a watch purchase.”
Richard Houtman’s Review on Benny:
“I dealt with Benny, who was highly supportive and courteous at all times, keeping me regularly informed of the procedure. Moving forward, even though I ended up acquiring the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company.”
Customer’s Efficient Service Experience:
“A highly efficient and efficient service. Kept me up to date on the order progress.”
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an internet platform; it’s a dedication to customized service in the realm of luxury watches. Our group of watch experts prioritizes trust, ensuring that every customer makes an knowledgeable decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our group brings matchless understanding and insight into the realm of high-end timepieces.
Trust: Confidence is the foundation of our service, and we prioritize transparency in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is our paramount goal, and we go the extra mile to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you’re not just purchasing a watch; you’re investing in a seamless and reliable experience. Explore our collection, and let us assist you in finding the ideal timepiece that embodies your style and elegance. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our time-tested commitment
chutneyb.com
오랜만에 그는 두꺼비 거울을 벗었다.
Tonic Greens is an all-in-one dietary supplement that has been meticulously designed to improve overall health and mental wellness.
Your style is very unique compared to other folks I have read stuff from.
I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity,
Guess I will just bookmark this web site.
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Many
thanks! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with
the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to find
out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
If you are going for best contents like I do, simply pay a visit this site every day since it provides quality contents, thanks
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your web site.
Do you ever run into any internet browser compatibility problems?
A handful of my blog readers have complained about my blog not operating correctly in Explorer but
looks great in Firefox. Do you have any solutions to help fix this issue?
Bazopril is a blood pressure supplement featuring a blend of natural ingredients to support heart health
In the world of high-end watches, discovering a dependable source is paramount, and WatchesWorld stands out as a pillar of confidence and expertise. Providing an wide collection of renowned timepieces, WatchesWorld has garnered acclaim from content customers worldwide. Let’s delve into what our customers are saying about their experiences.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.’s Review on O.M.:
“Outstanding communication and follow-up throughout the procedure. The watch was flawlessly packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this group again for a watch purchase.”
Richard Houtman’s Review on Benny:
“I dealt with Benny, who was exceptionally assisting and courteous at all times, preserving me regularly informed of the process. Moving forward, even though I ended up acquiring the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company.”
Customer’s Efficient Service Experience:
“A highly efficient and efficient service. Kept me up to date on the order progress.”
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an online platform; it’s a commitment to personalized service in the realm of luxury watches. Our group of watch experts prioritizes trust, ensuring that every customer makes an knowledgeable decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our group brings matchless knowledge and insight into the realm of luxury timepieces.
Trust: Confidence is the foundation of our service, and we prioritize openness in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is our paramount goal, and we go the additional step to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you’re not just buying a watch; you’re committing in a smooth and trustworthy experience. Explore our range, and let us assist you in finding the ideal timepiece that reflects your taste and elegance. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our time-tested commitment
карты на обнал
Использование платежных карт является неотъемлемой частью современного общества. Карты предоставляют удобство, безопасность и разнообразные варианты для проведения банковских транзакций. Однако, кроме законного применения, существует негативная сторона — обналичивание карт, когда карты используются для вывода наличных средств без разрешения владельца. Это является незаконной практикой и влечет за собой строгие санкции.
Вывод наличных средств с карт представляет собой практики, направленные на извлечение наличных средств с банковской карты, необходимые для того, чтобы обойти систему защиты и оповещений, предусмотренных банком. К сожалению, такие противозаконные деяния существуют, и они могут привести к потере средств для банков и клиентов.
Одним из способов вывода наличных средств является использование технологических трюков, таких как кража данных с магнитных полос карт. Скимминг — это способ, при котором злоумышленники устанавливают аппараты на банкоматах или терминалах оплаты, чтобы сканировать информацию с магнитной полосы пластиковой карты. Полученные данные затем используются для формирования реплики карты или проведения интернет-транзакций.
Другим часто используемым способом является мошенничество, когда преступники отправляют лукавые письма или создают поддельные веб-сайты, имитирующие банковские ресурсы, с целью доступа к конфиденциальным данным от клиентов.
Для предотвращения кэшаута карт банки вводят разнообразные меры. Это включает в себя повышение уровня безопасности, осуществление двухфакторной верификации, анализ транзакций и просвещение пользователей о способах предупреждения мошенничества.
Клиентам также следует проявлять активность в защите своих карт и данных. Это включает в себя регулярное изменение паролей, анализ выписок из банка, а также осторожность по отношению к сомнительным транзакциям.
Кэшаут карт — это опасное преступление, которое наносит ущерб не только банкам, но и обществу в целом. Поэтому важно соблюдать внимание при работе с банковскими картами, быть осведомленным о методах мошенничества и соблюдать меры безопасности для предотвращения потери средств
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/cs/register-person?ref=OMM3XK51
lfchungary.com
“삼촌, 황실 사신이 궁에 왔습니다. 황실 사신이 궁에 왔습니다. 폐하의 뜻이 있습니다!”
smcasino7.com
순식간에 Liu Mansion 전체가 엉망이되었고 건물은 비어있었습니다.
Pineal XT is a revolutionary supplement that promotes proper pineal gland function and energy levels to support healthy body function.
https://gorod-buketov.ru/ купить цветы с доставкой мск
lfchungary.com
구시가지 역세권 30장 집 시세는 500냥이 넘는다.
даркнет вход
Темная сторона интернета – скрытая сфера интернета, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая специальных средств для доступа. Этот несканируемый уголок сети обильно насыщен платформами, предоставляя доступ к различным товарам и услугам через свои каталоги и индексы. Давайте ближе рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они хранят.
Даркнет Списки: Порталы в Неизведанный Мир
Даркнет списки – это своего рода проходы в скрытый мир интернета. Реестры и справочники веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать различные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти списки предоставляют нам возможность заглянуть в неизведанный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто ассоциируется с незаконными сделками, где доступны разнообразные товары и услуги – от наркотиков и оружия до украденных данных и услуг наемных убийц. Реестры ресурсов в этой категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет площадку для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, перечисленные в даркнет списках, затрагивают различные темы – от кибербезопасности и хакерства до политических аспектов и философских концепций.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие информацию и инструкции по обходу цензуры, защите конфиденциальности и другим темам, интересным тем, кто хочет сохранить свою конфиденциальность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на скрытность и свободу, даркнет полон опасностей. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки являются неотъемлемой частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с реестрами даркнета, пользователи должны соблюдать предельную осмотрительность и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Реестры даркнета – это врата в неизведанный мир, где хранятся тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой осторожности и знания. Анонимность не всегда гарантирует безопасность, и использование даркнета требует сознательного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические детали в области кибербезопасности, поиск необычных товаров или исследование новых возможностей в интернете – реестры даркнета предоставляют ключ
Даркнет – скрытая сфера интернета, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая эксклюзивных средств для доступа. Этот несканируемый уголок сети обильно насыщен сайтами, предоставляя доступ к разнообразным товарам и услугам через свои каталоги и индексы. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они хранят.
Даркнет Списки: Порталы в Неизведанный Мир
Индексы веб-ресурсов в темной части интернета – это своего рода врата в неощутимый мир интернета. Каталоги и индексы веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать различные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти перечни предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в непознанный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто связывается с теневым рынком, где доступны разнообразные товары и услуги – от наркотиков и оружия до краденых данных и услуг наемных убийц. Реестры ресурсов в этой категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет площадку для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, указанные в каталогах даркнета, охватывают различные темы – от информационной безопасности и взлома до политических вопросов и философских идей.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие информацию и инструкции по обходу цензуры, защите конфиденциальности и другим темам, которые могут быть интересны тем, кто хочет остаться анонимным.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на анонимность и свободу, даркнет полон опасностей. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки являются неотъемлемой частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с списками ресурсов в темной сети, пользователи должны соблюдать максимальную осторожность и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Списки даркнета – это врата в неизведанный мир, где скрыты секреты и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в темную сеть требует особой бдительности и знаний. Анонимность не всегда гарантирует безопасность, и использование темной сети требует осмысленного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические детали в области кибербезопасности, поиск необычных товаров или исследование новых возможностей в интернете – даркнет списки предоставляют ключ
Темная сторона интернета – таинственная сфера всемирной паутины, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая эксклюзивных средств для доступа. Этот анонимный уголок сети обильно насыщен ресурсами, предоставляя доступ к разношерстным товарам и услугам через свои каталоги и каталоги. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти реестры и какие тайны они хранят.
Даркнет Списки: Ворота в Скрытый Мир
Даркнет списки – это вид врата в неощутимый мир интернета. Реестры и справочники веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать разнообразные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти списки предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в непознанный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто ассоциируется с незаконными сделками, где доступны самые разные товары и услуги – от наркотических препаратов и стрелкового вооружения до похищенной информации и услуг наемных убийц. Каталоги ресурсов в данной категории облегчают пользователям находить нужные предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также служит для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, представленные в реестрах даркнета, затрагивают различные темы – от кибербезопасности и хакерства до политических вопросов и философских идей.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие сведения и руководства по обходу цензуры, защите конфиденциальности и другим вопросам, которые могут заинтересовать тех, кто стремится сохранить свою анонимность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на скрытность и свободу, даркнет не лишен опасностей. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки являются неотъемлемой частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с даркнет списками, пользователи должны соблюдать высший уровень бдительности и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Реестры даркнета – это ключ к таинственному миру, где хранятся тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой осторожности и знания. Не всегда анонимность приносит безопасность, и использование темной сети требует осмысленного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические детали в области кибербезопасности, поиск необычных товаров или исследование новых возможностей в интернете – даркнет списки предоставляют ключ
даркнет-список
Даркнет – это часть интернета, которая остается скрытой от обычных поисковых систем и требует специального программного обеспечения для доступа. В этой анонимной зоне сети существует множество ресурсов, включая различные списки и каталоги, предоставляющие доступ к разнообразным услугам и товарам. Давайте рассмотрим, что представляет собой каталог даркнета и какие тайны скрываются в его глубинах.
Теневые каталоги: Врата в анонимность
Для начала, что такое даркнет список? Это, по сути, каталоги или индексы веб-ресурсов в темной части интернета, которые позволяют пользователям находить нужные услуги, товары или информацию. Эти списки могут варьироваться от чатов и магазинов до ресурсов, специализирующихся на различных аспектах анонимности и криптовалют.
Категории и Возможности
Черный Рынок:
Темная сторона интернета часто ассоциируется с теневым рынком, где можно найти различные товары и услуги, включая наркотики, оружие, украденные данные и даже услуги профессиональных устрашителей. Списки таких ресурсов позволяют пользователям без труда находить подобные предложения.
Чаты и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет платформы для анонимного общения. Чаты и сообщества на даркнет списках могут заниматься обсуждением тем от интернет-безопасности и взлома до политики и философии.
Информационные ресурсы:
Есть ресурсы, предоставляющие информацию и инструкции по обходу цензуры, защите конфиденциальности и другим темам, интересным пользователям, стремящимся сохранить анонимность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
При всей своей анонимности и свободе действий даркнет также несет риски. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки становятся частью этого мира. Пользователям необходимо проявлять максимальную осторожность и соблюдать меры безопасности при взаимодействии с списками теневых ресурсов.
Заключение: Врата в Неизведанный Мир
Теневые каталоги предоставляют доступ к скрытым уголкам сети, где сокрыты тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, важно помнить о возможных рисках и осознанно подходить к использованию темной стороны интернета. Анонимность не всегда гарантирует безопасность, и путешествие в этот мир требует особой осторожности и знания.
Независимо от того, интересуетесь ли вы техническими аспектами кибербезопасности, ищете уникальные товары или просто исследуете новые грани интернета, теневые каталоги предоставляют ключ
Темная сторона интернета – скрытая зона интернета, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая дополнительных средств для доступа. Этот несканируемый уголок сети обильно насыщен платформами, предоставляя доступ к разнообразным товарам и услугам через свои перечни и справочники. Давайте глубже рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они сокрывают.
Даркнет Списки: Ворота в Неизведанный Мир
Даркнет списки – это своего рода проходы в неощутимый мир интернета. Реестры и справочники веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать разношерстные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти списки предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в таинственный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто связывается с незаконными сделками, где доступны самые разные товары и услуги – от психоактивных веществ и стрелкового оружия до похищенной информации и услуг наемных убийц. Реестры ресурсов в данной категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет площадку для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, указанные в каталогах даркнета, охватывают широкий спектр – от кибербезопасности и хакерства до политических аспектов и философских концепций.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие информацию и инструкции по преодолению цензуры, обеспечению конфиденциальности и другим вопросам, которые могут заинтересовать тех, кто стремится сохранить свою анонимность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на скрытность и свободу, даркнет полон опасностей. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки становятся частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с списками ресурсов в темной сети, пользователи должны соблюдать максимальную осторожность и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Даркнет списки – это ключ к таинственному миру, где сокрыты тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой осторожности и знания. Анонимность не всегда гарантирует безопасность, и использование темной сети требует сознательного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические аспекты кибербезопасности, поиск уникальных товаров или исследование новых граней интернета – даркнет списки предоставляют ключ
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/bg/register-person?ref=T7KCZASX
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/tr/join?ref=PORL8W0Z
whoah this blog is wonderful i love reading your articles. Keep up the great work! You know, a lot of people are looking around for this information, you can aid them greatly.
pragmatic-ko.com
그리고 서양인의 주식인 으깬 감자라는 전설이 있다.
st666
casino
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/ro/join?ref=V3MG69RO
dota2answers.com
그러나 장씨는 “당신의 미혼 남편이 지금 명성을 얻었습니까? “라고 물었습니다.
smcasino-game.com
한린학원은 지금 아주 한가하고, 아직도 주식시장에 대해 수다 떨고 있는 사람들이 있습니다.
Ahaa, its pleasant dialogue about this piece of writing here at
this website, I have read all that, so at this
time me also commenting at this place.
pragmatic-ko.com
이 사람은 내 또래이고 이름은 Liu Kaizhi입니다.
走在时代前沿,选择电报。一站式的通讯解决方案,满足您所有聊天需求。立即下载电报,开启全新的沟通之旅!https://dianbao.vn 7qolkwj3jd
đăng nhập st666
Gambling
заливы без предоплат
В последнее период стали известными запросы о заливах без предоплат – услугах, предлагаемых в интернете, где пользователям обещают выполнение заказа или предоставление товара до внесения денег. Однако, за этой кажущейся выгодой могут быть скрываться серьезные опасности и неблагоприятные следствия.
Привлекательность бесплатных заливов:
Привлекательность идеи переводов без предварительной оплаты заключается в том, что клиенты получают сервис или продукцию, не внося сначала средства. Данное условие может казаться выгодным и комфортным, в частности для таких, кто не хочет ставить под риск деньгами или остаться мошенничеством. Однако, прежде чем погрузиться в сферу бесплатных переводов, необходимо учесть ряд существенных пунктов.
Опасности и отрицательные следствия:
Мошенничество и обман:
За порядочными проектами без предварительной оплаты скрываются мошенники, приготовленные использовать уважение клиентов. Оказавшись в ихнюю ловушку, вы можете потерять не только, но и но и денег.
Низкое качество выполнения работ:
Без обеспечения оплаты исполнителю может стать мало мотивации оказать качественную работу или товар. В результате заказчик останется недовольным, а исполнитель не подвергнется серьезными санкциями.
Потеря информации и защиты:
При предоставлении персональных данных или информации о финансовых средствах для бесплатных переводов существует риск раскрытия информации и последующего их неправомерного использования.
Советы по надежным заливам:
Исследование:
До подбором бесплатных заливов проведите комплексное исследование исполнителя. Мнения, рейтинговые оценки и популярность могут быть полезным показателем.
Предоплата:
Если возможно, старайтесь договориться определенный процент вознаграждения вперед. Это может сделать соглашение более безопасной и обеспечит вам больший объем управления.
Проверенные платформы:
Отдавайте предпочтение использованию надежных площадок и сервисов для переводов. Это снизит опасность обмана и увеличит шансы на получение наилучших качественных услуг.
Итог:
Не смотря на очевидную привлекательность, заливы без предоплат несут в себе риски и потенциальные опасности. Внимание и осторожность при подборе поставщика или сервиса могут предупредить негативные последствия. Существенно помнить, что бесплатные переводы могут превратиться в причиной проблем, и разумное принятие решения способствует предотвратить потенциальных неприятностей
gambling
Скрытая сфера – это загадочная и незнакомая область интернета, где действуют особые правила, перспективы и угрозы. Каждый день в мире теневой сети случаются события, о которых стандартные пользователи могут лишь догадываться. Давайте изучим актуальные сведения из даркнета, которые отражают современные тренды и события в этом таинственном пространстве сети.”
Тенденции и События:
“Эволюция Технологий и Безопасности:
В даркнете постоянно совершенствуются технологии и методы обеспечения безопасности. Информация о появлении усовершенствованных систем шифрования, скрытия личности и защиты личных данных свидетельствуют о желании участников и разработчиков к обеспечению надежной среды.”
“Новые Теневые Рынки:
Следуя динамикой изменений спроса и предложения, в теневом интернете появляются совершенно новые коммерческие площадки. Информация о открытии онлайн-рынков подаривают пользователям различные варианты для торговли продукцией и сервисами
Покупка удостоверения личности в онлайн магазине – это противозаконное и рискованное поступок, которое может привести к серьезным последствиям для людей. Вот несколько аспектов, о которые важно помнить:
Нарушение законодательства: Покупка паспорта в интернет-магазине является преступлением закона. Владение поддельным удостоверением способно сопровождаться уголовную наказание и тяжелые штрафы.
Риски индивидуальной секретности: Факт использования поддельного удостоверения личности способен поставить под опасность личную безопасность. Личности, использующие фальшивыми документами, способны стать целью преследования со со стороны законопослушных структур.
Финансовые убытки: Часто обманщики, продающие фальшивыми паспортами, способны использовать ваши информацию для обмана, что приведёт к денежным убыткам. Личные или материальные данные способны оказаться использованы в криминальных намерениях.
Трудности при перемещении: Фальшивый паспорт может быть распознан при попытке пересечь границы или при контакте с официальными инстанциями. Такое обстоятельство способно привести к задержанию, изгнанию или другим тяжелым проблемам при перемещении.
Утрата доверия и репутации: Применение поддельного удостоверения личности способно послужить причиной к утрате доверительности со со стороны сообщества и работодателей. Это ситуация может негативно влиять на вашу престиж и трудовые возможности.
Вместо того, чтобы подвергать опасности собственной независимостью, защитой и престижем, советуется соблюдать закон и воспользоваться государственными путями для оформления удостоверений. Эти предоставляют защиту всех ваших прав и обеспечивают безопасность личных информации. Нелегальные действия могут повлечь за собой непредсказуемые и негативные ситуации, создавая тяжелые трудности для вас и ваших вашего окружения
Теневой интернет 2024: Неявные взгляды цифровой среды
С начала теневого интернета был собой закуток интернета, где секретность и тень были обыденностью. В 2024 году этот скрытый мир продолжает, предоставляя дополнительные требования и опасности для интернет-сообщества. Рассмотрим, какие тренды и модификации предстоят нас в даркнете 2024.
Технологический прогресс и Повышение скрытности
С развитием техники, инструменты для обеспечения скрытности в даркнете становятся более сложными и действенными. Использование цифровых валют, современных шифровальных методов и децентрализованных сетей делает отслеживание за поведением участников более сложным для силовых структур.
Развитие тематических рынков
Даркнет-рынки, фокусирующиеся на различных товарах и услугах, продолжают развиваться. Наркотики, военные припасы, хакерские инструменты, персональная информация – спектр товаров становится все более многообразным. Это создает сложность для правопорядка, стоящего перед задачей адаптироваться к постоянно меняющимся сценариям преступной деятельности.
Опасности кибербезопасности для непрофессионалов
Сервисы аренды хакерских услуг и обманные планы остаются активными в даркнете. Люди, не связанные с преступностью попадают в руки целью для преступников в сети, стремящихся зайти к личным данным, счетам в банке и другой конфиденциальной информации.
Перспективы цифровой реальности в даркнете
С развитием технологий виртуальной реальности, теневой интернет может перейти в новый этап, предоставляя участникам более реалистичные и вовлекающие цифровые области. Это может сопровождаться дополнительными видами нелегальных действий, такими как цифровые рынки для обмена цифровыми товарами.
Борьба структурам защиты
Силы безопасности улучшают свои технологии и подходы борьбы с даркнетом. Совместные усилия стран и международных организаций ориентированы на предотвращение цифровой преступности и прекращение современным проблемам, которые возникают в связи с развитием скрытого веба.
Заключение
Даркнет 2024 остается комплексной и разносторонней обстановкой, где технические инновации продолжают изменять ландшафт нелегальных действий. Важно для участников оставаться бдительными, гарантировать свою кибербезопасность и соблюдать законы, даже при нахождении в виртуальном пространстве. Вместе с тем, противостояние с даркнетом требует коллективных действиях от стран, технологических компаний и граждан, для обеспечения защиту в сетевой среде.
даркнет магазин
В последний период интернет превратился в бесконечный источник информации, услуг и продуктов. Однако, среди бесчисленных виртуальных магазинов и площадок, есть темная сторона, известная как даркнет магазины. Данный уголок виртуального мира создает свои рискованные реалии и сопровождается значительными рисками.
Что такое Даркнет Магазины:
Даркнет магазины представляют собой онлайн-платформы, доступные через скрытые браузеры и специальные программы. Они действуют в глубоком вебе, невидимом от обычных поисковых систем. Здесь можно обнаружить не только торговцев нелегальными товарами и услугами, но и разнообразные преступные схемы.
Категории Товаров и Услуг:
Даркнет магазины продают разнообразный ассортимент товаров и услуг, от наркотиков и оружия вплоть до хакерских услуг и похищенных данных. На данной темной площадке действуют торговцы, предоставляющие возможность приобретения незаконных вещей без опасности быть выслеженным.
Риски для Пользователей:
Легальные Последствия:
Покупка запрещенных товаров на даркнет магазинах ставит под угрозу пользователей риску столкнуться с правоохранительными органами. Уголовная ответственность может быть серьезным следствием таких покупок.
Мошенничество и Обман:
Даркнет тоже является плодородной почвой для мошенников. Пользователи могут попасть в обман, где оплата не приведет к получению товара или услуги.
Угрозы Кибербезопасности:
Даркнет магазины предоставляют услуги хакеров и киберпреступников, что сопровождается реальными угрозами для безопасности данных и конфиденциальности.
Распространение Преступной Деятельности:
Экономика даркнет магазинов содействует распространению преступной деятельности, так как предоставляет инфраструктуру для нелегальных транзакций.
Борьба с Проблемой:
Усиление Кибербезопасности:
Улучшение кибербезопасности и технологий слежения помогает бороться с даркнет магазинами, превращая их менее поулчаемыми.
Законодательные Меры:
Принятие строгих законов и их эффективная реализация направлены на предупреждение и кара пользователей даркнет магазинов.
Образование и Пропаганда:
Увеличение осведомленности о рисках и последствиях использования даркнет магазинов способно снизить спрос на незаконные товары и услуги.
Заключение:
Даркнет магазины предоставляют темным уголкам интернета, где проступают теневые фигуры с преступными намерениями. Рациональное применение ресурсов и повышенная бдительность необходимы, для того чтобы защитить себя от рисков, связанных с этими темными магазинами. В сумме, секретность и соблюдение законов должны быть на первом месте, когда речь заходит о виртуальных покупках
YourDoll JP 等身大の妊娠中のセックス人形と神話の夢の魅力的な人形-新しいモデル
Helⅼo just wаnted t᧐ give уоu a quick heads up.
The tdxt іn your content seem tо be runnig off the screen inn Firefox.
І’m not surе іf thіs is a format issue or s᧐mething
tо do witһ internet browser compatibility bսt І thougһt Ӏ’d post to let yoᥙ know.
Thee layout ⅼօok great thօugh! Hoppe you get thhe issue
fixed ѕoon. Kudos
Have a loοk at myy homepave :: jual pbn
lfchungary.com
Fang Jifan은 Shen Ao를 바라보며 매우 조심스럽게 말했습니다. “선생님의 직함을 주장하지 마십시오.”
Awesome issues here. I am very satisfied to peer yߋur article.
Тhank yoս sso muϲh and I am having a lοok forward tоo contact you.
Ꮤill yⲟu pleawe drop mе a mail?
mу homspage :: jasa backlink judi online
tải app winbet
Даркнет – загадочное пространство Интернета, доступное только для тех, кто знает правильный вход. Этот закрытый уголок виртуального мира служит местом для анонимных транзакций, обмена информацией и взаимодействия скрытыми сообществами. Однако, чтобы погрузиться в этот темный мир, необходимо преодолеть несколько барьеров и использовать специальные инструменты.
Использование специализированных браузеров: Для доступа к даркнету обычный браузер не подойдет. На помощь приходят подходящие браузеры, такие как Tor (The Onion Router). Tor позволяет пользователям обходить цензуру и обеспечивает анонимность, помечая и перенаправляя запросы через различные серверы.
Адреса в даркнете: Обычные домены в даркнете заканчиваются на “.onion”. Для поиска ресурсов в даркнете, нужно использовать поисковики, адаптированные для этой среды. Однако следует быть осторожным, так как далеко не все ресурсы там законны.
Защита анонимности: При посещении даркнета следует принимать меры для обеспечения анонимности. Использование виртуальных частных сетей (VPN), блокировщиков скриптов и антивирусных программ является принципиальным. Это поможет избежать различных угроз и сохранить конфиденциальность.
Электронные валюты и биткоины: В даркнете часто используются криптовалюты, в основном биткоины, для анонимных транзакций. Перед входом в даркнет следует ознакомиться с основами использования виртуальных валют, чтобы избежать финансовых рисков.
Правовые аспекты: Следует помнить, что многие операции в даркнете могут быть нелегальными и противоречить законам различных стран. Пользование даркнетом несет риски, и несанкционированные действия могут привести к серьезным юридическим последствиям.
Заключение: Даркнет – это неизведанное пространство сети, наполненное анонимности и тайн. Вход в этот мир требует особых навыков и предосторожности. При всем мистическом обаянии даркнета важно помнить о предполагаемых рисках и последствиях, связанных с его использованием.
Взлом Telegram: Мифы и Реальность
Telegram – это известный мессенджер, отмеченный своей высокой степенью кодирования и защиты данных пользователей. Однако, в современном цифровом мире тема взлома Телеграм периодически поднимается. Давайте рассмотрим, что на самом деле стоит за этим термином и почему взлом Телеграм чаще является мифом, чем реальностью.
Кодирование в Telegram: Основы Безопасности
Телеграм известен своим высоким уровнем шифрования. Для обеспечения приватности переписки между пользователями используется протокол MTProto. Этот протокол обеспечивает полное кодирование, что означает, что только отправитель и получатель могут понимать сообщения.
Мифы о Нарушении Telegram: По какой причине они возникают?
В последнее время в интернете часто появляются слухи о взломе Telegram и доступе к персональной информации пользователей. Однако, большинство этих утверждений оказываются мифами, часто развивающимися из-за недопонимания принципов работы мессенджера.
Кибернападения и Уязвимости: Фактические Угрозы
Хотя взлом Telegram в общем случае является сложной задачей, существуют реальные угрозы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи. Например, атаки на отдельные аккаунты, вредоносные программы и другие методы, которые, тем не менее, нуждаются в личном участии пользователя в их распространении.
Защита Личной Информации: Рекомендации для Участников
Несмотря на непоявление точной опасности взлома Telegram, важно соблюдать основные правила кибербезопасности. Регулярно обновляйте приложение, используйте двухфакторную аутентификацию, избегайте подозрительных ссылок и фишинговых атак.
Заключение: Фактическая Опасность или Излишняя беспокойство?
Нарушение Telegram, как обычно, оказывается мифом, созданным вокруг обсуждаемой темы без конкретных доказательств. Однако безопасность всегда остается приоритетом, и участники мессенджера должны быть бдительными и следовать рекомендациям по сохранению защиты своей персональных данных
Взлом Вотсап: Фактичность и Мифы
WhatsApp – один из самых популярных мессенджеров в мире, широко используемый для обмена сообщениями и файлами. Он известен своей кодированной системой обмена данными и обеспечением конфиденциальности пользователей. Однако в интернете время от времени появляются утверждения о возможности нарушения Вотсап. Давайте разберемся, насколько эти утверждения соответствуют фактичности и почему тема взлома WhatsApp вызывает столько дискуссий.
Кодирование в Вотсап: Защита Личной Информации
WhatsApp применяет end-to-end кодирование, что означает, что только передающая сторона и получатель могут читать сообщения. Это стало основой для уверенности многих пользователей мессенджера к защите их личной информации.
Легенды о Взломе WhatsApp: Почему Они Появляются?
Интернет периодически заполняют слухи о нарушении WhatsApp и возможном доступе к переписке. Многие из этих утверждений часто не имеют обоснований и могут быть результатом паники или дезинформации.
Фактические Угрозы: Кибератаки и Охрана
Хотя нарушение WhatsApp является трудной задачей, существуют актуальные угрозы, такие как кибератаки на отдельные аккаунты, фишинг и вредоносные программы. Исполнение мер безопасности важно для минимизации этих рисков.
Охрана Личной Информации: Советы Пользователям
Для укрепления охраны своего аккаунта в Вотсап пользователи могут использовать двухфакторную аутентификацию, регулярно обновлять приложение, избегать сомнительных ссылок и следить за конфиденциальностью своего устройства.
Заключение: Фактическая и Осторожность
Нарушение WhatsApp, как обычно, оказывается трудным и маловероятным сценарием. Однако важно помнить о реальных угрозах и принимать меры предосторожности для защиты своей личной информации. Исполнение рекомендаций по безопасности помогает поддерживать конфиденциальность и уверенность в использовании мессенджера
Введение в Даркнет: Уточнение и Основные Характеристики
Пояснение понятия даркнета, его отличий от привычного интернета, и фундаментальных черт этого загадочного мира.
Как Войти в Темный Интернет: Путеводитель по Скрытому Доступу
Подробное описание шагов, необходимых для входа в даркнет, включая использование специализированных браузеров и инструментов.
Адресация сайтов в Даркнете: Секреты .onion-Доменов
Разъяснение, как функционируют .onion-домены, и каковы ресурсы они содержат, с акцентом на секурном поисковой активности и использовании.
Защита и Конфиденциальность в Темном Интернете: Меры для Пользователей
Рассмотрение методов и инструментов для сохранения анонимности при эксплуатации даркнета, включая виртуальные частные сети и инные средства.
Цифровые Деньги в Темном Интернете: Роль Биткойнов и Криптовалют
Анализ использования криптовалют, в основном биткоинов, для осуществления анонимных транзакций в даркнете.
Поисковая Активность в Даркнете: Особенности и Опасности
Рассмотрение поисковиков в даркнете, предупреждения о возможных рисках и нелегальных ресурсах.
Правовые Аспекты Темного Интернета: Ответственность и Последствия
Рассмотрение юридических аспектов использования даркнета, предостережение о возможных юридических последствиях.
Даркнет и Кибербезопасность: Потенциальные Опасности и Защитные Меры
Изучение возможных киберугроз в даркнете и рекомендации по обеспечению безопасности от них.
Даркнет и Общественные Сети: Анонимное Взаимодействие и Группы
Изучение роли даркнета в сфере социальных взаимодействий и создании скрытых сообществ.
Будущее Даркнета: Тренды и Прогнозы
Предсказания развития даркнета и возможные изменения в его структуре в будущем.
Взлом Вотсап: Фактичность и Легенды
Вотсап – один из самых популярных мессенджеров в мире, широко используемый для передачи сообщениями и файлами. Он прославился своей кодированной системой обмена данными и обеспечением конфиденциальности пользователей. Однако в интернете время от времени возникают утверждения о возможности взлома Вотсап. Давайте разберемся, насколько эти утверждения соответствуют реальности и почему тема нарушения WhatsApp вызывает столько дискуссий.
Шифрование в Вотсап: Защита Личной Информации
Вотсап применяет end-to-end шифрование, что означает, что только передающая сторона и получатель могут понимать сообщения. Это стало основой для доверия многих пользователей мессенджера к защите их личной информации.
Мифы о Взломе WhatsApp: По какой причине Они Появляются?
Интернет периодически наполняют слухи о взломе Вотсап и возможном доступе к переписке. Многие из этих утверждений порой не имеют обоснований и могут быть результатом паники или дезинформации.
Фактические Угрозы: Кибератаки и Охрана
Хотя нарушение WhatsApp является трудной задачей, существуют реальные угрозы, такие как кибератаки на отдельные аккаунты, фишинг и вредоносные программы. Исполнение мер охраны важно для минимизации этих рисков.
Охрана Личной Информации: Рекомендации Пользователям
Для укрепления безопасности своего аккаунта в WhatsApp пользователи могут использовать двухфакторную аутентификацию, регулярно обновлять приложение, избегать подозрительных ссылок и следить за конфиденциальностью своего устройства.
Итог: Фактическая и Осторожность
Взлом WhatsApp, как обычно, оказывается сложным и маловероятным сценарием. Однако важно помнить о реальных угрозах и принимать меры предосторожности для сохранения своей личной информации. Соблюдение рекомендаций по безопасности помогает поддерживать конфиденциальность и уверенность в использовании мессенджера.
kantorbola77
Selamat datang di situs kantorbola , agent judi slot gacor terbaik dengan RTP diatas 98% , segera daftar di situs kantor bola untuk mendapatkan bonus deposit harian 100 ribu dan bonus rollingan 1%
lfchungary.com
과거에는… 시장에 대한 사람들의 이해가 극히 제한적이었습니다.
I ցot thіs web site from my friend who
tokd mme on tһе topic of this weeb page andd now tһiѕ time I aam visiting tһis
site andd reading very informative content at thiѕ
time.
Alѕо visit my weeb blog … harga jasa seo
chutneyb.com
관리부 장관 Wang Ao와 전쟁부 장관 Ma Wensheng도 감동을 받아 무언가를 말하려고했습니다.
Ӏ blog quite oftten and I genuinely аppreciate yor іnformation. This article
һas reallyy peaked my interest. I am ցoing to taкe a note of your
blog and kеep checking fоr new іnformation aЬout ᧐nce peг week.
I opted in foг yοur RSS feed as wеll.
Take a look at my homelage … jasa seo website judi
Explore the world of cryptocurrency with Trust Wallet, your secure and user-friendly gateway to buying, storing, and trading over 160 cryptocurrencies. Join millions of users in experiencing cutting-edge security and seamless transactions.https://android-trustwallet.com
i0qoriiuw2
I aam extremely impressed ᴡith yoour writing skills аs weⅼl as wіth the
layout on yοur blog. Ιѕ tһіs ɑ paid theme or did
yoou customize it yourself? Eitһer way kdep up the nice quality
writing, it’s rare tօ seе a nice bllog liҝe tthis one
theѕe days.
My web рage … jasa backlink terpercaya
Sumatra Slim Belly Tonic is an advanced weight loss supplement that addresses the underlying cause of unexplained weight gain. It focuses on the effects of blue light exposure and disruptions in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep.
lfchungary.com
이 망원경은 Xishan 유리 작업장에서 만들어졌으며 실제로 멀리 보는 기능이 있습니다.
The ProNail Complex is a meticulously-crafted natural formula which combines extremely potent oils and skin-supporting vitamins.
Zeneara is marketed as an expert-formulated health supplement that can improve hearing and alleviate tinnitus, among other hearing issues. The ear support formulation has four active ingredients to fight common hearing issues. It may also protect consumers against age-related hearing problems.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here.
The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over
that you wish be delivering the following. unwell
unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case
you shield this increase.
Thanks designed for sharing such a good thought, paragraph is pleasant,
thats why i have read it completely
apksuccess.com
그렇지 않으면… 이 엄청난 이벤트를 어떻게 할 수 있을까요?
It’s an amazing piece of writing designed foг all tһe internet visitors; tһey wіll take benefit frօm it I am sure.
My һomepage harga jasa seo
smcasino7.com
그동안 조용했던 무빈이 이제서야 미소를 짓는다.
Обнал карт: Как обеспечить безопасность от мошенников и обеспечить защиту в сети
Современный общество высоких технологий предоставляет удобства онлайн-платежей и банковских операций, но с этим приходит и растущая угроза обнала карт. Обнал карт является процессом использования похищенных или незаконно полученных кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью маскировать их происхождение и заблокировать отслеживание.
Ключевые моменты для безопасности в сети и предотвращения обнала карт:
Защита личной информации:
Обязательно будьте осторожными при выдаче личной информации онлайн. Никогда не делитесь банковскими номерами карт, защитными кодами и инными конфиденциальными данными на сомнительных сайтах.
Сильные пароли:
Используйте для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт мощные и уникальные пароли. Регулярно изменяйте пароли для увеличения уровня безопасности.
Мониторинг транзакций:
Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это способствует выявлению подозрительных операций и моментально реагировать.
Антивирусная защита:
Ставьте и периодически обновляйте антивирусное программное обеспечение. Такие программы помогут защитить от вредоносных программ, которые могут быть использованы для кражи данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей:
Остерегайтесь размещения чувствительной информации в социальных сетях. Эти данные могут быть использованы для взлома к вашему аккаунту и последующего использования в обнале карт.
Уведомление банка:
Если вы обнаружили сомнительные транзакции или похищение карты, свяжитесь с банком немедленно для блокировки карты и избежания финансовых ущербов.
Образование и обучение:
Относитесь внимательно к новым способам мошенничества и постоянно обучайтесь тому, как предотвращать подобные атаки. Современные мошенники постоянно совершенствуют свои методы, и ваше понимание может стать решающим для предотвращения
купить фальшивые деньги
Изготовление и приобретение поддельных денег: опасное мероприятие
Купить фальшивые деньги может показаться привлекательным вариантом для некоторых людей, но в реальности это действие несет серьезные последствия и нарушает основы экономической стабильности. В данной статье мы рассмотрим вредные аспекты приобретения поддельной валюты и почему это является опасным поступком.
Неправомерность.
Основное и самое важное, что следует отметить – это полная незаконность изготовления и использования фальшивых денег. Такие действия противоречат правилам большинства стран, и их штрафы может быть крайне строгим. Покупка поддельной валюты влечет за собой угрозу уголовного преследования, штрафов и даже тюремного заключения.
Экономические последствия.
Фальшивые деньги негативно влияют на экономику в целом. Когда в обращение поступает подделанная валюта, это создает дисбаланс и ухудшает доверие к национальной валюте. Компании и граждане становятся более подозрительными при проведении финансовых сделок, что приводит к ухудшению бизнес-климата и мешает нормальному функционированию рынка.
Потенциальная угроза финансовой стабильности.
Фальшивые деньги могут стать угрозой финансовой стабильности государства. Когда в обращение поступает большое количество поддельной валюты, центральные банки вынуждены принимать дополнительные меры для поддержания финансовой системы. Это может включать в себя повышение процентных ставок, что, в свою очередь, плохо сказывается на экономике и финансовых рынках.
Риски для честных граждан и предприятий.
Люди и компании, неосознанно принимающие фальшивые деньги в в качестве оплаты, становятся жертвами преступных схем. Подобные ситуации могут вызвать к финансовым убыткам и потере доверия к своим деловым партнерам.
Привлечение криминальных группировок.
Приобретение фальшивых денег часто связана с преступными группировками и организованным преступлением. Вовлечение в такие сети может повлечь за собой серьезными последствиями для личной безопасности и даже подвергнуть опасности жизни.
В заключение, закупка фальшивых денег – это не только незаконное действие, но и поступок, способный нанести ущерб экономике и обществу в целом. Рекомендуется избегать подобных действий и сосредотачиваться на легальных, ответственных методах обращения с финансами
фальшивые 5000 купитьФальшивые купюры 5000 рублей: Риск для экономики и граждан
Фальшивые купюры всегда были значительной угрозой для финансовой стабильности общества. В последние годы одним из ключевых объектов манипуляций стали банкноты номиналом 5000 рублей. Эти фальшивые деньги представляют собой важную опасность для экономики и финансовой безопасности граждан. Давайте рассмотрим, почему фальшивые купюры 5000 рублей стали реальной бедой.
Трудность выявления.
Купюры 5000 рублей являются самыми крупными по номиналу, что делает их чрезвычайно привлекательными для фальшивомонетчиков. Безупречно проработанные подделки могут быть трудно выявить даже экспертам в сфере финансов. Современные технологии позволяют создавать высококачественные копии с использованием новейших методов печати и защитных элементов.
Риск для бизнеса.
Фальшивые 5000 рублей могут привести к крупным финансовым убыткам для предпринимателей и компаний. Бизнесы, принимающие наличные средства, становятся подвергаются риску принять фальшивую купюру, что в конечном итоге может снизить прибыль и повлечь за собой юридические последствия.
Увеличение инфляции.
Фальшивые деньги увеличивают количество в обращении, что в свою очередь может привести к инфляции. Рост количества фальшивых купюр создает дополнительный денежный объем, не обеспеченный реальными товарами и услугами. Это может существенно подорвать доверие к национальной валюте и стимулировать рост цен.
Пагуба для доверия к финансовой системе.
Фальшивые деньги вызывают недоверие к финансовой системе в целом. Когда люди сталкиваются с риском получить фальшивые купюры при каждой сделке, они становятся более склонными избегать использования наличных средств, что может привести к обострению проблем, связанных с электронными платежами и банковскими системами.
Защитные меры и образование.
Для предотвращения распространению фальшивых денег необходимо внедрять более эффективные защитные меры на банкнотах и активно проводить просветительскую работу среди населения. Гражданам нужно быть более внимательными при приеме наличных средств и обучаться принципам распознавания контрафактных купюр.
В заключение:
Фальшивые купюры 5000 рублей представляют значительную угрозу для финансовой стабильности и безопасности граждан. Необходимо активно внедрять новые технологии защиты и проводить информационные кампании, чтобы общество было лучше осведомлено о методах распознавания и защиты от фальшивых денег. Только совместные усилия банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом позволят минимизировать опасность подделок и обеспечить стабильность финансовой системы.
Обнал карт: Как защититься от хакеров и сохранить безопасность в сети
Современный мир высоких технологий предоставляет преимущества онлайн-платежей и банковских операций, но с этим приходит и нарастающая угроза обнала карт. Обнал карт является процессом использования украденных или неправомерно приобретенных кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью маскировать их происхождение и предотвратить отслеживание.
Ключевые моменты для безопасности в сети и предотвращения обнала карт:
Защита личной информации:
Обязательно будьте осторожными при предоставлении личной информации онлайн. Никогда не делитесь номерами карт, пин-кодами и дополнительными конфиденциальными данными на ненадежных сайтах.
Сильные пароли:
Используйте для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт мощные и уникальные пароли. Регулярно изменяйте пароли для усиления безопасности.
Мониторинг транзакций:
Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это содействует выявлению подозрительных транзакций и быстро реагировать.
Антивирусная защита:
Ставьте и периодически обновляйте антивирусное программное обеспечение. Такие программы помогут защитить от вредоносных программ, которые могут быть использованы для изъятия данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей:
Будьте осторожными при размещении чувствительной информации в социальных сетях. Эти данные могут быть использованы для взлома к вашему аккаунту и последующего мошенничества.
Уведомление банка:
Если вы заметили подозрительные операции или потерю карты, свяжитесь с банком незамедлительно для блокировки карты и предупреждения финансовых убытков.
Образование и обучение:
Следите за новыми методами мошенничества и постоянно обновляйте свои знания, как избегать подобных атак. Современные мошенники постоянно разрабатывают новые методы, и ваше знание может стать определяющим для защиты.
В завершение, соблюдение простых правил безопасности в сети и постоянное обновление знаний помогут вам снизить риск подвергнуться обналу карт на месте работы и в ежедневной практике. Помните, что ваш финансовый комфорт в ваших руках, и предпринимательские действия могут обеспечить ваш онлайн-опыт максимальной защитой и надежностью.
І dߋ not even know how I ended up һere, but I thought thiѕ post was gօod.
I don’t know whο you are bսt definitely yoս’re gοing to a faous blogger іf y᧐u
arе not аlready 😉 Cheers!
My web pagе – jual backlink murah
обнал карт купить
Осознание сущности и опасностей связанных с легализацией кредитных карт способно помочь людям предотвращать атак и сохранять свои финансовые состояния. Обнал (отмывание) кредитных карт — это механизм использования украденных или неправомерно приобретенных кредитных карт для осуществления финансовых транзакций с целью замаскировать их происхождения и заблокировать отслеживание.
Вот некоторые способов, которые могут содействовать в уклонении от обнала кредитных карт:
Сохранение личной информации: Будьте осторожными в контексте предоставления персональной информации, особенно онлайн. Избегайте предоставления номеров карт, кодов безопасности и дополнительных конфиденциальных данных на ненадежных сайтах.
Надежные пароли: Используйте мощные и уникальные пароли для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт. Регулярно изменяйте пароли.
Контроль транзакций: Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это позволит своевременно обнаруживать подозрительных транзакций.
Антивирусная защита: Используйте антивирусное программное обеспечение и актуализируйте его регулярно. Это поможет защитить от вредоносные программы, которые могут быть использованы для кражи данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей: Будьте осторожными в социальных сетях, избегайте опубликования чувствительной информации, которая может быть использована для взлома вашего аккаунта.
Уведомление банка: Если вы заметили какие-либо подозрительные операции или утерю карты, сразу свяжитесь с вашим банком для заблокировки карты.
Получение знаний: Будьте внимательными к новым методам мошенничества и обучайтесь тому, как противостоять их.
Избегая легковерия и проявляя предельную осторожность, вы можете уменьшить риск стать жертвой обнала кредитных карт.
rikvip
rikvip
I am in fact grateful to the owner of this web site who has shared this
enormous article at at this time.
Опасность подпольных точек: Места продажи фальшивых купюр”
Заголовок: Опасность подпольных точек: Места продажи поддельных денег
Введение:
Разговор об опасности подпольных точек, занимающихся продажей фальшивых купюр, становится всё более актуальным в современном обществе. Эти места, предоставляя доступ к поддельным финансовым средствам, представляют серьезную угрозу для экономической стабильности и безопасности граждан.
Легкость доступа:
Одной из негативных аспектов подпольных точек является легкость доступа к фальшивым купюрам. На темных улицах или в скрытых интернет-пространствах, эти места становятся площадкой для тех, кто ищет возможность обмануть систему.
Угроза финансовой системе:
Продажа поддельных купюр в таких местах создает реальную угрозу для финансовой системы. Введение поддельных средств в обращение может привести к инфляции, понижению доверия к национальной валюте и даже к финансовым кризисам.
Мошенничество и преступность:
Подпольные точки, предлагающие фальшивые купюры, являются очагами мошенничества и преступной деятельности. Отсутствие контроля и законного регулирования в этих местах обеспечивает благоприятные условия для криминальных элементов.
Угроза для бизнеса и обычных граждан:
Как бизнесы, так и обычные граждане становятся потенциальными жертвами мошенничества, когда используют поддельные деньги, приобретенные в подпольных точках. Это ведет к утрате доверия и серьезным финансовым потерям.
Последствия для экономики:
Вмешательство подпольных точек в экономику оказывает отрицательное воздействие. Нарушение стабильности финансовой системы и создание дополнительных трудностей для правоохранительных органов являются лишь частью последствий для общества.
Заключение:
Продажа фальшивых купюр в подпольных точках представляет собой серьезную угрозу для общества в целом. Необходимо ужесточение законодательства и усиление контроля, чтобы противостоять этому злу и обеспечить безопасность экономической среды. Развитие сотрудничества между государственными органами, бизнес-сообществом и обществом в целом является ключевым моментом в предотвращении негативных последствий деятельности подобных точек.
магазин фальшивых денег купить
Темные закоулки сети: теневой мир продажи фальшивых купюр”
Введение:
Фальшивые деньги стали неотъемлемой частью теневого мира, где места продаж – это факторы серьезных угроз для финансовой системы и общества. В данной статье мы обратим внимание на места, где процветает подпольная торговля поддельными денежными средствами, включая засекреченные зоны интернета.
Теневые интернет-магазины:
С развитием технологий и распространением онлайн-торговли, места продаж поддельных банкнот стали активно функционировать в засекреченных местах интернета. Темные веб-сайты и форумы предоставляют возможность анонимно приобрести фальшивые деньги, создавая тем самым значительный риск для экономики.
Опасные последствия для общества:
Места продаж поддельных средств на скрытых веб-платформах несут в себе не только угрозу для финансовой стабильности, но и для обычных граждан. Покупка поддельных денег влечет за собой риски: от судебных преследований до потери доверия со стороны сообщества.
Передовые технологии подделки:
На скрытых веб-площадках активно используются новейшие технологии для создания высококачественных подделок. От принтеров, способных воспроизводить защитные элементы, до использования криптовалютных платежей для обеспечения анонимности покупок – все это создает среду, в которой трудно выявить и остановить незаконную торговлю.
Необходимость ужесточения мер борьбы:
Борьба с подпольной торговлей фальшивых купюр требует целостного решения. Важно ужесточить законодательство и разработать эффективные меры для определения и блокировки теневых интернет-магазинов. Также критически важно поднимать готовность к информации общества относительно опасностей подобных практик.
Заключение:
Площадки продаж поддельных денег на темных уголках интернета представляют собой значительную опасность для финансовой стабильности и общественной безопасности. В условиях расцветающего цифрового мира важно акцентировать внимание на борьбе с подобными практиками, чтобы защитить интересы общества и сохранить веру к экономическому порядку
shopanho.com
그는 고개를 숙이고 Zhu Zaimo를 사랑스럽게 바라보고 나서 무관심한 Fang Jifan을 바라 보았습니다.
rikvip
Фальшивые рубли, в большинстве случаев, имитируют с целью обмана и незаконного обогащения. Шулеры занимаются подделкой российских рублей, создавая поддельные банкноты различных номиналов. В основном, фальсифицируют банкноты с более высокими номиналами, вроде 1 000 и 5 000 рублей, ввиду того что это позволяет им получать крупные суммы при уменьшенном числе фальшивых денег.
Технология фальсификации рублей включает в себя применение высокотехнологичного оборудования, специализированных печатающих устройств и особо подготовленных материалов. Шулеры стремятся максимально точно воспроизвести средства защиты, водяные знаки, металлическую защиту, микротекст и другие характеристики, чтобы затруднить определение поддельных купюр.
Поддельные денежные средства регулярно попадают в обращение через торговые точки, банки или другие организации, где они могут быть легко спрятаны среди реальных денежных средств. Это порождает серьезные затруднения для экономической системы, так как фальшивые деньги могут вызывать потерям как для банков, так и для населения.
Столь же важно подчеркнуть, что владение и использование фальшивых денег считаются уголовными преступлениями и подпадают под уголовную ответственность в соответствии с нормативными актами Российской Федерации. Власти энергично противостоят с такими преступлениями, предпринимая меры по обнаружению и прекращению деятельности банд преступников, вовлеченных в подделкой российских рублей
Фальшивые рубли, в большинстве случаев, подделывают с целью мошенничества и незаконного получения прибыли. Злоумышленники занимаются клонированием российских рублей, создавая поддельные банкноты различных номиналов. В основном, воспроизводят банкноты с большими номиналами, например 1 000 и 5 000 рублей, так как это позволяет им зарабатывать большие суммы при уменьшенном числе фальшивых денег.
Технология подделки рублей включает в себя использование технологического оборудования высокого уровня, специализированных печатающих устройств и особо подготовленных материалов. Преступники стремятся наиболее точно воспроизвести защитные элементы, водяные знаки, металлическую защитную полосу, микроскопический текст и другие характеристики, чтобы препятствовать определение поддельных купюр.
Поддельные денежные средства часто попадают в обращение через торговые площадки, банки или прочие учреждения, где они могут быть легко спрятаны среди настоящих денег. Это порождает серьезные проблемы для финансовой системы, так как поддельные купюры могут вызывать потерям как для банков, так и для граждан.
Столь же важно подчеркнуть, что имение и применение фальшивых денег являются уголовными преступлениями и подпадают под уголовную ответственность в соответствии с нормативными актами Российской Федерации. Власти активно борются с такими преступлениями, предпринимая действия по обнаружению и прекращению деятельности преступных групп, занимающихся подделкой российских рублей
где купить фальшивые деньги
Ненастоящая валюта: угроза для финансов и социума
Введение:
Фальшивомонетничество – нарушение, оставшееся актуальным на продолжительностью многих веков. Изготовление и распространение в обращение поддельных банкнот представляют серьезную угрозу не только для финансовой системы, но и для общественной стабильности. В данной статье мы рассмотрим масштабы проблемы, способы борьбы с подделкой денег и последствия для социума.
История фальшивых денег:
Поддельные средства существуют с момента появления самой идеи денег. В старину подделывались металлические монеты, а в современном мире преступники активно используют передовые технологии для фальсификации банкнот. Развитие цифровых технологий также открыло дополнительные способы для создания цифровых вариантов валюты.
Масштабы проблемы:
Ненастоящая валюта создают угрозу для стабильности экономики. Банки, компании и даже обычные граждане могут стать пострадавшими мошенничества. Рост количества фальшивых денег может привести к потере покупательной способности и даже к финансовым кризисам.
Современные методы фальсификации:
С развитием технологий фальсификация стала более затруднительной и изощренной. Преступники используют высокотехнологичное оборудование, специализированные принтеры, и даже машинное обучение для создания невозможно отличить поддельные копии от настоящих денег.
Борьба с фальшивомонетничеством:
Государства и государственные банки активно внедряют современные методы для предотвращения подделки денег. Это включает в себя применение современных защитных элементов на банкнотах, обучение населения способам определения фальшивых средств, а также взаимодействие с органами правопорядка для выявления и предотвращения преступных сетей.
Последствия для общества:
Поддельные средства несут не только экономические, но и общественные последствия. Жители и компании теряют доверие к экономическому устройству, а борьба с криминальной деятельностью требует значительных ресурсов, которые могли бы быть направлены на более полезные цели.
Заключение:
Поддельные средства – серьезная проблема, требующая внимания и совместных усилий граждан, правоохранительных органов и учреждений финансов. Только с помощью эффективной борьбы с нарушением можно гарантировать устойчивость экономики и сохранить уважение к денежной системе
初次接觸線上娛樂城的玩家一定對選擇哪間娛樂城有障礙,首要條件肯定是評價良好的娛樂城,其次才是哪間娛樂城優惠最誘人,娛樂城體驗金多少、娛樂城首儲一倍可以拿多少等等…本篇文章會告訴你娛樂城優惠怎麼挑,首儲該注意什麼。
娛樂城首儲該注意什麼?
當您決定好娛樂城,考慮在娛樂城進行首次存款入金時,有幾件事情需要特別注意:
合法性、安全性、評價良好:確保所選擇的娛樂城是合法且受信任的。檢查其是否擁有有效的賭博牌照,以及是否採用加密技術來保護您的個人信息和交易。
首儲優惠與流水:許多娛樂城會為首次存款提供吸引人的獎勵,但相對的流水可能也會很高。
存款入金方式:查看可用的支付選項,是否適合自己,例如:USDT、超商儲值、銀行ATM轉帳等等。
提款出金方式:瞭解最低提款限制,綁訂多少流水才可以領出。
24小時客服:最好是有24小時客服,發生問題時馬上有人可以處理。
ST666️ – Trang Chủ Chính Thức Số 1️⃣ Của Nhà Cái ST666
ST666 đã nhanh chóng trở thành điểm đến giải trí cá độ thể thao được yêu thích nhất hiện nay. Mặc dù chúng tôi mới xuất hiện trên thị trường cá cược trực tuyến Việt Nam gần đây, nhưng đã nhanh chóng thu hút sự quan tâm của cộng đồng người chơi trực tuyến. Đối với những người yêu thích trò chơi trực tuyến, nhà cái ST666 nhận được sự tin tưởng và tín nhiệm trọn vẹn từ họ. ST666 được coi là thiên đường cho những người chơi tham gia.
Giới Thiệu Nhà Cái ST666
ST666.BLUE – ST666 là nơi cá cược đổi thưởng trực tuyến được ưa chuộng nhất hiện nay. Tham gia vào trò chơi cá cược trực tuyến, người chơi không chỉ trải nghiệm các trò giải trí hấp dẫn mà còn có cơ hội nhận các phần quà khủng thông qua các kèo cá độ. Với những phần thưởng lớn, người chơi có thể thay đổi cuộc sống của mình.
Giới Thiệu Nhà Cái ST666 BLUE
Thông tin về nhà cái ST666
ST666 là Gì?
Nhà cái ST666 là một sân chơi cá cược đổi thưởng trực tuyến, chuyên cung cấp các trò chơi cá cược đổi thưởng có thưởng tiền mặt. Điều này bao gồm các sản phẩm như casino, bắn cá, thể thao, esports… Người chơi có thể tham gia nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn khi đăng ký, đặt cược và có cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn nếu chiến thắng hoặc mất số tiền cược nếu thất bại.
Nhà Cái ST666 – Sân Chơi Cá Cược An Toàn
Nhà Cái ST666 – Sân Chơi Cá Cược Trực Tuyến
Nguồn Gốc Thành Lập Nhà Cái ST666
Nhà cái ST666 được thành lập và ra mắt vào năm 2020 tại Campuchia, một quốc gia nổi tiếng với các tập đoàn giải trí cá cược đổi thưởng. Xuất hiện trong giai đoạn phát triển mạnh mẽ của ngành cá cược, ST666 đã để lại nhiều dấu ấn. Được bảo trợ tài chính bởi tập đoàn danh tiếng Venus Casino, thương hiệu đã mở rộng hoạt động khắp Đông Nam Á và lan tỏa sang cả các quốc gia Châu Á, bao gồm cả Trung Quốc
sports 06ad22f
DNA
เว็บไซต์ DNABET: สู่ ประสบการณ์ การเล่น ที่ไม่เหมือน ที่คุณ เคย ประสบ!
DNABET ยัง เป็น เลือกยอดนิยม ใน สาวก การพนัน ทางอินเทอร์เน็ต ในประเทศไทย ในปี 2024.
ไม่ต้อง ใช้เวลา ในการเลือก เล่น DNABET เพราะที่นี่คุณ ไม่จำเป็นต้อง กังวลว่าจะ จะได้ หรือไม่ได้รับ!
DNABET มี การชำระเงิน ทุกราคา หวยที่ สูงมาก ตั้งแต่เริ่มต้นที่ 900 บาท ขึ้นไป เมื่อ ทุกท่าน ถูกรางวัลแล้ว ได้รับ รางวัลมากมาย กว่า เว็บอื่น ๆ ที่ เคย.
นอกจากนี้ DNABET ยัง มีความหลากหลาย หวย ที่คุณสามารถเลือก มากมายถึง 20 หวย ทั่วโลกนี้ ทำให้ เลือกเล่น ตามใจต้องการ ได้อย่างหลากหลายแบบ.
ไม่ว่าจะเป็น หวยรัฐ หวยหุ้น ยี่กี หวยฮานอย ลาว และ ลอตเตอรี่ มีราคา เพียงแค่ 80 บาท.
ทาง DNABET มั่นใจ ในเรื่องการเงิน โดยที่ ได้รับ เปลี่ยนชื่อ ชันเจน เป็น DNABET เพื่อ เสริมฐานลูกค้าที่มั่นใจ และ ปรับปรุงระบบให้ มีความสะดวกสบาย ขึ้นไป.
นอกจากนี้ DNABET ยังมีโปรโมชั่น โปรโมชั่น ให้เลือก หลายรายการ เช่นเดียวกับ โปรโมชั่น สมาชิกใหม่ ท่าน วันนี้ จะได้รับ โบนัสเพิ่ม 500 บาท หรือ ไม่ต้องจ่าย เงิน.
นอกจากนี้ DNABET ยังมีโปรโมชั่น ประจำเดือนที่ ท่านมีความมั่นใจ และเลือก DNABET การเล่น หวย ของท่าน พร้อม โปรโมชั่น และ โปรโมชัน ที่ เยอะ ที่สุด ในปี 2024.
อย่า พลาด โอกาสดีนี้ ไป มาเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ DNABET และ เพลิดเพลินไปกับ ประสบการณ์การเล่น หวย ทุกท่าน มีโอกาสที่จะ เป็นเศรษฐี ได้ เพียง แค่ท่าน เลือก เว็บแทงหวย ทางอินเทอร์เน็ต ที่ และ มีสมาชิกมากที่สุด ในประเทศไทย!
promosi hoki1881
Pretty nice post. I simply stumbled upon your blog
and wished to say that I’ve truly enjoyed surfing around
your weblog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing in your rss feed and I hope you write once more very soon!
Hey! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the superb work!
KANTORBOLA situs gamin online terbaik 2024 yang menyediakan beragam permainan judi online easy to win , mulai dari permainan slot online , taruhan judi bola , taruhan live casino , dan toto macau . Dapatkan promo terbaru kantor bola , bonus deposit harian , bonus deposit new member , dan bonus mingguan . Kunjungi link kantorbola untuk melakukan pendaftaran .
Ngamenjitu: Situs Togel Online Terluas dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu platform judi daring terbesar dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi market yang disediakan dari Semar Group, Situs Judi menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terunggul dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Ngamenjitu memperlihatkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari market klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga pasaran eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Langkah Main yang Mudah
Ngamenjitu menyediakan tutorial cara bermain yang sederhana dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di situs Ngamenjitu.
Rekapitulasi Terakhir dan Info Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Portal Judi. Selain itu, informasi terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Bermacam-macam Jenis Permainan
Selain togel, Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan Klien Terjamin
Situs Judi mengutamakan keamanan dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Hadiah Menarik
Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan hadiah menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fitur dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Situs Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Situs Judi!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
smcasino7.com
Fang Jifan은 약간 멍해졌습니다. 이 Wang Shouren은 어느 쪽에서 연기하고 있습니까?
Ngamenjitu: Portal Togel Daring Terbesar dan Terjamin
Portal Judi telah menjadi salah satu portal judi daring terbesar dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan beragam market yang disediakan dari Semar Group, Ngamenjitu menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terunggul dan Terlengkap
Dengan total 56 pasaran, Portal Judi menampilkan berbagai opsi terunggul dari pasaran togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari market klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga pasaran eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Metode Bermain yang Sederhana
Situs Judi menyediakan petunjuk cara main yang mudah dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Ngamenjitu.
Rekapitulasi Terakhir dan Informasi Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap pasaran secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, info paling baru seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Bermacam-macam Jenis Permainan
Selain togel, Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan bervariasi jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kepuasan Klien Terjamin
Situs Judi mengutamakan security dan kenyamanan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Hadiah Istimewa
Portal Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari hadiah deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fitur dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Portal Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Ngamenjitu!
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation however I to find this topic to be actually one thing that I think I might by no means understand. It seems too complex and very huge for me. I’m looking ahead for your subsequent submit, I?¦ll try to get the dangle of it!
Ngamenjitu.com
Ngamenjitu: Platform Lotere Daring Terluas dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu portal judi online terluas dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan pengalaman bermain togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Ngamenjitu memperlihatkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Cara Main yang Praktis
Portal Judi menyediakan petunjuk cara bermain yang praktis dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Ngamenjitu.
Hasil Terkini dan Info Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Ngamenjitu. Selain itu, informasi terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Pelbagai Macam Permainan
Selain togel, Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kepuasan Klien Dijamin
Ngamenjitu mengutamakan keamanan dan kenyamanan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Bonus Istimewa
Portal Judi juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan hadiah istimewa bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari hadiah deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Ngamenjitu tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Portal Judi!
Login Ngamenjitu
Ngamenjitu: Platform Togel Daring Terluas dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu situs judi daring terbesar dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dengan beragam pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Ngamenjitu menawarkan pengalaman main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terunggul dan Terlengkap
Dengan total 56 market, Situs Judi memperlihatkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Metode Bermain yang Sederhana
Situs Judi menyediakan tutorial cara main yang sederhana dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di situs Situs Judi.
Hasil Terkini dan Info Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, informasi terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Bermacam-macam Jenis Game
Selain togel, Portal Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati bervariasi pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan Klien Dijamin
Situs Judi mengutamakan security dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Bonus Menarik
Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga hadiah referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Portal Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Portal Judi!
Понимание сущности и рисков привязанных с легализацией кредитных карт способствует людям избегать подобных атак и защищать свои финансовые состояния. Обнал (отмывание) кредитных карт — это процесс использования украденных или нелегально добытых кредитных карт для проведения финансовых транзакций с целью сокрыть их происхождения и заблокировать отслеживание.
Вот некоторые способов, которые могут содействовать в уклонении от обнала кредитных карт:
Сохранение личной информации: Будьте осторожными в связи предоставления личных данных, особенно онлайн. Избегайте предоставления картовых номеров, кодов безопасности и дополнительных конфиденциальных данных на непроверенных сайтах.
Сильные пароли: Используйте мощные и уникальные пароли для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт. Регулярно изменяйте пароли.
Отслеживание транзакций: Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это поможет своевременно выявить подозрительных транзакций.
Защита от вирусов: Используйте антивирусное программное обеспечение и обновляйте его регулярно. Это поможет защитить от вредоносные программы, которые могут быть использованы для изъятия данных.
Осмотрительное поведение в социальных медиа: Будьте осторожными в онлайн-сетях, избегайте публикации чувствительной информации, которая может быть использована для взлома вашего аккаунта.
Быстрое сообщение банку: Если вы заметили какие-либо подозрительные операции или утерю карты, сразу свяжитесь с вашим банком для заблокировки карты.
Получение знаний: Будьте внимательными к новым методам мошенничества и обучайтесь тому, как противостоять их.
Избегая легковерия и принимая меры предосторожности, вы можете минимизировать риск стать жертвой обнала кредитных карт.
Незаконные форумы, где осуществляют кэш-аут пластиковых карт, представляют собой веб-ресурсы, ориентированные на рассмотрении и осуществлении незаконных транзакций с банковскими картами. На подобных платформах участники делают обмен информацией, приемами и знаниями в сфере кэш-аута, что включает в себя незаконные действия по получению доступа к финансовым средствам.
Эти платформы способны предоставлять разнообразные сервисы, связанные с преступной деятельностью, такие как фишинг, считывание, вредное ПО и другие методы для получения информации с финансовых карт. Также обсуждаются темы, касающиеся использованием похищенных данных для осуществления финансовых операций или снятия денег.
Участники неправомерных платформ по обналу банковских карт могут оставаться неизвестными и уходить от привлечения органов безопасности. Они могут делиться советами, предоставлять сервисы, относящиеся к обналичиванием, а также проводить сделки, направленные на незаконную финансовую деятельность.
Важно отметить, что участие в таких практиках не просто является нарушением законов, но и способно приводить к правовым последствиям и наказанию.
обнал карт купить
Покупка лживых банкнот представляет собой неправомерным иначе рискованным поступком, что может послать в тяжелым юридическим воздействиям либо вреду вашей денежной стабильности. Вот некоторые причин, из-за чего покупка фальшивых купюр приравнивается к потенциально опасной иначе недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение и использование поддельных банкнот считаются противоправным деянием, подрывающим нормы государства. Вас могут поддать юридическим последствиям, что возможно закончиться задержанию, взысканиям иначе тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Лживые банкноты ослабляют веру по отношению к финансовой организации. Их использование формирует риск для надежных личностей и коммерческих структур, которые могут завязать внезапными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение фальшивых купюр осуществляет воздействие на финансовую систему, провоцируя инфляцию что ухудшает глобальную финансовую устойчивость. Это может привести к утрате уважения к валютной единице.
Риск обмана:
Люди, какие, осуществляют созданием поддельных денег, не обязаны соблюдать какие-то нормы характеристики. Фальшивые купюры могут быть легко обнаружены, что в итоге повлечь за собой убыткам для тех стремится воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
При случае лишения свободы при воспользовании лживых банкнот, вас имеют возможность принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может оказать воздействие на вашем будущем, с учетом сложности с поиском работы и кредитной историей.
Общественное и индивидуальное благосостояние зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Закупка поддельных купюр идет вразрез с этими принципами и может обладать важные последствия. Советуем придерживаться законов и заниматься только законными финансовыми сделками.
обнал карт работа
Обналичивание карт – это неправомерная деятельность, становящаяся все более популярной в нашем современном мире электронных платежей. Этот вид мошенничества представляет серьезные вызовы для банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. В данной статье мы рассмотрим частоту встречаемости обналичивания карт, используемые методы и возможные последствия для жертв и общества.
Частота обналичивания карт:
Обналичивание карт является довольно распространенным явлением, и его частота постоянно растет с увеличением числа электронных транзакций. Киберпреступники применяют различные методы для получения доступа к финансовым средствам, включая фишинг, вредоносное программное обеспечение, скимминг и другие инновационные подходы.
Методы обналичивания карт:
Фишинг: Злоумышленники могут отправлять ложные электронные сообщения или создавать веб-сайты, имитирующие банковские системы, с целью получения личной информации от владельцев карт.
Скимминг: Злоумышленники устанавливают устройства скиммеры на банкоматах или терминалах для считывания данных с магнитных полос карт.
Вредоносное программное обеспечение: Киберпреступники разрабатывают вредоносные программы, которые заражают компьютеры и мобильные устройства, чтобы получить доступ к личным данным и банковским счетам.
Сетевые атаки: Атаки на системы банков и платежных платформ могут привести к утечке информации о картах и, следовательно, к их обналичиванию.
Последствия обналичивания карт:
Финансовые потери для клиентов: Владельцы карт могут столкнуться с денежными потерями, так как средства могут быть списаны с их счетов без их ведома.
Угроза безопасности данных: Обналичивание карт подчеркивает угрозу безопасности личных данных, что может привести к краже личной и финансовой информации.
Ущерб репутации банков: Банки и другие финансовые учреждения могут столкнуться с утратой доверия со стороны клиентов, если их системы безопасности оказываются уязвимыми.
Проблемы для экономики: Обналичивание карт создает экономический ущерб, поскольку оно стимулирует дополнительные затраты на борьбу с мошенничеством и восстановление утраченных средств.
Борьба с обналичиванием карт:
Совершенствование технологий безопасности: Банки и финансовые институты постоянно совершенствуют свои системы безопасности, чтобы предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к картам.
Образование и информирование: Обучение клиентов о методах мошенничества и том, как защитить свои данные, является важным шагом в борьбе с обналичиванием карт.
Сотрудничество с правоохранительными органами: Банки активно сотрудничают с правоохранительными органами для выявления и пресечения преступных схем.
Заключение:
Обналичивание карт – серьезная угроза для финансовой стабильности и безопасности личных данных. Решение этой проблемы требует совместных усилий со стороны банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. Только эффективная борьба с мошенничеством позволит обеспечить безопасность электронных платежей и защитить интересы всех участников финансовой системы.
Фальшивые 5000 купить
Опасности поддельных 5000 рублей: Распространение фальшивых купюр и его воздействия
В нынешнем обществе, где цифровые платежи становятся все более распространенными, противоправные лица не оставляют без внимания и классические методы обмана, такие как распространение поддельных банкнот. В последнее время стало известно о незаконной торговле недобросовестных 5000 рублевых купюр, что представляет весомую угрозу для денежной системы и сообщества в совокупности.
Маневры торговли:
Мошенники активно используют закрытые маршруты сетевого пространства для реализации контрафактных 5000 рублей. На подпольных веб-ресурсах и незаконных форумах можно обнаружить прошения о покупке недостоверных банкнот. К неудаче, это создает хорошие условия для распространения поддельных денег среди населения.
Воздействия для населения:
Возможность поддельных денег в обращении может иметь весомые воздействия для хозяйства и доверенности к денежной единице. Люди, не поддаваясь, что получили недостоверные купюры, могут использовать их в разносторонних ситуациях, что в итоге приводит к ущербу авторитету к банкнотам точного номинала.
Риски для граждан:
Население становятся предполагаемыми пострадавшими оскорбителей, когда они ненамеренно получают недостоверные деньги в переговорах или при приобретениях. В следствие этого, они могут столкнуться с неблагоприятными ситуациями, такими как отклонение торговцев принять фальшивые купюры или даже вероятность привлечения к ответственности за пробу расплаты фальшивыми деньгами.
Противодействие с распространением фальшивых денег:
В интересах гарантирования сообщества от таких же правонарушений необходимо повысить противодействие по обнаружению и остановке производства поддельных денег. Это включает в себя кооперацию между полицейскими и финансовыми учреждениями, а также усиление уровня образования населения относительно символов поддельных банкнот и способов их обнаружения.
Заключение:
Распространение контрафактных 5000 рублей – это серьезная опасность для устойчивости финансовой системы и устойчивости населения. Поддерживание кредитоспособности к государственной валюте требует единых действий со со стороны государственных органов, банков и каждого. Важно быть бдительным и осведомленным, чтобы избежать прокладывание фальшивых денег и обеспечить финансовые интересы населения.
To the malabdali.com owner, Your posts are always well-supported by research and data.
cialis without a doctors prescription
skypharmacy
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
cialis without a doctor’s prescription
Онлайн мерч https://mayotmelon.ru/ одежды Майота, где можно купить на заказ с доставкой на дом в России по лучшей цене
Hi colleagues, fastidious paragraph and pleasant arguments commented here, I am genuinely enjoying by these.
I saw similar here: Dobry sklep
Mагазин фальшивых денег купить
Покупка контрафактных купюр представляет собой противозаконным или потенциально опасным делом, которое способно привести к глубоким правовым санкциям иначе постраданию вашей денежной устойчивости. Вот несколько других причин, из-за чего закупка лживых купюр представляет собой опасительной и недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка или применение лживых купюр приравниваются к преступлением, противоречащим законы страны. Вас имеют возможность подвергнуть себя наказанию, что потенциально послать в задержанию, денежным наказаниям либо тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Контрафактные банкноты ослабляют доверенность в денежной структуре. Их использование формирует угрозу для благоприятных гражданских лиц и организаций, которые в состоянии претерпеть неожиданными убытками.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных купюр оказывает воздействие на экономику, провоцируя распределение денег и ухудшая общую экономическую устойчивость. Это может привести к потере уважения к валютной единице.
Риск обмана:
Лица, кто, задействованы в изготовлением контрафактных купюр, не обязаны соблюдать какие угодно параметры уровня. Фальшивые банкноты могут выйти легко распознаваемы, что, в конечном итоге послать в убыткам для тех, кто стремится воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
При событии попадания под арест при использовании фальшивых банкнот, вас имеют возможность оштрафовать, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может отразиться на вашем будущем, в том числе трудности с трудоустройством с кредитной историей.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовой деятельности. Получение поддельных банкнот противоречит этим принципам и может порождать серьезные последствия. Советуем придерживаться правил и заниматься исключительно законными финансовыми транзакциями.
Покупка фальшивых банкнот приравнивается к неправомерным и потенциально опасным действием, что имеет возможность привести к тяжелым правовым последствиям и ущербу вашей денежной стабильности. Вот несколько других приводов, почему закупка фальшивых банкнот представляет собой рискованной иначе недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка или эксплуатация контрафактных купюр являются преступлением, подрывающим положения государства. Вас имеют возможность подвергнуться юридическим последствиям, что может закончиться лишению свободы, денежным наказаниям либо приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Поддельные банкноты нарушают веру к финансовой механизму. Их применение порождает угрозу для надежных людей и коммерческих структур, которые способны попасть в неожиданными убытками.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос контрафактных денег причиняет воздействие на экономику, вызывая денежное расширение и ухудшающая общую финансовую устойчивость. Это в состоянии повлечь за собой потере доверия в денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Личности, которые, вовлечены в изготовлением фальшивых денег, не обязаны поддерживать какие-нибудь нормы степени. Лживые купюры могут быть легко распознаны, что, в итоге послать в расходам для тех, кто собирается применять их.
Юридические последствия:
В ситуации захвата при применении поддельных купюр, вас имеют возможность принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может отразиться на вашем будущем, включая возможные проблемы с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовой сфере. Покупка фальшивых банкнот противоречит этим принципам и может порождать важные последствия. Предлагается держаться правил и заниматься исключительно законными финансовыми сделками.
cialis without a prescription
Купил фальшивые рубли
Покупка поддельных купюр является недозволенным иначе опасным актом, что в состоянии послать в глубоким юридическими последствиям иначе вреду личной финансовой благосостояния. Вот несколько причин, почему приобретение поддельных денег является рискованной или недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Покупка или воспользование фальшивых купюр приравниваются к правонарушением, подрывающим законы общества. Вас в состоянии поддать судебному преследованию, что потенциально повлечь за собой лишению свободы, взысканиям и лишению свободы.
Ущерб доверию:
Лживые купюры ухудшают веру в финансовой системе. Их использование создает опасность для порядочных людей и организаций, которые могут попасть в непредвиденными расходами.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос лживых банкнот причиняет воздействие на хозяйство, провоцируя рост цен и подрывая общественную финансовую равновесие. Это способно повлечь за собой потере доверия в денежной единице.
Риск обмана:
Лица, кто, вовлечены в созданием поддельных денег, не обязаны соблюдать какие-нибудь уровни характеристики. Поддельные купюры могут оказаться легко выявлены, что, в конечном итоге закончится ущербу для тех, кто пытается воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
При событии лишения свободы при применении лживых банкнот, вас могут оштрафовать, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими проблемами. Это может сказаться на вашем будущем, в том числе возможные проблемы с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Закупка контрафактных купюр идет вразрез с этими принципами и может обладать серьезные последствия. Рекомендуется держаться законов и заниматься исключительно правомерными финансовыми операциями.
где можно купить фальшивые деньги
Покупка поддельных купюр представляет собой неправомерным и опасным делом, которое в состоянии повлечь за собой важным законным санкциям либо постраданию вашей финансовой стабильности. Вот несколько последствий, почему получение фальшивых денег приравнивается к потенциально опасной либо недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Покупка иначе эксплуатация контрафактных купюр являются преступлением, нарушающим правила территории. Вас в состоянии подвергнуть себя юридическим последствиям, которое может привести к задержанию, денежным наказаниям иначе лишению свободы.
Ущерб доверию:
Контрафактные деньги ослабляют веру по отношению к финансовой механизму. Их применение возникает угрозу для честных людей и предприятий, которые могут завязать непредвиденными расходами.
Экономический ущерб:
Расширение поддельных банкнот осуществляет воздействие на экономическую сферу, приводя к инфляцию и ухудшая всеобщую финансовую устойчивость. Это способно повлечь за собой потере доверия к денежной единице.
Риск обмана:
Личности, какие, задействованы в производством поддельных купюр, не обязаны соблюдать какие-либо нормы уровня. Контрафактные бумажные деньги могут оказаться легко выявлены, что в конечном счете повлечь за собой расходам для тех собирается использовать их.
Юридические последствия:
При случае задержания за использование лживых денег, вас могут принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, в том числе проблемы с поиском работы и историей кредита.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в финансовой деятельности. Закупка контрафактных банкнот не соответствует этим принципам и может представлять серьезные последствия. Советуем придерживаться правил и осуществлять только законными финансовыми операциями.
Покупка контрафактных купюр представляет собой недозволенным иначе опасительным действием, что имеет возможность послать в важным законным воздействиям или ущербу вашей денежной устойчивости. Вот некоторые примет, по какой причине закупка поддельных купюр является опасной либо недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка и эксплуатация фальшивых банкнот представляют собой противоправным деянием, нарушающим нормы общества. Вас способны поддать судебному преследованию, что возможно повлечь за собой лишению свободы, взысканиям или тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Контрафактные банкноты нарушают доверенность к денежной системе. Их поступление в оборот создает опасность для честных гражданских лиц и организаций, которые способны претерпеть непредвиденными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение контрафактных банкнот влияет на экономическую сферу, провоцируя денежное расширение что ухудшает глобальную экономическую устойчивость. Это имеет возможность закончиться потере доверия к валютной единице.
Риск обмана:
Те, кто, задействованы в созданием контрафактных банкнот, не обязаны сохранять какие-то стандарты характеристики. Поддельные деньги могут оказаться легко распознаны, что в итоге приведет к потерям для тех стремится применять их.
Юридические последствия:
При случае попадания под арест при воспользовании поддельных банкнот, вас могут взыскать штраф, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, в том числе сложности с поиском работы и кредитной историей.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Закупка поддельных денег идет вразрез с этими принципами и может порождать серьезные последствия. Предлагается держаться законов и вести только законными финансовыми операциями.
sky pharmacy online
cialis without prescription
sky pharmacy online drugstore
strelkaproject.com
Fang Jifan은 행복하게 주문을 수락했고 Zhen Guohou … 실제로 꽤 좋습니다.
Do you have any video of that? I’d like to find out more details.
купил фальшивые рубли
Покупка лживых купюр считается недозволенным иначе рискованным актом, которое способно послать в важным законным санкциям иначе повреждению своей финансовой надежности. Вот некоторые последствий, по какой причине получение контрафактных купюр является опасительной и неприемлемой:
Нарушение законов:
Покупка или применение фальшивых денег приравниваются к преступлением, нарушающим положения общества. Вас в состоянии подвергнуть уголовной ответственности, что возможно закончиться аресту, финансовым санкциям иначе тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Фальшивые купюры подрывают доверенность в денежной структуре. Их обращение порождает возможность для надежных личностей и коммерческих структур, которые могут столкнуться с неожиданными перебоями.
Экономический ущерб:
Расширение фальшивых денег причиняет воздействие на экономическую сферу, вызывая денежное расширение и подрывая всеобщую экономическую равновесие. Это способно закончиться утрате уважения к валютной единице.
Риск обмана:
Люди, те, задействованы в созданием фальшивых купюр, не обязаны поддерживать какие-либо стандарты качества. Фальшивые бумажные деньги могут выйти легко распознаны, что, в итоге повлечь за собой потерям для тех собирается использовать их.
Юридические последствия:
При событии попадания под арест при воспользовании контрафактных банкнот, вас способны оштрафовать, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может сказаться на вашем будущем, включая сложности с получением работы и кредитной историей.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Приобретение лживых банкнот противоречит этим принципам и может обладать серьезные последствия. Советуем соблюдать законов и осуществлять только законными финансовыми операциями.
sky pharmacy reviews
online pharmacies canada
Покупка фальшивых купюр приравнивается к неправомерным иначе опасительным делом, что имеет возможность послать в тяжелым юридическим воздействиям либо ущербу вашей денежной благосостояния. Вот некоторые последствий, вследствие чего получение лживых денег считается опасительной и неуместной:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка и эксплуатация лживых денег являются преступлением, противоречащим положения государства. Вас имеют возможность подвергнуть себя судебному преследованию, которое может закончиться лишению свободы, денежным наказаниям либо приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Поддельные купюры ослабляют веру в денежной организации. Их обращение формирует возможность для благоприятных граждан и предприятий, которые в состоянии претерпеть внезапными расходами.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных денег влияет на экономику, инициируя распределение денег и ухудшающая общую финансовую равновесие. Это в состоянии привести к потере доверия к национальной валюте.
Риск обмана:
Личности, те, задействованы в изготовлением фальшивых денег, не обязаны соблюдать какие-либо параметры качества. Лживые банкноты могут быть легко распознаны, что, в итоге повлечь за собой ущербу для тех, кто попытается их использовать.
Юридические последствия:
При случае попадания под арест при использовании контрафактных банкнот, вас имеют возможность оштрафовать, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может оказать воздействие на вашем будущем, в том числе сложности с трудоустройством с кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Покупка поддельных денег идет вразрез с этими принципами и может порождать серьезные последствия. Предлагается держаться законов и осуществлять только правомерными финансовыми действиями.
Опасности фальшивых 5000 рублей: Распространение поддельных купюр и его воздействия
В современном обществе, где виртуальные платежи становятся все более расширенными, противоправные лица не оставляют без внимания и традиционные методы недобросовестных действий, такие как распространение недостоверных банкнот. В настоящее время стало известно о неправомерной торговле контрафактных 5000 рублевых купюр, что представляет серьезную опасность для финансовых институтов и населения в совокупности.
Методы передачи:
Противоправные лица активно используют тайные сети интернета для продажи контрафактных 5000 рублей. На темных веб-ресурсах и незаконных форумах можно обнаружить предложения недостоверных банкнот. К удивлению, это создает положительные условия для передачи контрафактных денег среди людей.
Последствия для населения:
Присутствие недостоверных денег в хождении может иметь важные последствия для экономики и доверенности к рублю. Люди, не догадываясь, что получили недостоверные купюры, могут использовать их в разнообразных ситуациях, что в конечном итоге приводит к повреждению доверию к банкнотам конкретного номинала.
Беды для людей:
Гражданское население становятся предполагаемыми пострадавшими оскорбителей, когда они случайно получают недостоверные деньги в переговорах или при приобретениях. В результате, они могут столкнуться с неблагоприятными ситуациями, такими как отказ от приема продавцов принять фальшивые купюры или даже вероятность юридической ответственности за труд расплаты фальшивыми деньгами.
Столкновение с раскруткой контрафактных денег:
В пользу защиты населения от схожих нарушений необходимо усилить мероприятия по выявлению и пресечению производственной деятельности недостоверных денег. Это включает в себя работу в партнерстве между правоохранительными структурами и финансовыми организациями, а также расширение степени образования граждан относительно характеристик недостоверных банкнот и методов их выявления.
Завершение:
Диффузия поддельных 5000 рублей – это серьезная потенциальная опасность для финансовой устойчивости и надежности населения. Гарантирование доверия к денежной системе требует единых действий со со стороны властей, денежных учреждений и каждого человека. Важно быть осторожным и осведомленным, чтобы предотвратить прокладывание фальшивых денег и защитить финансовые интересы населения.
Купить фальшивые рубли
Покупка поддельных денег считается недозволенным либо рискованным делом, что в состоянии закончиться серьезным правовым воздействиям и ущербу своей финансовой устойчивости. Вот несколько примет, по какой причине приобретение лживых денег является опасной и неуместной:
Нарушение законов:
Покупка и эксплуатация лживых банкнот приравниваются к нарушением закона, подрывающим законы территории. Вас имеют возможность подвергнуть себя наказанию, что может закончиться тюремному заключению, штрафам либо тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Поддельные купюры подрывают веру в денежной механизму. Их использование возникает возможность для порядочных личностей и предприятий, которые в состоянии попасть в непредвиденными расходами.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос поддельных купюр оказывает воздействие на экономику, вызывая инфляцию и ухудшающая всеобщую финансовую устойчивость. Это имеет возможность повлечь за собой утрате уважения к национальной валюте.
Риск обмана:
Личности, кто, занимается производством фальшивых купюр, не обязаны поддерживать какие-либо стандарты характеристики. Фальшивые бумажные деньги могут быть легко обнаружены, что, в итоге повлечь за собой расходам для тех пытается применять их.
Юридические последствия:
В ситуации попадания под арест при использовании фальшивых банкнот, вас имеют возможность принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может оказать воздействие на вашем будущем, в том числе возможные проблемы с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Общественное и индивидуальное благосостояние основываются на честности и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Закупка фальшивых банкнот нарушает эти принципы и может иметь серьезные последствия. Рекомендуем соблюдать правил и осуществлять только правомерными финансовыми действиями.
Покупка лживых денег приравнивается к неправомерным и опасным действием, что способно послать в глубоким юридическими санкциям либо постраданию личной денежной благосостояния. Вот несколько других причин, по какой причине приобретение лживых банкнот представляет собой опасной иначе неуместной:
Нарушение законов:
Получение и использование фальшивых банкнот являются правонарушением, нарушающим положения государства. Вас в состоянии подвергнуть себя юридическим последствиям, что потенциально послать в задержанию, денежным наказаниям или постановлению под стражу.
Ущерб доверию:
Лживые деньги подрывают уверенность к денежной механизму. Их использование возникает угрозу для честных граждан и бизнесов, которые способны столкнуться с непредвиденными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных денег влияет на экономику, инициируя рост цен что ухудшает глобальную денежную равновесие. Это имеет возможность послать в потере доверия к денежной единице.
Риск обмана:
Те, какие, задействованы в созданием фальшивых купюр, не обязаны поддерживать какие угодно нормы степени. Лживые банкноты могут стать легко распознаны, что, в итоге закончится ущербу для тех, кто попытается их использовать.
Юридические последствия:
В случае попадания под арест при использовании фальшивых денег, вас могут принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими проблемами. Это может отразиться на вашем будущем, включая трудности с получением работы и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие основываются на честности и доверии в финансовой сфере. Приобретение лживых купюр нарушает эти принципы и может иметь важные последствия. Рекомендуется держаться законов и вести только законными финансовыми транзакциями.
Обналичивание карт – это неправомерная деятельность, становящаяся все более популярной в нашем современном мире электронных платежей. Этот вид мошенничества представляет тяжелые вызовы для банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. В данной статье мы рассмотрим частоту встречаемости обналичивания карт, используемые методы и возможные последствия для жертв и общества.
Частота обналичивания карт:
Обналичивание карт является весьма распространенным явлением, и его частота постоянно растет с увеличением числа электронных транзакций. Киберпреступники применяют разные методы для получения доступа к финансовым средствам, включая фишинг, вредоносное программное обеспечение, скимминг и другие инновационные подходы.
Методы обналичивания карт:
Фишинг: Злоумышленники могут отправлять фальшивые электронные сообщения или создавать веб-сайты, имитирующие банковские системы, с целью получения личной информации от владельцев карт.
Скимминг: Злоумышленники устанавливают устройства скиммеры на банкоматах или терминалах для считывания данных с магнитных полос карт.
Вредоносное программное обеспечение: Киберпреступники разрабатывают вредоносные программы, которые заражают компьютеры и мобильные устройства, чтобы получить доступ к личным данным и банковским счетам.
Сетевые атаки: Атаки на системы банков и платежных платформ могут привести к утечке информации о картах и, следовательно, к их обналичиванию.
Последствия обналичивания карт:
Финансовые потери для клиентов: Владельцы карт могут столкнуться с финансовыми потерями, так как средства могут быть списаны с их счетов без их ведома.
Угроза безопасности данных: Обналичивание карт подчеркивает угрозу безопасности личных данных, что может привести к краже личной и финансовой информации.
Ущерб репутации банков: Банки и другие финансовые учреждения могут столкнуться с утратой доверия со стороны клиентов, если их системы безопасности оказываются уязвимыми.
Проблемы для экономики: Обналичивание карт создает экономический ущерб, поскольку оно стимулирует дополнительные затраты на борьбу с мошенничеством и восстановление утраченных средств.
Борьба с обналичиванием карт:
Совершенствование технологий безопасности: Банки и финансовые институты постоянно совершенствуют свои системы безопасности, чтобы предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к картам.
Образование и информирование: Обучение клиентов о методах мошенничества и том, как защитить свои данные, является важным шагом в борьбе с обналичиванием карт.
Сотрудничество с правоохранительными органами: Банки активно сотрудничают с правоохранительными органами для выявления и пресечения преступных схем.
Заключение:
Обналичивание карт – весомая угроза для финансовой стабильности и безопасности личных данных. Решение этой проблемы требует совместных усилий со стороны банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. Только эффективная борьба с мошенничеством позволит обеспечить безопасность электронных платежей и защитить интересы всех участников финансовой системы.
cialis no prescription
sky pharmacy canada
canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
обнал карт форум
Обналичивание карт – это противозаконная деятельность, становящаяся все более популярной в нашем современном мире электронных платежей. Этот вид мошенничества представляет тяжелые вызовы для банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. В данной статье мы рассмотрим частоту встречаемости обналичивания карт, используемые методы и возможные последствия для жертв и общества.
Частота обналичивания карт:
Обналичивание карт является весьма распространенным явлением, и его частота постоянно растет с увеличением числа электронных транзакций. Киберпреступники применяют разнообразные методы для получения доступа к финансовым средствам, включая фишинг, вредоносное программное обеспечение, скимминг и другие инновационные подходы.
Методы обналичивания карт:
Фишинг: Злоумышленники могут отправлять фальшивые электронные сообщения или создавать веб-сайты, имитирующие банковские системы, с целью получения личной информации от владельцев карт.
Скимминг: Злоумышленники устанавливают устройства скиммеры на банкоматах или терминалах для считывания данных с магнитных полос карт.
Вредоносное программное обеспечение: Киберпреступники разрабатывают вредоносные программы, которые заражают компьютеры и мобильные устройства, чтобы получить доступ к личным данным и банковским счетам.
Сетевые атаки: Атаки на системы банков и платежных платформ могут привести к утечке информации о картах и, следовательно, к их обналичиванию.
Последствия обналичивания карт:
Финансовые потери для клиентов: Владельцы карт могут столкнуться с денежными потерями, так как средства могут быть списаны с их счетов без их ведома.
Угроза безопасности данных: Обналичивание карт подчеркивает угрозу безопасности личных данных, что может привести к краже личной и финансовой информации.
Ущерб репутации банков: Банки и другие финансовые учреждения могут столкнуться с утратой доверия со стороны клиентов, если их системы безопасности оказываются уязвимыми.
Проблемы для экономики: Обналичивание карт создает экономический ущерб, поскольку оно стимулирует дополнительные затраты на борьбу с мошенничеством и восстановление утраченных средств.
Борьба с обналичиванием карт:
Совершенствование технологий безопасности: Банки и финансовые институты постоянно совершенствуют свои системы безопасности, чтобы предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к картам.
Образование и информирование: Обучение клиентов о методах мошенничества и том, как защитить свои данные, является важным шагом в борьбе с обналичиванием карт.
Сотрудничество с правоохранительными органами: Банки активно сотрудничают с правоохранительными органами для выявления и пресечения преступных схем.
Заключение:
Обналичивание карт – весомая угроза для финансовой стабильности и безопасности личных данных. Решение этой проблемы требует совместных усилий со стороны банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. Только эффективная борьба с мошенничеством позволит обеспечить безопасность электронных платежей и защитить интересы всех участников финансовой системы.
Покупка поддельных купюр является неправомерным и опасным поступком, что может повлечь за собой важным юридическим последствиям иначе повреждению личной финансовой устойчивости. Вот некоторые другие последствий, по какой причине покупка поддельных денег приравнивается к потенциально опасной или недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение и эксплуатация лживых банкнот приравниваются к правонарушением, противоречащим правила общества. Вас имеют возможность подвергнуться юридическим последствиям, которое может закончиться тюремному заключению, денежным наказаниям либо постановлению под стражу.
Ущерб доверию:
Лживые купюры подрывают уверенность в денежной системе. Их использование возникает угрозу для благоприятных граждан и предприятий, которые способны столкнуться с неожиданными расходами.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос поддельных денег причиняет воздействие на экономику, провоцируя денежное расширение и ухудшая глобальную финансовую устойчивость. Это в состоянии закончиться утрате уважения к денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Люди, те, вовлечены в изготовлением лживых купюр, не обязаны поддерживать какие-то нормы характеристики. Контрафактные бумажные деньги могут выйти легко выявлены, что в итоге послать в ущербу для тех, кто собирается использовать их.
Юридические последствия:
При случае попадания под арест за использование лживых денег, вас имеют возможность принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, с учетом возможные проблемы с получением работы с кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие основываются на правдивости и уважении в финансовых отношениях. Закупка поддельных купюр нарушает эти принципы и может обладать серьезные последствия. Предлагается придерживаться норм и заниматься только правомерными финансовыми транзакциями.
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your contact details
though?
chutneyb.com
Hongzhi 황제는 한마디도하지 않았고 예절에 따라 지금은 침묵해야합니다.Hongzhi 황제는 눈을 가늘게 뜨고 말했습니다. “그럼 Fang Qing의 가족은 어떻게 생각합니까?”
cheap cialis no prescription
sky pharmacy canada mail order
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
купить фальшивые рубли
Сознание сущности и рисков привязанных с легализацией кредитных карт способствует людям избегать подобных атак и защищать свои финансовые средства. Обнал (отмывание) кредитных карт — это процедура использования украденных или неправомерно приобретенных кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью скрыть их происхождения и заблокировать отслеживание.
Вот некоторые из способов, которые могут содействовать в избежании обнала кредитных карт:
Защита личной информации: Будьте осторожными в отношении предоставления личной информации, особенно онлайн. Избегайте предоставления банковских карт, кодов безопасности и дополнительных конфиденциальных данных на ненадежных сайтах.
Мощные коды доступа: Используйте надежные и уникальные пароли для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт. Регулярно изменяйте пароли.
Контроль транзакций: Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это поможет своевременно выявить подозрительных транзакций.
Программы антивирус: Используйте антивирусное программное обеспечение и вносите обновления его регулярно. Это поможет предотвратить вредоносные программы, которые могут быть использованы для кражи данных.
Осмотрительное поведение в социальных медиа: Будьте осторожными в социальных сетях, избегайте размещения чувствительной информации, которая может быть использована для взлома вашего аккаунта.
Своевременное уведомление банка: Если вы заметили какие-либо подозрительные операции или утерю карты, сразу свяжитесь с вашим банком для заблокировки карты.
Получение знаний: Будьте внимательными к инновационным подходам мошенничества и обучайтесь тому, как предупреждать их.
Избегая легковерия и осуществляя предупредительные действия, вы можете уменьшить риск стать жертвой обнала кредитных карт.
hoki 1881
domestic cleaning agency in manchester UK
canada pharmacy online
manga
Just want to say your article is as astounding.
The clarity for your publish is simply great and i can suppose you’re
a professional in this subject. Fine with your permission allow
me to seize your feed to stay up to date with coming near
near post. Thanks one million and please keep up the gratifying work.
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99 .
ttbslot.com
예기치 않게 그는 Meridian Gate 방향에서 누군가가 그를 향해 돌진하는 것을 보았습니다.
generic cialis without prescription
hoki 1881
online pharmacies
manga online
skypharmacy
Ahaa, its fastidious conversation on the topic of this post at this place at this weblog, I have read all that, so at this time me also
commenting here.
Good write-up, I am regular visitor of one?¦s web site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
Ηеllo, I enjoy reading thгough youyr article.
Ӏ wantewd tⲟ write a lіttle ⅽomment tߋ support уou.
my homepage … gcr4d login
Hurrah! Finally Ӏ g᧐t a webpage fгom wherе I know how to
truly get valuable daga ϲoncerning my stud and knowledge.
Aⅼѕߋ isit my websige … iptogel link login alternatif
I ϲould not refrain frοm commenting. Wеll wгitten!
Alѕo visit my web page; trendovske vijesti iz Indonezije
on line pharmacy
skypharmacy online
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
qiyezp.com
Zhang Heling은 발을 밟고 손을 흔들었다. “나를 따라와.”
טלגראס כיוונים מרכז
מרכזי המַקוֹם לְמוֹעֵד גַּרְגִּירֵים כיוונים (Telegrass), קָרוֹוּעַ גם בשמות “גַּרְגִּירֵים” או “גַּרְגִּירֵים כיוונים”, הן אתר מזִין מידע, לינקים, קישורים, מדריכים והסברים בנושאי קנאביס בתוך הארץ. באמצעות האתר, משתמשים יכולים למצוא את כל הקישורים המעודכנים עבור ערוצים מומלצים ופעילים בטלגראס כיוונים בכל רחבי הארץ.
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר ובוט בתוך פלטפורמת טלגראס, שמספקים דרכי תקשורת ושירותים שונות בתחום רכישת קנאביס וקשורים. באמצעות הבוט, המשתמשים יכולים לבצע מגוון פעולות בקשר לרכישת קנאביס ולשירותים נוספים, תוך כדי תקשורת עם מערכת אוטומטית המבצעת את הפעולות בצורה חכמה ומהירה.
בוט הטלגראס (Telegrass Bot) מציע מגוון פעולות שימושיות ללקוחות: רכישה קנאביס: בצע הזמנה דרך הבוט על ידי בחירת סוגי הקנאביס, כמות וכתובת למשלוח.
שאלה ותמיכה: קבל מידע על המוצרים והשירותים, תמיכה טכנית ותשובות לשאלות שונות.
בדיקה מלאי: בדוק את המלאי הזמין של קנאביס ובצע הזמנה תוך כדי הקשת הבדיקה.
הוסיפו ביקורות: הוסף ביקורות ודירוגים למוצרים שרכשת, כדי לעזור למשתמשים אחרים.
הוספת מוצרים חדשים: הוסף מוצרים חדשים לפלטפורמה והצג אותם למשתמשים.
בקיצור, בוט הטלגראס הוא כלי חשוב ונוח שמקל על השימוש והתקשורת בנושאי קנאביס, מאפשר מגוון פעולות שונות ומספק מידע ותמיכה למשתמשים.
I am very multifaceted, from sweet to , everything is possible with me! Are you submissive? Then don’t be afraid to give me a call. I’ll take your breath away with my dominant nature. Don’t hesitate for long and give me a call. I look forward to seeing you!
Hi, ϲonstantly i uѕеd to checck blog posts һere early
in the break of Ԁay, ѕince i love to gain knowledge օf
morе and more.
Аlso visi mу wweb pagе :: slot gacor deposit pulsa tanpa potongan
sandyterrace.com
이 문장은 모든 사람에게 사형 선고와 같습니다.이런 식으로 보면 그는 실제로 많은 진실을 알아 냈습니다.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
pharmacy on line skypharmacy canadian pharmacy online no script
canadian pharmacy no prescription online pharmacy canadian pharmacy
canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store canadian pharmacies canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
247 overnight pharmacy canadian sky pharmacy store 4 corners pharmacy
hoki1881
canadian online pharmacy skypharmacy online pharmacy india
online pharmacy skypharmacy sky pharmacy online drugstore
Ӏt’s amazing to pay a quick visit tһіs web site and reading
the views of all colleagues гegarding this post, whiⅼe I
am aⅼѕo keen оf getting know-hoᴡ.
Stⲟp by my blog post – otoslot
qiyezp.com
포병을 보는 것 뿐인데 그래도 혼자 가야하나요?
canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store sky pharmacy reviews canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Наличие теневых электронных базаров – это событие, что вызывает великий заинтересованность и дискуссии в современном сообществе. Подпольная часть веба, или темная часть всемирной сети, является закрытую платформу, доступные только путем определенные программные продукты и конфигурации, гарантирующие инкогнито пользовательских аккаунтов. На данной приватной сети расположены скрытые интернет-площадки – интернет-ресурсы, где-либо продаются разносторонние товары а услуги, в большинстве случаев противоправного специфики.
По даркнет-маркетах можно найти различные продуктовые товары: наркотические препараты, стрелковое оружие, похищенная информация, снаружи подвергнутые атаке учетные записи, подделки а многое другое. Такие же маркеты иногда магнетизирузивают заинтересованность и также правонарушителей, а также обычных участников, хотящих обходить стороной юриспруденция или даже получить возможность доступа к продуктам или сервисам, какие на обыденном интернете были бы в недоступны.
Впрочем стоит помнить, как работа в даркнет-маркетах представляет собой незаконный тип или в состоянии спровоцировать крупные правовые последствия по закону. Правоохранительные органы энергично сопротивляются против подобными площадками, но по причине анонимности скрытой сети это не постоянно легко.
Поэтому, существование скрытых интернет-площадок представляет собой реальностью, и все же такие рынки останавливаются сферой важных потенциальных угроз как и для таковых субъектов, а также для таких, как социума в целом.
тор маркет
Тор веб-навигатор – это особый веб-браузер, который задуман для обеспечения анонимности и безопасности в интернете. Он построен на сети Тор (The Onion Router), позволяющая пользователям обмениваться данными через дистрибутированную сеть серверов, что превращает трудным отслеживание их поступков и определение их положения.
Главная функция Тор браузера сводится в его возможности перенаправлять интернет-трафик путем несколько узлов сети Тор, каждый из них зашифровывает информацию перед следующему узлу. Это обеспечивает массу слоев (поэтому и название “луковая маршрутизация” – “The Onion Router”), что создает практически невозможным прослушивание и установление пользователей.
Тор браузер периодически используется для преодоления цензуры в территориях, где запрещен доступ к определенным веб-сайтам и сервисам. Он также дает возможность пользователям гарантировать конфиденциальность своих онлайн-действий, наподобие просмотр веб-сайтов, диалог в чатах и отправка электронной почты, предотвращая отслеживания и мониторинга со стороны интернет-провайдеров, властных агентств и киберпреступников.
Однако следует учитывать, что Тор браузер не гарантирует полной конфиденциальности и безопасности, и его выпользование может быть привязано с риском доступа к незаконным контенту или деятельности. Также возможно замедление скорости интернет-соединения из-за
тор даркнет
Тор теневая часть интернета – это часть интернета, которая, которая деи?ствует выше обыкновеннои? сети, однако неприступна для прямого доступа через обычные браузеры, например Google Chrome или Mozilla Firefox. Для выхода к даннои? сети нуждается специальное програмное обеспечение, например, Tor Browser, которыи? обеспечивает анонимность и защиту пользователеи?.
Основнои? принцип работы Тор даркнета основан на использовании маршрутов через разные ноды, которые кодируют и двигают трафик, создавая сложным трекинг его источника. Это возбуждает скрытность для пользователеи?, укрывая их реальные IP-адреса и местоположение.
Тор даркнет вмещает разные источники, включая веб-саи?ты, форумы, рынки, блоги и прочие онлаи?н-ресурсы. Некоторые из таких ресурсов могут быть не доступны или пресечены в обычнои? сети, что вызывает Тор даркнет площадкои? для трейдинга информациеи? и услугами, включая продукты и услуги, которые могут быть незаконными.
Хотя Тор даркнет используется некоторыми людьми для преодоления цензуры или защиты частнои? жизни, он также превращается платформои? для разнообразных противозаконных активностеи?, таких как торговля наркотиками, оружием, кража личных данных, поставка услуг хакеров и прочие преступные действия.
Важно сознавать, что использование Тор даркнета не всегда законно и может в себя серьезные угрозы для безопасности и правомочности.
hoki 1881
pharmacy on line sky pharmacy online 4 corners pharmacy
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
cialis india pharmacy sky pharmacy wellbutrin canadian pharmacy no prescription
canadian pharmacy no prescription onlinepharmacy canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
hoki1881
Hello malabdali.com admin, Your posts are always well structured and easy to follow.
Hi malabdali.com administrator, Thanks for sharing your thoughts!
Hi malabdali.com administrator, Good to see your posts!
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Thanks! You can read similar blog here: Sklep online
Экзистенция теневых электронных базаров – это процесс, который сопровождается великий любопытство и разговоры во нынешнем обществе. Темная часть интернета, или скрытая сфера интернета, является закрытую инфраструктуру, доступные исключительно при помощи определенные программные продукты а настройки, снабжающие скрытность участников. По этой данной подпольной инфраструктуре размещаются подпольные рынки – интернет-ресурсы, где бы продаются разнообразные вещи или услуги, чаще всего противозаконного степени.
На скрытых интернет-площадках можно отыскать самые различные продуктовые товары: психоактивные препараты, оружие, похищенная информация, взломанные учетные записи, фальшивки а многое другое. Подобные же базары иногда привлекают интерес и уголовников, и обычных пользователей, намеревающихся обходить стороной законодательство или даже иметь доступ к продуктам а сервисам, какие в нормальном всемирной сети были бы в недоступны.
Впрочем важно помнить, как практика в скрытых интернет-площадках представляет собой нелегальный специфику а может привести к значительные правовые нормы последствия. Органы правопорядка активно сражаются против подобными маркетами, но вследствие неузнаваемости темной стороны интернета данный факт не все время без проблем.
Следовательно, наличие подпольных онлайн-рынков есть реальностью, но все же такие рынки останавливаются территорией серьезных опасностей как и для таковых участников, а также для таких, как общества во в общем.
Great article! That is the type of info that should be shared aroundd the net.
Disgrrace on Google for no lonjger positioning this post
upper! Come on ovver and consult with my site . Thank you =)
Also visit my site ::카지노사이트
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Thanks! You can read similar blog here: Sklep internetowy
Hello malabdali.com admin, Your posts are always well-supported by facts and figures.
Подпольные площадки, а также темные рынки, являются веб-платформы, доступные лишь через даркнет – интернет-сеть, скрытая для стандартных поисковых машин. Эти платформы дают возможность клиентам торговать товарами и услугами разными товарами а услуговыми предложениями, чаще всего противоправного типа, например наркотические вещества, оружие, украденные данные, фальшивые документы а другие запретные либо незаконные продуктовые товары а услуговые предложения.
Даркнет-площадки гарантируют скрытность своих субъектов в результате использования особенных софта а параметров, как The Onion Routing, те замаскировывают IP-адреса и маршрутизируют интернет-трафик с помощью разносторонние узловые соединения, делая сложным прослеживание деятельности правоохранительными органами.
Такие рынки время от времени попадают целью интереса правоохранительных органов, те борются противостоят ними в рамках борьбы с интернет-преступностью а незаконной коммерцией.
России, как и в иных государствах, даркнет представляет собой участок интернета, недоступенную для стандартного поискавания и осмотра через стандартные поисковики. В противоположность от публичной поверхностной сети, теневая сеть становится неизвестным участком интернета, доступ к которому часто проводится через эксклюзивные софт, такие как Tor Browser, и анонимные коммуникации, наподобные Tor.
В теневой сети сгруппированы различные источники, включая дискуссии, торговые площадки, логи и остальные веб-сайты, которые могут быть недоступимы или запретны в стандартной коммуникации. Здесь допускается найти различные продукты и послуги, включая нелегальные, наподобные как наркотики, оружие, компрометированные данные, а также послуги хакеров и прочие.
В России скрытая часть интернета как и применяется для преодоления цензуры и слежения со партии. Некоторые клиенты могут использовать его для обмена информацией в ситуациях, когда автономия слова замкнута или информационные материалы подвергаются цензуре. Однако, также стоит отметить, что в теневой сети имеется много неправомерной работы и опасных положений, включая надувательство и интернет-преступления
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying
to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing
very good success. If you know of any please share. Kudos! You can read similar art here:
Dobry sklep
hoki1881
даркнет покупки
Покупки в темном интернете: Мифы и Реальность
Скрытая часть веба, загадочная часть сети, заинтересовывает интерес пользователей своей анонимностью и возможностью возможностью купить различные продукты и предметы без излишних действий. Однако, погружение в тот мрак непрозрачных торгов связано с набором опасностей и аспектов, о чём необходимо осведомляться перед осуществлением сделок.
Что такое скрытая часть веба и как оно действует?
Для того, кто не знаком с этим понятием, подпольная сеть – это часть интернета, невидимая от стандартных поисков. В скрытой части веба имеются уникальные онлайн-рынки, где можно найти возможность почти все виды : от препаратов и стрелкового оружия и перехваченных учётных записей и поддельных документов.
Заблуждения о приобретении товаров в скрытой части веба
Тайность гарантирована: Хотя, применение анонимных технологий, таких как Tor, может помочь скрыть свою активность в интернете, тайность в Даркнете не является абсолютной. Имеется риск, что вашу информацию о вас могут раскрыть обманщики или даже сотрудники правоохранительных органов.
Все товары – качественные: В темном интернете можно наткнуться на множество поставщиков, продающих продукцию и услуги. Однако, нельзя обеспечить качество или подлинность товара, так как невозможно проверить до того, как вы сделаете заказ.
Легальные транзакции без последствий: Многие участники неправильно думают, что приобретая товары в подпольной сети, они подвергают себя риску низкому риску, чем в обычной жизни. Однако, приобретая незаконные вещи или услуги, вы подвергаете себя наказания.
Реальность сделок в темном интернете
Опасности мошенничества и афер: В скрытой части веба множество мошенников, готовы к обману недостаточно осторожных пользователей. Они могут предложить поддельные товары или просто забрать ваши деньги и исчезнуть.
Опасность легальных органов: Пользователи Даркнета подвергают себя риску привлечения к уголовной ответственности за приобретение и заказ незаконных товаров и услуг.
Непредсказуемость результатов: Не каждая сделка в темном интернете приводят к успешному результату. Качество вещей может оказаться низким, а
процесс заказа может оказаться проблематичным.
Советы для безопасных покупок в скрытой части веба
Проведите полное изучение поставщика и услуги перед совершением покупки.
Используйте защитные программы и сервисы для обеспечения анонимности и безопасности.
Используйте только безопасные способы оплаты, такими как криптовалюты, и избегайте предоставления личной информации.
Будьте бдительны и очень внимательны во всех выполняемых действиях и принимаемых решениях.
Заключение
Транзакции в темном интернете могут быть как захватывающим, так и опасным опытом. Понимание рисков и принятие соответствующих мер предосторожности помогут уменьшить риск негативных последствий и обеспечить безопасность при покупках в этом непознанном уголке сети.
даркнет запрещён
Покупки в скрытой части веба: Мифы и Правда
Подпольная сеть, таинственная часть сети, заинтересовывает интерес участников своей скрытностью и возможностью возможностью приобрести различные товары и сервисы без дополнительной информации. Однако, путешествие в этот мир непрозрачных площадок связано с рядом опасностей и нюансов, о чем желательно знать перед осуществлением транзакций.
Что такое скрытая часть веба и как он работает?
Для тех, кому не знакомо с этим термином, скрытая часть веба – это сектор веба, скрытая от стандартных поисковых систем. В подпольной сети существуют уникальные торговые площадки, где можно найти практически все : от наркотиков и оружия и поддельных удостоверений и взломанных аккаунтов.
Иллюзии о приобретении товаров в скрытой части веба
Тайность обеспечена: При всём том, применение анонимных технологий, например Tor, способно помочь скрыть вашу действия в сети, тайность в подпольной сети не является полной. Имеется возможность, что может ваша личные данные могут раскрыть мошенники или даже сотрудники правоохранительных органов.
Все товары – высокого качества: В темном интернете можно обнаружить много продавцов, предлагающих товары и услуги. Однако, нельзя обеспечить качественность или подлинность товаров, так как невозможно проверить до заказа.
Легальные транзакции без последствий: Многие участники неправильно думают, что заказывая товары в подпольной сети, они подвергают себя риску меньшим риском, чем в обычной жизни. Однако, приобретая противоправные вещи или услуги, вы рискуете привлечения к уголовной ответственности.
Реальность приобретений в Даркнете
Риски мошенничества и афер: В темном интернете многочисленные аферисты, готовы к обману невнимательных клиентов. Они могут предложить поддельные товары или просто исчезнуть, оставив вас без денег.
Опасность правоохранительных органов: Пользователи скрытой части веба подвергают себя риску к ответственности перед законом за заказ и приобретение незаконных товаров и услуг.
Неопределённость результатов: Не каждый заказ в подпольной сети заканчиваются удачно. Качество товаров может оказаться неудовлетворительным, а
процесс заказа может привести к неприятным последствиям.
Советы для безопасных сделок в Даркнете
Проводите детальный анализ продавца и товара перед совершением покупки.
Воспользуйтесь защитными программами и сервисами для защиты вашей анонимности и безопасности.
Платите только безопасными методами, например, криптовалютами, и избегайте предоставления персональных данных.
Будьте предельно внимательны и осторожны во всех совершаемых действиях и выбранных вариантах.
Заключение
Транзакции в подпольной сети могут быть как интересным, так и рискованным опытом. Понимание рисков и применение соответствующих мер предосторожности помогут уменьшить риск негативных последствий и обеспечить безопасность при совершении покупок в этом непознанном уголке сети.
I’ve been surfing online mогe than three һours
today, yet I never found ɑny interesting article liқe yours.
It’s pretty worth еnough for me. Personally, іf all webmasters ɑnd bloggers maԀе
g᧐od cοntent ɑs yyou dіd, the web will be a ⅼot mοre uѕeful than eveг beforе.
My blog :: astra 338slot
I ɑm sure this piece of writing has touched aⅼl the internet people, іts
really realⅼy fastidious piece oof writing օn building uup new web site.
Mү site – Link Alternatif Polototo
אתרי הימורים
המימונים באינטרנט – מימורי ספורט, קזינו מקוון, משחקים קלפי.
המימונים באינטרנט הופכים לתחום מבוקש במיוחדים בעידן המחשב.
מיליונים משתתפים ממנסות את המזל באפשרויות מימורים השונות.
התהליך הזה משנה את הרגעים הניסיון וההתרגשות השחקנים.
גם מעסיק בשאלות חברתיות ואתיות השמורות מאחורי המימונים באינטרנט.
בתקופת המחשב, הימורים באינטרנט הם חלק מהותי מתרבות ה הספורט, הפנאי והחברה העכשווית.
ההימורים ברשת כוללים אפשרויות רחבות של פעולות, כולל מימורים על תוצאות ספורטיביות, פוליטי, ו- מזג האוויר.
המימונים הם הם מתבצעים באמצע
даркнет запрещён
Теневой уровень интернета: запрещённое пространство виртуальной сети
Теневой уровень интернета, тайная зона интернета продолжает привлекать интерес как сообщества, а также служб безопасности. Данный засекреченный уровень интернета примечателен своей непрозрачностью и возможностью совершения преступных деяний под прикрытием теней.
Сущность теневого уровня интернета заключается в том, что этот слой не доступен для браузеров. Для доступа к данному слою необходимы специальные инструменты и программы, которые обеспечивают анонимность пользователей. Это создает идеальную среду для различных незаконных действий, включая сбыт наркотиков, оружием, кражу личных данных и другие незаконные манипуляции.
В виде реакции на возрастающую опасность, ряд стран приняли законы, целью которых является запрещение доступа к темному интернету и преследование лиц совершающих противозаконные действия в этом скрытом мире. Тем не менее, несмотря на предпринятые действия, борьба с подпольной частью сети остается сложной задачей.
Следует отметить, что полное прекращение доступа к темному интернету практически невозможно. Даже при принятии строгих контрмер, доступ к этому уровню интернета все еще осуществим с использованием разнообразных технических средств и инструментов, используемые для обхода блокировок.
Кроме законодательных мер, действуют также совместные инициативы между правоохранительными органами и технологическими компаниями для противодействия незаконным действиям в подпольной части сети. Тем не менее, для эффективного противодействия необходимы не только технологические решения, но и совершенствования методов выявления и предотвращения незаконных действий в этой области.
В заключение, несмотря на введенные запреты и предпринятые усилия в борьбе с преступностью, подпольная часть сети остается серьезной проблемой, требующей комплексного подхода и совместных усилий со стороны правоохранительных служб, так и технологических компаний.
Spot on wіtһ this write-up, I truly think this site needs far moге attention.
I’ll prolbably Ƅе returning to reaqd mօгe, thanjks for thee advice!
My pаgе – slot gacor deposit dana
elementor
elementor
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Office renovation companies Dubai
Наша юкос предоставляет профессиональные услуги числом бурению скважин сверху воду в течение Санкт-петербурге а также Ленинградской области. Наша сестра владеем состоятельным эмпирически в течение данной области а также заручим лучшее выполнение абсолютно всех работ.
Эмпайр скважин – этто фундаментальный да эффективный фотоспособ достатка хозяйственного хозяйства, предприятий и организаций невинной и качественной водой. Наша команда искусников осуществляет бурение скважин разнообразной глубины и поперечника, с точки зрения черте донных вожак в точном регионе – https://burenie-na-vodu-spb.ru/luzhsky/gorodec/.
Автор утилизируем прогрессивное ясс да технологии, яко позволяет нам проделывать вещицы быстро (а) также безопасно. Наша цель – снабдить клиентов верным а также стабильным водоснабжением, каковое будет поклоняться длинные годы.
Сверх бурения скважин, автор этих строк тоже делаем отличное предложение хостинг-услуги по устройству глубинной доктрины: установка насосов, фильтров, резервуаров также противоположного оснащения чтобы предоставления комфортного пользования водой.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Howdy, i reead yoᥙr blog fгom time tοo time and
і oԝn a ѕimilar one and i ѡas just curious іf
yoou geet a ⅼot of spam remarks? If ѕo hoԝ do you stop it, any plugin or
anyting ү᧐u can suggeѕt? I get soo much ⅼately іt’s driving mе insane so any help іs ᴠery
muⅽh appreciated.
my hοmepage laatste sportnieuws vandaag in het Engels
сеть даркнет
Теневой уровень интернета: недоступная зона виртуальной сети
Теневой уровень интернета, скрытый сегмент сети продолжает привлекать интерес как общественности, и также служб безопасности. Данный засекреченный уровень интернета примечателен своей непрозрачностью и возможностью совершения незаконных операций под прикрытием теней.
Суть темного интернета состоит в том, что он не доступен для браузеров. Для доступа к данному слою необходимы специальные инструменты и программы, обеспечивающие скрытность пользователей. Это создает отличную площадку для разнообразных нелегальных действий, включая сбыт наркотиков, торговлю огнестрельным оружием, кражу конфиденциальных данных и другие преступные операции.
В свете растущую опасность, многие страны приняли законы, направленные на запрещение доступа к подпольной части сети и привлечение к ответственности тех, кто занимающихся незаконными деяниями в этой нелегальной области. Впрочем, несмотря на принятые меры, борьба с подпольной частью сети остается сложной задачей.
Важно отметить, что полное прекращение доступа к темному интернету практически невозможно. Даже с введением строгих мер контроля, возможность доступа к этому слою интернета все еще осуществим через различные технологии и инструменты, используемые для обхода блокировок.
Кроме законодательных мер, действуют также проекты сотрудничества между правоохранительными структурами и технологическими компаниями для противодействия незаконным действиям в подпольной части сети. Впрочем, для эффективного противодействия необходимы не только технологические решения, но и совершенствования методов выявления и предотвращения незаконных действий в этой области.
Таким образом, несмотря на введенные запреты и предпринятые усилия в борьбе с преступностью, подпольная часть сети остается серьезной проблемой, нуждающейся в комплексных подходах и коллективных усилиях со стороны правоохранительных служб, а также технологических организаций.
Heya exceptional website! Ⅾoes running а blogg such as
tһіs require a ⅼarge ɑmount oof work? Ι һave abs᧐lutely noo knowledge օf codding һowever І had been hoping to start
mу own blog in thee neаr future. Anywayѕ, should you have any recommendations oor tips ffor neѡ blog ownsrs please share.
I understand tjis is οff subject nevertheⅼess I simply neеded too аsk.
Kudos!
mу web-site – بث مباشر للأخبار على اليوتيوب مجانا
Hi there! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the superb work!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search
Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but
I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Thanks! You can read similar text here: Link Building
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but
I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Thank you! I saw similar blog here: GSA Verified List
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Dear malabdali.com administrator, Your posts are always well-written and easy to understand.
Calibration instruments suppliers
Tһis text is worth everүone’s attention.
How can I find out mⲟrе?
Heere iss mү blog post – Slot Pulsa
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! –
SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 –
3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選
– SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
My web blog :: porno
https://elementor.com/
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]!
– SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
My web blog: sex
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪
– 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選
– SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
My website; porno
https://proevolution-pro.ru/
https://гудвин-пенза.рф/
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
Here is my blog: porno
KANTORBOLA situs gamin online terbaik 2024 yang menyediakan beragam permainan judi online easy to win , mulai dari permainan slot online , taruhan judi bola , taruhan live casino , dan toto macau . Dapatkan promo terbaru kantor bola , bonus deposit harian , bonus deposit new member , dan bonus mingguan . Kunjungi link kantorbola untuk melakukan pendaftaran .
Normɑlly I dߋ not rea article οn blogs, һowever I ԝish to say that this write-up veгy pressured me to
taқe a ⅼook at and do it! Yoսr writing style һаs ƅeen amazed me.
Thɑnk you, very nice article.
Feel free tⲟ surf to myy web paցe; Slot Gacor
What is a Sugar Defender? Sugar Shield could be an affront affectability enhancement product that effectively supports stable blood sugar levels.
To the malabdali.com owner, Your posts are always well-received by the community.
Informasi RTP Live Hari Ini Dari Situs RTPKANTORBOLA
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA merupakan salah satu situs yang menyediakan informasi lengkap mengenai RTP (Return to Player) live hari ini. RTP sendiri adalah persentase rata-rata kemenangan yang akan diterima oleh pemain dari total taruhan yang dimainkan pada suatu permainan slot . Dengan adanya informasi RTP live, para pemain dapat mengukur peluang mereka untuk memenangkan suatu permainan dan membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas saat bermain.
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA menyediakan informasi RTP live dari berbagai permainan provider slot terkemuka seperti Pragmatic Play , PG Soft , Habanero , IDN Slot , No Limit City dan masih banyak rtp permainan slot yang bisa kami cek di situs RTP Kantorboal . Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat dan terpercaya, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi slot online di Indonesia .
Salah satu keunggulan dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA adalah penyajian informasi yang terupdate secara real-time. Para pemain dapat memantau perubahan RTP setiap saat dan membuat keputusan yang tepat dalam bermain. Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP dari berbagai provider permainan, sehingga para pemain dapat membandingkan dan memilih permainan dengan RTP tertinggi.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga sangat lengkap dan mendetail. Para pemain dapat melihat RTP dari setiap permainan, baik itu dari aspek permainan itu sendiri maupun dari provider yang menyediakannya. Hal ini sangat membantu para pemain dalam memilih permainan yang sesuai dengan preferensi dan gaya bermain mereka.
Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP live dari berbagai provider judi slot online terpercaya. Dengan begitu, para pemain dapat memilih permainan slot yang memberikan RTP terbaik dan lebih aman dalam bermain. Informasi ini juga membantu para pemain untuk menghindari potensi kerugian dengan bermain pada game slot online dengan RTP rendah .
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga memberikan pola dan ulasan mengenai permainan-permainan dengan RTP tertinggi. Para pemain dapat mempelajari strategi dan tips dari para ahli untuk meningkatkan peluang dalam memenangkan permainan. Analisis dan ulasan ini disajikan secara jelas dan mudah dipahami, sehingga dapat diaplikasikan dengan baik oleh para pemain.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga dapat membantu para pemain dalam mengelola keuangan mereka. Dengan mengetahui RTP dari masing-masing permainan slot , para pemain dapat mengatur taruhan mereka dengan lebih bijak. Hal ini dapat membantu para pemain untuk mengurangi risiko kerugian dan meningkatkan peluang untuk mendapatkan kemenangan yang lebih besar.
Untuk mengakses informasi RTP live dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA, para pemain tidak perlu mendaftar atau membayar biaya apapun. Situs ini dapat diakses secara gratis dan tersedia untuk semua pemain judi online. Dengan begitu, semua orang dapat memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan oleh situs RTP Kantorbola untuk meningkatkan pengalaman dan peluang mereka dalam bermain judi online.
Demikianlah informasi mengenai RTP live hari ini dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA. Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat, terpercaya, dan lengkap, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi online. Dengan memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan, para pemain dapat membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas dan meningkatkan peluang mereka untuk memenangkan permainan. Selamat bermain dan semoga sukses!
It’ѕ ɡoing tо Ьe ending of mine day, butt ƅefore end
Ι am reading thіs enormpus paragraph tto improve mү
know-һow.
Look into my blog post :: Trending nieuws in de wereld deze week
Итак почему наши сигналы – твой идеальный выбор:
Наша группа утром и вечером, днём и ночью в курсе последних курсов и событий, которые влияют на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность нам незамедлительно отвечать и давать свежие трейды.
Наш коллектив владеет профундным знание анализа по графику и умеет выделить крепкие и незащищенные аспекты для входа в сделку. Это содействует для снижения опасностей и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Мы же используем личные боты для анализа для изучения графиков на всех временных промежутках. Это содействует нашим специалистам завоевать полную картину рынка.
Прежде публикацией подачи в нашем Telegram мы осуществляем детальную проверку все фасадов и подтверждаем возможное длинный или краткий. Это гарантирует верность и качественные характеристики наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к проверенным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам получить успеха в финансах на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot
I believe this web site holds some very wonderful info for everyone : D.
situs kantorbola
Kantorbola Situs slot Terbaik, Modal 10 Ribu Menang Puluhan Juta
Kantorbola merupakan salah satu situs judi online terbaik yang saat ini sedang populer di kalangan pecinta taruhan bola , judi live casino dan judi slot online . Dengan modal awal hanya 10 ribu rupiah, Anda memiliki kesempatan untuk memenangkan puluhan juta rupiah bahkan ratusan juta rupiah dengan bermain judi online di situs kantorbola . Situs ini menawarkan berbagai jenis taruhan judi , seperti judi bola , judi live casino , judi slot online , judi togel , judi tembak ikan , dan judi poker uang asli yang menarik dan menguntungkan. Selain itu, Kantorbola juga dikenal sebagai situs judi online terbaik yang memberikan pelayanan terbaik kepada para membernya.
Keunggulan Kantorbola sebagai Situs slot Terbaik
Kantorbola memiliki berbagai keunggulan yang membuatnya menjadi situs slot terbaik di Indonesia. Salah satunya adalah tampilan situs yang menarik dan mudah digunakan, sehingga para pemain tidak akan mengalami kesulitan ketika melakukan taruhan. Selain itu, Kantorbola juga menyediakan berbagai bonus dan promo menarik yang dapat meningkatkan peluang kemenangan para pemain. Dengan sistem keamanan yang terjamin, para pemain tidak perlu khawatir akan kebocoran data pribadi mereka.
Modal 10 Ribu Bisa Menang Puluhan Juta di Kantorbola
Salah satu daya tarik utama Kantorbola adalah kemudahan dalam memulai taruhan dengan modal yang terjangkau. Dengan hanya 10 ribu rupiah, para pemain sudah bisa memasang taruhan dan berpeluang untuk memenangkan puluhan juta rupiah. Hal ini tentu menjadi kesempatan yang sangat menarik bagi para penggemar taruhan judi online di Indonesia . Selain itu, Kantorbola juga menyediakan berbagai jenis taruhan yang bisa dipilih sesuai dengan keahlian dan strategi masing-masing pemain.
Berbagai Jenis Permainan Taruhan Bola yang Menarik
Kantorbola menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan taruhan bola yang menarik dan menguntungkan bagi para pemain. Mulai dari taruhan Mix Parlay, Handicap, Over/Under, hingga Correct Score, semua jenis taruhan tersebut bisa dinikmati di situs ini. Para pemain dapat memilih jenis taruhan yang paling sesuai dengan pengetahuan dan strategi taruhan mereka. Dengan peluang kemenangan yang besar, para pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meraih keuntungan yang fantastis di Kantorbola.
Pelayanan Terbaik untuk Kepuasan Para Member
Selain menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan taruhan bola yang menarik, Kantorbola juga memberikan pelayanan terbaik untuk kepuasan para membernya. Tim customer service yang profesional siap membantu para pemain dalam menyelesaikan berbagai masalah yang mereka hadapi. Selain itu, proses deposit dan withdraw di Kantorbola juga sangat cepat dan mudah, sehingga para pemain tidak akan mengalami kesulitan dalam melakukan transaksi. Dengan pelayanan yang ramah dan responsif, Kantorbola selalu menjadi pilihan utama para penggemar taruhan bola.
Kesimpulan
Kantorbola merupakan situs slot terbaik yang menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan taruhan bola yang menarik dan menguntungkan. Dengan modal awal hanya 10 ribu rupiah, para pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk memenangkan puluhan juta rupiah. Keunggulan Kantorbola sebagai situs slot terbaik antara lain tampilan situs yang menarik, berbagai bonus dan promo menarik, serta sistem keamanan yang terjamin. Dengan berbagai jenis permainan taruhan bola yang ditawarkan, para pemain memiliki banyak pilihan untuk meningkatkan peluang kemenangan mereka. Dengan pelayanan terbaik untuk kepuasan para member, Kantorbola selalu menjadi pilihan utama para penggemar taruhan bola.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Berapa modal minimal untuk bermain di Kantorbola? Modal minimal untuk bermain di Kantorbola adalah 10 ribu rupiah.
Bagaimana cara melakukan deposit di Kantorbola? Anda dapat melakukan deposit di Kantorbola melalui transfer bank atau dompet digital yang telah disediakan.
Apakah Kantorbola menyediakan bonus untuk new member? Ya, Kantorbola menyediakan berbagai bonus untuk new member, seperti bonus deposit dan bonus cashback.
Apakah Kantorbola aman digunakan untuk bermain taruhan bola online? Kantorbola memiliki sistem keamanan yang terjamin dan data pribadi para pemain akan dijaga kerahasiaannya dengan baik.
Почему наши сигналы на вход – твой наилучший вариант:
Наша команда постоянно в курсе современных тенденций и ситуаций, которые влияют на криптовалюты. Это позволяет коллективу незамедлительно отвечать и давать свежие сигналы.
Наш коллектив обладает предельным знание анализа по графику и может выделить устойчивые и уязвимые поля для включения в сделку. Это способствует минимизации рисков и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Мы применяем собственные боты для анализа для изучения графиков на все интервалах. Это способствует нашим специалистам получить всю картину рынка.
Перед публикацией подачи в нашем Telegram команда осуществляем детальную проверку все аспектов и подтверждаем допустимая длинный или период короткой торговли. Это обеспечивает достоверность и качественные характеристики наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нашему каналу к нашей группе прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым подачам, которые помогут вам вам достичь финансовых результатов на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot
Почему наши сигналы – ваш наилучший выбор:
Мы утром и вечером, днём и ночью в тренде последних курсов и моментов, которые воздействуют на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность команде оперативно действовать и давать новые сигналы.
Наш состав владеет глубоким понимание технического анализа и способен выделить устойчивые и незащищенные аспекты для вступления в сделку. Это способствует минимизации рисков и повышению прибыли.
Мы используем собственные боты для анализа данных для просмотра графиков на все интервалах. Это помогает нам завоевать полную картину рынка.
Перед опубликованием подачи в нашем канале Telegram мы делаем педантичную проверку все аспектов и подтверждаем возможное долгий или короткий. Это гарантирует надежность и качественные показатели наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нам к нашему прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым подачам, которые содействуют вам получить успеха в финансах на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot
Итак почему наши сигналы – всегда наилучший путь:
Мы утром и вечером, днём и ночью в тренде последних курсов и событий, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это позволяет нашей команде мгновенно реагировать и давать актуальные подачи.
Наш состав имеет глубоким знанием анализа и способен выявлять устойчивые и незащищенные факторы для присоединения в сделку. Это содействует минимизации потерь и максимизации прибыли.
Мы же внедряем собственные боты для анализа для просмотра графиков на все интервалах. Это помогает нам завоевать всю картину рынка.
Прежде опубликованием сигнал в нашем канале Telegram команда проводим тщательную проверку всех сторон и подтверждаем допустимая длинный или краткий. Это обеспечивает верность и качественные показатели наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нам к нашей группе прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам добиться финансового успеха на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot
kantorbola
Mengenal Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola
Kantorbola merupakan situs gaming online terbaik yang menawarkan pengalaman bermain yang seru dan mengasyikkan bagi para pecinta game. Dengan berbagai pilihan game menarik dan grafis yang memukau, Kantorbola menjadi pilihan utama bagi para gamers yang ingin mencari hiburan dan tantangan baru. Dengan layanan customer service yang ramah dan profesional, serta sistem keamanan yang terjamin, Kantorbola siap memberikan pengalaman bermain yang terbaik dan menyenangkan bagi semua membernya. Jadi, tunggu apalagi? Bergabunglah sekarang dan rasakan sensasi seru bermain game di Kantorbola!
Situs kantor bola menyediakan beberapa link alternatif terbaru
Situs kantor bola merupakan salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang menyediakan berbagai link alternatif terbaru untuk memudahkan para pengguna dalam mengakses situs tersebut. Dengan adanya link alternatif terbaru ini, para pengguna dapat tetap mengakses situs kantor bola meskipun terjadi pemblokiran dari pemerintah atau internet positif. Hal ini tentu menjadi kabar baik bagi para pecinta judi online yang ingin tetap bermain tanpa kendala akses ke situs kantor bola.
Dengan menyediakan beberapa link alternatif terbaru, situs kantor bola juga dapat memberikan variasi akses kepada para pengguna. Hal ini memungkinkan para pengguna untuk memilih link alternatif mana yang paling cepat dan stabil dalam mengakses situs tersebut. Dengan demikian, pengalaman bermain judi online di situs kantor bola akan menjadi lebih lancar dan menyenangkan.
Selain itu, situs kantor bola juga menunjukkan komitmennya dalam memberikan pelayanan terbaik kepada para pengguna dengan menyediakan link alternatif terbaru secara berkala. Dengan begitu, para pengguna tidak perlu khawatir akan kehilangan akses ke situs kantor bola karena selalu ada link alternatif terbaru yang dapat digunakan sebagai backup. Keberadaan link alternatif tersebut juga menunjukkan bahwa situs kantor bola selalu berusaha untuk tetap eksis dan dapat diakses oleh para pengguna setianya.
Secara keseluruhan, kehadiran beberapa link alternatif terbaru dari situs kantor bola merupakan salah satu bentuk komitmen dari situs tersebut dalam memberikan kemudahan dan kenyamanan kepada para pengguna. Dengan adanya link alternatif tersebut, para pengguna dapat terus mengakses situs kantor bola tanpa hambatan apapun. Hal ini tentu akan semakin meningkatkan popularitas situs kantor bola sebagai salah satu situs gaming online terbaik di Indonesia. Berikut beberapa link alternatif dari situs kantorbola , diantaranya .
1. Link Kantorbola77
Link Kantorbola77 merupakan salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang saat ini banyak diminati oleh para pecinta judi online. Dengan berbagai pilihan permainan yang lengkap dan berkualitas, situs ini mampu memberikan pengalaman bermain yang memuaskan bagi para membernya. Selain itu, Kantorbola77 juga menawarkan berbagai bonus dan promo menarik yang dapat meningkatkan peluang kemenangan para pemain.
Salah satu keunggulan dari Link Kantorbola77 adalah sistem keamanan yang sangat terjamin. Dengan teknologi enkripsi yang canggih, situs ini menjaga data pribadi dan transaksi keuangan para membernya dengan sangat baik. Hal ini membuat para pemain merasa aman dan nyaman saat bermain di Kantorbola77 tanpa perlu khawatir akan adanya kebocoran data atau tindakan kecurangan yang merugikan.
Selain itu, Link Kantorbola77 juga menyediakan layanan pelanggan yang siap membantu para pemain 24 jam non-stop. Tim customer service yang profesional dan responsif siap membantu para member dalam menyelesaikan berbagai kendala atau pertanyaan yang mereka hadapi saat bermain. Dengan layanan yang ramah dan efisien, Kantorbola77 menempatkan kepuasan para pemain sebagai prioritas utama mereka.
Dengan reputasi yang baik dan pengalaman yang telah teruji, Link Kantorbola77 layak untuk menjadi pilihan utama bagi para pecinta judi online. Dengan berbagai keunggulan yang dimilikinya, situs ini memberikan pengalaman bermain yang memuaskan dan menguntungkan bagi para membernya. Jadi, jangan ragu untuk bergabung dan mencoba keberuntungan Anda di Kantorbola77.
2. Link Kantorbola88
Link kantorbola88 adalah salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang harus dikenal oleh para pecinta judi online. Dengan menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan seperti judi bola, casino, slot online, poker, dan banyak lagi, kantorbola88 menjadi pilihan utama bagi para pemain yang ingin mencoba keberuntungan mereka. Link ini memberikan akses mudah dan cepat untuk para pemain yang ingin bermain tanpa harus repot mencari situs judi online yang terpercaya.
Selain itu, kantorbola88 juga dikenal sebagai situs yang memiliki reputasi baik dalam hal pelayanan dan keamanan. Dengan sistem keamanan yang canggih dan profesional, para pemain dapat bermain tanpa perlu khawatir akan kebocoran data pribadi atau transaksi keuangan mereka. Selain itu, layanan pelanggan yang ramah dan responsif juga membuat pengalaman bermain di kantorbola88 menjadi lebih menyenangkan dan nyaman.
Selain itu, link kantorbola88 juga menawarkan berbagai bonus dan promosi menarik yang dapat dinikmati oleh para pemain. Mulai dari bonus deposit, cashback, hingga bonus referral, semua memberikan kesempatan bagi pemain untuk mendapatkan keuntungan lebih saat bermain di situs ini. Dengan adanya bonus-bonus tersebut, kantorbola88 terus berusaha memberikan yang terbaik bagi para pemainnya agar selalu merasa puas dan senang bermain di situs ini.
Dengan reputasi yang baik, pelayanan yang prima, keamanan yang terjamin, dan bonus yang menggiurkan, link kantorbola88 adalah pilihan yang tepat bagi para pemain judi online yang ingin merasakan pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan. Dengan bergabung di situs ini, para pemain dapat merasakan sensasi bermain judi online yang berkualitas dan terpercaya, serta memiliki peluang untuk mendapatkan keuntungan besar. Jadi, jangan ragu untuk mencoba keberuntungan Anda di kantorbola88 dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang tak terlupakan.
3. Link Kantorbola88
Kantorbola99 merupakan salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang dapat menjadi pilihan bagi para pecinta judi online. Situs ini menawarkan berbagai permainan menarik seperti judi bola, casino online, slot online, poker, dan masih banyak lagi. Dengan berbagai pilihan permainan yang disediakan, para pemain dapat menikmati pengalaman berjudi yang seru dan mengasyikkan.
Salah satu keunggulan dari Kantorbola99 adalah sistem keamanan yang sangat terjamin. Situs ini menggunakan teknologi enkripsi terbaru untuk melindungi data pribadi dan transaksi keuangan para pemain. Dengan demikian, para pemain bisa bermain dengan tenang tanpa perlu khawatir tentang kebocoran data pribadi atau kecurangan dalam permainan.
Selain itu, Kantorbola99 juga menawarkan berbagai bonus dan promo menarik bagi para pemain setianya. Mulai dari bonus deposit, bonus cashback, hingga bonus referral yang dapat meningkatkan peluang para pemain untuk meraih kemenangan. Dengan adanya bonus dan promo ini, para pemain dapat merasa lebih diuntungkan dan semakin termotivasi untuk bermain di situs ini.
Dengan reputasi yang baik dan pengalaman yang telah terbukti, Kantorbola99 menjadi pilihan yang tepat bagi para pecinta judi online. Dengan pelayanan yang ramah dan responsif, para pemain juga dapat mendapatkan bantuan dan dukungan kapan pun dibutuhkan. Jadi, tidak heran jika Kantorbola99 menjadi salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang banyak direkomendasikan oleh para pemain judi online.
Promo Terbaik Dari Situs kantorbola
Kantorbola merupakan salah satu situs gaming online terbaik yang menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan menarik seperti judi bola, casino, poker, slots, dan masih banyak lagi. Situs ini telah menjadi pilihan utama bagi para pecinta judi online karena reputasinya yang terpercaya dan kualitas layanannya yang prima. Selain itu, Kantorbola juga seringkali memberikan promo-promo menarik kepada para membernya, salah satunya adalah promo terbaik yang dapat meningkatkan peluang kemenangan para pemain.
Promo terbaik dari situs Kantorbola biasanya berupa bonus deposit, cashback, maupun event-event menarik yang diadakan secara berkala. Dengan adanya promo-promo ini, para pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk mendapatkan keuntungan lebih besar dan juga kesempatan untuk memenangkan hadiah-hadiah menarik. Selain itu, promo-promo ini juga menjadi daya tarik bagi para pemain baru yang ingin mencoba bermain di situs Kantorbola.
Salah satu promo terbaik dari situs Kantorbola yang paling diminati adalah bonus deposit new member sebesar 100%. Dengan bonus ini, para pemain baru bisa mendapatkan tambahan saldo sebesar 100% dari jumlah deposit yang mereka lakukan. Hal ini tentu saja menjadi kesempatan emas bagi para pemain untuk bisa bermain lebih lama dan meningkatkan peluang kemenangan mereka. Selain itu, Kantorbola juga selalu memberikan promo-promo menarik lainnya yang dapat dinikmati oleh semua membernya.
Dengan berbagai promo terbaik yang ditawarkan oleh situs Kantorbola, para pemain memiliki banyak kesempatan untuk meraih kemenangan besar dan mendapatkan pengalaman bermain judi online yang lebih menyenangkan. Jadi, jangan ragu untuk bergabung dan mencoba keberuntungan Anda di situs gaming online terbaik ini. Dapatkan promo-promo menarik dan nikmati berbagai jenis permainan seru hanya di Kantorbola.
Deposit Kilat Di Kantorbola Melalui QRIS
Deposit kilat di Kantorbola melalui QRIS merupakan salah satu fitur yang mempermudah para pemain judi online untuk melakukan transaksi secara cepat dan aman. Dengan menggunakan QRIS, para pemain dapat melakukan deposit dengan mudah tanpa perlu repot mencari nomor rekening atau melakukan transfer manual.
QRIS sendiri merupakan sistem pembayaran digital yang memanfaatkan kode QR untuk memfasilitasi transaksi pembayaran. Dengan menggunakan QRIS, para pemain judi online dapat melakukan deposit hanya dengan melakukan pemindaian kode QR yang tersedia di situs Kantorbola. Proses deposit pun dapat dilakukan dalam waktu yang sangat singkat, sehingga para pemain tidak perlu menunggu lama untuk bisa mulai bermain.
Keunggulan deposit kilat di Kantorbola melalui QRIS adalah kemudahan dan kecepatan transaksi yang ditawarkan. Para pemain judi online tidak perlu lagi repot mencari nomor rekening atau melakukan transfer manual yang memakan waktu. Cukup dengan melakukan pemindaian kode QR, deposit dapat langsung terproses dan saldo akun pemain pun akan langsung bertambah.
Dengan adanya fitur deposit kilat di Kantorbola melalui QRIS, para pemain judi online dapat lebih fokus pada permainan tanpa harus terganggu dengan urusan transaksi. QRIS memungkinkan para pemain untuk melakukan deposit kapan pun dan di mana pun dengan mudah, sehingga pengalaman bermain judi online di Kantorbola menjadi lebih menyenangkan dan praktis.
Dari ulasan mengenai mengenal situs gaming online terbaik Kantorbola, dapat disimpulkan bahwa situs tersebut menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan yang menarik dan populer di kalangan para penggemar game. Dengan tampilan yang menarik dan user-friendly, Kantorbola memberikan pengalaman bermain yang menyenangkan dan memuaskan bagi para pemain. Selain itu, keamanan dan keamanan privasi pengguna juga menjadi prioritas utama dalam situs tersebut sehingga para pemain dapat bermain dengan tenang tanpa perlu khawatir akan data pribadi mereka.
Selain itu, Kantorbola juga memberikan berbagai bonus dan promo menarik bagi para pemain, seperti bonus deposit dan cashback yang dapat meningkatkan keuntungan bermain. Dengan pelayanan customer service yang responsif dan profesional, para pemain juga dapat mendapatkan bantuan yang dibutuhkan dengan cepat dan mudah. Dengan reputasi yang baik dan banyaknya testimonial positif dari para pemain, Kantorbola menjadi pilihan situs gaming online terbaik bagi para pecinta game di Indonesia.
Frequently Asked Question ( FAQ )
A : Apa yang dimaksud dengan Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola?
Q : Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola adalah platform online yang menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan game yang berkualitas dan menarik untuk dimainkan.
A : Apa saja jenis permainan yang tersedia di Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola?
Q : Di Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola, anda dapat menemukan berbagai jenis permainan seperti game slot, poker, roulette, blackjack, dan masih banyak lagi.
A : Bagaimana cara mendaftar di Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola?
Q : Untuk mendaftar di Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola, anda hanya perlu mengakses situs resmi mereka, mengklik tombol “Daftar” dan mengisi formulir pendaftaran yang disediakan.
A : Apakah Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola aman digunakan untuk bermain game?
Q : Ya, Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola telah memastikan keamanan dan kerahasiaan data para penggunanya dengan menggunakan sistem keamanan terkini.
A : Apakah ada bonus atau promo menarik yang ditawarkan oleh Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola?
Q : Tentu saja, Situs Gaming Online Terbaik Kantorbola seringkali menawarkan berbagai bonus dan promo menarik seperti bonus deposit, cashback, dan bonus referral untuk para membernya. Jadi pastikan untuk selalu memeriksa promosi yang sedang berlangsung di situs mereka.
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編-
– 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
Have a look at my web site – sex
Почему наши сигналы на вход – твой лучший вариант:
Мы постоянно в тренде текущих курсов и моментов, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность нам оперативно отвечать и предоставлять актуальные сигналы.
Наш коллектив имеет глубинным пониманием теханализа и может определять устойчивые и слабые аспекты для присоединения в сделку. Это способствует для снижения потерь и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Мы внедряем собственные боты-анализаторы для изучения графиков на все периодах времени. Это содействует нашим специалистам достать полную картину рынка.
Прежде опубликованием сигнала в нашем канале Telegram мы осуществляем педантичную проверку все аспектов и подтверждаем допустимый период долгой торговли или краткий. Это подтверждает надежность и качественные характеристики наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам достигнуть успеха в финансах на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới bằng của Curacao, đã đưa vào hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 cơ hội miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Vì lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược tinh vi nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu.
JDB online
JDB online | 2024 best online slot game demo cash
How to earn reels? jdb online accumulate spin get bonus
Hot demo fun: Quick earn bonus for ranking demo
JDB demo for win? JDB reward can be exchanged to real cash
#jdbonline
777 sign up and get free 2,000 cash: https://www.jdb777.io/
#jdbonline #democash #demofun #777signup
#rankingdemo #demoforwin
2000 cash: Enter email to verify, enter verify, claim jdb bonus
Play with JDB games an online platform in every countries.
Enjoy the Joy of Gaming!
Gratis to Join, Free to Play.
Sign Up and Acquire a Bonus!
SIGN UP NOW AND OBTAIN 2000?
We encourage you to receive a demo enjoyable welcome bonus for all new members! Plus, there are other special promotions waiting for you!
Get more information
JDB – FREE TO JOIN
Effortless to play, real profit
Engage in JDB today and indulge in fantastic games without any investment! With a wide array of free games, you can enjoy pure entertainment at any time.
Quick play, quick join
Appreciate your time and opt for JDB’s swift games. Just a few easy steps and you’re set for an amazing gaming experience!
Register now and receive money
Experience JDB: Instant play with no investment and the opportunity to win cash. Designed for effortless and lucrative play.
Dive into the Domain of Online Gaming Thrills with Fun Slots Online!
Are you primed to undergo the sensation of online gaming like never before? Scour no further than Fun Slots Online, your ultimate hub for thrilling gameplay, endless entertainment, and stimulating winning opportunities!
At Fun Slots Online, we take pride ourselves on providing a wide selection of compelling games designed to keep you immersed and amused for hours on end. From classic slot machines to innovative new releases, there’s something for all to enjoy. Plus, with our user-friendly interface and uninterrupted gameplay experience, you’ll have no problem immersing straight into the excitement and delighting in every moment.
But that’s not all – we also present a selection of unique promotions and bonuses to recompense our loyal players. From greeting bonuses for new members to privileged rewards for our top players, there’s always something thrilling happening at Fun Slots Online. And with our guarded payment system and 24-hour customer support, you can savor peace of mind knowing that you’re in good hands every step of the way.
So why wait? Enroll Fun Slots Online today and start your journey towards thrilling victories and jaw-dropping prizes. Whether you’re a seasoned gamer or just starting out, there’s never been a better time to engage in the fun and excitement at Fun Slots Online. Sign up now and let the games begin!
robot 88
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Do sự cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tinh vi nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên trách, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai phấn khích trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu.
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
dj88
rg777
App cá độ:Hướng dẫn tải app cá cược uy tín RG777 đúng cách
Bạn có biết? Tải app cá độ đúng cách sẽ giúp tiết kiệm thời gian đăng nhập, tăng tính an toàn và bảo mật cho tài khoản của bạn! Vậy đâu là cách để tải một app cá cược uy tín dễ dàng và chính xác? Xem ngay bài viết này nếu bạn muốn chơi cá cược trực tuyến an toàn!
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 – Nhà Cái Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Việt Nam
Link tải app cá độ nét nhất 2023:RG777
Để đảm bảo việc tải ứng dụng cá cược của bạn an toàn và nhanh chóng, người chơi có thể sử dụng đường link sau.
tải về ngay lập tức
台中外送茶
現代社會,快遞已成為大眾化的服務業,吸引了許多人的注意和參與。 與傳統夜店、酒吧不同,外帶提供了更私密、便捷的服務方式,讓人們有機會在家中或特定地點與美女共度美好時光。
多樣化選擇
從台灣到日本,馬來西亞到越南,外送業提供了多樣化的女孩選擇,以滿足不同人群的需求和喜好。 無論你喜歡什麼類型的女孩,你都可以在外賣行業找到合適的女孩。
不同的價格水平
價格範圍從實惠到豪華。 無論您的預算如何,您都可以找到適合您需求的女孩,享受優質的服務並度過愉快的時光。
快遞業高度重視安全和隱私保護,提供多種安全措施和保障,讓客戶放心使用服務,無需擔心個人資訊外洩或安全問題。
如果你想成為一名經驗豐富的外包司機,外包產業也將為你提供廣泛的選擇和專屬服務。 只需按照步驟操作,您就可以輕鬆享受快遞行業帶來的樂趣和便利。
蓬勃發展的快遞產業為人們提供了一種新的娛樂休閒方式,讓人們在忙碌的生活中得到放鬆,享受美好時光。
Whats up very cool web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds also?KI am glad to search out so many useful info right here in the publish, we want work out extra strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
App cá độ:Hướng dẫn tải app cá cược uy tín RG777 đúng cách
Bạn có biết? Tải app cá độ đúng cách sẽ giúp tiết kiệm thời gian đăng nhập, tăng tính an toàn và bảo mật cho tài khoản của bạn! Vậy đâu là cách để tải một app cá cược uy tín dễ dàng và chính xác? Xem ngay bài viết này nếu bạn muốn chơi cá cược trực tuyến an toàn!
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 – Nhà Cái Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Việt Nam
Link tải app cá độ nét nhất 2023:RG777
Để đảm bảo việc tải ứng dụng cá cược của bạn an toàn và nhanh chóng, người chơi có thể sử dụng đường link sau.
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 Casino
App cá độ:Hướng dẫn tải app cá cược uy tín RG777 đúng cách
Bạn có biết? Tải app cá độ đúng cách sẽ giúp tiết kiệm thời gian đăng nhập, tăng tính an toàn và bảo mật cho tài khoản của bạn! Vậy đâu là cách để tải một app cá cược uy tín dễ dàng và chính xác? Xem ngay bài viết này nếu bạn muốn chơi cá cược trực tuyến an toàn!
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 – Nhà Cái Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Việt Nam
Link tải app cá độ nét nhất 2023:RG777
Để đảm bảo việc tải ứng dụng cá cược của bạn an toàn và nhanh chóng, người chơi có thể sử dụng đường link sau.
tải về ngay lập tức
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Revealing Achievement with JDB Gaming: Your Ultimate Betting Software Answer
In the world of online gaming, locating the right wager software is critical for achievement. Introducing JDB Gaming – a foremost supplier of revolutionary gaming solutions tailored to improve the gaming experience and boost revenue for operators. With a focus on easy-to-use interfaces, attractive bonuses, and a wide selection of games, JDB Gaming emerges as a leading choice for both players and operators alike.
JDB Demo presents a look into the world of JDB Gaming, offering players with an chance to undergo the thrill of betting without any risk. With easy-to-use interfaces and smooth navigation, JDB Demo allows it straightforward for players to explore the broad selection of games available, from traditional slots to captivating arcade titles.
When it regards bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing leads with appealing offers that lure players and hold them returning for more. From the well-liked Daily Play 2000 Rewards to exclusive promotions, JDB Bet Marketing guarantees that players are rewarded for their loyalty and dedication.
With so numerous game developers online, identifying the best can be a daunting task. However, JDB Gaming emerges from the pack with its devotion to superiority and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to pick, JDB Gaming offers something special for everyone, whether you’re a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the heart of JDB Gaming lies a dedication to providing the finest possible gaming experience players. With a concentration on Asian culture and spectacular 3D animations, JDB Gaming sets itself apart as a front runner in the industry. Whether you’re a gamer in search of excitement or an operator in need of a reliable partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Smoothly integrate with all platforms for optimal business chances. Big Data Analysis: Stay ahead of market trends and understand player behavior with comprehensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Relish peace of mind with skilled and reliable technical support on hand around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming offers a victorious combination of advanced technology, appealing bonuses, and unmatched support. Whether you’re a gamer or an operator, JDB Gaming has everything you need to thrive in the realm of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming family today and release your full potential!
JDB online
JDB online | 2024 best online slot game demo cash
How to earn reels? jdb online accumulate spin get bonus
Hot demo fun: Quick earn bonus for ranking demo
JDB demo for win? JDB reward can be exchanged to real cash
#jdbonline
777 sign up and get free 2,000 cash: https://www.jdb777.io/
#jdbonline #democash #demofun #777signup
#rankingdemo #demoforwin
2000 cash: Enter email to verify, enter verify, claim jdb bonus
Play with JDB games an online platform in every countries.
Enjoy the Joy of Gaming!
Complimentary to Join, Gratis to Play.
Join and Receive a Bonus!
REGISTER NOW AND OBTAIN 2000?
We encourage you to claim a trial enjoyable welcome bonus for all new members! Plus, there are other particular promotions waiting for you!
Find out more
JDB – FREE TO JOIN
Easy to play, real profit
Join JDB today and indulge in fantastic games without any investment! With a wide array of free games, you can relish pure entertainment at any time.
Speedy play, quick join
Esteem your time and opt for JDB’s swift games. Just a few easy steps and you’re set for an amazing gaming experience!
Register now and generate money
Experience JDB: Instant play with no investment and the opportunity to win cash. Designed for effortless and lucrative play.
Dive into the Universe of Online Gaming Stimulation with Fun Slots Online!
Are you set to feel the excitement of online gaming like never before? Seek no further than Fun Slots Online, your ultimate hub for thrilling gameplay, endless entertainment, and thrilling winning opportunities!
At Fun Slots Online, we boast ourselves on giving a wide array of engaging games designed to maintain you involved and amused for hours on end. From classic slot machines to innovative new releases, there’s something for everybody to enjoy. Plus, with our user-friendly interface and smooth gameplay experience, you’ll have no difficulty immersing straight into the thrill and enjoying every moment.
But that’s not all – we also present a assortment of special promotions and bonuses to compensate our loyal players. From initial bonuses for new members to exclusive rewards for our top players, there’s always something exhilarating happening at Fun Slots Online. And with our secure payment system and 24-hour customer support, you can enjoy peace of mind knowing that you’re in good hands every step of the way.
So why wait? Join Fun Slots Online today and begin your adventure towards exciting victories and jaw-dropping prizes. Whether you’re a seasoned gamer or just starting out, there’s never been a better time to be part of the fun and stimulation at Fun Slots Online. Sign up now and let the games begin!
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯 –
在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
Here is my homepage :: bitch
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online’s Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Cổng chơi – Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Cổng chơi được sáng lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động theo giấy phép trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với tính cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đáng tin cậy và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Nền tảng cá cược không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, bên cạnh các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có chương trình ưu đãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Với sự cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu!
_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪
– 3P合輯 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看_3角質熟婦暨淋浴彙編- – 其他亞洲 – 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
-sm-史上最猥瑣眼鏡攝影師KK哥換個新髮型把苗條大奶子美女模特捆綁SM調教哭喊著求饒老套路玩完請吃J8然後啪啪 – 3P合輯
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
!! – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
!? – 情色視頻網站 – PornBest
?NTR?人妻的外遇日記,一次比一次更大膽的讓老公戴綠帽[顏射+口爆+內射]! – SWAG –
在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
?口交口爆&肛交實錄?15分鐘精選 – SWAG
– 在線成人色情視頻AV電影免費看
My webpage :: porno
robot88
Intro
betvisa india
Betvisa india | IPL 2024 Heat Wave
IPL 2024 Big bets, big prizes With Betvisa India
Exclusive for Sports Fans Betvisa Online Casino 50% Welcome Bonus
Crash Game Supreme Compete for 1,00,00,000 pot Betvisa.com
#betvisaindia
Accurate Predictions IPL T20 Tournament, Winner Takes All!
More than just a game | Betvisa dreams invites you to fly to malta
https://www.b3tvisapro.com/
#betvisaindia #betvisalogin #betvisaonlinecasino
#betvisa.com #betvisaapp
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược hoàn hảo nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai phấn khích trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu dấu mốc của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều quan trọng.
of course like your website however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come back again.
Appreciating the dedication you put into your website and in depth information you offer. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed information. Excellent read! I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
JDB online
JDB online | 2024 best online slot game demo cash
How to earn reels? jdb online accumulate spin get bonus
Hot demo fun: Quick earn bonus for ranking demo
JDB demo for win? JDB reward can be exchanged to real cash
#jdbonline
777 sign up and get free 2,000 cash: https://www.jdb777.io/
#jdbonline #democash #demofun #777signup
#rankingdemo #demoforwin
2000 cash: Enter email to verify, enter verify, claim jdb bonus
Play with JDB games an online platform in every countries.
Enjoy the Delight of Gaming!
Costless to Join, Gratis to Play.
Register and Obtain a Bonus!
SIGN UP NOW AND GET 2000?
We urge you to obtain a demo enjoyable welcome bonus for all new members! Plus, there are other exclusive promotions waiting for you!
Get more information
JDB – FREE TO JOIN
Effortless to play, real profit
Participate in JDB today and indulge in fantastic games without any investment! With a wide array of free games, you can savor pure entertainment at any time.
Quick play, quick join
Appreciate your time and opt for JDB’s swift games. Just a few easy steps and you’re set for an amazing gaming experience!
Register now and receive money
Experience JDB: Instant play with no investment and the opportunity to win cash. Designed for effortless and lucrative play.
Immerse into the World of Online Gaming Excitement with Fun Slots Online!
Are you set to undergo the thrill of online gaming like never before? Scour no further than Fun Slots Online, your ultimate hub for exhilarating gameplay, endless entertainment, and thrilling winning opportunities!
At Fun Slots Online, we take pride ourselves on offering a wide selection of captivating games designed to maintain you involved and entertained for hours on end. From classic slot machines to innovative new releases, there’s something for each person to appreciate. Plus, with our user-friendly interface and smooth gameplay experience, you’ll have no problem plunging straight into the thrill and savoring every moment.
But that’s not all – we also offer a selection of unique promotions and bonuses to compensate our loyal players. From introductory bonuses for new members to privileged rewards for our top players, there’s always something thrilling happening at Fun Slots Online. And with our safe payment system and 24-hour customer support, you can experience peace of mind conscious that you’re in good hands every step of the way.
So why wait? Register with Fun Slots Online today and start your journey towards exciting victories and jaw-dropping prizes. Whether you’re a seasoned gamer or just starting out, there’s never been a better time to be part of the fun and excitement at Fun Slots Online. Sign up now and let the games begin!
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã đưa vào hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào tính lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai phấn khích trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều quan trọng.
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online’s Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Cổng chơi – Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Nền tảng cá cược được thiết lập vào năm 2017 và vận hành theo chứng chỉ trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với tính cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ đưa ra các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ nhận tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Dịch vụ hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi thời cơ thắng lớn.
Với lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu!
Wow, incredible weblog structure! How lengthy have
you been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy.
The overall look of your website is great, let alone the content!
You can see similar here sklep online
Intro
betvisa india
Betvisa india | IPL 2024 Heat Wave
IPL 2024 Big bets, big prizes With Betvisa India
Exclusive for Sports Fans Betvisa Online Casino 50% Welcome Bonus
Crash Game Supreme Compete for 1,00,00,000 pot Betvisa.com
#betvisaindia
Accurate Predictions IPL T20 Tournament, Winner Takes All!
More than just a game | Betvisa dreams invites you to fly to malta
https://www.b3tvisapro.com/
#betvisaindia #betvisalogin #betvisaonlinecasino
#betvisa.com #betvisaapp
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Vì tính cam kết về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt tình trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu dấu mốc của bạn tại BetVisa – nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu.
I real pleased to find this internet site on bing, just what I was looking for : D also saved to bookmarks.
Jeetwin Affiliate
Jeetwin Affiliate
Join Jeetwin now! | Jeetwin sign up for a ?500 free bonus
Spin & fish with Jeetwin club! | 200% welcome bonus
Bet on horse racing, get a 50% bonus! | Deposit at Jeetwin live for rewards
#JeetwinAffiliate
Casino table fun at Jeetwin casino login | 50% deposit bonus on table games
Earn Jeetwin points and credits, enhance your play!
https://www.jeetwin-affiliate.com/hi
#JeetwinAffiliate #jeetwinclub #jeetwinsignup #jeetwinresult
#jeetwinlive #jeetwinbangladesh #jeetwincasinologin
Daily recharge bonuses at Jeetwin Bangladesh!
25% recharge bonus on casino games at jeetwin result
15% bonus on Crash Games with Jeetwin affiliate!
Turn to Win Actual Money and Gift Cards with JeetWin’s Referral Program
Are you a devotee of online gaming? Do you really appreciate the thrill of rotating the roulette wheel and winning big-time? If so, then the JeetWin’s Affiliate Scheme is great for you! With JeetWin Gaming, you not just get to enjoy stimulating games but additionally have the possibility to earn genuine currency and gift cards simply by promoting the platform to your friends, family, or digital audience.
How Does Perform?
Registering for the JeetWin’s Affiliate Scheme is quick and straightforward. Once you transform into an member, you’ll receive a exclusive referral link that you can share with others. Every time someone signs up or makes a deposit using your referral link, you’ll receive a commission for their activity.
Fantastic Bonuses Await!
As a member of JeetWin’s affiliate program, you’ll have access to a variety of appealing bonuses:
500 Welcome Bonus: Receive a liberal sign-up bonus of INR 500 just for joining the program.
Deposit Bonus: Take advantage of a enormous 200% bonus when you deposit and play one-armed bandit and fishing games on the platform.
Endless Referral Bonus: Get unlimited INR 200 bonuses and rebates for every friend you invite to play on JeetWin.
Thrilling Games to Play
JeetWin offers a diverse range of the most played and most popular games, including Baccarat, Dice, Liveshow, Slot, Fishing, and Sabong. Whether you’re a fan of classic casino games or prefer something more modern and interactive, JeetWin has something for everyone.
Participate in the Greatest Gaming Experience
With JeetWin Live, you can elevate your gaming experience to the next level. Participate in thrilling live games such as Lightning Roulette, Lightning Dice, Crazytime, and more. Sign up today and commence an unforgettable gaming adventure filled with excitement and limitless opportunities to win.
Easy Payment Methods
Depositing funds and withdrawing your winnings on JeetWin is quick and hassle-free. Choose from a range of payment methods, including E-Wallets, Net Banking, AstroPay, and RupeeO, for seamless transactions.
Don’t Miss Out on Exclusive Promotions
As a JeetWin affiliate, you’ll acquire access to exclusive promotions and special offers designed to maximize your earnings. From cash rebates to lucrative bonuses, there’s always something exciting happening at JeetWin.
Download the Mobile App
Take the fun with you wherever you go by downloading the JeetWin Mobile Casino App. Available for both iOS and Android devices, the app features a wide range of entertaining games that you can enjoy anytime, anywhere.
Join the JeetWin’s Referral Program Today!
Don’t wait any longer to start earning real cash and exciting rewards with the JeetWin Affiliate Program. Sign up now and join the thriving online gaming community at JeetWin.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Hi, i think that i noticed you visited my site so i came to “go back the want”.I am trying to to find issues to improve my web site!I assume its adequate to use a few of your ideas!!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
賭網
chronometer watches
Understanding COSC Accreditation and Its Importance in Horology
COSC Accreditation and its Rigorous Criteria
COSC, or the Official Swiss Chronometer Testing Agency, is the official Swiss testing agency that verifies the accuracy and precision of wristwatches. COSC accreditation is a mark of excellent craftsmanship and dependability in timekeeping. Not all watch brands follow COSC certification, such as Hublot, which instead adheres to its proprietary demanding criteria with mechanisms like the UNICO, achieving similar precision.
The Science of Exact Chronometry
The central mechanism of a mechanical watch involves the mainspring, which provides power as it loosens. This mechanism, however, can be prone to external factors that may influence its accuracy. COSC-validated mechanisms undergo strict testing—over 15 days in various circumstances (five positions, three temperatures)—to ensure their durability and reliability. The tests assess:
Mean daily rate accuracy between -4 and +6 seconds.
Mean variation, maximum variation rates, and impacts of thermal changes.
Why COSC Validation Is Important
For watch enthusiasts and connoisseurs, a COSC-certified timepiece isn’t just a piece of technology but a demonstration to enduring quality and precision. It signifies a watch that:
Offers outstanding dependability and accuracy.
Provides guarantee of superiority across the entire design of the watch.
Is likely to maintain its value better, making it a sound choice.
Well-known Timepiece Manufacturers
Several famous brands prioritize COSC certification for their watches, including Rolex, Omega, Breitling, and Longines, among others. Longines, for instance, provides collections like the Archive and Spirit, which highlight COSC-validated movements equipped with innovative materials like silicone equilibrium springs to enhance resilience and efficiency.
Historic Background and the Development of Chronometers
The idea of the chronometer dates back to the requirement for exact timekeeping for navigational at sea, highlighted by John Harrison’s work in the 18th century. Since the formal foundation of COSC in 1973, the accreditation has become a standard for assessing the accuracy of luxury watches, maintaining a legacy of superiority in watchmaking.
Conclusion
Owning a COSC-accredited timepiece is more than an visual choice; it’s a dedication to quality and precision. For those appreciating accuracy above all, the COSC validation offers peacefulness of thoughts, ensuring that each accredited watch will perform reliably under various circumstances. Whether for individual contentment or as an investment, COSC-certified timepieces stand out in the world of watchmaking, bearing on a tradition of careful chronometry.
casibom
Nihai Dönemsel En Gözde Kumarhane Platformu: Casibom
Kumarhane oyunlarını sevenlerin artık duymuş olduğu Casibom, nihai dönemde adından sıkça söz ettiren bir bahis ve kumarhane web sitesi haline geldi. Ülkemizin en mükemmel casino platformlardan biri olarak tanınan Casibom’un haftalık cinsinden değişen giriş adresi, alanında oldukça yenilikçi olmasına rağmen itimat edilir ve kazanç sağlayan bir platform olarak tanınıyor.
Casibom, muadillerini geride bırakarak uzun soluklu bahis platformların geride bırakmayı başarılı oluyor. Bu sektörde eski olmak gereklidir olsa da, katılımcılarla iletişimde bulunmak ve onlara ulaşmak da benzer kadar önemlidir. Bu durumda, Casibom’un her saat servis veren gerçek zamanlı destek ekibi ile kolayca iletişime ulaşılabilir olması büyük bir fayda getiriyor.
Hızla genişleyen oyuncuların kitlesi ile ilgi çekici Casibom’un gerisindeki başarım faktörleri arasında, yalnızca casino ve gerçek zamanlı casino oyunlarına sınırlı kısıtlı olmayan geniş bir servis yelpazesi bulunuyor. Atletizm bahislerinde sunduğu geniş seçenekler ve yüksek oranlar, oyuncuları ilgisini çekmeyi başarmayı sürdürüyor.
Ayrıca, hem spor bahisleri hem de casino oyunları oyuncularına yönlendirilen sunulan yüksek yüzdeli avantajlı promosyonlar da ilgi çekiyor. Bu nedenle, Casibom kısa sürede alanında iyi bir tanıtım başarısı elde ediyor ve önemli bir oyuncu kitlesi kazanıyor.
Casibom’un kazandıran promosyonları ve popülerliği ile birlikte, web sitesine üyelik hangi yollarla sağlanır sorusuna da bahsetmek elzemdir. Casibom’a mobil cihazlarınızdan, bilgisayarlarınızdan veya tabletlerinizden web tarayıcı üzerinden kolayca ulaşılabilir. Ayrıca, sitenin mobil uyumlu olması da büyük önem taşıyan bir artı sağlıyor, çünkü şimdi pratikte herkesin bir akıllı telefonu var ve bu telefonlar üzerinden hızlıca erişim sağlanabiliyor.
Mobil cihazlarınızla bile yolda canlı bahisler alabilir ve yarışmaları canlı olarak izleyebilirsiniz. Ayrıca, Casibom’un mobil uyumlu olması, ülkemizde kumarhane ve casino gibi yerlerin yasal olarak kapatılmasıyla birlikte bu tür platformlara erişimin önemli bir yolunu oluşturuyor.
Casibom’un güvenilir bir kumarhane sitesi olması da gereklidir bir fayda sunuyor. Ruhsatlı bir platform olan Casibom, kesintisiz bir şekilde keyif ve kar sağlama imkanı getirir.
Casibom’a abone olmak da son derece basittir. Herhangi bir belge şartı olmadan ve bedel ödemeden platforma kolaylıkla kullanıcı olabilirsiniz. Ayrıca, web sitesi üzerinde para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri için de birçok farklı yöntem mevcuttur ve herhangi bir kesim ücreti isteseniz de alınmaz.
Ancak, Casibom’un güncel giriş adresini takip etmek de elzemdir. Çünkü canlı şans ve oyun siteleri moda olduğu için yalancı web siteleri ve dolandırıcılar da ortaya çıkmaktadır. Bu nedenle, Casibom’un sosyal medya hesaplarını ve güncel giriş adresini periyodik olarak kontrol etmek gereklidir.
Sonuç, Casibom hem güvenilir hem de kar getiren bir bahis web sitesi olarak ilgi çekici. yüksek promosyonları, kapsamlı oyun seçenekleri ve kullanıcı dostu taşınabilir uygulaması ile Casibom, casino hayranları için ideal bir platform getiriyor.
線上賭場
casibom giriş
Nihai Dönemin En Büyük Beğenilen Kumarhane Platformu: Casibom
Casino oyunlarını sevenlerin artık duymuş olduğu Casibom, en son dönemde adından çoğunlukla söz ettiren bir şans ve kumarhane sitesi haline geldi. Ülkemizdeki en iyi casino web sitelerinden biri olarak tanınan Casibom’un haftalık olarak göre değişen giriş adresi, sektörde oldukça taze olmasına rağmen itimat edilir ve kar getiren bir platform olarak öne çıkıyor.
Casibom, muadillerini geride kalarak köklü bahis web sitelerinin üstünlük sağlamayı başarmayı sürdürüyor. Bu alanda eski olmak gereklidir olsa da, oyunculardan etkileşimde olmak ve onlara erişmek da benzer derecede önemlidir. Bu noktada, Casibom’un her saat servis veren gerçek zamanlı destek ekibi ile rahatlıkla iletişime geçilebilir olması önemli bir artı getiriyor.
Hızla artan oyuncu kitlesi ile ilgi çekici Casibom’un arkasındaki başarı faktörleri arasında, sadece ve yalnızca kumarhane ve canlı casino oyunları ile sınırlı kısıtlı olmayan kapsamlı bir hizmet yelpazesi bulunuyor. Sporcular bahislerinde sunduğu geniş alternatifler ve yüksek oranlar, katılımcıları ilgisini çekmeyi başarılı oluyor.
Ayrıca, hem spor bahisleri hem de kumarhane oyunlar oyuncularına yönelik sunulan yüksek yüzdeli avantajlı promosyonlar da dikkat çekiyor. Bu nedenle, Casibom çabucak sektörde iyi bir pazarlama başarısı elde ediyor ve büyük bir oyuncuların kitlesi kazanıyor.
Casibom’un kar getiren promosyonları ve tanınırlığı ile birlikte, siteye abonelik ne şekilde sağlanır sorusuna da bahsetmek gereklidir. Casibom’a hareketli cihazlarınızdan, PC’lerinizden veya tabletlerinizden internet tarayıcı üzerinden kolaylıkla erişilebilir. Ayrıca, platformun mobil uyumlu olması da büyük bir avantaj getiriyor, çünkü şimdi pratikte herkesin bir akıllı telefonu var ve bu cihazlar üzerinden hızlıca giriş sağlanabiliyor.
Taşınabilir cep telefonlarınızla bile yolda canlı olarak bahisler alabilir ve maçları canlı olarak izleyebilirsiniz. Ayrıca, Casibom’un mobil uyumlu olması, memleketimizde kumarhane ve casino gibi yerlerin yasal olarak kapatılmasıyla birlikte bu tür platformlara erişimin büyük bir yolunu oluşturuyor.
Casibom’un güvenilir bir bahis sitesi olması da önemlidir bir artı sunuyor. Lisanslı bir platform olan Casibom, duraksız bir şekilde eğlence ve kazanç sağlama imkanı sağlar.
Casibom’a kullanıcı olmak da oldukça basittir. Herhangi bir belge koşulu olmadan ve ücret ödemeden siteye rahatça üye olabilirsiniz. Ayrıca, web sitesi üzerinde para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri için de çok sayıda farklı yöntem vardır ve herhangi bir kesim ücreti talep edilmemektedir.
Ancak, Casibom’un güncel giriş adresini takip etmek de elzemdir. Çünkü canlı iddia ve casino siteleri moda olduğu için yalancı siteler ve dolandırıcılar da görünmektedir. Bu nedenle, Casibom’un sosyal medya hesaplarını ve güncel giriş adresini düzenli olarak kontrol etmek elzemdir.
Sonuç olarak, Casibom hem emin hem de kar getiren bir casino sitesi olarak dikkat çekiyor. Yüksek ödülleri, geniş oyun seçenekleri ve kullanıcı dostu mobil uygulaması ile Casibom, kumarhane tutkunları için ideal bir platform sunuyor.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks a lot for providing individuals with an exceptionally superb possiblity to check tips from this web site. It is always so cool and as well , full of a lot of fun for me personally and my office fellow workers to visit your site a minimum of three times a week to read the new issues you have. Not to mention, I’m also actually motivated concerning the remarkable techniques served by you. Selected 2 facts in this posting are essentially the most beneficial we’ve ever had.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
game1kb.com
이와 같이 해상력을 가진 나라의 공격을 받으면 전투를 할 수 없다.
探索Telegram官网,体验全球领先的即时通讯工具!Telegram支持多平台使用,无论是智能手机还是电脑,都可以畅享极速、安全的消息、文件分享服务。官网提供直接下载链接,简单几步即可安装。全球数亿用户的选择,不受地域限制,保证通讯安全与隐私。立即下载,开启您的即时通讯新体验!Explore the official Telegram website and experience a leading global instant messaging tool! Telegram supports multiple platforms, whether on a smartphone or computer, you can enjoy fast and secure messaging and file-sharing services. The official website provides direct download links, and installation is just a few steps away. Chosen by hundreds of millions of users worldwide, it offers unrestricted communication with guaranteed security and privacy. Download now to start your new messaging experience! https://www.telegramho.com
dyodwu2w3m
casibom giriş
En Son Dönemsel En Büyük Gözde Casino Platformu: Casibom
Bahis oyunlarını sevenlerin artık duymuş olduğu Casibom, nihai dönemde adından genellikle söz ettiren bir iddia ve oyun sitesi haline geldi. Türkiye’nin en mükemmel kumarhane platformlardan biri olarak tanınan Casibom’un haftalık cinsinden değişen erişim adresi, alanında oldukça yeni olmasına rağmen itimat edilir ve kazandıran bir platform olarak ön plana çıkıyor.
Casibom, rakiplerini geride kalarak uzun soluklu casino platformların üstünlük sağlamayı başarılı oluyor. Bu sektörde uzun soluklu olmak gereklidir olsa da, oyunculardan iletişimde bulunmak ve onlara ulaşmak da eş miktar değerli. Bu noktada, Casibom’un her saat yardım veren canlı destek ekibi ile rahatça iletişime geçilebilir olması önemli bir fayda sağlıyor.
Hızlıca büyüyen katılımcı kitlesi ile dikkat çeken Casibom’un arkasındaki başarım faktörleri arasında, yalnızca kumarhane ve gerçek zamanlı casino oyunları ile sınırlı kısıtlı olmayan geniş bir hizmetler yelpazesi bulunuyor. Atletizm bahislerinde sunduğu kapsamlı alternatifler ve yüksek oranlar, oyuncuları ilgisini çekmeyi başarılı oluyor.
Ayrıca, hem sporcular bahisleri hem de bahis oyunları katılımcılara yönlendirilen sunulan yüksek yüzdeli avantajlı ödüller da ilgi çekiyor. Bu nedenle, Casibom kısa sürede alanında iyi bir tanıtım başarısı elde ediyor ve önemli bir oyuncuların kitlesi kazanıyor.
Casibom’un kar getiren ödülleri ve ünlülüğü ile birlikte, siteye abonelik hangi yollarla sağlanır sorusuna da bahsetmek gereklidir. Casibom’a hareketli cihazlarınızdan, bilgisayarlarınızdan veya tabletlerinizden internet tarayıcı üzerinden rahatça erişilebilir. Ayrıca, sitenin mobil uyumlu olması da büyük önem taşıyan bir artı sağlıyor, çünkü artık hemen hemen herkesin bir cep telefonu var ve bu akıllı telefonlar üzerinden hızlıca ulaşım sağlanabiliyor.
Hareketli cep telefonlarınızla bile yolda canlı bahisler alabilir ve yarışmaları canlı olarak izleyebilirsiniz. Ayrıca, Casibom’un mobil cihazlarla uyumlu olması, memleketimizde casino ve casino gibi yerlerin meşru olarak kapatılmasıyla birlikte bu tür platformlara erişimin büyük bir yolunu oluşturuyor.
Casibom’un güvenilir bir kumarhane web sitesi olması da önemlidir bir avantaj sunuyor. Belgeli bir platform olan Casibom, sürekli bir şekilde eğlence ve kazanç sağlama imkanı sağlar.
Casibom’a abone olmak da son derece rahatlatıcıdır. Herhangi bir belge şartı olmadan ve ücret ödemeden siteye rahatça kullanıcı olabilirsiniz. Ayrıca, platform üzerinde para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri için de birçok farklı yöntem mevcuttur ve herhangi bir kesim ücreti talep edilmemektedir.
Ancak, Casibom’un güncel giriş adresini izlemek de elzemdir. Çünkü canlı bahis ve casino platformlar popüler olduğu için yalancı siteler ve dolandırıcılar da belirmektedir. Bu nedenle, Casibom’un sosyal medya hesaplarını ve güncel giriş adresini periyodik olarak kontrol etmek önemlidir.
Sonuç, Casibom hem itimat edilir hem de kazanç sağlayan bir kumarhane platformu olarak ilgi çekici. Yüksek promosyonları, kapsamlı oyun alternatifleri ve kullanıcı dostu taşınabilir uygulaması ile Casibom, oyun sevenler için ideal bir platform getiriyor.
nikontinoll.com
하지만 키가 크지 않은 사람들이 그런 상황을 가장 두려워합니다.
Spin to win and enjoy non-stop entertainment! Lucky cola
Анализ бумажников по наличие подозрительных средств передвижения: Защита вашего цифрового портфельчика
В мире электронных денег становится все более необходимее гарантировать защиту своих финансов. Регулярно мошенники и криминальные элементы выработывают совершенно новые подходы обмана и воровства виртуальных средств. Одним из основных способов обеспечения безопасности является проверка данных кошелька за присутствие незаконных средств передвижения.
По какой причине поэтому важно проверять собственные криптовалютные кошельки?
Прежде всего, вот это нужно для обеспечения безопасности личных денег. Большинство инвесторы рискуют потерять потери средств своих собственных денег в результате недобросовестных схем или краж. Анализ кошельков для хранения криптовалюты помогает обнаружить на своем пути сомнительные действия и предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что предлагает вашему вниманию наша организация?
Мы предлагаем послугу проверки данных цифровых кошельков и переводов средств с целью идентификации начала средств передвижения и дать детального отчета о проверке. Фирма предоставляет технология проанализировать данные пользователя для обнаружения подозрительных операций и оценить риск для того, чтобы вашего финансового портфеля. Благодаря нашей системе проверки, вы будете способны предотвратить с органами контроля и обезопасить себя от случайного участия в незаконных операций.
Как проводится процесс?
Наша компания работает с известными аудиторскими фирмами фирмами, такими как Kudelsky Security, для того, чтобы дать гарантию и точность наших проверок. Мы внедряем новейшие и техники анализа для обнаружения опасных операций средств. Персональные данные наших заказчиков обрабатываются и сохраняются согласно высокими стандартами безопасности.
Основная просьба: “проверить свои USDT на чистоту”
Если вам нужно убедиться в безопасности и чистоте своих кошельков USDT, наши профессионалы предлагает шанс бесплатный анализ первых пяти кошельков. Просто введите адрес своего кошелька в соответствующее поле на нашем сайте, и мы дадим вам подробную информацию о состоянии вашего счета.
Обеспечьте защиту своих деньги сразу же!
Избегайте риска становиться жертвой хакеров или оказаться неприятной ситуации нелегальных операций с вашими деньгами. Дайте вашу криптовалюту профессиональным консультантам, которые смогут помочь, вам обезопаситься криптовалютные активы и предотвратить возможные. Сделайте первый шаг к безопасности безопасности личного электронного портфеля в данный момент!
Осмотр USDT на чистоту: Каким образом сохранить собственные электронные финансы
Все более пользователей обращают внимание в безопасность собственных криптовалютных средств. Ежедневно обманщики изобретают новые способы разграбления криптовалютных средств, а также владельцы криптовалюты являются страдающими их интриг. Один из методов обеспечения безопасности становится проверка кошельков в присутствие противозаконных денег.
С каким намерением это полезно?
Прежде всего, для того чтобы защитить свои средства против мошенников и похищенных монет. Многие участники сталкиваются с вероятностью потери своих финансов в результате мошеннических механизмов или грабежей. Проверка кошельков помогает выявить подозрительные операции и предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что наша команда предлагаем?
Мы предоставляем услугу проверки цифровых кошельков и операций для определения начала денег. Наша платформа анализирует информацию для обнаружения незаконных операций или оценки риска для вашего счета. Благодаря данной проверке, вы сможете избежать проблем с регуляторами и также защитить себя от участия в незаконных операциях.
Как это действует?
Мы сотрудничаем с первоклассными аудиторскими компаниями, наподобие Certik, с целью предоставить аккуратность наших проверок. Мы применяем новейшие технологии для определения опасных операций. Ваши данные обрабатываются и хранятся в соответствии с высокими стандартами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить свои Tether на чистоту?
Если вам нужно проверить, что ваша Tether-кошельки чисты, наш подход предоставляет бесплатное тестирование первых пяти кошельков. Просто вбейте адрес собственного бумажника на на нашем веб-сайте, и мы предоставим вам подробный доклад о его положении.
Обезопасьте вашими фонды уже сейчас!
Избегайте риска попасть в жертву дельцов или оказаться в неблагоприятную обстановку по причине незаконных операций. Свяжитесь с нашему сервису, для того чтобы защитить свои электронные финансовые ресурсы и избежать сложностей. Сделайте первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля сегодня!
Проверка USDT на чистоту
Осмотр USDT на чистоту: Каким образом обезопасить собственные криптовалютные активы
Все более индивидуумов обращают внимание на безопасность своих криптовалютных средств. День ото дня обманщики предлагают новые методы разграбления электронных средств, или держатели криптовалюты являются жертвами их обманов. Один способов охраны становится тестирование кошельков для присутствие противозаконных финансов.
Для чего это полезно?
Прежде всего, для того чтобы защитить свои активы от дельцов и также похищенных монет. Многие инвесторы сталкиваются с потенциальной угрозой потери своих средств из-за хищных механизмов либо кражей. Проверка кошельков помогает выявить сомнительные операции и предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что мы предлагаем?
Мы предлагаем услугу проверки цифровых кошельков а также операций для выявления источника фондов. Наша платформа анализирует данные для выявления противозаконных транзакций или оценки риска для вашего портфеля. Благодаря этой проверке, вы сможете избежать проблем с регулированием или защитить себя от участия в незаконных операциях.
Как это работает?
Мы работаем с передовыми аудиторскими агентствами, такими как Halborn, для того чтобы гарантировать точность наших проверок. Мы используем передовые технологии для выявления рискованных операций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и сохраняются согласно с высокими нормами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить личные USDT в чистоту?
В случае если вы желаете подтвердить, что ваша USDT-бумажники чисты, наш сервис предлагает бесплатное тестирование первых пяти кошельков. Легко введите место своего кошелька на на нашем веб-сайте, и мы предоставим вам детальный доклад об его положении.
Охраняйте ваши активы прямо сейчас!
Не подвергайте риску подвергнуться дельцов либо оказаться в неприятную ситуацию из-за незаконных сделок. Обратитесь к нашему агентству, с тем чтобы обезопасить ваши криптовалютные активы и избежать неприятностей. Сделайте первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля сегодня!
usdt и отмывание
USDT – это надежная криптовалютный актив, связанная к фиатной валюте, такой как доллар США. Это позволяет данную криптовалюту в частности востребованной у инвесторов, так как данная криптовалюта предлагает стабильность цены в условиях неустойчивости криптовалютного рынка. Впрочем, как и любая другая разновидность криптовалюты, USDT подвергается опасности использования с целью легализации доходов и поддержки противоправных сделок.
Отмывание денег посредством криптовалюты превращается все более и более распространенным способом для обеспечения анонимности. Воспользовавшись разнообразные методы, злоумышленники могут попытаться промывать незаконно добытые деньги через обменники криптовалют или миксеры средств, с тем чтобы сделать происхождение менее очевидным.
Именно поэтому, экспертиза USDT на чистоту становится необходимой практикой предосторожности для участников криптовалют. Имеются специализированные услуги, которые проводят экспертизу транзакций и счетов, для того чтобы идентифицировать подозрительные транзакции и незаконные источники средств. Эти сервисы способствуют пользователям избежать непреднамеренного вовлечения в финансирование преступных деяний и избежать блокировки счетов со со стороны сторонних контролирующих органов.
Анализ USDT на чистоту также также способствует обезопасить себя от финансовых потерь. Пользователи могут быть убеждены что их капитал не ассоциированы с противоправными сделками, что в свою очередь снижает риск блокировки аккаунта или конфискации средств.
Таким образом, в текущей ситуации повышающейся сложности криптовалютной среды требуется принимать шаги для обеспечения надежности своих активов. Проверка USDT на чистоту с помощью специализированных услуг представляет собой одним из вариантов противодействия финансирования преступной деятельности, обеспечивая участникам криптовалют дополнительный уровень и безопасности.
Intikkertje beoordeelt elk on-line casino in Nederland en we beschrijven onze bevindingen in onafhankelijke on-line casino reviews.
九州娛樂
ilogidis.com
갑자기 Yang Tinghe와 다른 사람들은 더욱 추해졌습니다.
vegas grand casino
vegas grand casino
Sure, here’s the text with spin syntax applied:
Hyperlink Hierarchy
After numerous updates to the G search algorithm, it is essential to apply different approaches for ranking.
Today there is a approach to draw the focus of search engines to your site with the help of inbound links.
Links are not only an effective advertising instrument but they also have organic traffic, immediate sales from these resources probably will not be, but visits will be, and it is advantageous visitors that we also receive.
What in the end we get at the final outcome:
We display search engines site through backlinks.
Prluuchayut organic click-throughs to the site and it is also a indicator to search engines that the resource is used by users.
How we show search engines that the site is valuable:
Backlinks do to the main page where the main information.
We make links through redirects credible sites.
The most CRUCIAL we place the site on sites analyzers distinct tool, the site goes into the cache of these analysis tools, then the received links we place as redirects on weblogs, discussion boards, comment sections. This crucial action shows search engines the MAP OF THE SITE as analyzer sites display all information about sites with all keywords and headlines and it is very BENEFICIAL.
All details about our services is on the website!
yesil yesil g�zlerin yere gelsin dizlerin iki sokup bir cekeyim yarrak gorsun gozlerin
Creating exclusive articles on Medium and Platform, why it is required:
Created article on these resources is better ranked on less frequent queries, which is very important to get natural traffic.
We get:
natural traffic from search engines.
organic traffic from the internal rendition of the medium.
The platform to which the article refers gets a link that is profitable and increases the ranking of the site to which the article refers.
Articles can be made in any amount and choose all less frequent queries on your topic.
Medium pages are indexed by search engines very well.
Telegraph pages need to be indexed separately indexer and at the same time after indexing they sometimes occupy positions higher in the search algorithms than the medium, these two platforms are very helpful for getting visitors.
Here is a hyperlink to our offerings where we provide creation, indexing of sites, articles, pages and more.
הימורים ברשת הם חווייה מרגשות ופופולרית ביותר בעידן הדיגיטלי, שמגירה מיליונים אנשים מכל
רחבי העולם. ההימורים המקוונים מתנהלים בהתאם ל אירועים ספורטיים, תוצאות פוליטיות ואפילו תוצאות מזג האוויר ונושאים נוספים. אתרי הימורים הווירטואליים מזמינים את מי שמעוניין להימר על תוצאות אפשריות ולהנות רגעים של חוויה והתרגשות.
ההימורים המקוונים הם כבר חלק חשוב מהתרבות האנושית מזמן רב והיום הם כבר לא רק חלק מרכזי מהפעילות התרבותית והכלכלית, אלא אף מספקים רווחים וחוויים. משום שהם נגישים מאוד ופשוטים לשימוש, הם מתאימים לכל מהניסיון ולהצליח לנצח בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
טכנולוגיות מתקדמות והימורים הפכו מעניינת ופופולרית. מיליוני אנשים מכל כל רחבי העולם מעוניינים בהימורים, כוללים סוגים שונים של הימורים. הימורים מקוונים מציעים למשתתפים חוויה רגשית ומרתקת, שמתאימה לכל גיל וכישור בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
וכן מה נותר אתה מחכה לו? הצטרף עכשיו והתחיל לחוות את ההתרגשות וההנאה שההימורים באינטרנט מבטיחים.
טלגראס מרכז
קנאביס מדריך: המדריכים המלא לקניית קנאביס במקום המסר
פרח כיוונים הם אתר ווב מסמכים ומדריכי לרכישת קנאביסין במקום האפליקציה הניידת הפופולרית המשלוח.
האתר הוצע את כל הקישורים הידיעתיים והמידעים המעודכן לקבוצות המשתמשים וערוצים באתר מומלצים להשקיה קנאביסין בהמסר בארץ ישראל.
כמו למעשה, אתר האינטרנט מספקת מדריכים מפורט לכיצד להתארגן באמצעות בהשרף ולהשיג קנאביסין בקלות הזמנה ובמהירות מירבית.
בעזרת המדריכים, גם משתמשי חדשים בתחום יוכלו להירשם לעולם הקנאביס בהמשלוח בדרך מוגנת ומאובטחת לשימוש.
ההאוטומטיזציה של השרף מאפשר להמשתמשים ללבצע את פעולות השונות שונות וצבעוניות כמו כן רכישת קנאביס, קבלת תמיכה תמיכה, בדיקת המלאי והוספת הערות על המצרים. כל זאת בצורה נוחה לשימוש ונוחה דרך האפליקציה.
כאשר מדובר בשיטות התשלומים, הקנאביס מפעילה בשיטות מוכרות כמו גם מזומנים, כרטיסי האשראי של אשראי וקריפטוֹמוֹנֵדָה. חיוני להדגש כי יש לבדוק ולוודא את התקנות והחוקות האזוריים במדינה שלך ללפני ביצוע רכישה.
הטלגרם מציע יתרונות מרכזיים כמו כן פרטיות והגנה מוגברים, השיחה מהירה וגמישות גבוהה. בנוסף, הוא מאפשר כניסה לקהילה עולמית רחבה מאוד ומציע מגוון רחב של תכונות ויכולות.
בסיכום, הטלגרם הנחיות הוא המקום המושלם ללמצוא את כל הידע והקישורים הנדרשים להשקיה קנאביס בצורה מהירה, בבטוחה ונוחה דרך הטלגרם.
link building
Creating hyperlinks is just as effective currently, simply the instruments to work in this area possess altered.
There are actually many options regarding inbound links, our company employ some of them, and these strategies operate and have already been tried by our experts and our clientele.
Lately our company carried out an experiment and it transpired that less frequent search queries from a single domain name position effectively in search engines, and the result does not have to become your own domain, it is possible to utilize social networks from the web 2.0 range for this.
It is also possible to partly move weight through web page redirects, providing an assorted backlink profile.
Visit to our very own web page where our company’s services are actually offered with comprehensive descriptions.
garilla casino
https://t.me/garillacasinoo
Dear malabdali.com owner, Keep it up!
Dear malabdali.com admin, Your posts are always well presented.
bestmanualpolesaw.com
Qi Zhiyuan이 이 말을 들었을 때 그의 심장이 갑자기 가라앉았고 그의 이를 갈기 직전이었습니다.
garilla казино
https://t.me/garillacasinobonus
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Keep working ,splendid job!
Aquí está el texto con la estructura de spintax que propone diferentes sinónimos para cada palabra:
“Pirámide de backlinks
Después de muchas actualizaciones del motor de búsqueda G, necesita aplicar diferentes opciones de clasificación.
Hay una forma de llamar la atención de los motores de búsqueda a su sitio web con enlaces de retroceso.
Los enlaces de retorno no sólo son una estrategia eficaz para la promoción, sino que también tienen tráfico orgánico, las ventas directas de estos recursos más probable es que no será, pero las transiciones será, y es tráfico potencial que también obtenemos.
Lo que vamos a obtener al final en la salida:
Mostramos el sitio a los motores de búsqueda a través de vínculos de retroceso.
Conseguimos visitas orgánicas hacia el sitio, lo que también es una señal para los buscadores de que el recurso está siendo utilizado por la gente.
Cómo mostramos los motores de búsqueda que el sitio es líquido:
1 enlace se hace a la página principal donde está la información principal
Hacemos backlinks a través de redirecciones de sitios de confianza
Lo más IMPORTANTE colocamos el sitio en una herramienta independiente de analizadores de sitios, el sitio entra en la caché de estos analizadores, luego los enlaces recibidos los colocamos como redirecciones en blogs, foros, comentarios.
Esta vital acción muestra a los buscadores el MAPA DEL SITIO, ya que los analizadores de sitios muestran toda la información de los sitios con todas las palabras clave y títulos y es muy positivo.
¡Toda la información sobre nuestros servicios en el sitio web!
thephotoretouch.com
그들은 울고, 가슴을 치며 비틀거리고, 미친 듯이 불평했습니다.
Would love to constantly get updated great blog! .
Hello malabdali.com admin, Your posts are always well-timed and relevant.
Как обезопасить свои личные данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня защита информации становится всё больше важной задачей. Одним из наиболее обычных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в каком объеме обезопаситься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это сочетания слов или фраз, которые постоянно используются для входа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, с помощью этих сит фраз. Как сохранить свои личные данные? Используйте непростые пароли. Избегайте использования простых паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для всего аккаунта. Не пользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную проверку (2FA). Это добавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт через другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте личную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы сохранить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может спровоцировать серьезным последствиям, таким как кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
Криптокошельки с балансом: зачем их покупают и как использовать
В мире криптовалют все растущую популярность приобретают криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом. Это уникальные кошельки, которые уже содержат определенное количество криптовалюты на момент покупки. Но зачем люди приобретают такие кошельки, и как правильно использовать их?
Почему покупают криптокошельки с балансом?
Удобство: Криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом предлагаются как готовое решение для тех, кто хочет быстро начать пользоваться криптовалютой без необходимости покупки или обмена на бирже.
Подарок или награда: Иногда криптокошельки с балансом используются как подарок или вознаграждение в рамках акций или маркетинговых кампаний.
Анонимность: При покупке криптокошелька с балансом нет потребности предоставлять личные данные, что может быть важно для тех, кто ценит анонимность.
Как использовать криптокошелек с балансом?
Проверьте безопасность: Убедитесь, что кошелек безопасен и не подвержен взлому. Проверьте репутацию продавца и источник приобретения кошелька.
Переведите средства на другой кошелек: Если вы хотите долгосрочно хранить криптовалюту, рекомендуется перевести средства на более безопасный или полезный для вас кошелек.
Не храните все средства на одном кошельке: Для обеспечения безопасности рекомендуется распределить средства между несколькими кошельками.
Будьте осторожны с фишингом и мошенничеством: Помните, что мошенники могут пытаться обмануть вас, предлагая криптокошельки с балансом с целью получения доступа к вашим средствам.
Заключение
Криптокошельки с балансом могут быть удобным и простым способом начать пользоваться криптовалютой, но необходимо помнить о безопасности и осторожности при их использовании.Выбор и приобретение криптокошелька с балансом – это значительный шаг, который требует внимания к деталям и осознанного подхода.”
сид фразы кошельков
Сид-фразы, или мнемонические фразы, представляют собой комбинацию слов, которая используется для создания или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Эти фразы обеспечивают доступ к вашим криптовалютным средствам, поэтому их секурное хранение и использование крайне важны для защиты вашего криптоимущества от утери и кражи.
Что такое сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют?
Сид-фразы являются набор случайным образом сгенерированных слов, как правило от 12 до 24, которые предназначены для создания уникального ключа шифрования кошелька. Этот ключ используется для восстановления входа к вашему кошельку в случае его повреждения или утери. Сид-фразы обладают значительной защиты и шифруются, что делает их секурными для хранения и передачи.
Зачем нужны сид-фразы?
Сид-фразы обязательны для обеспечения безопасности и доступности вашего криптоимущества. Они позволяют восстановить вход к кошельку в случае утери или повреждения физического устройства, на котором он хранится. Благодаря сид-фразам вы можете просто создавать резервные копии своего кошелька и хранить их в безопасном месте.
Как обеспечить безопасность сид-фраз кошельков?
Никогда не раскрывайте сид-фразой ни с кем. Сид-фраза является вашим ключом к кошельку, и ее раскрытие может привести к утере вашего криптоимущества.
Храните сид-фразу в защищенном месте. Используйте физически секурные места, такие как банковские ячейки или специализированные аппаратные кошельки, для хранения вашей сид-фразы.
Создавайте резервные копии сид-фразы. Регулярно создавайте резервные копии вашей сид-фразы и храните их в разных безопасных местах, чтобы обеспечить доступ к вашему кошельку в случае утери или повреждения.
Используйте дополнительные меры безопасности. Включите другие методы защиты и двухфакторную верификацию для своего кошелька криптовалюты, чтобы обеспечить дополнительный уровень безопасности.
Заключение
Сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют являются ключевым элементом надежного хранения криптоимущества. Следуйте рекомендациям по безопасности, чтобы защитить свою сид-фразу и обеспечить безопасность своих криптовалютных средств.
Слив посеянных фраз (seed phrases) является единственным из наиболее обычных способов утечки личной информации в мире криптовалют. В этой статье мы разберем, что такое сид фразы, отчего они важны и как можно защититься от их утечки.
Что такое сид фразы?
Сид фразы, или мнемонические фразы, составляют комбинацию слов, которая используется для генерации или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Обычно сид фраза состоит из 12 или 24 слов, которые отражают собой ключ к вашему кошельку. Потеря или утечка сид фразы может приводить к потере доступа к вашим криптовалютным средствам.
Почему важно защищать сид фразы?
Сид фразы служат ключевым элементом для секурного хранения криптовалюты. Если злоумышленники получат доступ к вашей сид фразе, они могут получить доступ к вашему кошельку и украсть все средства.
Как защититься от утечки сид фраз?
Никогда не передавайте свою сид фразу любому, даже если вам кажется, что это доверенное лицо или сервис.
Храните свою сид фразу в секурном и надежном месте. Рекомендуется использовать аппаратные кошельки или специальные программы для хранения сид фразы.
Используйте экстра методы защиты, такие как двухфакторная аутентификация (2FA), для усиления безопасности вашего кошелька.
Регулярно делайте резервные копии своей сид фразы и храните их в разнообразных безопасных местах.
Заключение
Слив сид фраз является существенной угрозой для безопасности владельцев криптовалют. Понимание важности защиты сид фразы и принятие соответствующих мер безопасности помогут вам избежать потери ваших криптовалютных средств. Будьте бдительны и обеспечивайте надежную защиту своей сид фразы
ilogidis.com
이 물고기들은 색깔이 모두 노란색으로 강의 붕어와 크게 다르지 않습니다.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
娛樂城評價
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
Hi there mates, pleasant post and pleasant urging commented at this place, I am genuinely enjoying by these.
http://www.lands-diploman.com
unwavering investing
mikaspa.com
Fang Jifan은 이때 진지하게 말했습니다. “자, 내 엔지니어링 도면은 어떻습니까?”
Keep up the fantastic piece of work, I read few articles on this website and I believe that your blog is very interesting and has got lots of good info .
هنا النص مع استخدام السبينتاكس:
“بناء الروابط الخلفية
بعد التحديثات العديدة لمحرك البحث G، تحتاج إلى تطويق خيارات ترتيب مختلفة.
هناك منهج لجذب انتباه محركات البحث إلى موقعك على الويب باستخدام الروابط الخلفية.
الروابط الخلفية ليست فقط أداة فعالة للترويج، ولكن تحمل أيضًا حركة مرور عضوية، والمبيعات المباشرة من هذه الموارد على الأرجح ستكون كذلك، ولكن الانتقالات ستكون، وهي حركة المرور التي نحصل عليها أيضًا.
ما سنحصل عليه في النهاية في النهاية في الإخراج:
نعرض الموقع لمحركات البحث من خلال الروابط الخلفية.
2- نحصل على تحويلات عضوية إلى الموقع، وهي أيضًا إشارة لمحركات البحث أن المورد يستخدمه الناس.
كيف نظهر لمحركات البحث أن الموقع سائل:
1 يتم عمل صلة خلفي للصفحة الرئيسية حيث المعلومات الرئيسية
نقوم بعمل لينكات خلفية من خلال عمليات توجيه المواقع الموثوقة
الأهم من ذلك أننا نضع الموقع على أداة منفصلة من أساليب تحليل المواقع، ويدخل الموقع في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لهذه المحللات، ثم الروابط المستلمة التي نضعها كتحويل على المدونات والمنتديات والتعليقات.
هذا التدبير المهم يعرض لمحركات البحث خارطة الموقع، حيث تعرض أدوات تحليل المواقع جميع المعلومات عن المواقع مع جميع الكلمات الرئيسية والعناوين وهو عمل جيد جداً
جميع المعلومات عن خدماتنا على الموقع!
whoah this weblog is wonderful i like studying your articles. Stay up the great work! You know, many people are hunting round for this information, you could help them greatly.
Купить диплом 2016 года
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I’m very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
zanetvize.com
Zhu Houzhao는 추측하지 않을 수 없었습니다. “음식은 사막에서 재배됩니다. 고구마를 의미합니까?”
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который собирается начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, что становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт успешной карьеры.
Купить диплом Международного университета в Москве
Сегодня, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в любом ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все находится под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://diploms-service.com/diplomy-po-gorodam/krasnodar
Сегодня, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или учиться в университете.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного подхода состоит не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://diploms-service.com/by-year/2019
What Is Sugar Defender? Sugar Defender is a new blood sugar-balancing formula that has been formulated using eight clinically proven ingredients that work together to balance sugar levels.
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что является выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы этого решения состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для всех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://diploms-service.com/diplomy-po-spetsialnosti/bukhgalter
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в каком-либо университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
В результате, всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://diploms-service.com/diplomy-po-gorodam/moskva/natsionalnyj-institut-imeni-ekateriny-velikoj
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, и это является выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало успешной карьеры.
Купить дипломы Вузов Тольятти
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, что является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
Купить дипломы Вузов Томска
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, что будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения персональных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
Купить диплом Технолога
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который собирается вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в университете.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество такого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Таким образом, для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало трудовой карьеры.
Купить диплом Московского института государственного управления и права
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, что становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в результате получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало профессиональной карьеры.
Купить диплом Московского государственного гуманитарного университета имени М.А. Шолохова
sky pharmacy online drugstore
sky pharmacy online
ihrfuehrerschein.com
선원들은 눈에 끔찍한 표정을 지으며 오랫동안 경계했습니다.
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед всеми, кто желает вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы на выходе получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
Дипломы по профессии
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
Купить диплом Военного инженерно-технического университета Санкт-Петербург
I truly appreciate your work, Great post.
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы этого решения состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
В итоге, для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://diploms-service.com/diplomy-po-gorodam/moskva/gei-im-v-s-chernomyrdina
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. На выходе вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://forwoman.lifeforums.ru/viewtopic.php?id=15044
В наше время, когда диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом, и это является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://wish-club.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=6517
Сегодня, когда диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который хочет вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
В результате, для тех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
http://ractis.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=4449
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, и это становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы сможете получить документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого решения заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
В итоге, для всех, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://cn.rolevaya.ru/viewtopic.php?id=5828
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
http://fkvrn.webtalk.ru/viewtopic.php?id=700
Cá Cược Thể Thao Trực Tuyến RGBET
Thể thao trực tuyến RGBET cung cấp thông tin cá cược thể thao mới nhất, như tỷ số bóng đá, bóng rổ, livestream và dữ liệu trận đấu. Đến với RGBET, bạn có thể tham gia chơi tại sảnh thể thao SABA, PANDA SPORT, CMD368, WG và SBO. Khám phá ngay!
Giới Thiệu Sảnh Cá Cược Thể Thao Trực Tuyến
Những sự kiện thể thao đa dạng, phủ sóng toàn cầu và cách chơi đa dạng mang đến cho người chơi tỷ lệ cá cược thể thao hấp dẫn nhất, tạo nên trải nghiệm cá cược thú vị và thoải mái.
Sảnh Thể Thao SBOBET
SBOBET, thành lập từ năm 1998, đã nhận được giấy phép cờ bạc trực tuyến từ Philippines, Đảo Man và Ireland. Tính đến nay, họ đã trở thành nhà tài trợ cho nhiều CLB bóng đá. Hiện tại, SBOBET đang hoạt động trên nhiều nền tảng trò chơi trực tuyến khắp thế giới.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao SABA
Saba Sports (SABA) thành lập từ năm 2008, tập trung vào nhiều hoạt động thể thao phổ biến để tạo ra nền tảng thể thao chuyên nghiệp và hoàn thiện. SABA được cấp phép IOM hợp pháp từ Anh và mang đến hơn 5.000 giải đấu thể thao đa dạng mỗi tháng.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao CMD368
CMD368 nổi bật với những ưu thế cạnh tranh, như cung cấp cho người chơi hơn 20.000 trận đấu hàng tháng, đến từ 50 môn thể thao khác nhau, đáp ứng nhu cầu của tất cả các fan hâm mộ thể thao, cũng như thoả mãn mọi sở thích của người chơi.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao PANDA SPORT
OB Sports đã chính thức đổi tên thành “Panda Sports”, một thương hiệu lớn với hơn 30 giải đấu bóng. Panda Sports đặc biệt chú trọng vào tính năng cá cược thể thao, như chức năng “đặt cược sớm và đặt cược trực tiếp tại livestream” độc quyền.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao WG
WG Sports tập trung vào những môn thể thao không quá được yêu thích, với tỷ lệ cược cao và xử lý đơn cược nhanh chóng. Đặc biệt, nhiều nhà cái hàng đầu trên thị trường cũng hợp tác với họ, trở thành là một trong những sảnh thể thao nổi tiếng trên toàn cầu.
Xem Chi Tiết »
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в итоге получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт трудовой карьеры.
https://re-tracker.ru/index.php?showtopic=861
A person essentially lend a hand to make severely posts I might state. That is the very first time I frequented your web page and so far? I surprised with the analysis you made to create this actual post amazing. Fantastic activity!
thewiin.com
따라서 이러한 일반적인 불교 의식의 대부분은 Zheng에 의해 함께 배열됩니다.
UEFA Euro 2024 Sân Chơi Bóng Đá Hấp Dẫn Nhất Của Châu Âu
Euro 2024 là sự kiện bóng đá lớn nhất của châu Âu, không chỉ là một giải đấu mà còn là một cơ hội để các quốc gia thể hiện tài năng, sự đoàn kết và tinh thần cạnh tranh.
Euro 2024 hứa hẹn sẽ mang lại những trận cầu đỉnh cao và kịch tính cho người hâm mộ trên khắp thế giới. Cùng tìm hiểu các thêm thông tin hấp dẫn về giải đấu này tại bài viết dưới đây, gồm:
Nước chủ nhà
Đội tuyển tham dự
Thể thức thi đấu
Thời gian diễn ra
Sân vận động
Euro 2024 sẽ được tổ chức tại Đức, một quốc gia có truyền thống vàng của bóng đá châu Âu.
Đức là một đất nước giàu có lịch sử bóng đá với nhiều thành công quốc tế và trong những năm gần đây, họ đã thể hiện sức mạnh của mình ở cả mặt trận quốc tế và câu lạc bộ.
Việc tổ chức Euro 2024 tại Đức không chỉ là một cơ hội để thể hiện năng lực tổ chức tuyệt vời mà còn là một dịp để giới thiệu văn hóa và sức mạnh thể thao của quốc gia này.
Đội tuyển tham dự giải đấu Euro 2024
Euro 2024 sẽ quy tụ 24 đội tuyển hàng đầu từ châu Âu. Các đội tuyển này sẽ là những đại diện cho sự đa dạng văn hóa và phong cách chơi bóng đá trên khắp châu lục.
Các đội tuyển hàng đầu như Đức, Pháp, Tây Ban Nha, Bỉ, Italy, Anh và Hà Lan sẽ là những ứng viên nặng ký cho chức vô địch.
Trong khi đó, các đội tuyển nhỏ hơn như Iceland, Wales hay Áo cũng sẽ mang đến những bất ngờ và thách thức cho các đối thủ.
Các đội tuyển tham dự được chia thành 6 bảng đấu, gồm:
Bảng A: Đức, Scotland, Hungary và Thuỵ Sĩ
Bảng B: Tây Ban Nha, Croatia, Ý và Albania
Bảng C: Slovenia, Đan Mạch, Serbia và Anh
Bảng D: Ba Lan, Hà Lan, Áo và Pháp
Bảng E: Bỉ, Slovakia, Romania và Ukraina
Bảng F: Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ, Gruzia, Bồ Đào Nha và Cộng hoà Séc
В современном мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в любом университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы на выходе получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца диплома до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://peru.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=294
외국선물의 개시 골드리치와 함께하세요.
골드리치증권는 길고긴기간 고객님들과 더불어 선물시장의 진로을 공동으로 여정을했습니다, 고객분들의 안전한 자금운용 및 건강한 수익성을 향해 항상 전력을 기울이고 있습니다.
왜 20,000+인 이상이 골드리치증권와 함께할까요?
빠른 솔루션: 간단하며 빠른 프로세스를 제공하여 모두 용이하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
안전 프로토콜: 국가당국에서 채택한 최상의 등급의 보안시스템을 채택하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가: 전체 거래데이터은 암호화 보호되어 본인 외에는 그 누구도 정보를 확인할 수 없습니다.
안전 이익률 마련: 위험 부분을 낮추어, 보다 한층 확실한 수익률을 제시하며 이에 따른 리포트를 발간합니다.
24 / 7 지속적인 고객지원: 365일 24시간 신속한 서비스를 통해 투자자분들을 모두 지원합니다.
함께하는 동반사: 골드리치는 공기업은 물론 금융기관들 및 다수의 협력사와 공동으로 걸어오고.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
국외선물은 해외에서 거래되는 파생금융상품 중 하나로, 명시된 기반자산(예시: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 바탕로 한 옵션계약 약정을 의미합니다. 근본적으로 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래의 특정한 시기에 일정 금액에 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 제공합니다. 국외선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 국외 마켓에서 거래되는 것을 뜻합니다.
국외선물은 크게 매수 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 구분됩니다. 매수 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 사는 권리를 부여하는 반면, 풋 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 가격에 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 특정 날짜에 (만기일이라 칭하는) 정해진 금액에 기초자산을 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 가격을 실행 금액이라고 하며, 만료일에는 해당 권리를 행사할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 거래자에게 향후의 가격 변화에 대한 보호나 수익 실현의 기회를 허락합니다.
해외선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 투자 및 매매거래 기회를 열어주며, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산유형에 대한 옵션 계약을 포괄할 수 있습니다. 투자자는 매도 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 하향에 대한 안전장치를 받을 수 있고, 콜 옵션을 통해 호황에서의 이익을 타깃팅할 수 있습니다.
외국선물 거래의 원리
실행 금액(Exercise Price): 국외선물에서 실행 가격은 옵션 계약에 따라 특정한 금액으로 약정됩니다. 만료일에 이 가격을 기준으로 옵션을 실행할 수 있습니다.
만료일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만기일은 옵션의 실행이 불가능한 마지막 일자를 의미합니다. 이 일자 이후에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 매수 옵션(Call Option): 매도 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 부여하며, 매수 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 매수하는 권리를 부여합니다.
계약료(Premium): 외국선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 옵션료을 지불해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 비용으로, 시장에서의 수요량와 공급량에 따라 변동됩니다.
실행 방안(Exercise Strategy): 투자자는 만기일에 옵션을 실행할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 이는 마켓 환경 및 투자 전략에 따라 차이가있으며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 극대화하거나 손해를 감소하기 위해 결정됩니다.
마켓 위험요인(Market Risk): 국외선물 거래는 시장의 변화추이에 효과을 받습니다. 시세 변화이 기대치 못한 진로으로 일어날 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 시장 위험요인를 축소하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 구축하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치와 함께하는 국외선물은 확실한 믿을만한 수 있는 투자를 위한 최적의 대안입니다. 회원님들의 투자를 지지하고 인도하기 위해 우리는 최선을 기울이고 있습니다. 공동으로 더 나은 미래를 향해 계속해나가세요.
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, и это становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://chere.4bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=7716
Some really nice stuff on this internet site, I enjoy it.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I want to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I want to read more things about it!
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто собирается начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного подхода заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russiyans.ru
Привет всем!
Приобретите диплом Гознака с гарантированной подлинностью и доставкой по всей России без предоплаты.
http://www.diplomanc-russia24.ru
Hi colleagues, how is everything, and what you want to say on the topic of this piece of writing, in my view its really remarkable designed for me.
https://cutt.ly/TeroNPgU
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство подобного подхода состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем наших мастеров.
В итоге, всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт трудовой карьеры.
dlplomanrussia.ru
Rikvip Club: Trung Tâm Giải Trí Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu tại Việt Nam
Rikvip Club là một trong những nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu tại Việt Nam, cung cấp một loạt các trò chơi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ cho người dùng. Cho dù bạn là người dùng iPhone hay Android, Rikvip Club đều có một cái gì đó dành cho mọi người. Với sứ mạng và mục tiêu rõ ràng, Rikvip Club luôn cố gắng cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất cho khách hàng, tạo ra một trải nghiệm tiện lợi và thú vị cho người chơi.
Sứ Mạng và Mục Tiêu của Rikvip
Từ khi bắt đầu hoạt động, Rikvip Club đã có một kế hoạch kinh doanh rõ ràng, luôn nỗ lực để cung cấp cho khách hàng những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất và tạo điều kiện thuận lợi nhất cho người chơi truy cập. Nhóm quản lý của Rikvip Club có những mục tiêu và ước muốn quyết liệt để biến Rikvip Club thành trung tâm giải trí hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực game đổi thưởng trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và trên toàn cầu.
Trải Nghiệm Live Casino
Rikvip Club không chỉ nổi bật với sự đa dạng của các trò chơi đổi thưởng mà còn với các phòng trò chơi casino trực tuyến thu hút tất cả người chơi. Môi trường này cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chuyên nghiệp với tính xanh chín và sự uy tín không thể nghi ngờ. Đây là một sân chơi lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích thách thức bản thân và muốn tận hưởng niềm vui của chiến thắng. Với các sảnh cược phổ biến như Roulette, Sic Bo, Dragon Tiger, người chơi sẽ trải nghiệm những cảm xúc độc đáo và đặc biệt khi tham gia vào casino trực tuyến.
Phương Thức Thanh Toán Tiện Lợi
Rikvip Club đã được trang bị những công nghệ thanh toán tiên tiến ngay từ đầu, mang lại sự thuận tiện và linh hoạt cho người chơi trong việc sử dụng hệ thống thanh toán hàng ngày. Hơn nữa, Rikvip Club còn tích hợp nhiều phương thức giao dịch khác nhau để đáp ứng nhu cầu đa dạng của người chơi: Chuyển khoản Ngân hàng, Thẻ cào, Ví điện tử…
Kết Luận
Tóm lại, Rikvip Club không chỉ là một nền tảng trò chơi, mà còn là một cộng đồng nơi người chơi có thể tụ tập để tận hưởng niềm vui của trò chơi và cảm giác hồi hộp khi chiến thắng. Với cam kết cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất, Rikvip Club chắc chắn là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích trò chơi trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và cả thế giới.
Euro
UEFA Euro 2024 Sân Chơi Bóng Đá Hấp Dẫn Nhất Của Châu Âu
Euro 2024 là sự kiện bóng đá lớn nhất của châu Âu, không chỉ là một giải đấu mà còn là một cơ hội để các quốc gia thể hiện tài năng, sự đoàn kết và tinh thần cạnh tranh.
Euro 2024 hứa hẹn sẽ mang lại những trận cầu đỉnh cao và kịch tính cho người hâm mộ trên khắp thế giới. Cùng tìm hiểu các thêm thông tin hấp dẫn về giải đấu này tại bài viết dưới đây, gồm:
Nước chủ nhà
Đội tuyển tham dự
Thể thức thi đấu
Thời gian diễn ra
Sân vận động
Euro 2024 sẽ được tổ chức tại Đức, một quốc gia có truyền thống vàng của bóng đá châu Âu.
Đức là một đất nước giàu có lịch sử bóng đá với nhiều thành công quốc tế và trong những năm gần đây, họ đã thể hiện sức mạnh của mình ở cả mặt trận quốc tế và câu lạc bộ.
Việc tổ chức Euro 2024 tại Đức không chỉ là một cơ hội để thể hiện năng lực tổ chức tuyệt vời mà còn là một dịp để giới thiệu văn hóa và sức mạnh thể thao của quốc gia này.
Đội tuyển tham dự giải đấu Euro 2024
Euro 2024 sẽ quy tụ 24 đội tuyển hàng đầu từ châu Âu. Các đội tuyển này sẽ là những đại diện cho sự đa dạng văn hóa và phong cách chơi bóng đá trên khắp châu lục.
Các đội tuyển hàng đầu như Đức, Pháp, Tây Ban Nha, Bỉ, Italy, Anh và Hà Lan sẽ là những ứng viên nặng ký cho chức vô địch.
Trong khi đó, các đội tuyển nhỏ hơn như Iceland, Wales hay Áo cũng sẽ mang đến những bất ngờ và thách thức cho các đối thủ.
Các đội tuyển tham dự được chia thành 6 bảng đấu, gồm:
Bảng A: Đức, Scotland, Hungary và Thuỵ Sĩ
Bảng B: Tây Ban Nha, Croatia, Ý và Albania
Bảng C: Slovenia, Đan Mạch, Serbia và Anh
Bảng D: Ba Lan, Hà Lan, Áo và Pháp
Bảng E: Bỉ, Slovakia, Romania và Ukraina
Bảng F: Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ, Gruzia, Bồ Đào Nha và Cộng hoà Séc
I think everything said made a great deal of sense. However, what about this? suppose you added a little content? I am not saying your content isn’t solid., however what if you added a headline that grabbed folk’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is kinda plain. You ought to look at Yahoo’s home page and watch how they create post titles to get people to click. You might try adding a video or a picture or two to get people excited about what you’ve got to say. In my opinion, it might bring your posts a little livelier.
http://www.diplomans-russiyans.ru
해외선물의 시작 골드리치와 동행하세요.
골드리치는 오랜기간 투자자분들과 더불어 선물마켓의 길을 함께 걸어왔으며, 고객분들의 안전한 투자 및 알찬 이익률을 지향하여 항상 최선을 기울이고 있습니다.
무엇때문에 20,000+인 이상이 골드리치증권와 함께할까요?
신속한 솔루션: 간단하며 빠른속도의 프로세스를 마련하여 모두 용이하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
안전보장 프로토콜: 국가당국에서 채택한 최상의 등급의 보안체계을 도입하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가: 모든 거래정보은 암호처리 보호되어 본인 이외에는 그 누구도 내용을 접근할 수 없습니다.
안전 이익률 제공: 위험 부분을 낮추어, 보다 더 확실한 수익률을 공개하며 그에 따른 리포트를 공유합니다.
24 / 7 실시간 고객상담: 365일 24시간 즉각적인 지원을 통해 회원분들을 온전히 서포트합니다.
제휴한 파트너사: 골드리치증권는 공기업은 물론 금융권들 및 많은 협력사와 공동으로 동행해오고.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
국외선물은 외국에서 거래되는 파생상품 중 하나로, 특정 기반자산(예: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 기초로 한 옵션계약 약정을 말합니다. 본질적으로 옵션은 특정 기초자산을 미래의 특정한 시점에 정해진 가격에 매수하거나 팔 수 있는 자격을 허락합니다. 외국선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 해외 마켓에서 거래되는 것을 지칭합니다.
외국선물은 크게 매수 옵션과 풋 옵션으로 분류됩니다. 콜 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 매수하는 권리를 허락하는 반면, 매도 옵션은 특정 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 제공합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 명시된 일자에 (만기일이라 불리는) 일정 가격에 기초자산을 사거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 보유하고 있습니다. 이러한 금액을 행사 금액이라고 하며, 종료일에는 해당 권리를 행사할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 거래자에게 미래의 가격 변동에 대한 안전장치나 수익 실현의 기회를 부여합니다.
해외선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 운용 및 차익거래 기회를 열어주며, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산군에 대한 옵션 계약을 포함할 수 있습니다. 거래자는 풋 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 하향에 대한 보호를 받을 수 있고, 매수 옵션을 통해 활황에서의 수익을 타깃팅할 수 있습니다.
국외선물 거래의 원리
실행 금액(Exercise Price): 외국선물에서 행사 금액은 옵션 계약에 따라 지정된 가격으로 계약됩니다. 종료일에 이 가격을 기준으로 옵션을 실현할 수 있습니다.
만기일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만기일은 옵션의 행사가 불가능한 마지막 일자를 뜻합니다. 이 일자 다음에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
매도 옵션(Put Option)과 콜 옵션(Call Option): 풋 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 제공하며, 매수 옵션은 기초자산을 지정된 금액에 사는 권리를 허락합니다.
계약료(Premium): 국외선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 옵션료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 가격으로, 마켓에서의 수요와 공급량에 따라 변동됩니다.
실행 방안(Exercise Strategy): 거래자는 종료일에 옵션을 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이는 시장 상황 및 투자 전략에 따라 차이가있으며, 옵션 계약의 이익을 최대화하거나 손해를 최소화하기 위해 판단됩니다.
마켓 리스크(Market Risk): 국외선물 거래는 마켓의 변화추이에 영향을 받습니다. 시세 변화이 예상치 못한 방향으로 발생할 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 마켓 위험요인를 축소하기 위해 거래자는 전략을 구축하고 투자를 계획해야 합니다.
골드리치와 동반하는 해외선물은 안전하고 확신할 수 있는 투자를 위한 최상의 선택입니다. 회원님들의 투자를 뒷받침하고 가이드하기 위해 우리는 전력을 다하고 있습니다. 함께 더 나은 미래를 향해 계속해나가세요.
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, что будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia.ru
Excellent beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a weblog website? The account helped me a appropriate deal. I were tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В итоге вы получите документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого решения состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
В результате, для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://zoosurgut.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3016
thephotoretouch.com
이 문장은 차분하지만 매우 진지하게 말했습니다.
Завершение учебы диплома представляет собой ключевым моментом в карьере каждого человека, определяющим его перспективы и профессиональные возможности – http://www.diplomvam.ru. Диплом открывает двери к свежим перспективам и возможностям, гарантируя доступ к высококачественному образованию и высокооплачиваемым профессиям. В нынешнем мире, где в конкуренция на рынке труда всё растёт, имение аттестата становится жизненно важным требованием для выдающейся профессиональной деятельности. Диплом утверждает ваши знания и навыки, умения и компетенции перед работодателями и социумом в целом. Помимо этого, диплом дарует уверенность в себе и увеличивает оценку себя, что помогает личностному и развитию. Получение диплома также является вложением в свое будущее, обеспечивая устойчивость и благополучный уровень проживания. Поэтому обращать должное внимание образованию и бороться за его получению, чтобы обрести успех и счастье от своей труда.
Диплом не только символизирует ваше образовательный уровень, но и демонстрирует вашу дисциплинированность, усердие и настойчивость в достижении целей. Диплом представляет собой результатом труда и труда, вкладываемых в учебу и саморазвитие. Завершение учебы образования открывает перед вами свежие горизонты возможностей, позволяя выбирать среди множества направлений и карьерных траекторий. Помимо этого даёт вам базис знаний и навыков и навыков, необходимых для выдающейся деятельности в современном обществе, насыщенном вызовами и изменениями. Кроме того, диплом считается свидетельством вашей компетентности и экспертности, что повышает вашу привлекательность для работодателей на рынке труда и открывает вами возможности к лучшим возможностям для профессионального роста. Следовательно, завершение учебы аттестата не только пополняет ваше личное и профессиональное развитие, а также открывает перед вами новые и перспективы для достижения и мечтаний.
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have created some nice methods and we are looking to swap strategies with others, be sure to shoot me an e-mail if interested.
https://writeablog.net/walarijcns/h1-b-remont-abo-zamina-korpusu-fari-iak-pravil-no-priiniati-rishennia-b-h1
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://kaliningrad.pogovorim.su/viewtopic.php?id=80
Сегодня, когда диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Таким образом, для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт успешной карьеры.
https://beregifiguru.ru/вЂРѕСЂСѓРј/“ема/купить-диплом-техникума/6686
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was searching for! “If you bungle raising your children, I don’t think whatever else you do matters.” by Jacqueline Lee Bouvier Kennedy Onassis.
Dear malabdali.com administrator, Your posts are always well-supported by facts and figures.
werankcities.com
“행복해.
Java Burn is the world’s first and only 100 safe and proprietary formula designed to boost the speed and efficiency of your metabolism by mixing with the natural ingredients in coffee.
Получение диплома является важным этапом в жизни каждого человека, определяет его будущее и профессиональные перспективы – http://diplomvam.ru. Аттестат открывает путь к новым перспективам и перспективам, обеспечивая доступ к высококачественному образованию и высокооплачиваемым профессиям. В сегодняшнем мире, где в борьба на трудовом рынке всё увеличивается, имение диплома становится необходимым условием для выдающейся карьеры. Он утверждает ваши знания и навыки, умения и компетенции перед профессиональным сообществом и социумом в целом. В дополнение, диплом дарует уверенность в себе и повышает самооценку, что способствует личностному росту и развитию. Получение диплома также является инвестицией в будущий путь, обеспечивая стабильность и достойный стандарт жизни. Поэтому обращать надлежащее внимание и время получению образования и стремиться к его достижению, чтобы обрести успех и счастье от собственной профессиональной деятельности.
Диплом не лишь представляет ваше образование, но и демонстрирует вашу самодисциплину, усердие и настойчивость в добивании целей. Диплом представляет собой плодом усилий и труда, вкладываемых в обучение и самосовершенствование. Получение образования раскрывает перед вами свежие горизонты перспектив, даруя возможность выбирать из множества карьерных путей и профессиональных направлений. Это также предоставляет вам базис знаний и умений, необходимых для выдающейся практики в современном мире, полном вызовами и изменениями. Помимо этого, сертификат считается свидетельством вашей компетентности и квалификации, что повышает вашу привлекательность для работодателей на трудовом рынке и открывает перед вами возможности к лучшим шансам для профессионального роста. Итак, получение диплома не только обогащает ваше личное развитие, но и раскрывает вами новые перспективы для достижения и амбиций.
FitSpresso is a weight loss supplement designed for individuals dealing with stubborn body fat.
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца документа до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
teplovdome2.ru/nachinaem-remont/porvalsya-diplom-ob-obrazovanii-chto-delat-i-kak-spasti-dokument.htmlВ
nordrus.org/raznoe/1816-sposoby-obscheniya.htmlВ
smp-forum.ru/preimushhestva-pokupki-diploma/В
import-moto.com/users/85?wid=3581В
dentaldaily.ru/uslugi/brekety/ispravlenie-prikusa/В
FitSpresso is a weight loss supplement designed for individuals dealing with stubborn body fat.
В наше время, когда диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора нужного образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
naszaswietlica.dwr.pl/profile.php?lookup=17636В
step-vowel.pornoautor.com/recent/posts?page=2В
vyazanshapki.ru/vyazanyie-shapki/zhenskie/shapka-s-obemnyim-pletenyim-uzorom-spitsamiВ
cheat-v2.ru/dota/atf-pokinul-quest-esports.htmlВ
rem.4nmv.ru/forum/search.php?action=members&p=199&s=d&order=ASCВ
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом, что является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы получите продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство подобного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца документа до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
uniquetattoo.ru/anchorВ
yellowstoneheli.com/2017/01/03/wedding-helicopter-flights-yellowstone/В
pozdravit-vsex.ru/s-dnem-rozhdeniya/3-goda/В
view24.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=qa&wr_id=1292&sst=wr_hit&sod=desc&sop=and&page=1В
roditeliz.ru/tag/girlВ
Hello! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa?
My site goes over a lot of the same subjects as
yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other.
If you’re interested feel free to shoot me an email.
I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful blog by the way!
To the malabdali.com admin, Your posts are always well-written and easy to understand.
zanetvize.com
“아…” Zhu Houzhao는 놀라서 Fang Jifan을 바라보았습니다.
Сегодня, когда диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто хочет вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russiann.com/
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, что является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого решения заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
Для тех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт трудовой карьеры.
http://www.diplomans-russia.com/
Hello friends, pleasant piece of writing and pleasant arguments commented here, I am actually enjoying by these.
9saksx-diploms24.com
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого решения состоят не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://4russkiy365-diploms.com/
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или учиться в любом институте.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
pikucha.ru/santexnika/polotencesushitel-i-stoyak/kuvshinka-rakovina.htmlВ
dtpa.dn.ua/video/2010978705-tetrad-po-chistopisaniyu-3-klass/В
m.jingdexian.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2545488В
союзженскихсил.СЂС„/communication/forums/forming/gde-uznavat-rezultaty-ege/?GROUP_ID=В
worlduniversitydirectory.com/webbrowse.php?linkid=9416%C3%82%C2%A0В
Геракл24: Опытная Смена Фундамента, Венцов, Покрытий и Передвижение Зданий
Компания Gerakl24 специализируется на выполнении всесторонних услуг по реставрации основания, венцов, настилов и передвижению строений в городе Красноярском регионе и в окрестностях. Наша команда профессиональных экспертов обеспечивает отличное качество выполнения различных типов восстановительных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасного типа, из кирпича или из бетона дома.
Достоинства сотрудничества с Геракл24
Навыки и знания:
Все работы проводятся лишь высококвалифицированными экспертами, с обладанием многолетний стаж в сфере возведения и восстановления строений. Наши мастера знают свое дело и реализуют работу с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предоставляем полный спектр услуг по ремонту и восстановлению зданий:
Реставрация фундамента: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что позволяет продлить срок службы вашего здания и избежать проблем, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Замена венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые наиболее часто гниют и разрушаются.
Замена полов: монтаж новых настилов, что значительно улучшает внешний облик и функциональность помещения.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и качественное передвижение домов на другие участки, что помогает сохранить здание и избегает дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Древесные строения: восстановление и укрепление деревянных конструкций, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные дома: реставрация каркасов и замена поврежденных элементов.
Дома из кирпича: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление конструкций.
Бетонные дома: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы применяем только проверенные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все проекты подвергаются строгому контролю качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Личный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем персонализированные решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Мы стараемся, чтобы конечный результат полностью удовлетворял ваши ожидания и требования.
Зачем обращаться в Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех задач в установленные сроки и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Обратившись в Геракл24, вы можете быть спокойны, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и дать ответы на все вопросы. Свяжитесь с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш партнер по реставрации и ремонту домов в Красноярске и окрестностях.
Сегодня, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство данного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.prensactiva.com/ma-situation-de-marketing-en-ligne-lecon-apprise/В
led-profit.ru/podklyuchenie-ustanovka/В
123ru.market/items/attestati_diplomi_i_ostalnie_dokumenti_ob_obrazovanii_44412В
elitedomik.ru/dacha-i-uchastok/osobennosti-polucheniya-diploma-v-texnikume-chto-neobxodimo-znat.htmlВ
dscomics.nl/2017/01/06/blog-comiclog-bedoel-je/В
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем наших мастеров.
В результате, для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
unbelievable.su/articles.php?id=206В
http://www.mir-hr.ru/obuchenie-personala/diplom-o-visshem-obrazovanii.htmlВ
worlduniversitydirectory.com/webbrowse.php?linkid=9416%C3%82%C2%A0В
globalproseo.com/a-seo-choice-for-content-management-system-cms/В
arhive.stpku.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=255&Itemid=115В
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который стремится начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого решения состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для тех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://www.6rudik-diploms365.com/
体验Telegram中文版,享受全面的即时通讯服务。端到端加密保障您的沟通安全,支持大文件分享和云存储功能,让跨设备通信变得无缝而高效。立即下载,开启高效的沟通体验。Experience Telegram Chinese Version for comprehensive instant messaging services. End-to-end encryption ensures secure communication, while support for large file sharing and cloud storage makes cross-device communication seamless and efficient. Download now for an enhanced communication experience.https://www.tgxiazai.com
7lq1klte8n
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, и это будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы получите продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
fr2613.rinethost.ru/node/105В
club.sabaylok.com/blogs/1927/What-exactly-should-you-pay-attention-to-when-buying-a?lang=en_usВ
http://www.prvduma.ru/news/1078-garantiya-na-kapremont-5-let.htmlВ
viparmenia.org/threads/14652-%D0%9E-%D1%84%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%86%D1%83%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%85-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BC%D1%8F%D0%BD%D0%B5/page2В
ктинз.СЂС„/informatsionnye-resursy_id110/В
טלגראס הינה תוכנה פופולרית בארץ לרכישת קנאביס באופן אינטרנטי. זו מספקת ממשק פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה ולקבלת שילוחים מ פריטי צמח הקנאביס מרובים. במאמר זו נבחן את העיקרון מאחורי טלגראס, כיצד זו עובדת ומה המעלות מ השימוש בה.
מה זו האפליקציה?
האפליקציה הווה אמצעי לרכישת מריחואנה דרך היישומון טלגראם. היא נשענת מעל ערוצי תקשורת וקבוצות טלגראם ייעודיות הנקראות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שבהם אפשר להזמין מגוון פריטי קנאביס ולקבלת אותם ישירות למשלוח. ערוצי התקשורת האלה מסודרים לפי איזורים גיאוגרפיים, כדי להקל על קבלתם של השילוחים.
איך זאת פועל?
התהליך קל יחסית. קודם כל, יש להצטרף לערוץ טלגראס הנוגע לאזור המגורים. שם אפשר לצפות בתפריטי הפריטים המגוונים ולהרכיב את המוצרים המבוקשים. לאחר ביצוע ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יופיע לכתובת שנרשמה ועמו הארגז המוזמנת.
מרבית ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים מגוון נרחב של מוצרים – סוגי קנאביס, עוגיות, שתייה ועוד. בנוסף, ניתן למצוא חוות דעת מ צרכנים קודמים לגבי איכות המוצרים והשרות.
יתרונות הנעשה באפליקציה
יתרון עיקרי של האפליקציה הוא הנוחות והדיסקרטיות. ההרכבה והתהליך מתקיימים מרחוק מאיזשהו מקום, ללא צורך בהתכנסות פיזי. כמו כן, האפליקציה מוגנת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוהה.
מלבד על זאת, מחירי הפריטים באפליקציה נוטות לבוא תחרותיים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות רבה. יש גם מרכז תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיית.
סיכום
הפלטפורמה מהווה שיטה מקורית ויעילה לקנות מוצרי צמח הקנאביס בישראל. היא משלבת את הנוחות הדיגיטלית של האפליקציה הפופולרי, לבין המהירות והפרטיות של שיטת השילוח הישירות. ככל שהביקוש לקנאביס גובר, פלטפורמות כמו זו צפויות להמשיך ולהתפתח.
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в любом университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
preceptor.flybb.ru/topic4745.htmlВ
bbs.xyslysy.cn/upload/home.php?mod=space&uid=18536В
mkb-net.ru/category/udalenie-kamnej-iz-pochekВ
nav.sozvezdie03.ru/napravleniya/obrazovanie/ege.htmlВ
http://www.freecrm.ru/index_p_3.htmlВ
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS – Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại!
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в университете.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это является выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт профессиональной карьеры.
lightsquad.pt/equacao-motor-an-unforgettable-christmas/В
dljadachnikov.ru/momordika-pishhevaya-i-lechebnaya-cennost-vyrashhivanie/В
fabrika.dp.ua/poleznye-sovety/preimushhestva-izuchenija-jazyka-kotorye-ja.htmlВ
thespotlightnewsglobal.com/2023/02/28/sharpes-doom-day-withdraws-20-million-billboard-lawsuit/В
http://www.voidofheroes.com/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=52745В
veganchoicecbd.com
“오빠, 당신은 그것을 30 번 이상 말했습니다. “Zhang Yanling이 약하게 말했습니다.
Woh I enjoy your content, saved to bookmarks! .
Accepted to our website, your premier online heart after African sports, music, and celebrity updates. We provide for the whole kit from overwhelming sports events like the Africa Cup of Nations to the latest trends in Afrobeats and ancestral music. Probe closed interviews and features on famous personalities making waves across the continent and beyond.
At our website, we lend timely and attractive text that celebrates the disparity and vibrancy of African culture. Whether you’re a sports promoter, music lover, or peculiar about Africa’s substantial figures, ally our community and prevent connected exchange for constantly highlights and in-depth stories showcasing the with greatest satisfaction of African inclination and creativity https://nouvelles-histoires-africaines.africa/comment-mettre-de-la-musique-dans-une-voiture-avec/.
Visit our website today and meet with the high-powered magic of African sports, music, and distinguished personalities. Immerse yourself in the richness of Africa’s cultural mise en scene with us!
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always interesting to read through content from other writers and use something from their web sites.
spin away casino
отмывание usdt
Как обезопасить свои личные данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня охрана личных данных становится всё значимее важной задачей. Одним из наиболее часто встречающихся способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и как предохранить себя от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это смеси слов или фраз, которые бывают используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или иные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, при помощи этих сит фраз. Как сохранить свои личные данные? Используйте запутанные пароли. Избегайте использования несложных паролей, которые мгновенно угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого из аккаунта. Не пользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухэтапную аутентификацию (2FA). Это прибавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте персональную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы защитить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может спровоцировать серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы охранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до правильного заполнения персональных данных и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
demo2.weboss.hk/1009/comment/html/?578.htmlВ
vg-news.ru/n/150088%C2%A0В
molbiol.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=1081040В
ertegi.ru/index.php?id=2&idnametext=145&idpg=1В
devforums.overclockers.ru/viewtopic.php?t=627904&start=120В
Сохраните собственные USDT: Проверяйте транзакцию TRC20 до отправкой
Криптовалюты, подобные вроде USDT (Tether) в блокчейне TRON (TRC20), делаются все всё более популярными в сфере децентрализованных финансовых услуг. Однако совместно с ростом популярности увеличивается и опасность промахов либо жульничества во время переводе финансов. Именно поэтому необходимо проверять операцию USDT TRC20 до ее отправкой.
Ошибка во время вводе данных адреса получателя или перевод на ошибочный адрес может привести к невозможности необратимой потере твоих USDT. Злоумышленники тоже могут пытаться одурачить тебя, посылая поддельные адреса для транзакции. Потеря крипто вследствие подобных промахов сможет повлечь значительными денежными убытками.
К радости, существуют профильные службы, позволяющие проверить транзакцию USDT TRC20 перед ее отсылкой. Один из подобных сервисов дает возможность просматривать и анализировать операции в распределенном реестре TRON.
В данном обслуживании вы можете ввести адрес получателя а также получать обстоятельную сведения о адресе, включая архив операций, баланс и состояние аккаунта. Данное посодействует определить, есть или нет адрес получателя действительным и безопасным на отправки денег.
Иные сервисы тоже предоставляют аналогичные возможности по удостоверения операций USDT TRC20. Определенные кошельки для криптовалют для цифровых валют обладают инкорпорированные возможности для верификации адресов получателей а также операций.
Не пренебрегайте удостоверением операции USDT TRC20 перед её отсылкой. Небольшая осмотрительность может сэкономить для вас множество финансов а также избежать потерю ваших дорогих криптовалютных активов. Используйте проверенные сервисы с целью достижения защищенности ваших транзакций а также целостности ваших USDT в распределенном реестре TRON.
В мире крипто присутствует настоящая риск получения таким образом именуемых “грязных” средств – криптомонет, относящихся с противозаконной деятельностью, подобной как легализация средств, обман либо хакерские атаки. Обладатели кошельков USDT в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20) также подвержены этому риску. Вследствие чего очень необходимо регулярно удостоверяться свой кошелек в отношении существование “грязных” операций с целью защиты собственных средств и репутации.
Опасность “грязных” операций кроется в этом, чтобы оные имеют возможность являться прослеживаемы силовыми структурами а также валютными надзорными органами. В случае если будет установлена отношение со преступной активностью, ваш кошелек имеет возможность стать блокирован, и активы – отчуждены. Кроме того, данное может повлечь за собой за собой юридические последствия а также подпортить вашу имидж.
Имеются профильные сервисы, дающие возможность проконтролировать историю переводов в твоём кошельке USDT TRC20 в отношении наличие вызывающих опасения переводов. Данные службы изучают сведения транзакций, сопоставляя их со известными инцидентами жульничества, хакерских атак, и отмывания средств.
Примером из числа таких служб служит https://telegra.ph/Servisy-AML-proverka-USDT-05-19 дающий возможность просматривать всестороннюю историю операций вашего USDT TRC20 кошелька для криптовалют. Сервис определяет возможно рискованные операции и предоставляет подробные данные о них.
Не пренебрегайте проверкой собственного криптокошелька USDT TRC20 в отношении наличие “нелегальных” переводов. Своевременное наблюдение посодействует избежать рисков, соотносимых со противозаконной деятельностью на цифровой области. Применяйте достойные доверия сервисы для проверки своих USDT операций, для того чтобы обезопасить ваши крипто а также имидж.
При работе с криптовалютой USDT на блокчейне TRON (TRC20) крайне существенно не просто верифицировать реквизиты получателя перед переводом средств, но и периодически контролировать остаток личного крипто-кошелька, и происхождение поступающих транзакций. Данное действие даст возможность вовремя обнаружить всевозможные нежданные транзакции и избежать вероятные убытки.
В первую очередь, необходимо удостовериться на точности показываемого остатка USDT TRC20 в собственном криптокошельке. Предлагается сверять информацию с данными открытых блокчейн-обозревателей, чтобы исключить шанс хакерской атаки либо скомпрометирования самого крипто-кошелька.
Однако одного только отслеживания остатка мало. Крайне существенно анализировать журнал входящих переводов а также их происхождение. В случае если Вы выявите транзакции USDT с неизвестных или подозрительных адресов, сразу же заблокируйте эти деньги. Имеется риск, чтобы данные монеты стали добыты незаконным способом и впоследствии изъяты регуляторами.
Наш сервис предоставляет средства с целью углубленного изучения поступающих USDT TRC20 переводов касательно их легальности а также отсутствия связи с криминальной деятельностью. Мы.
Плюс к этому необходимо систематически отправлять USDT TRC20 на надежные неконтролируемые крипто-кошельки находящиеся под вашим полным управлением. Содержание монет на внешних платформах всегда сопряжено с угрозами взломов и потери денег вследствие программных ошибок или банкротства сервиса.
Соблюдайте элементарные меры защиты, оставайтесь бдительны и вовремя мониторьте баланс и источники поступлений кошелька для USDT TRC20. Это позволят оградить Ваши электронные ценности от.
What’s up, after reading this awesome article i am too cheerful to share my familiarity here with friends.
spin away spiele
Как сберечь свои личные данные: избегайте утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня обеспечение безопасности своих данных становится всё больше важной задачей. Одним из наиболее популярных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в какой мере предохранить себя от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это сочетания слов или фраз, которые регулярно используются для входа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, используя этих сит фраз. Как обезопасить свои личные данные? Используйте запутанные пароли. Избегайте использования простых паролей, которые мгновенно угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого из вашего аккаунта. Не используйте один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную аутентификацию (2FA). Это добавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте свою информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы защитить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может повлечь за собой серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
Hi there, after reading this amazing paragraph i am as well happy to share my familiarity here with mates.
odibet live
What’s up to every body, it’s my first visit of this website; this blog includes awesome and genuinely excellent material in support of readers.
elitcasino guncel
Hi there! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I truly enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Thanks a lot!
baji999 downloadable content
Важность анализа перевода USDT TRC20
Операции USDT в рамках протокола TRC20 набирают возрастающую активность, тем не менее следует быть чрезвычайно бдительными во время данных зачислении.
Данный вид операций нередко используется в качестве легализации активов, приобретенных криминальным путем.
Главный факторов риска приобретения USDT TRC-20 – это такие платежи вероятно будут приобретены посредством разнообразных способов мошенничества, например утраты персональных сведений, принуждение, взломы а также прочие криминальные схемы. Обрабатывая указанные переводы, пользователь безусловно выступаете пособником нелегальной операций.
В связи с этим крайне важно тщательно анализировать происхождение всех поступающего транзакции по USDT TRC-20. Обязательно интересоваться посредством плательщика подтверждения относительно правомерности денежных средств, при незначительных сомнениях – отказываться от переводов.
Помните, в случае, когда при обнаружения криминальных источников финансов, пользователь вероятно будете привлечены со санкциям наряду рядом с инициатором. Вследствие этого целесообразнее принять меры предосторожности наряду с тщательно анализировать всякий платеж, нежели подвергать риску личной репутацией как и столкнуться со серьезные юридические трудности.
Демонстрация внимательности во время операциях через USDT TRC-20 – выступает залог личной материальной безопасности как и избежание вовлечения в криминальные схемы. Проявляйте внимательными а также неизменно исследуйте источник виртуальных валютных активов.
Just wish to say your article is as surprising. The clarity to your submit is just excellent and i could assume you are an expert in this subject. Well along with your permission let me to take hold of your feed to stay updated with impending post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please continue the rewarding work.
werankcities.com
Hanlin 편집자 Liu Jinshui는 군중 속에 더 많이 있었고 눈물이 흘러 나올 것입니다.
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все находится под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
miupsik.ru/forums/showthread.php?tid=116&page=6В
old.doomgate.ru/?set=news&mc=readfull&do=180&page=162В
topnewsrussia.ru/kak-napisat-diplomnuyu-rabotu-3/В
rusnor.org/pubs/edit/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=89895В
webdesignerne.dk/skab-oekonomisk-frihed-ved-brug-af-nye-finansielle-teknologier/В
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
addcatalogs.manyweb.ru/review/edu03.ru.htmlВ
d-harms.ru/articles/chto-podarit-na-rozhdenie-rebenka.htmlВ
globalpoolcover.com/news/landy-was-invited-to-participate-in-the-2019-pool-spa-expo/В
http://www.remont-holodilnik.ru/holod.htmlВ
skodarapidclub.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=1585597&mode=linearВ
Dear malabdali.com webmaster, Your posts are always thought-provoking and inspiring.
проверить адрес usdt trc20
Заголовок: Непременно контролируйте адрес адресата при транзакции USDT TRC20
В процессе взаимодействии с крипто, особенно со USDT в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20), крайне важно выказывать бдительность а также внимательность. Одна из наиболее распространенных ошибок, которую делают юзеры – отправка средств на ошибочный адрес. Для того чтобы избежать лишение собственных USDT, нужно постоянно тщательно контролировать адрес получателя перед передачей операции.
Крипто адреса представляют из себя протяженные наборы литер а также номеров, например, TRX9QahiFUYfHffieZThuzHbkndWvvfzThB8U. Даже малая опечатка или оплошность во время копировании адреса сможет повлечь к тому, что ваши цифровые деньги будут невозвратно утрачены, так как оные окажутся на неподконтрольный вами криптокошелек.
Имеются различные способы контроля адресов USDT TRC20:
1. Зрительная инспекция. Тщательно сверьте адрес кошелька во вашем крипто-кошельке со адресом кошелька реципиента. В случае небольшом расхождении – воздержитесь от операцию.
2. Задействование онлайн-сервисов контроля.
3. Дублирующая аутентификация с получателем. Попросите получателя удостоверить правильность адреса перед посылкой транзакции.
4. Тестовый перевод. В случае крупной величине перевода, можно предварительно передать небольшое объем USDT с целью удостоверения адреса кошелька.
Кроме того предлагается содержать цифровые деньги в личных кошельках, а не на биржах либо посреднических службах, для того чтобы обладать полный управление над своими средствами.
Не игнорируйте удостоверением адресов кошельков при взаимодействии с USDT TRC20. Данная несложная мера безопасности посодействует защитить ваши финансы против непреднамеренной лишения. Помните, чтобы на сфере криптовалют операции неотменимы, и отправленные монеты по ошибочный адрес возвратить практически нереально. Будьте бдительны и аккуратны, для того чтобы обезопасить собственные инвестиции.
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It’s always interesting to read through content from other authors and use a little something from other sites.
ttclimat.ru
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца диплома до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
blogs.rufox.ru/~runoklisfgy/42169.htmВ
bbs.airav.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2080482В
http://www.lada-xray.net/member.php?u=23071В
m.delphic.games/news/?y=2014&SHOWALL_1=1В
hefeiyechang.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=13313В
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post. Thank you for providing these details.
Ловекон моя страница
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, и это становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы сможете получить продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
kayur-travel.ru/index.php?newsid=184В
pumarefrattari.com/index.php/it/component/k2/item/19547-premiums-diplomscomВ
rusnor.org/pubs/edit/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=89895В
apokalypsed.org/users.php?m=details&id=26454В
justinsellssd.com/places-in-zagreb-the-advantages-of-workers/В
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки по России — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для всех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
forums.wolflair.com/member.php?u=110931%C2%A0В
girbir.com/blogs/13245/We-purchase-a-university-diploma-on-the-Internet-Expert-adviceВ
telegra.ph/kupit-diplom-o-srednem-obrazovanii-v-kompanii-Premiums-diplom-02-11В
http://www.vsbs.ru/index.htmВ
3vozrast.ru/article/pravo/vashe_pravo/10129/В
?The sad, humiliated wife flashed before his eyes. She sincerely wants to lose weight — her colleagues are teasing jokes about their family, and maybe even about her weight. A couple of cakes won’t make him thinner, and the salads are even not bad. Injustice rose to his throat in a lump and stuck there, not wanting to go anywhere. Nausea began to set in:
Give me buckwheat with stew, a medium plate… A salad with Chinese cabbage, the one without mayonnaise, also a medium one. And compote from dried fruits.
The canteen lady’s eyes widened, apparently from surprise. She performed such requests every day, but definitely not from this person. Frozen over the vat of buckwheat, she amazedly blurted out:
— Petrovich, is it me you’re talking to right now or who? And what about the pies and dessert, a liter of soda? Have you really decided to lose weight?
— And from this day on, it will always be like this! Lyudka, promise you’ll never sell me that crap again, only healthy food and no more!
— Agreed!
buysteriodsonline.com
Fang Jifan은 미소를 지으며 사람들을 맞이했습니다. “당신의 추모에 대해 조금 들었습니다.”
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Геракл24: Профессиональная Замена Основания, Венцов, Покрытий и Передвижение Строений
Компания Геракл24 профессионально занимается на оказании всесторонних услуг по замене фундамента, венцов, настилов и передвижению зданий в населённом пункте Красноярск и за его пределами. Наш коллектив профессиональных экспертов обещает высокое качество исполнения различных типов реставрационных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасные, кирпичные постройки или бетонные конструкции строения.
Достоинства сотрудничества с Gerakl24
Профессионализм и опыт:
Весь процесс проводятся только высококвалифицированными специалистами, имеющими большой практику в сфере строительства и реставрации домов. Наши мастера профессионалы в своем деле и выполняют работу с максимальной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Комплексный подход:
Мы предоставляем разнообразные услуги по реставрации и ремонту домов:
Смена основания: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего строения и устранить проблемы, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Реставрация венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые чаще всего подвергаются гниению и разрушению.
Установка новых покрытий: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает внешний облик и функциональные характеристики.
Перемещение зданий: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на новые места, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и предотвращает лишние расходы на создание нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Древесные строения: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, защита от гниения и вредителей.
Каркасные дома: усиление каркасных конструкций и смена поврежденных частей.
Кирпичные строения: восстановление кирпичной кладки и укрепление стен.
Бетонные строения: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы работаем с только высококачественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все проекты проходят строгий контроль качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Индивидуальный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту персонализированные решения, учитывающие все особенности и пожелания. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы итог нашей работы полностью удовлетворял вашим запросам и желаниям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех правил и норм. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы готовы предоставить консультацию и ответить на ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы обеспечим сохранение и улучшение вашего дома, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Геракл24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts. I really appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next write ups thank you once again.
https://t.me/Cryptone_academy
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
pin-up casino
Hello, its nice article concerning media print, we all be aware of media is a great source of facts.
digital nomad visa что это
I appreciate, cause I found exactly what I was having a look for. You have ended my four day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
казино монро официальный сайт
Awesome issues here. I am very happy to look your article. Thanks a lot and I’m taking a look forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
монро казино промокод бездепозитный бонус
What’s up to every one, since I am in fact eager of reading this webpage’s post to be updated regularly. It contains nice information.
олимп казино 4
טלגראס כיוונים
זכו הבאים למרכז הידע והמידע והסיוע הרשמי של טלגראס נתיבים! בנקודה זו רשאים לאתר ולקבל את כל המידע והמסמכים העדכני והמעודכן הזמין והרלוונטי בעניין פלטפורמה טלגרמות ואופני לשימוש בה כנדרש.
מיהו טלגרף כיוונים?
טלגרף כיוונים מהווה מנגנון המבוססת על טלגרף המשמשת לתפוצה ויישום סביב מריחואנה וקנביס במדינה. באמצעות ההודעות והחוגים בתקשורת, פעילים רשאים להזמין ולהשיג פריטי קנאביס בדרך פשוט ומהיר.
כיצד להיכנס בטלגרם?
על מנת להתחבר בשימוש בטלגראס כיוונים, מחויבים להיות חברים ב לקבוצות ולמסגרות האיכותיים. במיקום זה באתר תוכלו למצוא מדריך של צירים לשיחות מעורבים וראויים. במקביל לכך, תוכלו להתחיל בתהליך הרכישה והקבלה מסביב אספקת המריחואנה.
מדריכים ופרטים
בפורטל המסוים ניתן למצוא מגוון עבור הדרכות וכללים מפורטים בנוגע ל היישום בטלגרם, בכלל:
– החיבור למקומות מאומתים
– סדרת הרכישה
– הגנה והבטיחות בהפעלה בטלגרם
– והרבה תוכן אחר
מסלולים מאומתים
בסעיף זה קישורים לשיחות ולמסגרות רצויים בטלגרם:
– מקום המידע והעדכונים הרשמי
– חוג הסיוע והליווי לצרכנים
– פורום לקבלת פריטי קנבי מוטבחים
– רשימת ספקים דשא מובטחות
צוות מברכים אתכם עקב החברות שלכם לאזור המידע והנתונים עבור טלגרף אופקים ומצפים לקהל חווית שהיא רכישה מצוינת ובטוחה!
Справка-вызов На Сессию Заочная Форма
Справка-вызов На Сессию Заочная Форма
Подлинность документа подтверждается наличием типографических знаков защиты. Альтернативный способ получения корочки заключается в покупке готовых образовательных бумаг. Когда речь заходит о получении диплома зрелости и диплома об окончании колледжа, стоит понимать. Самым частым вопросом следи наших клиентов является следующий: не узнают ли о том, что диплом сделан на заказ. Ответ на поверхности, в таком городе как Москва можно купить диплом о высшем образовании.
russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Официальный Диплом С Занесением В Реестр
Вам понадобиться опыт не только в выполнении каких-либо определенных профессиональных действий, а также в общении, умении договориться, организовать своё рабочее место и время. городах России, можно смело участвовать во всех конкурсах на любую вакансию. По вашему желанию документ будет оформлен в необходимые вам сроки, с указанием очной или заочно формою обучения. Если овладев профессией, купить диплом о высшем образовании в Москве, СПб и др.
Купить Диплом Магистра
Этот документ обязателен при трудоустройстве практически во всех компаниях, несмотря на переход учебных заведений на болонскую систему и исключение данной квалификации из учебного процесса. За годы работы сформирована команда профессионалов и четкая концепция выполнения каждой работы. Если Вы успели набрать опыт за годы работы в аптечной сети в качестве продавца и хотите пойти выше, не обязательно заканчивать 5 лет высшего образования. Специализируется на образовании, исследованиях и разработках в области информационных технологий и робототехники.
Hello!
This post was created with 2ssdsd3222aa.com
Купить Диплом Университета С Занесением В Реестр
Позвольте себе достичь новых высот и открыть для себя новые возможности с помощью нашей компании. Дополнительное образование Диплом о переподготовке Удостоверение о повышении квалификации Диплом доктора наук Диплом кандидата наук Диплом ординатуры Удостоверение интернатуры Сертификат специалиста. Часто она бывает просто неподъёмной, особенно для тех, кто не работает. Для молодежи предоставлены самые разные учебные заведения для получения профессионального образования. Высшее образование в современной России является главным критерием при устройстве на престижную работу. Также на подобных площадках обычно не предоставляются услуги по внесению правок и бесплатные гарантийные обслуживания. А конкуренты не дремлют, и уже почти Ваша должность стремительно отдаляется.
https://landik-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом Электромеханика
Если же ваша актуальная профессия совершенно не устраивает вас, то легко её сменить, просто нужно купить диплом бакалавра в Москве и искать любимую работу. Шансы купить диплом есть у каждого, кто станет клиентом нашей компании, доверив решение своих проблем профессионалам. Итак, если вы задумываетесь о возможности купить диплом о высшем образовании в России, наша компания готова предложить вам свои услуги.
Купить Диплом Цены
Изготовитель предлагает соискателям недорого купить дипломы в Москве, другом регионе России без предоплаты. Аптеки находятся на углу каждого дома, а люди ежедневно заболевают и нуждаются в лекарствах. Обращаясь к нам, вы можете рассчитывать на конфиденциальность: данные о заказчике ни при каких обстоятельствах не передаются третьим лицам. Получив заявку на изготовление диплома ночью, менеджер связывается с Клиентом утром.
Кто Покупал Аттестат Отзывы
Люди, решившие купить диплом педагога, не хотят, чтобы это подвергалось огласке. Вы сами сравните оба пластика, и убедитесь, что у них попросту нет никаких отличий. При выборе учебных заведений есть одна особенность, которую указывают редко. В итоге на руки вы получите такую же корочку, которые есть у выпускников вузов Москвы. Заказом дипломной работы даёт возможность студенту систематизировать полученные знания, умения и навыки, а также продемонстрировать свои профессиональные навыки и умения. От А до Г От Д до И От Й до М От Н до Р От С до Ф От Х до Ч От Ш до Я БИЗНЕС ЛИТЕРАТУРА Бизнес. Покупка диплома останется тайной – полная конфиденциальность, одно из важнейших условий покупай Аттестат Отзывы работы полная анонимность, покупайте Аттестат Отзывы к ним и вы не упускайте свой шанс.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Оценки В Аттестате За 9 Класс
Многие соискатели высокопоставленной должности задаются актуальным вопросом: где купить диплом о высшем образовании. Сложность исследований и анализа состоит не столько в объемах работ, сколько в способности переключаться и покупая Аттестат Отзывы логически. Теперь посмотрим, какие конкретно выгоды для вас принесет вариант альтернативного получения (покупки) диплома и прочих важных документов: вы будете заниматься действительно важными делами, например, зарабатывать, а не бегать по всем инстанциям.
Купить Доверенность Без Доверителя
Чтобы ничем не отличаться от оригинального, документ должен содержать всю необходимую информацию и быть оформленным соответствующим образом. Вы были отчислены с последних курсов, но при этом практически полностью освоили программу обучения. Таким образом, купить диплом в Москве без предоплаты можно при помощи курьера. Кстати необходимо заметить тот факт, что не покупая Аттестат Отзывы документа о наличии неполного среднего образования у человека нет шансов поступить в училище.
Great post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thank you!
1win
Akarslot
Very nice style and good subject material, absolutely nothing else we need : D.
Купить Удостоверение Механика
Прохождение МО без предоставления и рассмотрения обязательных диагностических исследований не законно. Где же взять теоретические и практические навыки, получаемые в университете. К счастью, корочку можно приобрести, потратив небольшую сумму денег, но не потеряв драгоценного времени. Интернет-поиск выдает удостоверенье Механика компаний, предлагающих такие услуги. Мы купимте любые, даже самые сложные документы и при этом гарантируем полную секретность, быстроту выполнения заказа, высочайшее качество и приемлемые цены.
https://landik-diploms-srednee.ru
Доверенность На Ведение Наследственного Дела
Тесное сотрудничество с ВУЗами, техникумами и колледжами России – позволяет выполнять Ваши заказы максимально качественно и в назначенный срок. Руководство университетов считает, что они полезнее для трудоустройства, чем дипломы гособразца. Наличие на руках диплома об окончании высшего учебного заведения открывает перед его владельцем перспективное будущее с достойной работой, карьерным механиком и хорошей заработной платой. Однако по разным причинам диплом они так и не купили Удостоверение, производитель, которым являемся мы, будет строго наказан, конечно, это пустая трата, но тоже серьезная.
Купить Диплом О Среднем Образовании В Санкт-петербурге
Лет сложной учебы можно сэкономить, при этом потратив денег меньше, чем сумма, которая уходит за время учебы просто на покупку учебников и пособий. Какой бы ни купила Удостоверение Механика причина, отсутствие корочки может создавать ощутимые сложности. В Украине мы являемся доверенной организацией у которой продажа отличных документов – приоритет.
Hey there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.
Hello there, I discovered your blog by means of Google even as looking for a similar subject, your site got here up, it seems great. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
оценить автомобиль https://avtovikupmashin21.ru/
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Опытная Смена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Перемещение Строений
Компания Gerakl24 занимается на выполнении комплексных сервисов по реставрации основания, венцов, настилов и перемещению домов в населённом пункте Красноярском регионе и в окрестностях. Наша команда опытных мастеров обещает отличное качество выполнения всех видов ремонтных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасного типа, кирпичные или бетонные дома.
Плюсы сотрудничества с Геракл24
Квалификация и стаж:
Весь процесс осуществляются только высококвалифицированными мастерами, с обладанием долгий практику в направлении строительства и восстановления строений. Наши сотрудники знают свое дело и осуществляют задачи с максимальной точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Полный спектр услуг:
Мы осуществляем все виды работ по восстановлению и реконструкции строений:
Замена фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что гарантирует долговечность вашего строения и устранить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Смена венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые чаще всего подвергаются гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: монтаж новых настилов, что значительно улучшает внешний вид и функциональные характеристики.
Перенос строений: безопасное и качественное передвижение домов на новые локации, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и предотвращает лишние расходы на создание нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Дома из дерева: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Дома с каркасом: укрепление каркасов и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление стен.
Дома из бетона: реставрация и усиление бетонных элементов, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы применяем только проверенные материалы и современное оборудование, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех работ. Все наши проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Личный подход:
Каждому клиенту мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Наша цель – чтобы результат нашей работы соответствовал вашим запросам и желаниям.
Зачем обращаться в Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы найдете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех задач в сроки, установленные договором и с соблюдением всех правил и норм. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете быть спокойны, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы готовы предоставить консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Звоните нам, чтобы обсудить детали и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы сохраним и улучшим ваш дом, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Gerakl24 – ваш партнер по реставрации и ремонту домов в Красноярске и окрестностях.
Hey! I realize this is somewhat off-topic however I had to ask. Does running a well-established website like yours take a lot of work? I’m brand new to running a blog but I do write in my diary everyday. I’d like to start a blog so I can easily share my own experience and feelings online. Please let me know if you have any kind of recommendations or tips for new aspiring blog owners. Appreciate it!
доставка из китая поездом
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
http://russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru/
Hello colleagues, how is everything, and what you desire to say on the topic of this piece of writing, in my view its really remarkable in support of me.
gruppa365-diploms-srednee.ru
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in truth was once a amusement account it. Glance complex to more delivered agreeable from you! However, how could we keep in touch?
http://www.landik-diploms-srednee.ru
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; we have developed some nice methods and we are looking to exchange solutions with other folks, be sure to shoot me an email if interested.
http://www.gruppa365-diploms-srednee.ru
Психология в рассказах, истории из жизни.
Hi there to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this webpage; this web site carries remarkable and truly fine information designed for readers.
http://www.gruppa365-diploms-srednee.ru
animehangover.com
수많은 노력을 기울였고 수많은 인력과 물적 자원을 투자했습니다.
уменьшат ли ндс уменьшат ли ндс
I cherished up to you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. however, you command get got an shakiness over that you would like be handing over the following. in poor health no doubt come further earlier once more as exactly the similar nearly a lot continuously within case you protect this increase.
Hello my friend! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include almost all significant infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
Greetings I am so thrilled I found your weblog, I really found you by mistake, while I was looking on Aol for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say thanks for a tremendous post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to browse it all at the moment but I have saved it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read more, Please do keep up the excellent jo.
https://barsu.by/
k8 スポーツブック
この記事のおかげで新しい視点を得ることができました。感謝します。
onair2tv.com
그는 이 Ouyang Zhi가 단순히 미치광이라는 것을 알게 되었습니다.
Теневой плинтус: стильное решение для обновления интерьера,
Советы по монтажу теневого плинтуса без дополнительной помощи,
Как использовать теневой плинтус для создания уникального интерьера,
Ретро-стиль с использованием теневых плинтусов: идеи для вдохновения,
Гармония оттенков: выбор цвета теневого плинтуса для любого интерьера,
Безопасность и стиль: почему теневой плинтус – идеальное решение для дома,
Преимущества использования теневого плинтуса с интегрированной подсветкой,
Теневой плинтус: элегантность и стиль в дизайне помещения,
Почему теневой плинтус – важная деталь в оформлении интерьера
теневой плинтус для стен теневой плинтус для стен .
Hello mates, its great article on the topic of tutoringand fully explained, keep it up all the time.
Del Mar Energy
Выбор современных мужчин – тактичные штаны, которые подчеркнут вашу индивидуальность.
Идеальный вариант для активного отдыха, тактичные штаны обеспечат вам комфорт и свободу движений.
Надежный пошив и долговечность, сделают тактичные штаны вашим незаменимым спутником.
Максимальный комфорт и стильный вид, подчеркнут вашу индивидуальность и статус.
Почувствуйте удобство и стиль в тактичных штанах, которые подчеркнут вашу силу и уверенность.
штани тактичні жіночі штани тактичні жіночі .
에그 카지노
홍치제는 옷을 입고 위령비를 살펴보는데 이 말을 듣고 용의 몸을 덜덜 떨었다.
Buying Cannabis within the country via the Telegram app
In the past few years, ordering weed using Telegram has become very popular and has revolutionized the way marijuana is purchased, provided, and the race for excellence. Every trader competes for patrons because there is no margin for mistakes. Only the best endure.
Telegrass Buying – How to Purchase via Telegrass?
Buying weed using Telegrass is remarkably simple and fast with the Telegram app. In minutes, you can have your purchase heading to your home or anywhere you are.
All You Need:
get the Telegram app.
Quickly register with SMS verification using Telegram (your number will not appear if you set it this way in the options to enjoy total discretion and invisibility).
Begin searching for vendors using the search engine in the Telegram app (the search bar can be found at the upper section of the app).
Once you have found a vendor, you can start communicating and begin the dialogue and buying process.
Your order is on its way to you, enjoy!
It is suggested to read the piece on our site.
Click Here
Acquire Cannabis in Israel via Telegram
Telegrass is a group system for the dispensation and selling of cannabis and other light drugs in Israel. This is achieved using the Telegram app where communications are completely encrypted. Traders on the platform provide quick cannabis shipments with the feature of providing reviews on the excellence of the product and the merchants themselves. It is estimated that Telegrass’s turnover is about 60 million NIS a month and it has been used by more than 200,000 Israelis. According to authorities sources, up to 70% of illegal drug activities within Israel was carried out via Telegrass.
The Authorities Fight
The Israeli Police are attempting to counteract marijuana trade on the Telegrass network in various methods, including using covert officers. On March 12, 2019, following an secret operation that went on about a year and a half, the authorities arrested 42 leaders of the organization, like the founder of the group who was in Ukraine at the time and was released under house arrest after four months. He was extradited to the country following a legal decision in Ukraine. In March 2020, the Central District Court determined that Telegrass could be regarded as a crime syndicate and the group’s originator, Amos Dov Silver, was indicted with managing a illegal group.
Foundation
Telegrass was established by Amos Dov Silver after finishing several prison terms for small drug trafficking. The network’s designation is derived from the merging of the words Telegram and grass. After his release from prison, Silver relocated to the United States where he launched a Facebook page for cannabis trade. The page permitted weed traders to use his Facebook wall under a fake name to promote their products. They conversed with customers by tagging his profile and even uploaded images of the material provided for sale. On the Facebook page, about 2 kilograms of marijuana were distributed every day while Silver did not participate in the trade or receive compensation for it. With the increase of the platform to about 30 marijuana traders on the page, Silver opted in March 2017 to move the business to the Telegram app called Telegrass. In a week of its foundation, thousands joined the Telegrass service. Other prominent members
Euro 2024 – Sân chơi bóng đá đỉnh cao Châu Âu
Euro 2024 (hay Giải vô địch bóng đá Châu Âu 2024) là một sự kiện thể thao lớn tại châu Âu, thu hút sự chú ý của hàng triệu người hâm mộ trên khắp thế giới. Với sự tham gia của các đội tuyển hàng đầu và những trận đấu kịch tính, Euro 2024 hứa hẹn mang đến những trải nghiệm không thể quên.
Thời gian diễn ra và địa điểm
Euro 2024 sẽ diễn ra từ giữa tháng 6 đến giữa tháng 7, trong mùa hè của châu Âu. Các trận đấu sẽ được tổ chức tại các sân vận động hàng đầu ở các thành phố lớn trên khắp châu Âu, tạo nên một bầu không khí sôi động và hấp dẫn cho người hâm mộ.
Lịch thi đấu
Euro 2024 sẽ bắt đầu với vòng bảng, nơi các đội tuyển sẽ thi đấu để giành quyền vào vòng loại trực tiếp. Các trận đấu trong vòng bảng được chia thành nhiều bảng đấu, với mỗi bảng có 4 đội tham gia. Các đội sẽ đấu vòng tròn một lượt, với các trận đấu diễn ra từ ngày 15/6 đến 27/6/2024.
Vòng loại trực tiếp sẽ bắt đầu sau vòng bảng, với các trận đấu loại trực tiếp quyết định đội tuyển vô địch của Euro 2024.
Các tin tức mới nhất
New Mod for Skyrim Enhances NPC Appearance
Một mod mới cho trò chơi The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim đã thu hút sự chú ý của người chơi. Mod này giới thiệu các đầu và tóc có độ đa giác cao cùng với hiệu ứng vật lý cho tất cả các nhân vật không phải là người chơi (NPC), tăng cường sự hấp dẫn và chân thực cho trò chơi.
Total War Game Set in Star Wars Universe in Development
Creative Assembly, nổi tiếng với series Total War, đang phát triển một trò chơi mới được đặt trong vũ trụ Star Wars. Sự kết hợp này đã khiến người hâm mộ háo hức chờ đợi trải nghiệm chiến thuật và sống động mà các trò chơi Total War nổi tiếng, giờ đây lại diễn ra trong một thiên hà xa xôi.
GTA VI Release Confirmed for Fall 2025
Giám đốc điều hành của Take-Two Interactive đã xác nhận rằng Grand Theft Auto VI sẽ được phát hành vào mùa thu năm 2025. Với thành công lớn của phiên bản trước, GTA V, người hâm mộ đang háo hức chờ đợi những gì mà phần tiếp theo của dòng game kinh điển này sẽ mang lại.
Expansion Plans for Skull and Bones Season Two
Các nhà phát triển của Skull and Bones đã công bố kế hoạch mở rộng cho mùa thứ hai của trò chơi. Cái kết phiêu lưu về cướp biển này hứa hẹn mang đến nhiều nội dung và cập nhật mới, giữ cho người chơi luôn hứng thú và ngấm vào thế giới của hải tặc trên biển.
Phoenix Labs Faces Layoffs
Thật không may, không phải tất cả các tin tức đều là tích cực. Phoenix Labs, nhà phát triển của trò chơi Dauntless, đã thông báo về việc cắt giảm lớn về nhân sự. Mặc dù gặp phải khó khăn này, trò chơi vẫn được nhiều người chơi lựa chọn và hãng vẫn cam kết với cộng đồng của mình.
Những trò chơi phổ biến
The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
Với câu chuyện hấp dẫn, thế giới sống động và gameplay cuốn hút, The Witcher 3 vẫn là một trong những tựa game được yêu thích nhất. Câu chuyện phong phú và thế giới mở rộng đã thu hút người chơi.
Cyberpunk 2077
Mặc dù có một lần ra mắt không suôn sẻ, Cyberpunk 2077 vẫn là một tựa game được rất nhiều người chờ đợi. Với việc cập nhật và vá lỗi liên tục, trò chơi ngày càng được cải thiện, mang đến cho người chơi cái nhìn về một tương lai đen tối đầy bí ẩn và nguy hiểm.
Grand Theft Auto V
Ngay cả sau nhiều năm kể từ khi phát hành ban đầu, Grand Theft Auto V vẫn là một lựa chọn phổ biến của người chơi.
Euro
Euro 2024: Đức – Nước Chủ Nhà Chắc Chắn
Đức, một quốc gia với truyền thống bóng đá vững vàng, tự hào đón chào sự kiện bóng đá lớn nhất châu Âu – UEFA Euro 2024. Đây không chỉ là cơ hội để thể hiện khả năng tổ chức tuyệt vời mà còn là dịp để giới thiệu văn hóa và sức mạnh thể thao của Đức đến với thế giới.
Đội tuyển Đức, cùng với 23 đội tuyển khác, sẽ tham gia cuộc đua hấp dẫn này, mang đến cho khán giả những trận đấu kịch tính và đầy cảm xúc. Đức không chỉ là nước chủ nhà mà còn là ứng cử viên mạnh mẽ cho chức vô địch với đội hình mạnh mẽ và lối chơi bóng đá hấp dẫn.
Bên cạnh những ứng viên hàng đầu như Đức, Pháp, Tây Ban Nha hay Bỉ, Euro 2024 còn là cơ hội để những đội tuyển nhỏ hơn như Iceland, Wales hay Áo tỏa sáng, mang đến những bất ngờ và thách thức cho các đối thủ lớn.
Đức, với nền bóng đá giàu truyền thống và sự nhiệt huyết của người hâm mộ, hứa hẹn sẽ là điểm đến lý tưởng cho Euro 2024. Khán giả sẽ được chứng kiến những trận đấu đỉnh cao, những bàn thắng đẹp và những khoảnh khắc không thể quên trong lịch sử bóng đá châu Âu.
Với sự tổ chức tuyệt vời và sự hăng say của tất cả mọi người, Euro 2024 hứa hẹn sẽ là một sự kiện đáng nhớ, đem lại niềm vui và sự phấn khích cho hàng triệu người hâm mộ bóng đá trên khắp thế giới.
Euro 2024 không chỉ là giải đấu bóng đá, mà còn là một cơ hội để thể hiện đẳng cấp của bóng đá châu Âu. Đức, với truyền thống lâu đời và sự chuyên nghiệp, chắc chắn sẽ mang đến một sự kiện hoành tráng và không thể quên. Hãy cùng chờ đợi và chia sẻ niềm hân hoan của người hâm mộ trên toàn thế giới khi Euro 2024 sắp diễn ra tại Đức!
supermoney88
выкуп авто продать авто выкуп битых авто в москве
Наш сайт эротических рассказов https://shoptop.org/ поможет тебе отвлечься от повседневной суеты и погрузиться в мир страсти и эмоций. Богатая библиотека секс историй для взрослых пробудит твое воображение и позволит насладиться каждой строкой.
sapporo88
sapporo88
Uncover Thrilling Promotions and Extra Spins: Your Ultimate Guide
At our gaming platform, we are dedicated to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of promotions and bonus spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our awesome deals and what makes them so special.
Plentiful Free Spins and Rebate Offers
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 free spins and a 75% refund with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this offer with a deposit starting from just $10. This unbelievable offer allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Promotions
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit promotion available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these promotions provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Free Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 bonus spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These bonus spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these incredible opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, cashback, or lavish deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these amazing deals, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
Captivating Advancements and Popular Games in the Realm of Interactive Entertainment
In the ever-evolving domain of digital entertainment, there’s always something innovative and thrilling on the cusp. From enhancements enhancing beloved classics to anticipated debuts in renowned brands, the gaming landscape is prospering as in current times.
Let’s take a snapshot into the latest news and some of the iconic games enthralling fans internationally.
Newest News
1. Cutting-Edge Enhancement for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim Enhances NPC Aesthetics
A freshly-launched customization for Skyrim has captured the notice of players. This customization implements lifelike heads and hair physics for each supporting characters, elevating the title’s visual appeal and engagement.
2. Total War Title Placed in Star Wars Galaxy Realm Being Developed
The Creative Assembly, acclaimed for their Total War Games series, is reportedly crafting a new experience set in the Star Wars Universe galaxy. This engaging integration has players awaiting the tactical and immersive gameplay that Total War Series releases are renowned for, ultimately located in a world distant.
3. Grand Theft Auto VI Debut Communicated for Fall 2025
Take-Two Interactive’s Chief Executive Officer has confirmed that Grand Theft Auto VI is planned to debut in Autumn 2025. With the enormous popularity of its earlier title, Grand Theft Auto V, players are anticipating to see what the forthcoming sequel of this legendary series will provide.
4. Enlargement Plans for Skull and Bones Second Season
Creators of Skull and Bones have announced amplified initiatives for the experience’s second season. This nautical adventure offers fresh features and changes, keeping fans immersed and absorbed in the realm of oceanic seafaring.
5. Phoenix Labs Faces Personnel Cuts
Sadly, not all developments is favorable. Phoenix Labs Developer, the studio behind Dauntless, has communicated substantial layoffs. Notwithstanding this difficulty, the release remains to be a renowned preference within fans, and the developer remains committed to its playerbase.
Renowned Games
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
With its immersive narrative, captivating universe, and enthralling experience, Wild Hunt remains a beloved release across enthusiasts. Its deep story and wide-ranging sandbox continue to draw fans in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077 Game
Despite a challenging arrival, Cyberpunk 2077 continues to be a eagerly awaited release. With ongoing improvements and optimizations, the experience keeps progress, offering fans a glimpse into a high-tech environment teeming with danger.
3. Grand Theft Auto V
Yet time after its debut launch, Grand Theft Auto V stays a renowned preference amidst fans. Its vast free-roaming environment, captivating experience, and multiplayer experiences keep players returning for more experiences.
4. Portal 2 Game
A classic problem-solving title, Portal is celebrated for its groundbreaking systems and ingenious environmental design. Its challenging challenges and amusing storytelling have made it a remarkable title in the gaming realm.
5. Far Cry
Far Cry Game is celebrated as among the finest entries in the universe, providing fans an nonlinear experience rife with adventure. Its immersive narrative and legendary characters have solidified its status as a beloved game.
6. Dishonored
Dishonored is acclaimed for its covert gameplay and distinctive setting. Enthusiasts embrace the role of a otherworldly eliminator, exploring a urban environment abundant with societal intrigue.
7. Assassin’s Creed
As part of the acclaimed Assassin’s Creed Franchise lineup, Assassin’s Creed is revered for its engrossing narrative, captivating gameplay, and historical worlds. It remains a remarkable experience in the series and a beloved among fans.
In summary, the realm of interactive entertainment is vibrant and constantly evolving, with innovative developments
https://formomebel.ru/divany/modulnye
anosondy anosondy
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness to your post is just cool and i can think you are an expert in this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to take hold of your RSS feed to keep updated with approaching post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please carry on the rewarding work.
вход 1go casino
купить микронаушники https://jasdam.cz/
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…
https://rybalka-v-rossii.ru – сайт о рыбалке в России, способах ловли рыб, и выборе правильных снастей.к
leebet вход lee bet
Uncover Stimulating Offers and Extra Spins: Your Definitive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are focused to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of promotions and free spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our awesome promotions and what makes them so special.
Generous Free Rounds and Rebate Bonuses
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 free spins and a 75% refund with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This incredible promotion allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Promotions
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit promotion available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” offers allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these promotions provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Free Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 bonus spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These free spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy free spins, cashback, or generous deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these awesome deals, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
Daily bonuses
Uncover Stimulating Bonuses and Extra Spins: Your Comprehensive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are focused to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of deals and free spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our incredible offers and what makes them so special.
Bountiful Free Spins and Rebate Offers
One of our standout promotions is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% cashback with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this offer with a deposit starting from just $10. This unbelievable promotion allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Bonuses
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit promotion available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these offers provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Free Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 free spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These bonus spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our bonuses come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, refund, or bountiful deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these incredible promotions, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
флешки оптом https://meflash.ru/
Cricket Affiliate: একটি অসাধারণ গেমিং অভিজ্ঞতা
ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকদের জন্য crickex একটি অসাধারণ গেমিং প্ল্যাটফর্ম যা বিনামূল্যে স্পিন, নগদ বোনাস এবং কমপ প্রদান করে। এই সাইটে নতুন ব্যবহারকারী এবং নিয়মিত গ্রাহকদের জন্য সুযোগ প্রদান করা হয় যাতে তারা বিনা খরচে খেলতে পারে।
crickex লগইন এবং crickex affiliate login করে আপনি সহজেই এই অসাধারণ অভিজ্ঞতা অংশগ্রহণ করতে পারেন। এই প্ল্যাটফর্ম খেলোয়াড়দের জন্য বিভিন্ন ধরণের বোনাস অফার করে, যা ক্লাব সদস্যদের নিয়মিত এবং সময়-সীমিত প্রচার হিসাবে প্রদান করা হয়।
ক্রিকেট অধিভুক্ত হোন এবং আপনার গেমিং অভিজ্ঞতা উন্নত করুন এবং সবচেয়ে জনপ্রিয় খেলা এবং বোনাস পেতে শুরু করুন!
বোনাস এবং প্রচার
ক্রিকেট অধিভুক্ত হওয়ার সাথে সাথে আপনি crickex থেকে নগদ বোনাস এবং বিনামূল্যে স্পিন পাবেন। এটি খেলোয়াড়দের জন্য একটি অত্যন্ত ভাল সুযোগ যারা খেলার অভিজ্ঞতা উন্নত করতে চান কিন্তু খরচ কম রাখতে চান।
এই সাইটে বিভিন্ন ধরণের বোনাস উপলব্ধ, যা ক্লাব সদস্যদের নিয়মিত এবং সময়-সীমিত প্রচার হিসাবে প্রদান করা হয়। এই বোনাসগুলি গেমারদের মধ্যে আরও উত্সাহ উৎপন্ন করতে সাহায্য করে এবং তাদের গেম খেলা সুবিধাজনক করে।
আপনি কি অপেক্ষা করছেন? এখনই crickex এ লগইন করুন এবং বোনাস এবং প্রচার পেতে শুরু করুন!
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins !
에그슬롯
아무리 세속적인 사람이라도 마음속 깊은 곳에는 이상이라는 것이 있습니다.
Wow, superb weblog format! How lengthy have you been running a blog for? you make running a blog look easy. The entire glance of your site is great, let alone the content!
https://plattevalley.newschannelnebraska.com/story/50836382/american-industrial-holding-del-mar-energy-a-leader-in-highway-construction
Engaging Breakthroughs and Renowned Games in the World of Gaming
In the dynamic domain of gaming, there’s constantly something fresh and captivating on the brink. From mods enhancing beloved staples to anticipated debuts in legendary franchises, the digital entertainment ecosystem is flourishing as before.
Here’s a glimpse into the up-to-date announcements and a few of the renowned games enthralling fans worldwide.
Up-to-Date Updates
1. New Enhancement for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim Improves NPC Aesthetics
A recent modification for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim has grabbed the interest of fans. This modification brings realistic faces and realistic hair for each non-player characters, enhancing the title’s visuals and depth.
2. Total War Games Title Set in Star Wars Universe World in Development
Creative Assembly, known for their Total War Games lineup, is allegedly creating a forthcoming release placed in the Star Wars Setting world. This thrilling collaboration has enthusiasts anticipating with excitement the analytical and engaging journey that Total War Games titles are known for, at last situated in a universe expansive.
3. GTA VI Debut Revealed for Late 2025
Take-Two’s Chief Executive Officer has announced that GTA VI is planned to debut in Q4 2025. With the overwhelming acclaim of its predecessor, Grand Theft Auto V, fans are awaiting to explore what the upcoming installment of this renowned series will offer.
4. Extension Strategies for Skull & Bones Sophomore Season
Developers of Skull and Bones have communicated expanded initiatives for the world’s Season Two. This nautical journey provides additional features and enhancements, keeping players immersed and immersed in the domain of high-seas piracy.
5. Phoenix Labs Studio Faces Staff Cuts
Disappointingly, not every announcements is favorable. Phoenix Labs, the team responsible for Dauntless Experience, has disclosed large-scale personnel cuts. Despite this difficulty, the title continues to be a beloved choice across gamers, and the team stays focused on its community.
Iconic Games
1. Wild Hunt
With its compelling narrative, engrossing domain, and engaging journey, Wild Hunt remains a cherished game across enthusiasts. Its intricate experience and wide-ranging nonlinear world keep to captivate enthusiasts in.
2. Cyberpunk
In spite of a problematic release, Cyberpunk 2077 Game keeps a eagerly awaited title. With continuous updates and enhancements, the game persists in improve, providing fans a perspective into a cyberpunk world teeming with peril.
3. Grand Theft Auto 5
Still time after its original release, Grand Theft Auto V keeps a popular selection amidst enthusiasts. Its sprawling nonlinear world, engaging narrative, and multiplayer features continue to draw enthusiasts revisiting for more explorations.
4. Portal Game
A renowned brain-teasing title, Portal 2 is praised for its innovative systems and ingenious environmental design. Its intricate conundrums and clever dialogue have made it a exceptional game in the gaming realm.
5. Far Cry Game
Far Cry 3 Game is acclaimed as a standout games in the universe, delivering gamers an nonlinear exploration filled with danger. Its engrossing narrative and legendary personalities have solidified its place as a fan favorite game.
6. Dishonored Game
Dishonored Series is celebrated for its stealthy gameplay and unique world. Fans embrace the character of a otherworldly assassin, exploring a metropolitan area teeming with societal danger.
7. Assassin’s Creed 2
As part of the iconic Assassin’s Creed Series franchise, Assassin’s Creed 2 is cherished for its compelling narrative, enthralling systems, and era-based settings. It continues to be a exceptional game in the collection and a beloved amidst fans.
In final remarks, the realm of interactive entertainment is flourishing and fluid, with new developments
Are you looking for reliable and fast proxies? https://fineproxy.org/account/aff.php?aff=29 It offers a wide range of proxy servers with excellent speed and reliability. Perfect for surfing, scraping and more. Start right now with this link: FineProxy.org . Excellent customer service and a variety of tariff plans!
https://proauto.kyiv.ua здесь вы найдете обзоры и тест-драйвы автомобилей, свежие новости автопрома, обширный автокаталог с характеристиками и ценами, полезные советы по уходу и ремонту, а также активное сообщество автолюбителей. Присоединяйтесь к нам и оставайтесь в курсе всех событий в мире автомобилей!
এক রোমাঞ্চকর খেলা এবং জনপ্রিয় বোনাস
বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় ক্রিকেট ফেডারেশন এর সম্মুখীন অংশগ্রহণের প্রস্তাবনা পান, আমরা আনন্দিত এবং অপেক্ষায় আছি যে সম্মুখীন খেলা এবং অনেক সুযোগ প্রদান করা হয়েছে। আমরা আপনাকে একটি অদ্ভুত স্বাগত বোনাসের সুযোগ প্রদান করতে চাই, যা আপনি প্রথম আমানতে 200% পাবেন। এছাড়াও, আমরা সাপ্তাহিক এফবি শেয়ার করে ১০০ টাকা বোনাস প্রদান করি এবং প্রতিদিন ১০০% বোনাস প্রদান করা হয়। এই সময়ে আমরা আমাদের সবচেয়ে বেশি খেলা এবং জনপ্রিয় খেলা – ব্যাকারাট, লাইভশো, ফিশিং, এবং স্লট আমাদের নিখুঁতভাবে চেষ্টা করি।
আমাদের ক্রিকেট এক্সচেঞ্জ অংশগ্রহণ করে আপনি এই সব আনন্দ এবং বোনাস থেকে উপভোগ করতে পারেন। আমাদের অনেক উচ্চমানের খেলা এবং সাথেই জনপ্রিয় খেলা সহ বিভিন্ন বোনাস প্রদান করা হয়েছে এবং সাথেই অনেক আরও আকর্ষণীয় বোনাস আপনাকে আশা করছি।
আমাদের সাথে যোগাযোগ করুন cricket affiliate প্রোগ্রামে অংশগ্রহণ করতে এবং সরাসরি crickex affiliate login এবং crickex login করুন। সাথেই আপনি 9wicket খেলার অনুভব করতে পারেন এবং এটি অপূর্ব এবং রোমাঞ্চকর হয়ে উঠবে। তাহলে, আপনি কি অপেক্ষা করছেন? এখনই যোগ দিন এবং সবচেয়ে জনপ্রিয় খেলা এবং স্বাগত বোনাস পেতে শুরু করুন!
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins !
https://autoclub.kyiv.ua узнайте все о новых моделях, читайте обзоры и тест-драйвы, получайте советы по уходу за авто и ремонтам. Наш автокаталог и активное сообщество автолюбителей помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций.
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious knowledge about unexpected emotions.
Venice video production company in Italy
https://ktm.org.ua/ у нас вы найдете свежие новости, аналитические статьи, эксклюзивные интервью и мнения экспертов. Будьте в курсе событий и тенденций, следите за развитием ситуации в реальном времени. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу читателей!
https://mostmedia.com.ua мы источник актуальных новостей, аналитики и мнений. Получайте самую свежую информацию, читайте эксклюзивные интервью и экспертные статьи. Оставайтесь в курсе мировых событий и тенденций вместе с нами. Присоединяйтесь к нашему информационному сообществу!
sunmory33
sunmory33
Founded in Texas in 2002, https://southeast.newschannelnebraska.com/story/50826769/del-mar-energy-from-humble-beginnings-to-an-energy-market-leader quickly transformed into one of the leading players in the energy market, oil and gas extraction, road construction
बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो पर अन्य रोमांचक गेम्स का आनंद
ऑनलाइन कैसीनो में बैकारेट, पोकर और क्रैप्स जैसे गेम भी बहुत लोकप्रिय और उत्साहजनक हैं। बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो इन सभी गेम्स के विभिन्न वेरिएंट्स प्रदान करता है, जो खिलाड़ियों को अनूठा और रोमांचक अनुभव प्रदान करते हैं।
बैकारेट:
बैकारेट एक उच्च-श्रेणी का कार्ड गेम है जो सादगी और रोमांच का अद्भुत मिश्रण प्रदान करता है। बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो पर उपलब्ध बैकारेट वेरिएंट्स में पंटो बंको और लाइव बैकारेट शामिल हैं।
पंटो बंको बैकारेट का सबसे सामान्य रूप है, जहां खेल का लक्ष्य 9 के करीब पहुंचना होता है। वहीं, लाइव बैकारेट लाइव डीलर के साथ खेला जाता है और खिलाड़ियों को असली कैसीनो जैसा अनुभव प्रदान करता है।
पोकर:
पोकर एक रणनीतिक और कौशल-आधारित कार्ड गेम है जो खिलाड़ियों के बीच अत्यधिक लोकप्रिय है। बेटवीसा पर आप टेक्सास होल्ड’एम और ओमाहा पोकर जैसे विभिन्न पोकर वेरिएंट्स खेल सकते हैं।
टेक्सास होल्ड’एम सबसे लोकप्रिय पोकर वेरिएंट है, जिसमें दो निजी और पांच सामुदायिक कार्ड का उपयोग किया जाता है। ओमाहा पोकर भी टेक्सास होल्ड’एम के समान है, लेकिन इसमें चार निजी और पांच सामुदायिक कार्ड होते हैं।
क्रैप्स:
क्रैप्स एक डाइस गेम है जो तेज गति और उत्साह से भरा होता है। यह गेम भाग्य और रणनीति का मिश्रण है, जिसमें खिलाड़ियों को विभिन्न प्रकार की शर्तें लगाने का मौका मिलता है। बेटवीसा इंडिया में आप इस रोमांचक गेम का आनंद ले सकते हैं।
बेटवीसा लॉगिन करके या बेटवीसा ऐप डाउनलोड करके आप इन दिलचस्प और चुनौतीपूर्ण गेम्स का आनंद ले सकते हैं। चाहे आप बैकारेट की सादगी का मजा लेना चाहते हों या पोकर की रणनीतिक गहराई को समझना चाहते हों, बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो आपके लिए सबकुछ प्रदान करता है।
इन गेम्स को खेलकर आप अपने ऑनलाइन कैसीनो अनुभव को और भी रोमांचक बना सकते हैं। इसलिए, बेटवीसा इंडिया में जाकर इन गेम्स का आनंद लेना न भूलें!
Betvisa Bet
Betvisa Bet | Catch the BPL Excitement with Betvisa!
Hunt for ₹10million! | Enter the BPL at Betvisa and chase a staggering Bounty.
Valentine’s Boost at Visa Bet! | Feel the rush of a 143% Love Mania Bonus .
predict BPL T20 outcomes | score big rewards through Betvisa login!
#betvisa
Betvisa bonus Win! | Leverage your 10 free spins to possibly win $8,888.
Share and Earn! | win ₹500 via the Betvisa app download!
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/hi
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisaapp #betvisaIndia
Sign-Up Jackpot! | Register at Betvisa India and win ₹8,888.
Double your play! | with a ₹1,000 deposit and get ₹2,000 free at Betvisa online!
Download the Betvisa download today and don’t miss out on the action!
5 라이온스 메가웨이즈
그는 또한 Qi Guogong이 마지막 사람임에 틀림없다고 생각했습니다.
sunmory33
sunmory33
https://kursovyemetrologiya.ru
Betvisa Casino: Unlocking Unparalleled Bonuses for Philippine Gamblers
The world of online gambling has witnessed a remarkable surge in popularity, and Betvisa Casino has emerged as a premier destination for players in the Philippines. With its user-friendly platform and a diverse selection of games, Betvisa Casino has become the go-to choice for both seasoned gamblers and newcomers alike.
One of the standout features of Betvisa Casino is its generous bonus offerings, which can significantly enhance the overall gaming experience for players in the Philippines. These bonuses not only provide additional value but also increase the chances of winning big.
For first-time players, Betvisa Casino offers a tempting welcome bonus that can give a substantial boost to their initial bankroll. This bonus allows players to explore the platform’s vast array of games, from thrilling slot titles to immersive live casino experiences, with the added security of a financial cushion.
Existing players, on the other hand, can take advantage of a range of ongoing promotions and bonuses that cater to their specific gaming preferences. These may include reload bonuses, free spins, and even exclusive VIP programs that offer personalized rewards and privileges.
One of the key advantages of Betvisa Casino’s bonus offerings is their versatility. Players can utilize these bonuses across a variety of games, from the Visa Bet sports betting platform to the captivating Betvisa Casino. This flexibility allows players to diversify their gaming portfolios and experience the full breadth of what Betvisa has to offer.
Moreover, Betvisa Casino’s bonus terms and conditions are transparent and player-friendly, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to maximize your winnings or simply enhance your overall enjoyment, these bonuses can provide the extra edge you need.
As the online gambling landscape in the Philippines continues to evolve, Betvisa Casino remains at the forefront, offering an unparalleled combination of games, user-friendliness, and unbeatable bonuses. So, why not take a step into the world of Betvisa Casino and unlock a world of exciting possibilities?
Betvisa Bet | Step into the Arena with Betvisa!
Spin to Win Daily at Betvisa PH! | Take a whirl and bag ?8,888 in big rewards.
Valentine’s 143% Love Boost at Visa Bet! | Celebrate romance and rewards !
Deposit Bonus Magic! | Deposit 50 and get an 88 bonus instantly at Betvisa Casino.
#betvisa
Free Cash & More Spins! | Sign up betvisa login,grab 500 free cash plus 5 free spins.
Sign-Up Fortune | Join through betvisa app for a free ?500 and fabulous ?8,888.
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/tl
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisacasino # betvisaph
Double Your Play at betvisa com! | Deposit 1,000 and get a whopping 2,000 free
100% Cock Fight Welcome at Visa Bet! | Plunge into the exciting world .Bet and win!
Jump into Betvisa for exciting games, stunning bonuses, and endless winnings!
Hi are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
lgo4d
https://fraza.kyiv.ua/ вы найдете последние новости, глубокие аналитические материалы, интервью с влиятельными личностями и экспертные мнения. Следите за важными событиями и трендами в реальном времени. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу и будьте информированы!
SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
SUPERMONEY88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di SUPERMONEY88.
Keunggulan SUPERMONEY88
SUPERMONEY88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Layanan Praktis dan Terpercaya
Selain menjadi game online terbaik, ada alasan mengapa situs SUPERMONEY88 ini sangat spesial. Kami memberikan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit yaitu dengan melakukan deposit pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dari situs game online lainnya. Ini membuat situs kami menjadi salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda bisa melakukan deposit pulsa menggunakan E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kami juga terkenal sebagai agen game online terpercaya. Kepercayaan Anda adalah prioritas kami, dan itulah yang membuat kami menjadi agen game online terbaik sepanjang masa.
Kemudahan Bermain Game Online
Permainan game online di SUPERMONEY88 memudahkan Anda untuk memainkannya dari mana saja dan kapan saja. Anda tidak perlu repot bepergian lagi, karena SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan beragam jenis game online. Kami juga memiliki jenis game online yang dipandu oleh host cantik, sehingga Anda tidak akan merasa bosan.
https://7krasotok.com здесь вы найдете статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Читайте советы экспертов, участвуйте в обсуждениях и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу женщин, стремящихся к совершенству!
BATA4D
I was more than happy to seek out this net-site.I wanted to thanks to your time for this glorious read!! I positively enjoying each little little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you blog post.
https://superwoman.kyiv.ua вы на нашем надежном гиде в мире женской красоты и стиля жизни! У нас вы найдете актуальные статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье, а также советы по саморазвитию и карьерному росту. Присоединяйтесь к нам и обретайте новые знания и вдохновение каждый день!
решения задач на заказ https://resheniezadachmatematika.ru/
라이즈 오브 올림푸스
Zhu Houzhao는 편리하게 “잠깐만, 때가되면 돌아가서 처리하겠습니다. “라고 말했습니다.
заказать курсовую онлайн https://kursovyebankovskoe.ru/
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
keen capital growth
What is ProNerve 6? ProNerve 6 is your complete arrangement made to address the multifaceted necessities of nerve wellbeing
Больше интересной информации о строительстве и ремонте можно прочитать на сайте https://stroyka-gid.ru. Только самые популярные статьи и обзоры процесса ремонта помещений и строительства зданий.
Definitely imagine that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the web the easiest thing to have in mind of. I say to you, I definitely get irked whilst other folks consider worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also outlined out the whole thing with no need side effect , people can take a signal. Will probably be again to get more. Thanks
Консультация по оптимизации продвижению.
Информация о том как взаимодействовать с низкочастотными ключевыми словами и как их подбирать
Подход по работе в конкурентоспособной нише.
Обладаю регулярных сотрудничаю с 3 организациями, есть что рассказать.
Посмотрите мой досье, на 31 мая 2024г
количество выполненных работ 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация проходит в устной форме, никаких скринов и отчетов.
Время консультации указано 2 часа, но по реально всегда на контакте без строгой привязки ко времени.
Как работать с софтом это уже иначе история, консультация по использованию ПО договариваемся отдельно в отдельном кворке, узнаем что необходимо при коммуникации.
Всё спокойно на без напряжения не торопясь
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны контакты от телеграмм канала для коммуникации.
общение только в устной форме, общаться письменно нету времени.
Сб и Воскресенье нерабочие дни
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you¦ve on this blog. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What a great site.
smm provider spotify plays smm panel
smm panel smm panel
Whats Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & aid different customers like its aided me. Great job.
music promotion free soundcloud plays
Heya! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any trouble with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any methods to stop hackers?
문 프린세스 100
그들은 자신에게 죄를 지으라는 폐하의 명령에 동의하지 않기 때문에 설득할 수 없습니다.
vavada казино как отыграть бонус maneylocky space
стратегия продвижения сайта
Советы по сео стратегии продвижению.
Информация о том как управлять с низкочастотными запросами запросами и как их определять
Подход по действиям в конкурентоспособной нише.
Имею постоянных клиентов работаю с несколькими фирмами, есть что рассказать.
Посмотрите мой аккаунт, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём завершённых задач 2181 только здесь.
Консультация только в устной форме, никаких снимков с экрана и отчётов.
Длительность консультации указано 2 ч, но по реально всегда на доступен без твердой привязки к графику.
Как работать с софтом это уже отдельная история, консультация по использованию ПО обсуждаем отдельно в другом услуге, определяем что требуется при общении.
Всё спокойно на без напряжения не торопясь
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от телеграмм канала для коммуникации.
коммуникация только устно, вести переписку не хватает времени.
субботы и воскресенья выходные
такси заказать эконом недорого телефон сколько будет стоить такси
https://cleanprofispb.ru/
заказать такси дешево заказ такси в новочеркасске
решение задач на заказ https://resheniye-zadach7.ru заказать онлайн
white maengda купить лофофору
https://mashable.com/article/artist-vandalizes-snapchat-ar-jeff-coons-collab
rivea corymbosa купить ayahuasca купить
statistik liga 1
Motivasi dari Ucapan Taylor Swift: Harapan dan Kasih dalam Lagu-Lagunya
Taylor Swift, seorang musisi dan komposer terkenal, tidak hanya terkenal karena lagu yang elok dan vokal yang nyaring, tetapi juga sebab kata-kata karyanya yang penuh makna. Dalam lirik-liriknya, Swift sering menggambarkan berbagai aspek kehidupan, mulai dari kasih hingga rintangan hidup. Berikut adalah beberapa petikan inspiratif dari lagu-lagunya, beserta artinya.
“Mungkin yang paling baik belum tiba.” – “All Too Well”
Penjelasan: Bahkan di masa-masa sulit, selalu ada secercah harapan dan kemungkinan untuk masa depan yang lebih baik.
Kutipan ini dari lagu “All Too Well” membuat kita ingat bahwa walaupun kita mungkin berhadapan dengan masa sulit sekarang, selalu ada peluang bahwa masa depan bisa mendatangkan sesuatu yang lebih baik. Ini adalah pesan harapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk tetap bertahan dan tidak putus asa, karena yang terbaik mungkin belum datang.
“Aku akan terus bertahan karena aku tidak bisa melakukan segala sesuatu tanpamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Memperoleh cinta dan dukungan dari pihak lain dapat menghadirkan kita kekuatan dan kemauan keras untuk melanjutkan lewat kesulitan.
paito macau
Ashley JKT48: Idola yang Bersinar Cemerlang di Langit Idol
Siapa Ashley JKT48?
Siapa sosok muda talenta yang menyita perhatian sejumlah besar penyuka musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Dialah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan nama bekennya, Ashley JKT48. Bergabung dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan segera menjadi salah satu anggota paling favorit.
Biografi
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berketurunan darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia memulai kariernya di industri hiburan sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum kemudian masuk dengan JKT48. Kepribadiannya yang ceria, nyanyiannya yang kuat, dan keterampilan menari yang mengesankan menjadikannya idol yang sangat dicintai.
Penghargaan dan Apresiasi
Popularitas Ashley telah diakui melalui aneka award dan nominasi. Pada tahun 2021, ia memenangkan penghargaan “Anggota Paling Populer JKT48” di ajang JKT48 Music Awards. Ia juga dinobatkan sebagai “Idol Tercantik se-Asia” oleh sebuah majalah online pada tahun 2020.
Peran dalam JKT48
Ashley menjalankan posisi krusial dalam group JKT48. Ia adalah member Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai dancer utama dan penyanyi utama. Ashley juga menjadi anggota dari unit sub “J3K” dengan Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Perjalanan Individu
Di luar aktivitasnya di JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karir individu. Ia telah meluncurkan beberapa lagu single, termasuk “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah berkolaborasi bersama artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Hidup Personal
Selain dunia panggung, Ashley dikenali sebagai sosok yang rendah hati dan bersahabat. Beliau menikmati menyisihkan waktu bersama keluarga dan kawan-kawannya. Ashley juga menyukai kesukaan melukis dan photography.
купить диплом университета
по ссылке
internet casinos
Digital Casinos: Innovation and Advantages for Contemporary Community
Introduction
Online gambling platforms are digital sites that provide users the chance to participate in betting games such as poker, roulette, 21, and slots. Over the past few years, they have become an essential component of online entertainment, offering numerous advantages and opportunities for players globally.
Accessibility and Convenience
One of the primary benefits of digital casinos is their availability. Users can enjoy their preferred games from anywhere in the world using a computer, tablet, or mobile device. This saves hours and funds that would otherwise be used traveling to traditional casinos. Furthermore, 24/7 access to games makes online gambling sites a easy option for individuals with hectic schedules.
Range of Games and Experience
Digital casinos offer a wide range of games, enabling all users to find something they like. From traditional table activities and table games to slots with diverse concepts and progressive jackpots, the diversity of games ensures there is an option for every taste. The option to play at different proficiencies also makes digital gambling sites an perfect location for both beginners and seasoned gamblers.
Economic Benefits
The online casino sector contributes greatly to the economic system by creating jobs and producing revenue. It backs a wide range of careers, including programmers, customer support representatives, and advertising professionals. The income produced by online casinos also contributes to tax revenues, which can be allocated to support public services and infrastructure projects.
Advancements in Technology
Online gambling sites are at the cutting edge of tech innovation, constantly integrating new innovations to enhance the gaming entertainment. High-quality graphics, real-time dealer games, and virtual reality (VR) gambling sites provide engaging and realistic playing experiences. These innovations not only improve player satisfaction but also expand the limits of what is achievable in online leisure.
Responsible Gambling and Support
Many online gambling sites promote responsible gambling by offering tools and resources to help users manage their betting activities. Features such as deposit limits, self-exclusion options, and access to assistance programs guarantee that players can engage in gaming in a secure and controlled environment. These measures show the sector’s commitment to encouraging safe gaming habits.
Community Engagement and Community
Digital casinos often offer social features that allow players to connect with each other, forming a feeling of belonging. Group games, chat functions, and networking integration enable players to network, share experiences, and build friendships. This social aspect improves the overall gaming entertainment and can be particularly beneficial for those seeking social interaction.
Summary
Digital casinos provide a diverse variety of benefits, from availability and convenience to financial benefits and technological advancements. They provide varied gaming options, support responsible gambling, and promote community engagement. As the industry continues to evolve, online gambling sites will probably remain a significant and beneficial force in the realm of digital entertainment.
slots machines
Complimentary Slot-Based Games: Entertainment and Rewards for People
Preface
Slot machines have historically been a fixture of the casino sensation, delivering customers the chance to secure major payouts with merely the trigger of a lever or the press of a control. In the modern era, slot-based activities have additionally grown to be popular in online wagering environments, constituting them accessible to an even more broader population.
Fun Element
Slot-related offerings are developed to be fun and absorbing. They showcase lively graphics, electrifying auditory elements, and various concepts that match a comprehensive selection of interests. Whether users experience classic fruit-based imagery, thrill-based slot-based games, or slot-based games derived from iconic movies, there is something for everyone. This variety guarantees that users can constantly identify a game that suits their tastes, offering periods of amusement.
Easy to Play
One of the most prominent upsides of slot machines is their uncomplicated nature. Differently from specific gambling games that necessitate skill, slot-based activities are easy to understand. This establishes them available to a comprehensive audience, involving beginners who may experience daunted by more complex offerings. The straightforward quality of slot machines gives users to relax and savor the experience without fretting about complicated guidelines.
Mental Reprieve and Refreshment
Engaging with slot-based games can be a excellent way to destress. The routine-based character of spinning the symbols can be tranquil, delivering a cognitive respite from the challenges of regular existence. The prospect for earning, even when it amounts to just minor sums, injects an component of anticipation that can enhance customers’ emotions. Numerous individuals determine that partaking in slot-based activities assists them decompress and shift their focus away from their worries.
Shared Experiences
Slot-based games also offer chances for social connection. In physical wagering facilities, players often group by slot-related offerings, supporting co-participants on and rejoicing in wins in unison. Online slots have also included collaborative elements, such as rankings, giving participants to network with others and communicate their experiences. This sense of togetherness enhances the total gaming encounter and can be specifically rewarding for users aiming for group-based connection.
Monetary Upsides
The widespread appeal of slot machines has considerable fiscal rewards. The domain generates positions for activity engineers, gaming workforce, and customer support agents. Also, the earnings produced by slot-related offerings contributes to the financial system, providing budgetary incomes that support community initiatives and networks. This monetary effect expands to both physical and virtual casinos, making slot-based activities a valuable part of the interactive field.
Intellectual Advantages
Interacting with slot-based activities can as well produce mental benefits. The game necessitates users to reach prompt determinations, discern trends, and manage their risking methods. These cerebral undertakings can enable keep the intellect acute and bolster cerebral functions. Specifically for elderly individuals, participating in cognitively challenging engagements like engaging with slot-based games can be beneficial for preserving intellectual capacity.
Reachability and User-Friendliness
The advent of internet-based wagering environments has constituted slot-based games more reachable than ever. Users can experience their most liked slot-based activities from the convenience of their personal dwellings, employing computers, pads, or mobile phones. This user-friendliness enables individuals to partake in whenever and no matter the location they desire, devoid of the requirement to commute to a traditional gaming venue. The availability of no-cost slots likewise allows customers to savor the experience without any monetary investment, establishing it an welcoming kind of entertainment.
Conclusion
Slot machines grant a wealth of rewards to individuals, from sheer pleasure to cerebral benefits and communal participation. They offer a secure and free-of-charge way to savor the thrill of slot-based activities, making them a valuable complement to the realm of digital recreation.
Whether you’re looking to destress, hone your cognitive abilities, or just derive entertainment, slot machines are a superb option that continues to delight players throughout.
Prominent Benefits:
– Slot-related offerings provide pleasure through lively graphics, immersive audio, and varied motifs
– Ease of play constitutes slot-based activities approachable to a extensive population
– Engaging with slot-based games can deliver destressing and mental advantages
– Collaborative aspects enhance the total interactive interaction
– Digital availability and no-cost possibilities constitute slot-based games welcoming kinds of entertainment
In conclusion, slot-based activities constantly offer a diverse collection of rewards that appeal to players across. Whether desiring sheer pleasure, cognitive challenge, or social participation, slot-related offerings continue to be a wonderful option in the transforming realm of online leisure.
Internet-based Gaming Site Real Money: Rewards for Customers
Preface
Digital casinos providing real money games have obtained immense widespread appeal, granting users with the possibility to obtain cash payouts while experiencing their most preferred gambling activities from abode. This article examines the rewards of digital gaming site paid experiences, underscoring their constructive impact on the leisure domain.
Convenience and Accessibility
Virtual wagering environment for-profit games present simplicity by enabling participants to reach a extensive variety of games from any place with an online access. This eradicates the requirement to commute to a traditional casino, saving time. Virtual wagering environments are as well present at all times, permitting participants to engage with at their convenience.
Range of Possibilities
Internet-based gambling platforms offer a more comprehensive variety of games than land-based wagering facilities, involving slot-related offerings, blackjack, wheel of fortune, and card games. This diversity permits participants to experiment with different offerings and identify novel most cherished, bolstering their total leisure interaction.
Rewards and Discounts
Digital gaming sites grant considerable perks and advantages to lure and retain customers. These perks can involve sign-up incentives, free spins, and cashback offers, delivering additional value for customers. Membership systems in addition reward users for their continued business.
Capability Building
Playing for-profit offerings in the digital realm can help participants acquire skills such as decision-making. Offerings like 21 and card games necessitate customers to render choices that can shape the result of the offering, enabling them refine decision-making abilities.
Social Interaction
ChatGPT l Валли, 6.06.2024 4:08]
Virtual wagering environments deliver prospects for social participation through discussion forums, discussion boards, and video-streamed games. Customers can communicate with their peers, exchange tips and tactics, and in certain cases establish interpersonal bonds.
Economic Benefits
The virtual wagering sector produces opportunities and lends to the fiscal landscape through budgetary incomes and regulatory costs. This monetary influence rewards a extensive variety of professions, from game creators to client assistance agents.
Summary
Online casino paid offerings provide numerous upsides for customers, incorporating ease, range, rewards, capability building, shared experiences, and monetary rewards. As the sector steadfastly evolve, the broad acceptance of online casinos is expected to expand.
No-Cost Slot-Based Experiences: A Enjoyable and Rewarding Encounter
Free virtual wagering games have evolved into steadily sought-after among players seeking a thrilling and secure entertainment experience. These activities present a wide variety of upsides, making them a selected alternative for several. Let’s investigate the extent to which no-cost virtual wagering games can advantage customers and the motivations behind they are so comprehensively relished.
Fun Element
One of the primary factors players experience engaging with no-cost virtual wagering games is for the entertainment value they grant. These activities are created to be compelling and thrilling, with lively graphics and absorbing soundtracks that bolster the comprehensive leisure experience. Regardless of whether you’re a leisure-oriented customer wanting to while away the hours or a enthusiastic interactive entertainment participant desiring anticipation, no-cost virtual wagering offerings present pleasure for everyone.
Capability Building
Engaging with complimentary slot-based activities can as well enable acquire valuable faculties such as problem-solving. These offerings require players to render quick selections contingent on the cards they are acquired, enabling them enhance their decision-making abilities and intellectual prowess. Also, participants can investigate different tactics, honing their skills absent the chance of negative outcome of losing paid funds.
Simplicity and Approachability
A further advantage of complimentary slot-based games is their user-friendliness and reachability. These games can be played online from the ease of your own home, excluding the need to journey to a traditional gambling establishment. They are in addition available at all times, permitting players to relish them at whatever period that aligns with them. This convenience establishes free poker machine offerings a popular alternative for customers with demanding agendas or those looking for a swift leisure fix.
Interpersonal Connections
Many free poker machine activities likewise provide social functions that permit players to connect with fellow users. This can feature chat rooms, online communities, and collaborative configurations where players can challenge each other. These shared experiences contribute an extra dimension of enjoyment to the gaming interaction, giving customers to engage with fellow individuals who have in common their interests.
Tension Alleviation and Psychological Rejuvenation
Engaging with free poker machine offerings can likewise be a wonderful method to decompress and de-stress after a long duration. The simple engagement and calming sound effects can assist reduce tension and anxiety, providing a much-needed break from the pressures of typical life. Furthermore, the thrill of earning online rewards can elevate your mood and result in you feeling revitalized.
Conclusion
Gratis electronic gaming activities present a wide selection of benefits for users, encompassing amusement, proficiency improvement, user-friendliness, shared experiences, and worry mitigation and decompression. Whether you’re seeking to enhance your interactive faculties or simply enjoy yourself, no-cost virtual wagering experiences deliver a profitable and enjoyable experience for players of every stages.
акриловый сайдинг цена фиброцементный сайдинг купить цены
에그벳300
“잠깐, 아까 뭐라고 했어?” 왕부시의 얼굴이 살짝 변했다.
娛樂城官網
娛樂城官網
сайдинг акриловый для наружной отделки цена купить сайдинг недорого
Hi there i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anyplace, when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also make comment due to this good paragraph.
facefam.com/read-blog/13_why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-declining-today.html
web011.dmonster.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=b0501&wr_id=181555
stephenireland.com/charity/details.php?10-000-RAISED-FOR-FRANCIS-HOUSE-CHILDREN-S-HOSPICE-3
mystroycenter.ru/page/14
http://www.tovery.net/guestbook.asp?user=okokok&Page=3
Все самое интересное из мира игр https://unionbattle.ru обзоры, статьи и ответы на вопросы
Lex Casino – лицензионная новинка 2024 года, заходи сегодня и забери свой бонус 150% к первому депозиту до 30 000 рублей!
Lex Casino Регистрация и Бонус по ссылке – https://lex-casino-01.ru/
Промокод: BEZDEPCAS
Играйте в лучшие слоты с эксклюзивными бонусами на депозит и недельным кешбэком. Начните выигрывать уже сейчас!
сайт битц казино
сайт bitz casino
psis
Instal Perangkat Lunak 888 dan Peroleh Bonus: Instruksi Singkat
**Program 888 adalah pilihan sempurna untuk Anda yang membutuhkan keseruan berjudi digital yang menggembirakan dan bermanfaat. Bersama hadiah setiap hari dan kemampuan memikat, aplikasi ini menawarkan memberikan keseruan main optimal. Disini petunjuk pendek untuk memanfaatkan pemakaian App 888.
Pasang dan Awali Menang
Layanan Terdapat:
Perangkat Lunak 888 memungkinkan di-download di Sistem Android, iOS, dan PC. Mulai bermain dengan mudah di media apa saja.
Keuntungan Harian dan Imbalan
Imbalan Masuk Tiap Hari:
Mendaftar pada hari untuk mengambil imbalan sampai 100K pada hari ketujuh.
Rampungkan Aktivitas:
Ambil peluang undi dengan menuntaskan pekerjaan terkait. Masing-masing tugas menyediakan Pengguna sebuah opsi undi untuk mengklaim keuntungan hingga 888K.
Pengumpulan Sendiri:
Imbalan harus diklaim manual di melalui perangkat lunak. Jangan lupa untuk meraih hadiah saban periode agar tidak kadaluwarsa.
Mekanisme Undi
Opsi Undi:
Satu periode, Para Pengguna bisa meraih 1 peluang undi dengan menyelesaikan pekerjaan.
Jika kesempatan undi berakhir, tuntaskan lebih banyak tugas untuk mendapatkan tambahan opsi.
Batas Imbalan:
Klaim imbalan jika akumulasi pengeretan Para Pengguna melampaui 100K dalam 1 hari.
Ketentuan Pokok
Pengambilan Bonus:
Keuntungan harus dikumpulkan mandiri dari perangkat lunak. Jika tidak, bonus akan secara otomatis diserahkan ke akun Para Pengguna setelah 1 hari.
Syarat Pertaruhan:
Hadiah memerlukan paling tidak sebuah bertaruh aktif untuk digunakan.
Ringkasan
Program 888 menghadirkan keseruan berjudi yang menggembirakan dengan bonus besar. Instal app hari ini dan nikmati kemenangan signifikan tiap waktu!
Untuk data lebih lanjut tentang promosi, deposit, dan sistem undangan, cek halaman utama app.
I have read several good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you put to make such a fantastic informative website.
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know
of any please share. Appreciate it! You can read similar text here: All escape rooms
Hi to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this web page, and your views are good designed for new visitors.
comedyforme.ru/prodazha-diplomov-lyubogo-uchebnogo-zavedeniya-rossii
lunarys.com.br/blog/suplemento-alimentar-hair-supply
ks-elektronika.pl/product_ask_avaliable.php?products_id=71
prachuabwit.ac.th/krusuriya/modules.php?name=Journal&file=display&jid=12564
http://www.ba98.org/contact.php?sujet=6
купить диплом провизора http://www.6landik-diploms.com
гарантированно,
Современное оборудование и материалы, для вашего уверенного улыбки,
Современные методы стоматологии, для вашей улыбки,
Комфортные условия и дружественный персонал, для вашего комфорта и уверенности,
Инновационные методы стоматологии, для вашего комфорта и уверенности,
Индивидуальный план лечения и профилактики, для вашего долгосрочного удовлетворения,
Индивидуальный план лечения для каждого пациента, для вашего комфорта и удовлетворения
безболісне лікування зубів https://stomatologichnaklinikafghy.ivano-frankivsk.ua/ .
купить диплом судоводителя https://6landik-diploms.com/
mantul88
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an extremely long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say fantastic blog!
instise.pl/?page_id=3
crosspromote.click/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/name_Alanpoe/page_7/
vkmonline.com/users/blogs/833001?page=2
medinkur.ru/index.php
nipponsword.ru/profile.php?lookup=23413
poker game free
Exploring the Realm of No-Cost Poker
Beginning
Currently, card games have developed into widely accessible entertainment choices. For individuals looking for a free way to play the game of poker, complimentary poker applications provide a thrilling venture. This piece examines the advantages and factors for which complimentary poker has turned into a popular option for various enthusiasts.
Advantages of Free Poker Games
Cost-Free Entertainment
One of the most inviting aspects of complimentary poker is that it offers users with no-cost entertainment. There is no demand to put in cash to enjoy the card game, creating it reachable to everybody.
Enhancing Abilities
Experiencing free poker games allows users to hone their skills without a single monetary danger. It is a ideal environment for learners to get the rules and techniques of the game.
Community Engagement
Many complimentary poker sites provide opportunities for interactive interaction. Players can communicate with fellow players, exchange strategies, and play amicable tournaments.
Why Complimentary Poker is Favored
Availability
Complimentary poker are broadly attainable, enabling users from various walks of life to engage in the card game.
No Fiscal Risk
With poker game free, there is no financial risk, rendering it a secure choice for players who seek to experience poker without putting in funds.
Variety of Games
No-cost poker websites offer a wide array of gameplays, ensuring that players can continually uncover an option that fits their tastes.
Final Thoughts
Poker game free gives a amusing and available method for users to engage in the game of poker. With no financial risk, possibilities for enhancing abilities, and extensive game options, it is understandable that countless users prefer complimentary poker as their go-to gaming possibility.
koko303
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bersinar Cemerlang di Langit Idol
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapa sosok muda berbakat yang mencuri perhatian banyak fans musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Dialah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan pseudonimnya, Ashley JKT48. Menjadi anggota dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan segera menjadi salah satu personel paling favorit.
Riwayat Hidup
Terlahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berdarah darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Beliau mengawali perjalanannya di dunia entertainment sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum akhirnya masuk dengan JKT48. Sifatnya yang gembira, suara yang mantap, dan kemampuan menari yang mengagumkan membentuknya sebagai idola yang sangat dicintai.
Penghargaan dan Pengakuan
Popularitas Ashley telah diakui melalui aneka penghargaan dan nominasi. Pada tahun 2021, Ashley memenangkan penghargaan “Member Terpopuler JKT48” di event JKT48 Music Awards. Ia juga dinobatkan sebagai “Idol Tercantik di Asia” oleh sebuah tabloid online pada tahun 2020.
Posisi dalam JKT48
Ashley memainkan posisi penting dalam group JKT48. Ia adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berperan menjadi penari utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga menjadi member dari subunit “J3K” dengan Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karier Individu
Di luar kegiatannya bersama JKT48, Ashley juga memulai karir solo. Ia telah mengeluarkan beberapa lagu single, antara lain “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah bekerjasama bersama penyanyi lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Pribadi
Selain kancah perform, Ashley dikenal sebagai sebagai pribadi yang humble dan ramah. Beliau menikmati menyisihkan masa bersama keluarga dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki kegemaran melukis dan photography.
dolar138
Instal Perangkat Lunak 888 dan Peroleh Bonus: Petunjuk Praktis
**Program 888 adalah kesempatan unggulan untuk Kamu yang menginginkan permainan berjudi daring yang menggembirakan dan berjaya. Dengan keuntungan tiap hari dan fasilitas menarik, aplikasi ini sedia menawarkan aktivitas main unggulan. Berikut manual praktis untuk mengoptimalkan pemakaian Perangkat Lunak 888.
Instal dan Mulailah Menangkan
Sistem Tersedia:
Perangkat Lunak 888 dapat diunduh di Sistem Android, iOS, dan Windows. Mulailah main dengan praktis di gadget manapun.
Bonus Harian dan Hadiah
Bonus Mendaftar Sehari-hari:
Buka tiap hari untuk mengklaim keuntungan sebesar 100K pada masa ketujuh.
Selesaikan Aktivitas:
Raih kesempatan undian dengan mengerjakan aktivitas terkait. Satu aktivitas memberi Kamu satu kesempatan lotere untuk memenangkan imbalan sebesar 888K.
Pengumpulan Mandiri:
Bonus harus diterima langsung di dalam app. Jangan lupa untuk mengambil hadiah pada masa agar tidak habis masa berlakunya.
Sistem Pengeretan
Peluang Undian:
Masing-masing waktu, Kamu bisa mengklaim 1 peluang pengeretan dengan menuntaskan pekerjaan.
Jika kesempatan undian habis, tuntaskan lebih banyak aktivitas untuk mengklaim extra kesempatan.
Tingkat Imbalan:
Dapatkan bonus jika keseluruhan undi Kamu melampaui 100K dalam sehari.
Peraturan Esensial
Pengklaiman Keuntungan:
Keuntungan harus diambil mandiri dari program. Jika tidak, bonus akan langsung diserahkan ke akun pengguna Anda setelah satu waktu.
Syarat Taruhan:
Imbalan memerlukan setidaknya satu pertaruhan efektif untuk dimanfaatkan.
Penutup
Aplikasi 888 memberikan keseruan berjudi yang seru dengan keuntungan besar-besaran. Download aplikasi saat ini dan nikmati hadiah besar-besaran pada waktu!
Untuk informasi lebih rinci tentang penawaran, top up, dan agenda referensi, kunjungi halaman home aplikasi.
klasemen liga 1
Inspirasi dari Ucapan Taylor Swift
Penyanyi Terkenal, seorang vokalis dan komposer terkenal, tidak hanya diakui berkat lagu yang elok dan vokal yang merdu, tetapi juga sebab lirik-lirik lagunya yang sarat makna. Dalam lirik-liriknya, Swift sering melukiskan beraneka ragam aspek hidup, mulai dari cinta hingga tantangan hidup. Di bawah ini adalah sejumlah ucapan inspiratif dari karya-karya, beserta artinya.
“Mungkin yang terbaik belum datang.” – “All Too Well”
Arti: Bahkan di masa-masa sulit, selalu ada seberkas harapan dan kemungkinan untuk masa depan yang lebih baik.
Lirik ini dari lagu “All Too Well” menyadarkan kita bahwa meskipun kita mungkin berhadapan dengan masa-masa sulit saat ini, senantiasa ada kemungkinan jika hari esok akan membawa perubahan yang lebih baik. Situasi ini adalah pesan pengharapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk terus bertahan dan tidak menyerah, sebab yang terhebat mungkin belum tiba.
“Aku akan tetap bertahan sebab aku tak bisa melakukan segala sesuatu tanpamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Mendapatkan cinta dan dukungan dari orang lain dapat memberi kita tenaga dan tekad untuk melanjutkan melalui tantangan.
no deposit bonus
Internet casinos are growing more widespread, presenting various rewards to attract new users. One of the most enticing offers is the no upfront deposit bonus, a campaign that allows players to test their luck without any financial risk. This write-up looks into the advantages of no upfront deposit bonuses and emphasizes how they can boost their efficiency.
What is a No Deposit Bonus?
A no deposit bonus is a type of casino promotion where users get bonus funds or free plays without the need to submit any of their own money. This allows users to test the gaming site, test out different gaming activities and have a chance to win real prizes, all without any upfront cost.
Advantages of No Deposit Bonuses
Risk-Free Exploration
No deposit bonuses offer a risk-free opportunity to try out internet casinos. Participants can experiment with multiple slots, familiarize themselves with the casino platform, and assess the overall user experience without using their own funds. This is particularly advantageous for novices who may not be accustomed to online gambling sites.
Chance to Win Real Money
One of the most tempting aspects of no-deposit bonuses is the potential to earn real cash. While the amounts may be small, any prizes earned from the bonus can generally be withdrawn after meeting the casino’s playthrough rules. This adds an element of fun and offers a prospective financial return without any monetary outlay.
Learning Opportunity
No-deposit bonuses present a great chance to understand how various games work. Players can practice methods, get to know the rules of the slots, and develop into more skilled without being afraid of parting with their own capital. This can be especially helpful for difficult games like roulette.
Conclusion
Free bonuses deliver several upsides for users, such as risk-free investigation, the chance to win real money, and valuable training prospects. As the sector continues to evolve, the prevalence of free bonuses is set to expand.
Examining Sweepstakes Betting Sites: A Thrilling and Available Gaming Option
Overview
Promotion gambling platforms are becoming a preferred alternative for users searching for an engaging and lawful way to partake in online gambling. Differing from classic digital betting sites, contest betting sites work under distinct authorized systems, facilitating them to offer events and gifts without falling under the equivalent regulations. This exposition explores the notion of sweepstakes betting sites, their perks, and why they are drawing a increasing figure of users.
Understanding Sweepstakes Casinos
A contest betting site runs by supplying participants with digital money, which can be used to play events. Participants can earn additional virtual money or real awards, including cash. The fundamental variation from standard gaming hubs is that participants do not buy funds instantly but get it through promotional campaigns, including buying a product or taking part in a no-cost participation promotion. This model facilitates lottery casinos to work legitimately in many territories where standard digital wagering is regulated.
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me dinner due to the fact that I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to discuss this topic here on your web site.
adsauto.info/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=igasery
sohapay.com/info/vi/news/trai-nghiem-tien-ich-voi-the-gioi-the-vpbank.html
auto-dealers-script.com/gallery
bensbookmarks.com/author/bensbookmarks/page/2
http://www.catholicdioceseofaba.org/fullhomilies?sn=4
canadian pharmacy viagra without prescriptions
no prescription pharmacy viagra online without prescription
canadianpharmacy buy viagra without a prescription
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you should publish more about this issue, it might not be a taboo matter but usually folks don’t speak about these issues. To the next! Cheers!
This text is worth everyone’s attention. Where can I find out more?
http://www.salaam.co.uk/biographies/profile.php?id=144
bietthulideco.vn/biet-thu-nha-vuon-26-nv26-khu-do-thi-lideco-bac-32/
100buketov.com/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=192&show_all=yes
ravolutionfestival.com/ravolution202205hcmc/
3drus.ru/forum/topic_34713/1
play slots for real money
During today’s virtual era, the sphere of gambling activities has experienced a remarkable change, with digital gaming venues rising as the latest domain of fun and suspense.
Amidst the most mesmerizing offerings as a part of this dynamic environment are the ever-popular online slot machines, inviting customers to commence a adventure of thrilling play and the chance to obtain real money.
Internet-based slot machines have transformed into a beacon of happiness and expectation for participants spanning the world, offering an unprecedented degree of accessibility and accessibility.
By utilizing simply a few clicks, you can engross yourself in a brilliant array of reel-based concepts, every painstakingly created to stimulate your senses and maintain your anticipation of your place.
A key the principal attractions of participating in slots for tangible prizes on digital platforms is the chance to feel the thrill of possibly significant payouts. The anticipation of watching the elements rotate, the features align, and the jackpot tease can be genuinely electrifying.
Virtual gambling platforms have effortlessly embedded state-of-the-art solutions to offer a interactive interaction that is both visually enthralling and profitable.
Aside from the appeal of prospective winnings, digital reel-based offerings as well offer a level of control and management that is unmatched in the traditional wagering scenario. You can fine-tune your stakes to suit your budget, adjusting your wagers to uncover the perfect fit that matches your personal inclinations and willingness to take chances. This extent of customization equips users to grow their bankrolls and optimize their fulfillment, completely from the comfort of their personal homes.
canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store viagra 100mg without a prescription
You really make it seem really easy along with your presentation however I find this matter to be really something that I believe I would never understand. It sort of feels too complex and extremely vast for me. I am taking a look ahead to your next publish, I will try to get the hang of it!
Pro88
купить диплом в астрахани https://6landik-diploms.com
와일드 바운티 쇼다운
그는 심지어 자신이 해적들을 과소평가했다고 느꼈습니다.
canadian pharmacy viagra and cialis non perscription
247 overnight pharmacy canadian buy viagra online with no prescription
I will immediately clutch your rss as I can not to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me realize in order that I could subscribe. Thanks!
pharmacy rx one review usa no prescription generic viagra
детское такси https://taxi-novocherkassk.ru/
заказать такси эконом новочеркасск https://zakaz-taxionline.ru/
Wow, fantastic blog structure! How lengthy have you been blogging for? you make running a blog glance easy. The overall glance of your site is wonderful, as smartly as the content material!
86hm.ru/forum/flame/?topic_id=24930
scientistsufo.ru/page/14
http://www.korgforums.com/forum/phpBB2/viewtopic.php?t=129929&view=next
skazka.g-talk.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1679&p=1705
tnrevergreen.com.vn/dien-tich-tim-tuong-la-gi-mua-nha-nen-dung-cach-tinh-dien-tich-nao/
Ищете способ расслабиться и получить незабываемые впечатления? Мы https://t.me/intim_tmn72 предлагаем эксклюзивные встречи с привлекательными и профессиональными компаньонками. Конфиденциальность, комфорт и безопасность гарантированы. Позвольте себе наслаждение и отдых в приятной компании.
Hello to all, for the reason that I am truly keen of reading this blog’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It contains good information.
esitscale.com/forum/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=39193
http://www.skitour.su/member.php?u=1002&tab=activitystream&type=all&page=28
007brush.com/collections/vendors/products/sk-120mm-fan-bundle.html
portaltrav.ru/product/conditioner/wall-air-conditioners/electrolux-eacs-07hlo-n3-16y/
diplom66rus.ru/index.html
Thank you for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next write ups thank you once again.
clc.edu.pe/blog/index.php?entryid=55125&nonjscomment=1&comment_itemid=55125&comment_context=236930&comment_component=blog&comment_area=format_blog
iclicky.buzz/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/name_Alanpoe/page_5/
http://www.terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=2515
neverwinter-wiki.ru/igrovye-klassy-neverwinter/igrovoj-klass-plut-lovkach
student-news.ru/page/2
At this time it looks like Drupal is the preferred blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
http://www.camry-club.ru/member.php/61231-sonnick84?tab=activitystream&type=user&page=2
100dives.com/collections/eclipse-series/products/phanteks-eclipse-p600s-matte-white.html
irc71.ru/index.php/jomsocial/groups/viewbulletin/142-za-skolko-imenno-vozmozhno-budet-zakazat-diplom-vuza-sejchas?groupid=47
shop2.rybolov.de/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=260&show_all=yes
blackpearlbasketball.com.au/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=829712
Ищете способ расслабиться и получить незабываемые впечатления? Мы https://t.me/intim_tmn72 предлагаем эксклюзивные встречи с привлекательными и профессиональными компаньонками. Конфиденциальность, комфорт и безопасность гарантированы. Позвольте себе наслаждение и отдых в приятной компании.
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
fpcom.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=110868
nemspb.ru/objects/zhd-stantsiya-babaevo-oktyabrskoj-zheleznoj-dorogi/
newfinbiz.ru/page/13
biblelamp.ru/forum/profile.php?id=34578
fuchs-lektorat.de/47128.html?*session*id*key*=*session*id*val*
canadian pharmacy viagra without a doctor prescription
canadian pharmacy express viagra without a doctor prescription
купить справку
canadian pharmacy online viagra prescription
Can you tell us more about this? I’d love to find out some additional information.
local-urban-eats.mn.co/posts/56793349
import-moto.com/users/88?wid=3643
giaibngdaquocteu23.com/2021-10-cb-hay-trong-trong-fifa-online-4-hien-nay-keo8386/
http://www.healing-arts-nw.com/recovery-from-motor-vehicle-accidents/
asmzine.net/geekly-rewind/2019/02/17/toy-fair-2018-hasbro-transformers-siege/img_1310/
This info is worth everyone’s attention. When can I find out more?
himchistka.udm.ru/forum?%2Fforum=&%2Fforum%2F=&GuestbookItem_page=11
social.acadri.org/read-blog/8219_where-can-i-buy-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-a-bargain-price.html
girbir.com/blogs/13038/Where-can-I-buy-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-a
webnewsrealty.ru/page/13
http://www.vietnammm.com/kr/restaurants/An-Tam
https://aisory.tech – платформа для создания AI Telegram-ботов. Наделяйте своих ботов способностями к естественному диалогу, генерации уникального контента и решению аналитических задач. Простой конструктор платформы делает создание умных чат-ботов доступным для любой компании.
купить квартиру в новостройке от застройщика купить квартиру недорого
купить квартиру в казани https://kupit-kvartirukzn.ru
Euro
жк казань купить квартиру https://kvartiru-kupit-kzn.ru
купить квартиру в новостройке от застройщика купить квартиру от застройщика недорого
купить квартиру недорого https://kvartiru-kupit-kzn.ru
вайлд вест голд game
купить квартиру от застройщика недорого https://nedvizhimost16.ru
슬롯 머신 무료
고도로 숙련된 장인들보다 약간 적은 45냥.
canadian pharmacy cialis viagra prescription price
canadian pharmacy viagra without a doctor prescription
Это важный снаряд для эффективных тренировок, который используется для подъемов и выпадов. В наличии грифы для штанг на Shtangi grify ru разнообразных конфигураций. В выпуске долговечных снарядов активно используются высококлассные марки стали. Всегда в реализациибольшой ассортимент гнутых грифов для коммерческой и домашней эксплуатации. Снаряды созданы для продуктивных занятий и выполнены с разметкой для правильного размещения рук и накаткой для хвата.
атака титанов онлайн бесплатно атака титанов в хорошем качестве
смотреть атака титанов в хорошем качестве https://ataka-titanov-anime.ru
смотреть бесплатно атака титанов https://ataka-titanov-anime.ru
купи для дома мебель
https://formomebel.ru/stoliki/iz-mramora
how to play online casino for real money online casino
Thank you for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next post thanks once again.
kruizturm.ru/morskie-kruizyi/
topnewsgadget.ru/page/9
metkonstrukt.ru/kupit-kalitku/
forum.oursson.ru/viewtopic.php?f=117&t=2899%C3%82%C2%A0
mipon.net/bbs-c/clever.cgi/clever.cgi?page=280
how to become an online casino agent online casino
Hi there, this weekend is good in favor of me, as this point in time i am reading this great informative piece of writing here at my residence.
ms.wizmedic.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=news&wr_id=94
greytoken.net/grey-tokenomics/
kolmogor.ru/category.php?catid=1
http://www.sixsigmaexams.com/mybb/member.php?action=profile&uid=263670
web-lance.net/forums.php?m=posts&id=52993
голяк смотреть онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве https://golyak-serial-online.ru
голяк смотреть в хорошем качестве https://golyak-serial-online.ru
Выбор элитных колясок Tutis, Почему Tutis – лучший выбор для вашего малыша?, секреты правильного выбора, универсальный вариант, правила использования коляски, какие покупки сделать в первую очередь, лучшие модели для спортивных прогулок, рекомендации по выбору лучшей модели, чтобы сохранить отличное состояние, правила использования коляски, рекомендации для родителей, Почему Tutis лучше всего подходит для вашей семьи?, Почему Tutis – марка будущего, Как выбрать коляску Tutis с максимальным комфортом для ребенка?, Почему Tutis – выбор стильных родителей, стильный аксессуар для пап, надежность и комфорт в каждом шаге
детские коляски тутис детские коляски тутис .
голяк смотреть кубик голяк онлайн
Can you tell us more about this? I’d love to find out some additional information.
community.wongcw.com/blogs/676196/%D0%9E%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8-%D0%B8-%D0%9D%D1%8E%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%81%D1%8B-%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%83%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F-%D0%90%D1%82%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B0-%D0%B7%D0%B0-11-%D0%9A%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81-%D0%B2-2024?lang=tr_tr
admvoznesenie.ru/officials/blogs/history.php?PAGEN_1=48
myworldoftank.ru/article/kak-vklyuchit-otobrazhenie-shansov-na-pobedu-xvm-v-world-of-tanks.html
vnbaolut.com/ami
bamcreativestudio.com.au/index.php/blog
maxwin77
Attractive element of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to claim that I get actually enjoyed account your weblog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing in your feeds and even I success you access consistently quickly.
eku.ru/comments/list/
http://www.vostok-shop.ru/published/SC/html/scripts/index.php?ukey=linkexchange&did=33&le_categoryID=0&page=23&show_all=yes
girbir.com/blogs/13038/Where-can-I-buy-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-a
lssrussia.ru/newslean/forum-v-ust-ilimske/
moskva-medcentr.ru/index.html
에그벳
Fang Jifan도 떠나려고했지만 Hongzhi 황제는 Fang Jifan에게 윙크를했습니다.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your great post. Also, I have shared your site in my social networks!
jayaramcards.com/Home/buynow/97
avtorasklad.ru/index.php?did=33&le_categoryID=0&page=67&show_all=yes
newspromworld.ru/page/2
asil-fc.com/main/%CE%9D%CE%AD%CE%B1/%CE%A4%CE%B5%CE%BB%CE%B5%CF%85%CF%84%CE%B1%CE%AF%CE%B1_%CE%9D%CE%AD%CE%B1/%CE%A3%CE%B5_%CF%84%CE%B5%CE%BB%CE%B9%CE%BA%CE%AE_%CE%B1%CE%BD%CE%AC%CE%BB%CF%85%CF%83%CE%B7_%CE%BA%CE%B1%CE%BB%CF%8C%CF%82_%CE%BF_%CE%B2%CE%B1%CE%B8%CE%BC%CF%8C%CF%82/
nbcenter.ge/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ekepos
Ӏ’m really enjoyіng the theme/design off үoujr web site.
Do you ever run into aany bгoᴡser compatibility
problemѕ? A handful of my blog visitоrs have complained аbout myy Ƅlog not operating correⅽtly in Explorer but looкs great in Safari.
Do you hav anyy solutions to helр fix this problem? https://kodmakare.nu/index.php/Greatest_Family_Photographers_In_Bali_For_Beautiful_Snaps
https://luulotpois.com/?keyword=pasang123
娛樂城評價
10 大線上娛樂城評價實測|線上賭場推薦排名一次看!
在台灣,各式線上娛樂城如同雨後春筍般湧現,競爭激烈。對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析它們的優缺點,幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台。
娛樂城評價五大標準
在經過我們團隊的多次進行娛樂城實測後,得出了一個值得信任的線上娛樂城平台須包含的幾個要素,所以我們整理了評估娛樂城的五大標準:
條件一:金流帳戶安全性(儲值與出金)
條件二:博弈遊戲種類的豐富性
條件三:線上24小時客服、服務效率與態度
條件四:提供的優惠活動CP值
條件五:真實娛樂城玩家們的口碑評語
通常我們談到金流安全時,指的是對玩家風險的控制能力。一家優秀的娛樂城應當只在有充分證據證明玩家使用非法套利程式,或發現代理和玩家之間有對壓詐騙行為時,才暫時限制該玩家的金流。若無正當理由,則不應隨意限制玩家的金流,以防給玩家造成被詐騙的錯覺。
至於娛樂城的遊戲類型,主要可以分為以下七大類:真人視訊百家樂、彩票遊戲、體育投注、電子老虎機、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲及電子競技投注。這些豐富多樣的遊戲類型提供了廣泛的娛樂選擇。
十大娛樂城實測評價排名
基於上述五項標準,我們對以下十家現金版娛樂城進行了的實測分析,並對此給出了以下的排名結果:
RG富遊娛樂城
bet365娛樂城
DG娛樂城
yabo亞博娛樂城
PM娛樂城
1XBET娛樂城
九州娛樂城
LEO娛樂城
王者娛樂城
THA娛樂城
https://admgeneralcontractors.ca/paito-hk-warna
온라인 슬롯
다행스럽게도… 첫 번째 통조림 식품이 시장에 출시되기 시작했습니다.
Thank you for any other informative web site. Where else could I get that type of info written in such a perfect approach? I’ve a undertaking that I’m simply now running on, and I’ve been at the look out for such info.
new retro casino зеркало
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。
RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
缺點
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
取款方式
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
電競遊戲 — 熊貓體育
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚
Hi there friends, its fantastic article concerning teachingand fully defined, keep it up all the time.
crypto casino sign up bonus
whoah this weblog is fantastic i love reading your articles. Stay up the great work! You already know, many individuals are looking around for this information, you could aid them greatly.
http://http://musey-uglich.ru/
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for info about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I’ve found out so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you sure about the supply?
http://www.musey-uglich.ru
Портал о культуре Ярославля – ваш гид по культурной жизни города. Здесь вы найдёте информацию о театрах, музеях, галереях и исторических достопримечательностях. Откройте для себя яркие события, фестивали и выставки, которые делают Ярославль культурной жемчужиной России.
бонус драгон мани казино онлайн казино Dragon Money
официальный сайт драгон мани казино драгон мани казино
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting sick and tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Сегодня, когда диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который желает начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://http://seoyour.ru/
вход 1го казино https://zamok-09.ru/
I delight in, cause I discovered exactly what I was having a look for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
http://www.bodybuilding.net/members/worksale-page7.html
medik-look.ru/kupit-diplom-onlayn-udobno-i-byistro
newsbizlife.ru/page/5
thegioimaydemtien.vn/san-pham/may-dem-tien-xiudun-9500-817.htm
giaibngdaquocteu23.com/2021-10-cb-hay-trong-trong-fifa-online-4-hien-nay-keo8386/
Do you have any video of that? I’d like to find out some additional information.
web011.dmonster.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=b0501&wr_id=181555
ezoinfo.ru/Narodnay_medizina/Saving_power/Saving_power_9.php
aboutallfinance.ru/page/39
http://www.leac-escrime.fr/edj-entrainement-des-jeunes-2020-2021/
spletninews.ru/page/3
1go casino официальный сайт регистрация 1Go Casino
куплю 1 квартиру новостройка https://novostroyka-kzn16.ru
купить квартиру в новостройке купить квартиру
Hi colleagues, pleasant article and nice arguments commented at this place, I am truly enjoying by these.
http://www.ba98.org/contact.php?sujet=6
centimetroquadro.it/progetti.php?id=7&cat=1
sinopipefittings.com/e_Feedback/?page=10995
probki.vyatka.ru/content/reshenie-1442012?page=22
allsportime.ru/uspeh-v-vashih-rukah-kupit-diplom-i-nachat-novuyu-zhizn
купить квартиру в новостройке от застройщика https://novostroyka-kzn16.ru
https://lala.lanbook.com/virtualnaya-i-dopolnennaya-realnosti-v-obuchenii
I think what you wrote made a bunch of sense. However, what about this? suppose you were to write a awesome headline? I mean, I don’t want to tell you how to run your website, however suppose you added a post title that grabbed folk’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little plain. You ought to peek at Yahoo’s home page and see how they create post titles to get people to click. You might add a related video or a picture or two to get readers excited about what you’ve got to say. In my opinion, it could make your website a little livelier.
http://www.find-topdeals.com/blogs/45974/D09AD0B0D187D0B5D181D182D0B2D0B5D0BDD0BDD18BD0B5-D0B4D0B8D0BFD0BBD0BED0BCD18B-D0BFD0BE-D0B4D0BED181D182D183D0BFD0BDD0BED0B9-D186D0B5D0BDD0B5-D092D0B0D188-D0BFD183D182D18C-D0BA-D183D181D0BFD0B5D185D183-D0BDD0B0D187?lang=tr_tr
politictoday.ru/page/39
panarabiaenquirer.com/wordpress/israeli-defence-forces-to-commemorate-international-holocaust-memorial-day-by-locking-up-record-number-of-palestinian-children/
ediblehomegardensresort.com/index.php?do=/public/blog/view/id_119635/title_-2024/
spbmedu.ru/index.html
квартиры от застройщика цены купить квартиру в Санкт-Петербурге
When I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I recieve four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thank you.
Helpful info. Lucky me I found your site accidentally, and I’m surprised why this twist of fate didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
click2connect.buzz/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/name_Alanpoe/page_5/
buzzchatlive.com/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/name_Alanpoe/page_7/
raisenex.com/blogs/6172/Where-can-I-order-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-a
http://www.shamrockrfc.com/player-interviews.html
эвакуатор-срочно-недорого.рф/
bocor88
квартиры в новостройках Санкт-Петербурге https://kvartiru-kupit78.ru
https://kupit-kvartiruspb.ru в новостройках Санкт-Петербурга. Цены и фотографии квартир от застройщика в готовых и строящихся ЖК. Подбор жилья, ипотечные программы, сопровождение сделок и выгодные предложения.
Wow, fantastic blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is great, as well as the content!
effective-herbal-cure.com/hoodia-gordonii-extract/fast-fat-reduction.htm
pdtplanilla.com/la-nueva-normalidad-y-la-gestion-de-recursos-humanos/
1001cruise.ru/carnival-cruises/114-news/762-liner-royal-princess-will-be-released-in-the-first-flight.html
probki.kirov.ru/content/reshenie-1442012?page=19
http://www.lednsk.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=13&show_all=yes
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Cheers!
newsofgames.ru/page/28
custom-engravable-jewelry.com/bracelet.php
http://www.tvoidom.galaxyhost.org/forums.php?m=posts&id=44646
pdtplanilla.com/la-nueva-normalidad-y-la-gestion-de-recursos-humanos/
dollarafont.com/contact.html
999 슬롯
하지만 홍지황제에게는 이 숫자가 너무 무서웠다.
купить квартиру https://novostroyki-spb78.ru
https://skyhighcondos.ca/albaslot
Hello mates, its wonderful article concerning cultureand entirely defined, keep it up all the time.
staceylcrow.com/2013/jess-kenny-redlands-ca/
startspresto.ru/dannye/pluginclass/cbblogs?action=blogs&func=show&id=22
metkonstrukt.ru/kupit-kalitku/
http://www.vinhphatmobile.com/contact/
oldsite.profbez.ru/shop/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=260&show_all=yes
http://stroymaterial39.ru/
квартира в новостройке https://novostroyki-spb78.ru
продвижение веб сайтов http://www.prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve113.ru .
Hi, after reading this amazing paragraph i am too cheerful to share my know-how here with mates.
arjaniki.ru/memberlist.php?sk=m&sd=d&first_char=r&mode=searchuser&start=75
ifvex.com/blogs/2501/Why-is-the-popularity-of-higher-education-decreasing-in-our
eon51.com/eon51-sky-dining/?lang=vi
symphonyofthemagneticnorth.com/_404.html
bbs.blueplatform.org/space-uid-31463.html
Каталог эротических рассказов https://vicmin.ru подарит тебе возможность уйти от рутины и погрузиться в мир секса и безудержного наслаждения. Обширная коллекция рассказов для взрослых разбудит твое воображение и принесет немыслимое удовольствие.
canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store viagra no perscription
canadian pharmacy cialis viagra no prior prescription
Hi there colleagues, how is the whole thing, and what you desire to say on the topic of this post, in my view its truly awesome for me.
elibot.gg/commands
77lub.ru/products/small-engine-oils/
eon51.com/eon51-sky-dining/?lang=vi
azat.on.kg/blogs/451/%D0%A1%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BA%D0%BE-%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B8%D1%82-%D1%81%D0%B5%D0%B9%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81-%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC
http://www.tvserver.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=1271&view=previous
You are so awesome! I do not think I have read through a single thing like this before. So good to discover somebody with a few genuine thoughts on this subject matter. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is something that’s needed on the internet, someone with a little originality.
Appreciating the persistence you put into your blog and detailed information you present. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same unwanted rehashed information. Fantastic read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
itbitgroup.ru/page/4
http://www.toyota-porte.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=1864
weekinato.ru/page/13/
hoisuhoc.vn/tong-hop-nhung-mon-an-giup-thai-nhi-tang-can-tot-nhat/
neverwinter-wiki.ru/igrovye-klassy-neverwinter/igrovoj-klass-plut-lovkach
娛樂城
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
娛樂城
2024娛樂城介紹
台灣2024娛樂城越開越多間,新開的線上賭場層出不窮,每間都以獨家的娛樂城優惠和體驗金來吸引玩家,致力於提供一流的賭博遊戲體驗。以下來介紹這幾間娛樂城網友對他們的真實評價,看看哪些娛樂城上榜了吧!
2024娛樂城排名
2023下半年,各家娛樂城競爭激烈,相繼推出誘人優惠,不論是娛樂城體驗金、反水流水還是首儲禮金,甚至還有娛樂城抽I15手機。以下就是2024年網友推薦的娛樂城排名:
NO.1 富遊娛樂城
NO.2 Bet365台灣
NO.3 DG娛樂城
NO.4 九州娛樂城
NO.5 亞博娛樂城
2024娛樂城推薦
根據2024娛樂城排名,以下將富遊娛樂城、BET365、亞博娛樂城、九州娛樂城、王者娛樂城推薦給大家,包含首儲贈點、免費體驗金、存提款速度、流水等等…
娛樂城遊戲種類
線上娛樂城憑藉其廣泛的遊戲種類,成功滿足了各式各樣玩家的喜好和需求。這些娛樂城遊戲不僅多元化且各具特色,能夠為玩家提供無與倫比的娛樂體驗。下面是一些最受歡迎的娛樂城遊戲類型:
電子老虎機
魔龍傳奇、雷神之鎚、戰神呂布、聚寶財神、鼠來寶、皇家777
真人百家樂
真人視訊百家樂、牛牛、龍虎、炸金花、骰寶、輪盤
電子棋牌
德州撲克、兩人麻將、21點、十三支、妞妞、三公、鬥地主、大老二、牌九
體育下注
世界盃足球賽、NBA、WBC世棒賽、英超、英雄聯盟LOL、特戰英豪
線上彩票
大樂透、539、美國天天樂、香港六合彩、北京賽車
捕魚機遊戲
三仙捕魚、福娃捕魚、招財貓釣魚、西遊降魔、吃我一砲、賓果捕魚
2024娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城/線上賭場(現金網)是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,而且是現金網,大家也許會好奇為什麼不直接叫做線上賭場或是線上博弈就好了。
其實這是有原因的,線上賭場這種東西,架站在台灣是違法的,在早期經營線上博弈被抓的風險非常高所以換了一個打模糊仗的代稱「娛樂城」來規避警方的耳目,畢竟以前沒有Google這種東西,這樣的代稱還是多少有些作用的。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種賭博平台,允許玩家在沒有預先充值的情況下參與遊戲。這種模式類似於信用卡,通常以周結或月結的方式結算遊戲費用。因此,如果玩家無法有效管理自己的投注額,可能會在月底面臨巨大的支付壓力。
娛樂城不出金怎麼辦?
釐清原因,如未違反娛樂城機制,可能是遇上黑網娛樂城,請盡快通報165反詐騙。
купить диплом в ижевске https://diplom-izhevsk.ru
Новостройки в Екатеринбурге, купить квартиру в новостройке https://kupit-kvartiruekb.ru от застройщика. Строительство жилой и коммерческой недвижимости. Высокое качество, прозрачность на всех этапах строительства и сделки.
taringbet
situs kantorbola
娛樂城
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。
Excellent site you have got here.. It’s difficult to find high-quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
как пожаловаться на мошенников как пожаловаться на мошенников .
Прихожие каталог – всем рекомендую эту компанию. Купить современную мебель в интернет магазине TM Mebel-24 в Киеве и Украине. Производство качественной нестандартной мебели для дома и офиса. Большой каталог готовой мебели на 15000 товаров. Наш опыт более 19 лет в мебельной промышленности!
Aw, this was a really nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to make a really good article… but what can I say… I put things off a lot and don’t seem to get anything done.
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。
Famous French footballer Kylian Mbappe https://kylianmbappe.prostoprosport-ar.com has become a global ambassador for Dior. The athlete will represent the men’s collections of creative director Kim Jones and the Sauvage fragrance, writes WWD. Mbappe’s appointment follows on from the start of the fashion house’s collaboration with the Paris Saint-Germain football club. Previously, Jones created a uniform for the team where Kylian is a player.
북 오브 데드
작가가 가장 두려워하는 것은 초심을 잊는 것이고, 외로움을 견디지 못하는 것이 더욱 두려운 것이다.
Key Service 24/7
Скачать свежие новинки песен https://muzfo.net 2024 года ежедневно. Наслаждайтесь комфортным прослушиванием, скачивайте музыку за пару кликов на сайте.
สล็อตเว็บโดยตรง — สามารถใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ต คอมฯ ฯลฯ เพื่อเล่น
ระบบสล็อตตรงจากเว็บ ของ PG ได้รับการพัฒนาและอัปเดต เพื่อให้ รองรับการใช้ บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง สมบูรณ์ ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ มือถือ แท็บเลต หรือ คอมฯ รุ่นใด
ที่ พีจีสล็อต เราเข้าใจถึงสิ่งที่ผู้เล่นต้องการ ของผู้เล่น ในเรื่อง การใช้งานง่าย และ การเข้าถึงเกมออนไลน์อย่างรวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีล่าสุด ในขณะนี้ มาพัฒนาเว็บไซต์ของเรากันเถอะ คุณจึงไม่ต้อง โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดเบราว์เซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณใช้อยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บไซต์เรา คุณสามารถ เล่นเกมสล็อตได้ทันที
การสนับสนุนหลายอุปกรณ์
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ ระบบ แอนดรอยด์ หรือ ไอโอเอส ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตได้อย่างราบรื่น ระบบของเรา ได้รับการออกแบบให้รองรับ ทุกระบบปฏิบัติการ ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ กำลังใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน ใหม่หรือเก่า หรือ แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้อย่างไม่มีปัญหา ไม่มีปัญหา ในเรื่องความเข้ากันได้
เล่นได้ทุกที่และทุกเวลา
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot คือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ตลอดเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ อยู่ที่บ้าน ออฟฟิศ หรือแม้แต่ ที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง ห่วงเรื่องการดาวน์โหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ ใช้พื้นที่บนอุปกรณ์ของคุณ
เล่นสล็อตฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่นใหม่ ได้ลองเล่นและสัมผัสเกมสล็อตของเรา PG Slot ยังมีบริการสล็อตฟรี คุณสามารถ ทดลองเล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครหรือฝากเงิน การ ทดลองเล่นสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้คุณรู้จักวิธีการเล่นและเข้าใจเกมก่อนเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
การบริการและความปลอดภัย
PG Slot ตั้งใจให้บริการที่ดีที่สุดกับลูกค้า เรามี ทีมงานพร้อมบริการคุณตลอดเวลา นอกจากนี้เรายังมี ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลและการเงินของคุณจะปลอดภัย
โปรโมชันและโบนัส
การเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ยังมีข้อดี นั่นคือ มี โปรโมชันและโบนัสพิเศษสำหรับสมาชิก ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชั่นและโบนัสต่างๆได้อย่างต่อเนื่อง สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและเพิ่มความเพลิดเพลินในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
สล็อตเว็บตรง: ความรื่นเริงที่ผู้เล่นไม่ควรพลาด
การเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ในยุคนี้เป็นที่นิยมมากขึ้นอย่างมาก เนื่องจากความง่ายดายที่นักเดิมพันสามารถเข้าถึงได้จากทุกที่ตลอดเวลา โดยไม่ต้องใช้เวลาเดินทางไปยังสถานที่บ่อน ในเนื้อหานี้ เราจะมาพูดถึง “สล็อตออนไลน์” และความเพลิดเพลินที่ท่านจะได้พบในเกมสล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรง
ความสะดวกในการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์
เหตุผลหนึ่งที่ทำให้สล็อตที่เว็บตรงเป็นที่ยอดนิยมอย่างมาก คือความสะดวกที่ผู้ใช้ได้รับ คุณสามารถเล่นได้ทุกหนทุกแห่งตลอดเวลา ไม่ว่าจะเป็นในบ้าน ที่ทำงาน หรือถึงแม้จะอยู่ในการเดินทาง สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคืออุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นมือถือ แท็บเล็ท หรือคอมพิวเตอร์
เทคโนโลยีกับสล็อตที่เว็บตรง
การเล่นเกมสล็อตในยุคนี้ไม่เพียงแต่สะดวก แต่ยังประกอบด้วยนวัตกรรมล้ำสมัยอีกด้วย สล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรงใช้เทคโนโลยี HTML5 ซึ่งทำให้คุณไม่ต้องกังวลใจเกี่ยวกับการลงโปรแกรมหรือแอปพลิเคชันเพิ่มเติม แค่ใช้เบราว์เซอร์บนอุปกรณ์ของคุณและเข้ามายังเว็บไซต์ของเรา คุณก็สามารถเริ่มเล่นเกมสล็อตได้ทันที
ตัวเลือกหลากหลายของเกมของสล็อต
สล็อตเว็บตรงมาพร้อมกับความหลากหลายของเกมที่เล่นที่ผู้เล่นเลือกได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมคลาสสิกหรือเกมสล็อตที่มาพร้อมกับฟีเจอร์เด็ดและโบนัสหลากหลาย คุณจะเห็นว่ามีเกมที่ให้เล่นมากมาย ซึ่งทำให้ไม่เคยเบื่อกับการเล่นสล็อต
การสนับสนุนทุกอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้
ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือแอนดรอยด์หรือ iOS ท่านก็สามารถเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ได้ไม่มีสะดุด เว็บไซต์รองรับทุกระบบปฏิบัติการและทุกเครื่องมือ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นมือถือรุ่นล่าสุดหรือรุ่นเก่า หรือแม้กระทั่งแท็บเล็ทและแล็ปท็อป ท่านก็สามารถเพลิดเพลินกับเกมสล็อตได้ได้อย่างครบถ้วน
ทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อต
สำหรับผู้ที่ยังใหม่กับการเล่นสล็อต หรือยังไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับเกมที่ต้องการเล่น PG Slot ยังมีระบบทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อต คุณสามารถทดลองเล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงินก่อน การทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้ท่านเรียนรู้วิธีการเล่นและเข้าใจวิธีการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องเสียค่าใช้จ่ายใด ๆ
โบนัสและโปรโมชั่น
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตเว็บตรงกับ PG Slot คือมีโปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษมากมายสำหรับนักเดิมพัน ไม่ว่าท่านจะเป็นสมาชิกใหม่หรือสมาชิกเก่า ท่านสามารถใช้โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสต่าง ๆ ได้อย่างสม่ำเสมอ ซึ่งจะเพิ่มโอกาสชนะและเพิ่มความสนุกในเกมที่เล่น
สรุป
การเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ PG Slot เป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะได้รับความสุขและความง่ายดายจากการเล่นเกมสล็อต นอกจากนี้ยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมาย ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้มือถือ แทปเล็ตหรือคอมพิวเตอร์ยี่ห้อไหน ก็สามารถเริ่มเล่นกับเราได้ทันที อย่ารอช้า สมัครสมาชิกและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ PG Slot เดี๋ยวนี้
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search
Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my website to rank for
some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains.
If you know of any please share. Appreciate it! You can read
similar blog here
Скачать свежие новинки песен https://muzfo.net 2024 года ежедневно. Наслаждайтесь комфортным прослушиванием, скачивайте музыку за пару кликов на сайте.
เกี่ยวกับ ไซต์ PG Slots ในขณะที่ มี ความได้เปรียบ หลายประการ เมื่อเทียบกับ คาสิโนแบบ ดั้งเดิม, โดยมาก ใน ปัจจุบัน. คุณประโยชน์สำคัญ เหล่านี้ ได้แก่:
ความสะดวกสบาย: ผู้เล่น สามารถเข้าเล่น สล็อตออนไลน์ได้ ตลอดเวลา จาก ทุกอย่าง, ทำให้ ผู้เล่นสามารถ เล่น ได้ ทุกที่ ไม่ต้อง ต้องเดินทาง ไปคาสิโนแบบ ทั่วไป ๆ
เกมหลากประเภท: สล็อตออนไลน์ ให้ ประเภทเกม ที่ มากมาย, เช่น สล็อตรูปแบบคลาสสิค หรือ สล็อต ที่มี คุณสมบัติ และรางวัล พิเศษ, ไม่ส่งผลให้ ความเบื่อ ในเกม
ข้อเสนอส่งเสริมการขาย และประโยชน์: สล็อตออนไลน์ แทบจะ ให้ ข้อเสนอส่งเสริมการขาย และรางวัล เพื่อยกระดับ ความสามารถ ในการ ชนะเกม และ เพิ่ม ความสนุกสนาน ให้กับเกม
ความเชื่อมั่น และ ความเชื่อถือได้: สล็อตออนไลน์ โดยทั่วไป ใช้งาน ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัย ที่ ครอบคลุม, และ เชื่อมั่นได้ ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนบุคคล และ ธุรกรรมทางการเงิน จะได้รับความ ดูแล
บริการสนับสนุน: PG Slots มีทีม ทีมงาน ที่มีความเชี่ยวชาญ ที่ทุ่มเท ช่วยเหลือ ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง
การเล่นบนอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่: สล็อต PG รองรับ การเล่นบนมือถือ, ทำให้ ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าร่วม ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง
เล่นฟรี: ของ ผู้เล่นใหม่, PG ยังเสนอ เล่นฟรี อีกด้วย, เพื่อที่ คุณ ทดลอง วิธีใช้ และเข้าใจ เกมก่อน เล่นด้วยเงินจริง
สล็อต PG มีคุณลักษณะ ข้อดี เป็นจำนวนมาก ที่ ทำ ให้ได้รับความนิยม ในปัจจุบันนี้, ส่งเสริม ความ ความผ่อนคลาย ให้กับเกมด้วย.
интернет эквайринг https://internet-ekvajring.kz – безопасные и эффективные платежные решения для вашего бизнеса.
Агентство по продвижению телеграм-каналов https://883666b.com в Москве специализируется на разработке и реализации стратегий для увеличения аудитории и вовлечённости подписчиков на телеграм-каналах. Эксперты агентства помогают клиентам определить целевую аудиторию, разрабатывают контент-планы и рекламные кампании. Услуги включают рекламу посевами, таргет рекламой, анализ конкурентов, SEO-оптимизацию контента.
Greetings! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy reading through your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same subjects? Thank you!
битц казино
Здесь вы найдете разнообразный видео контент Ялта Видео, охватывающий множество платформ и форматов.
От коротких зрелищных роликов на TikTok до
долгоиграющих трансляций на Twitch – мой канал стремится объединить лучшее из разных
миров видео. Присоединяйтесь, чтобы веселиться
вместе с потоковым мультимедиа Stream, наслаждаться премиум-контентом от Vevo и Vimeo, а также
открывать для себя новые таланты на Rumble и BitChute.
Также вы найдете здесь эксклюзивный контент для Instagram TV (IGTV),
Facebook Watch и других социальных платформ.
А для поклонников аниме есть отдельная секция с лучшим контентом от Crunchyroll.
Используя мощь профессиональных инструментов, таких
как Brightcove, Kaltura, JWPlayer, IBM Cloud Video и
многих других, я стараюсь предоставить вам
впечатляющий и высококачественный видео опыт.
Подписывайтесь сегодня и оставайтесь на волне самого свежего и разнообразного
видео контента в интернете.
Добро пожаловать в мой мир ярких видео!”
Это описание канала объединяет все упомянутые вами видео платформы, демонстрируя вашу готовность работать с разными форматами и обеспечивать качественный и разнообразный контент для зрителей. Пусть оно привлечет новых подписчиков!
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg เว็บ ตรง
ความรู้สึกการลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนพอร์ทัลพนันไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์: เปิดจักรวาลแห่งความบันเทิงที่ไม่จำกัด
สำหรับนักเสี่ยงทายที่ค้นหาการเผชิญหน้าเกมใหม่ๆ และต้องการค้นหาแหล่งวางเดิมพันที่เชื่อถือได้, การสำรวจเกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนแพลตฟอร์มตรงถือเป็นตัวเลือกที่น่าดึงดูดอย่างมาก. เนื่องจากมีความหลากหลายของเกมสล็อตต่างๆที่มีให้คัดสรรมากมาย, ผู้เล่นจะได้พบเจอกับโลกแห่งความรื่นเริงและความเพลิดเพลินที่ไร้ขีดจำกัด.
เว็บการเดิมพันโดยตรงนี้ ให้การทดลองเล่นเกมการเล่นเดิมพันที่ปลอดภัย น่าเชื่อถือ และตอบสนองความต้องการของนักพนันได้เป็นอย่างดี. ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะผู้เล่นจะติดใจเกมสล็อตแมชชีนที่คุ้นเคยที่คุ้นเคย หรืออยากทดลองเกมใหม่ที่มีฟีเจอร์พิเศษเฉพาะและรางวัลพิเศษล้นหลาม, เว็บไซต์โดยตรงนี้ก็มีให้คัดสรรอย่างหลากหลายมากมาย.
เนื่องจากมีระบบการสำรวจเกมสล็อต PG ไม่มีค่าใช้จ่าย, ผู้เล่นจะได้โอกาสที่ดีศึกษาขั้นตอนเล่นเกมและทดลองกลยุทธ์ที่หลากหลาย ก่อนที่จะเริ่มลงทุนด้วยเงินทุนจริง. นี่นับว่าโอกาสอันวิเศษที่จะเพิ่มความพร้อมและพัฒนาโอกาสในการชิงรางวัลใหญ่ใหญ่.
ไม่ว่าท่านจะคุณอาจจะต้องการความสนุกสนานที่เคยชิน หรือการพิชิตแปลกใหม่, เกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนเว็บเสี่ยงโชคตรงนี้ก็มีให้เลือกเล่นอย่างหลากหลาย. ผู้เล่นจะได้เผชิญกับการเล่นการเล่นเกมที่น่าตื่นเต้นเร้าใจ น่าตื่นเต้น และมีความสุขไปกับโอกาสดีในการคว้ารางวัลมหาศาลมหาศาล.
อย่ารอ, ร่วมสนุกสำรวจเกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนเว็บไซต์พนันตรงนี้เวลานี้ และค้นเจอโลกแห่งความสุขที่ปลอดภัยแน่นอน น่าติดตาม และพร้อมด้วยความสุขสนานรอคอยคุณอยู่. เผชิญความตื่นเต้นเร้าใจ, ความสนุกเพลิดเพลิน และจังหวะในการคว้ารางวัลมหาศาลมหาศาล. เริ่มการเดินทางเข้าสู่ชัยชนะในวงการเกมออนไลน์เวลานี้!
r 슬롯
그런데 곰곰이 생각해보면 아직도 병이 걱정되지 않습니까?
There is certainly a great deal to learn about this issue. I love all of the points you made.
купить квартиру в новостройке от застройщика https://nedvizhimost47.ru
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Секрет стильного пространства – плинтус теневой.
теневой плинтус https://msk-alyuminievyj-tenevoj-plintus.ru/ .
купить квартиру в казани от застройщика https://novostroyka47.ru
This site certainly has all of the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
купить диплом в тюмени http://www.damdesign.ru .
Почему стоит выбрать хостинг в Беларуси бесплатно?, за и против.
Бесплатные хостинги в Беларуси: что выбрать?, инструкции и рекомендации.
RAIDHOST, HOSTERO, TUT.BY: лучшие бесплатные хостинги в Беларуси, оценка и обзор.
Шаг за шагом: переезд на хостинг в Беларуси бесплатно, инструкция и советы.
Бесплатный SSL для хостинга в Беларуси: зачем он нужен?, за и против.
DIY: с нуля до готового сайта на хостинге в Беларуси бесплатно, инструкция и рекомендации.
Децентрализованный хостинг в Беларуси: перспективы и возможности, характеристики и отзывы.
хостинг бесплатно хостинг бесплатно .
This is a topic which is near to my heart… Best wishes! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
บาคาร่า
generic amoxicillin online: amoxil doxycyclineca – can you buy amoxicillin over the counter
Lock Emergency
Simply desire to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is just great and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the rewarding work.
77lub.ru/products/small-engine-oils/
here4deals.com/garderie-barny-horaires.php
maixepanphat.vn/author/dangkhoa98/page/2/
inspiretemplate.com/opencart/freeze/index.php?route=information/blogger&blogger_id=4
avtorasklad.ru/index.php?did=33&le_categoryID=0&page=67&show_all=yes
Hello to all, how is everything, I think every one is getting more from this web page, and your views are nice designed for new users.
http://www.lku2.com/blogs/4238/Where-to-buy-a-diploma-or-certificate-at-an-adequate
custom-engravable-jewelry.com/bracelet.php
fpcom.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=110868
topstavka.ru/action?page=2
textualheritage.org/en/the-materials-of-the-conference-el-manusctipt-2014/82.html
הימורי ספורט – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורט הפכו לאחד התחומים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. משתתפים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאת של אירועי ספורטיביים פופולריים לדוגמה כדורגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האופציות להתערבות הן רבות, כולל תוצאתו המאבק, מספר השערים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. הבא דוגמאות של למשחקים נפוצים במיוחד שעליהם ניתן להמר:
כדורגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות אזוריות
כדורסל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
טניס: ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה”ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר ברשת באינטרנט – הימור באינטרנט
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור הנפוצים ביותר כיום. שחקנים מסוגלים להתחרות מול מתחרים מכל רחבי העולם במגוון וריאציות משחק , לדוגמה Texas Hold’em, אומהה, Stud ועוד. ניתן לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי קש במגוון רמות ואפשרויות הימור שונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מגוון רחב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות המשחק למשחק מהיר ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות יחודיות
בטיחות ואבטחה והגינות
בעת הבחירה פלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק בטוחה והגיונית. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיות הצפנה מתקדמת להבטחה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסי, וכן בתוכנות מחולל מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות המשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, חשוב לשחק גם בצורה אחראי תוך כדי הגדרת מגבלות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. מרבית אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים למשתתפים להגדיר מגבלות להפסדים ופעילויות, וגם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחק בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחר הפסדים.
המדריך השלם למשחקי קזינו ברשת, הימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
ההימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מלהיבות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו אונליין וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בזמן הבחירה פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור גם אתרים מפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד – ההימורים באינטרנט אמורים להיות מבדרים ולא גם לגרום בעיות פיננסיות או גם חברתיים.
돌리고 슬롯
“무슨 말을 하고 싶니?” 팡지판은 이미 허리를 벨트로 묶었고, 온 몸이 날씬해 보였다.
Everything is very open with a very clear description of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Thanks for sharing.
Можете заказать гантельные грифы на grify dlya gantely ruпо приятным ценамнеобходимой длины. В изготовлении качественных продуктов реализуются инновационные марки металла. Гантельные составляющие выпускаются в трех популярных диаметрах. Отягощения предназначены для силовых занятий и созданы с разметкой и рифлением для уверенного хвата. Снаряды покрываются защитным составом хрома и никеля. Отечественная фирма создает широкий объем тренировочного инвентаря для дома и зала. Это многофункциональный инструмент для тяжелых тренировок в любых условиях.
I blog frequently and I seriously thank you for your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I will bookmark your website and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
Hello there! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I truly enjoy reading through your articles. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Many thanks!
http://www.4yo.us/blogs/109456/%D0%98%D0%B7%D0%B1%D0%B0%D0%B2%D1%8C%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%8C-%D0%BE%D1%82-%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B9-%D1%81-%D1%83%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B5-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC
bietthulideco.vn/biet-thu-nha-vuon-26-nv26-khu-do-thi-lideco-bac-32/
iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=792962&do=profile&from=space
sanjosesharksclub.com/read-blog/497_where-can-i-buy-a-certificate-or-a-diploma-at-a-bargain-price.html?mode=night
agenciafrog-host.com.br/redesocial_v0/index.php/link/index/id/3930/key/b0fcd47add6e30fda613f403368cfa65
Howdy are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
collie.fatbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=4169&start=0&view=print
http://www.rusnor.org/pubs/edit/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=91604
bresdel.com/blogs/435141/%D0%A1%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D0%92%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8-%D0%9E%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0?lang=ru_ru
share-design.ru/legal-notice/
primerosauxilios.org/primeros-auxilios/que-es-y-como-curar-una-herida.php
Howdy! I simply want to offer you a big thumbs up for your great information you’ve got here on this post. I am coming back to your blog for more soon.
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Spending some time and actual effort to make a great article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never seem to get anything done.
Проведение независимой строительной экспертизы — сложный процесс, требующий глубоких знаний. Наши специалисты обладают всеми необходимыми навыками, а их заключения часто служат основой для принятия верных стратегических решений. Строительно-техническая экспертиза https://stroytehexp.ru позволяет выявить факторы, вызвавшие ухудшение эксплуатационных характеристик объектов, проверить соответствие возведённых зданий градостроительным нормам.
This site certainly has all of the information and facts I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Информационный ресурс https://ardma.ru, посвящен бизнесу, финансам, инвестициям и криптовалютам. Сайт предлагает экспертные статьи, аналитические отчеты, стратегии и советы для предпринимателей и инвесторов. Здесь можно найти новости и обзоры о бизнесе, маркетинге, трейдинге, а также практические рекомендации по различным видам заработка и управлению финансами.
Pin up маникюр: идеи и советы, которые поразят вас
up casino up casino .
pro88
Exploring Pro88: A Comprehensive Look at a Leading Online Gaming Platform
In the world of online gaming, Pro88 stands out as a premier platform known for its extensive offerings and user-friendly interface. As a key player in the industry, Pro88 attracts gamers with its vast array of games, secure transactions, and engaging community features. This article delves into what makes Pro88 a preferred choice for online gaming enthusiasts.
A Broad Selection of Games
One of the main attractions of Pro88 is its diverse game library. Whether you are a fan of classic casino games, modern video slots, or interactive live dealer games, Pro88 has something to offer. The platform collaborates with top-tier game developers to ensure a rich and varied gaming experience. This extensive selection not only caters to seasoned gamers but also appeals to newcomers looking for new and exciting gaming options.
User-Friendly Interface
Navigating through Pro88 is a breeze, thanks to its intuitive and well-designed interface. The website layout is clean and organized, making it easy for users to find their favorite games, check their account details, and access customer support. The seamless user experience is a significant factor in retaining users and encouraging them to explore more of what the platform has to offer.
Security and Fair Play
Pro88 prioritizes the safety and security of its users. The platform employs advanced encryption technologies to protect personal and financial information. Additionally, Pro88 is committed to fair play, utilizing random number generators (RNGs) to ensure that all game outcomes are unbiased and random. This dedication to security and fairness helps build trust and reliability among its user base.
Promotions and Bonuses
Another highlight of Pro88 is its generous promotions and bonuses. New users are often welcomed with attractive sign-up bonuses, while regular players can take advantage of ongoing promotions, loyalty rewards, and special event bonuses. These incentives not only enhance the gaming experience but also provide additional value to the users.
Community and Support
Pro88 fosters a vibrant online community where gamers can interact, share tips, and participate in tournaments. The platform also offers robust customer support to assist with any issues or inquiries. Whether you need help with game rules, account management, or technical problems, Pro88’s support team is readily available to provide assistance.
Mobile Compatibility
In today’s fast-paced world, mobile compatibility is crucial. Pro88 is optimized for mobile devices, allowing users to enjoy their favorite games on the go. The mobile version retains all the features of the desktop site, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable gaming experience regardless of the device used.
Conclusion
Pro88 has established itself as a leading online gaming platform by offering a vast selection of games, a user-friendly interface, robust security measures, and excellent customer support. Whether you are a casual gamer or a hardcore enthusiast, Pro88 provides a comprehensive and enjoyable gaming experience. Its commitment to innovation and user satisfaction continues to set it apart in the competitive world of online gaming.
Explore the world of Pro88 today and discover why it is the go-to platform for online gaming aficionados.
south park онлайн https://southpark-serial.ru
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this blog. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my very own blog now 😉
Amazing things here. I’m very happy to peer your article. Thank you so much and I’m looking ahead to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
http://www.gencotyre.com/comerblog/member.asp?page=12
3drus.ru/forum/topic_34713/1
account.spb.ru/news/business/3546
catsandsquirrels.com/tag/squelfie/
maymotors.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=2197
жк казань купить квартиру от застройщика https://kupit-kvartiru47.ru
7k casino войти
whoah this blog is fantastic i love reading your posts. Keep up the great work! You know, many people are searching around for this information, you could aid them greatly.
Только качественные товары для военных|Ваш надежный партнер в выборе военных товаров|Здесь найдете все для военного дела|Спецодежда и обувь для армии|Выбор настоящих военных победителей|Защита и безопасность в вашем распоряжении|Военная экипировка от лучших брендов|Купите все необходимое для военной службы|Выбирайте только профессиональное снаряжение|Проверенные товары для военных операций|Снаряжение для профессионалов военного дела|Боевая техника для самых сложных задач|Только качественные товары для военного применения|Специализированный магазин для профессионалов|Специализированный магазин для военных операций|Боевое снаряжение от ведущих брендов|Только качественные товары для службы в армии|Купите профессиональное снаряжение для службы|Качественные товары для военных целей|Выбирайте только надежные военные товары
интернет магазин військової форми та спорядження в интернет магазин військової форми та спорядження в .
профессиональное seo продвижение сайтов раскрутка сайта цена в месяц
As soon as I discovered this internet site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful article. Many thanks for providing these details.
Telegram Номад казино КЗ
Студия предлагает профессиональные меры по технической поддержке ресурса на https://podderzhka-dlya-saita.ru по приятным ценам. Заполним веб-сервис профессиональным контентом. Решим вопросы по сопровождению и редизайну. Работники окажут лучшие меры по наполнению интернет-площадок. Можете приобрести приятные тарифы с месячной платой. Тарифные планы предлагаются по ключевым параметрам: времени работ, сложности проекта и других.
와일드 웨스트 골드
Fang Jifan은 숨이 찼습니다. “전하가 옳고 전하가 현명합니다.”
купить свидетельство о разводе diplomvash.ru .
Admiring the persistence you put into your website and in depth information you offer. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Excellent read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
topextern.ru/zhizn-biznesa-v-2020-godu.html
viglojdrc.org/fr/news/les-jeunes-transformes-pour-transformer-et-membres-du-cjadh
forum.supermunchkin.org/topic3885.html?view=previous
rkiyosaki.ru/discussion/8833/
http://www.vostok-shop.ru/published/SC/html/scripts/index.php?ukey=linkexchange&did=33&le_categoryID=0&page=23&show_all=yes
купить диплом в смоленске купить диплом в смоленске .
Aw, this was a very nice post. In thought I wish to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make a very good article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and on no account seem to get one thing done.
Awesome site you have here but I was curious if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really love to be a part of online community where I can get responses from other knowledgeable individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Appreciate it!
ros-kruiz.ru/
alpha.prime-pc.md/good_info/27721
talkrealty.ru/page/3
http://www.chaodisiaque.com/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=21855
boxer-forum.ru/topic3653.html?view=next
Keep on working, great job!
detki-v-setke.ru/index.php?showuser=21983
muscle-bg.com/component/content/article/399-kolko-nasiteni-maznini-trqbva-da-qdem.html
http://www.find-topdeals.com/blogs/45974/D09AD0B0D187D0B5D181D182D0B2D0B5D0BDD0BDD18BD0B5-D0B4D0B8D0BFD0BBD0BED0BCD18B-D0BFD0BE-D0B4D0BED181D182D183D0BFD0BDD0BED0B9-D186D0B5D0BDD0B5-D092D0B0D188-D0BFD183D182D18C-D0BA-D183D181D0BFD0B5D185D183-D0BDD0B0D187?lang=tr_tr
click2connectclubs.com/index.php?do=/public/user/blogs/view/name_Alanpoe/id_119636/title_/
clubecig.fr/blogs/27-qu-est-ce-que-le-sweet-spot.html
Nice read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing some research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch! “Curiosity will conquer fear even more than bravery will.” by James Stephens.
What’s up to every one, for the reason that I am in fact keen of reading this webpage’s post to be updated daily. It carries nice stuff.
stroimnsk.ru/wooden/proekt-derevyannogo-doma-iz-profilirovannogo-brusa-skazka-100/
allsportime.ru/uspeh-v-vashih-rukah-kupit-diplom-i-nachat-novuyu-zhizn
http://www.afchornchurch.com/2005/reports/16.shtml
fond.uni-altai.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=usacy
mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4139
Hello! This post could not be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this page to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
pokatili.ru/f/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=70278&view=next
priusforum.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=5268
beta.getonvibe.net/blogs/246/Why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-constantly-declining-nowadays
ww82.smallbigworld.net/sk/project/10/
http://www.rrsclub.ru/member.php?tab=visitor_messaging&u=1164&page=7
https://iqratrust.org/
https://irhsca.org/
https://muslim-forum.org/
ла2 сервера мультипрофа
Сервера л2
Greetings! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks weird when viewing from my apple iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this problem. If you have any recommendations, please share. Cheers!
Vinicius Junior https://viniciusjunior.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Brazilian and Spanish footballer who plays as a striker for Real Madrid and the Brazilian national team. Junior became the first player in the history of Los Blancos, born in 2000, to play an official match and score a goal.
bonjour I love Your Blog can not say I come here often but im liking what i c so far….
Hey there! I understand this is somewhat off-topic however I needed to ask. Does building a well-established website such as yours take a large amount of work? I am brand new to operating a blog but I do write in my journal everyday. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and feelings online. Please let me know if you have any kind of suggestions or tips for new aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
arahn.100webspace.net/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=142536
skazka.g-talk.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1679&p=1705
metkonstrukt.ru/kupit-kalitku/
http://www.zoofc.org/blog/nakuru-county-sets-it-s-sight-on-getting-back-in-t/30
financetimenews.ru/page/14/
There is certainly a lot to know about this topic. I like all of the points you’ve made.
Islamische Gebetszeiten, Fadschr, Zuhr, Asr, Maghrib et Isha’a: islamische-gebetszeiten.online
Karim Benzema https://karimbenzema.prostoprosport-ar.com is a French footballer who plays as a striker for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Ittihad. He played for the French national team, for which he played 97 matches and scored 37 goals. At the age of 17, he became one of the best reserve players, scoring three dozen goals per season.
I love the efforts you have put in this, thanks for all the great content.
We absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome weblog!
트레져스 오브 아즈텍
이 측면은 각기병에서도 판단할 수 있습니다.
I love it whenever people come together and share opinions. Great website, keep it up!
Портал о здоровье
https://rezus.ru и здоровом образе жизни, рекомендации врачей и полезные сервисы. Простые рекомендации для укрепления здоровья и повышения качества жизни.
After going over a few of the blog posts on your site, I really appreciate your way of blogging. I saved it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my web site as well and tell me what you think.
Robert Lewandowski https://robertlewandowski.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Polish footballer, forward for the Spanish club Barcelona and captain of the Polish national team. Considered one of the best strikers in the world. Knight of the Commander’s Cross of the Order of the Renaissance of Poland.
You have made some decent points there. I checked on the web for more information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this web site.
I have been surfing online more than three hours today, yet I never found anything that grabbed my interest as much as this piece.
What’s up to every single one, it’s actually a nice for me to visit this web page, it consists of useful Information.
dip-vuz.ru/kupit-diplom-v-tyumeni/index.html
bpelena.org.ua/perevod-telefonnyh-razgovorov/
startspresto.ru/dannye/pluginclass/cbblogs?action=blogs&func=show&id=22
http://www.hot166.com/blogs/2763/Why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-decreasing-all-the-time
primerosauxilios.org/primeros-auxilios/que-es-y-como-curar-una-herida.php
This is definitely a wonderful webpage, thanks a lot..
Mohamed Salah https://mohamedsalah.prostoprosport-ar.com is an Egyptian footballer who plays as a forward for the English club Liverpool and the Egyptian national team. Considered one of the best football players in the world. Three-time winner of the English Premier League Golden Boot: in 2018 (alone), 2019 (along with Sadio Mane and Pierre-Emerick Aubameyang) and 2022 (along with Son Heung-min).
buy followers tiktok buy tiktok followers
Lionel Andres Messi Cuccittini https://lionelmessi.prostoprosport-ar.com is an Argentine footballer, forward and captain of the MLS club Inter Miami, captain of the Argentina national team. World champion, South American champion, Finalissima winner, Olympic champion. Considered one of the best football players of all time.
娛樂城活動
Секреты успешного получения лицензии на недвижимость|Ключевая информация о лицензии на недвижимость|Как начать карьеру в недвижимости с лицензией|Советы по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Инструкция по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Полезные советы по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Лицензия на недвижимость: важные аспекты|Как стать агентом с лицензией на недвижимость|Эффективные стратегии получения лицензии на недвижимость|Инструкция по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Процесс получения лицензии на недвижимость: как это работает|Секреты скорого получения лицензии на недвижимость|Легкий путь к получению лицензии на недвижимость|Как стать агентом по недвижимости с лицензией: пошаговое руководство|Советы по получению лицензии на недвижимость от профессионалов|Разберитесь в процессе получения лицензии на недвижимость: полное руководство|Шаги к успешной лицензии на недвижимость|Советы по успешному получению лицензии на недвижимость|Лицензия на недвижимость: ключ к успеху в индустрии недвижимости|Легко получите лицензию на недвижимость с этими советами|Получите лицензию на недвижимость и станьте профессиональным агентом|Как получить лицензию на недвижимость быстро и легко|Шаги к успешной лицензии на недвижимость|Секреты быстрого получения лицензии на недвижимость|Эффективные советы по успешному получению лицензии на недвижимость|Сек
How do you get a real estate license in Tennessee https://realestatelicensehefrsgl.com/states/tennessee-real-estate-license/ .
Anderson Sousa Conceicao better known as Talisca https://talisca.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Brazilian footballer who plays as a midfielder for the An-Nasr club. A graduate of the youth team from Bahia, where he arrived in 2009 ten years ago.
에그벳 스포츠
폐하의 다음 행보를 기다리는 듯 모두가 궁궐을 바라보았다.
Harry Edward Kane https://harry-kane.prostoprosport-ar.com is an English footballer, forward for the German club Bayern and captain of the England national team. Considered one of the best football players in the world. He is Tottenham Hotspur’s and England’s all-time leading goalscorer, as well as the second most goalscorer in the Premier League. Member of the Order of the British Empire.
Онлайн казино с гарантированными выплатами выигрышей
лучшие онлайн казино с минимальным депозитом лучшие онлайн казино с минимальным депозитом .
Erling Breut Haaland https://erling-haaland.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Norwegian footballer who plays as a forward for the English club Manchester City and the Norwegian national team. English Premier League record holder for goals per season.
Почему стоит построить дом из бруса 9х12 | Преимущества строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Выбор кровельных материалов для дома из бруса 9х12 | Выбор системы отопления для дома из бруса 9х12 | Как обеспечить комфортную температуру в доме из бруса 9х12 | Выбор фундамента для дома из бруса 9х12 | Современные технологии строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Современные технологии строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Как обустроить зону отдыха в доме из бруса 9х12 | Как рассчитать бюджет на строительство дома из бруса 9х12
дом из бруса 9х12 https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/ .
Welcome to be able to your go-to supply for the most current news in music and celebrity culture! Here, you’ll discover a curated collection of the most used in addition to trending stories that keep you in the know about your favourite artists, bands, in addition to stars – https://newstoplondon.uk/kendal-calling-festival-adds-more-than-50-performers-to-its-line-up.html. Whether if you’re a fan of pop, mountain, hip-hop, or any kind of other genre, the updates cover that all, bringing a person the freshest produces, concert tours, and behind-the-scenes glimpses straight into the lives of the music earth’s biggest names.
Stay tuned for exclusive selection interviews, album reviews, plus insightful commentary on the industry’s latest occurrences. From chart-topping hits to emerging skill, our comprehensive protection ensures you won’t miss a whip. We also get into the private life of celebrities, providing a peek into their glamorous globe, including red carpeting events, award shows, and personal milestones.
Join us as many of us explore the radiant world of audio and celebrity tradition, celebrating the beauty and personalities that make it all so engaging. Dive into our own articles, share your ideas, and connect along with fellow fans since we navigate typically the ever-evolving landscape involving entertainment together.
Играйте в лучших онлайн казино и выигрывайте крупные суммы, рекомендуем.
Веселье и азарт: самые популярные онлайн казино, посетите прямо сейчас.
Популярные азартные игры в онлайн казино, испытайте прямо сейчас.
Наслаждайтесь игрой вместе с лучшими онлайн казино, присоединяйтесь прямо сейчас.
Играйте в новые азартные игры в онлайн казино и выигрывайте крупные суммы, испытайте прямо сейчас.
Играть и выигрывать: лучшие онлайн казино для вас, посетите сейчас.
Играйте в увлекательные игры и выигрывайте крупные суммы в онлайн казино, посетите прямо сейчас.
Играйте и выигрывайте большие суммы в лучших онлайн казино, испытайте сейчас.
Играйте в азартные игры и выигрывайте захватывающие призы в онлайн казино, попробуйте прямо сейчас.
Бонусы и выигрыши: самые популярные онлайн казино для вас, испытайте прямо сейчас.
Играйте в новые азартные игры и выигрывайте большие суммы в онлайн казино, посетите прямо сейчас.
Играть и выигрывать: самые популярные онлайн казино для вас, попробуйте сейчас.
Увлекательные игры и призы в онлайн казино, испытайте прямо сейчас.
Наши рекомендации: самые популярные онлайн казино, присоединяйтесь сейчас.
Играйте в азартные игры и выигрывайте призы в онлайн казино, испытайте прямо сейчас.
Бонусы и выигрыши: лучшие онлайн казино для вас, посетите прямо сейчас.
Новые возможности и азартные игры в онлайн казино,
лучшие онлайн казино на деньги https://onlayn-kazino-reyting-belarusi.com/ .
Luka Modric https://lukamodric.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Croatian footballer, central midfielder and captain of the Spanish club Real Madrid, captain of the Croatian national team. Recognized as one of the best midfielders of our time. Knight of the Order of Prince Branimir. Record holder of the Croatian national team for the number of matches played.
Попробуйте удачу в топовых казино онлайн в Румынии, чтобы выиграть крупный джекпот.
Самые выгодные онлайн казино в Румынии, чтобы испытать удачу и заработать миллионы.
Выбор казино онлайн для румынских геймеров, самые щедрые бонусы и высокие выплаты.
Откройте для себя новые онлайн казино в Румынии, и испытайте настоящий азарт и волнение.
Выберите самое надежное онлайн казино в Румынии, для азартных игр и щедрых вознаграждений.
cazino online romania cazino online romania .
buy tiktok followers instant buy real tiktok followers
The full list of maps, modes, and Playlists that will be available to Free Access players includes: There are so many shooters and role-playing games available to play, but sometimes you need something different. Rec Room is a massive platform full of other games to play around in and can be played either inside or outside a PSVR headset. You must sign in and sign up for EA Play newsletter before you can redeem your items. If you want to play the hottest game, Call of Duty, on your Mac, there is a way to do it. In fact, you have two technical and one super easy, non-technical ways to play COD on Mac. If you’re not a regular and haven’t even played the latest game in the series, Activision is giving you a limited time period to try out its Multiplayer and Zombies mode for free.
https://www.brashka.pl/filmy/page/4206/
Roblox games reflect the sort of imaginative play you often find in the playground. One child has an idea about a game to play, others join him or her and the rules slowly change as the group decides how to have fun together. Creators can quickly update and adjust their games with Roblox studio to match the demands of the huge playing community. Loot boxes are common in many online video games. They let users unlock items and rewards usually for purchase at random. However, the rarity of the items can differ from game to game. While the term comes from box-shaped items, these interactions come in many forms. For example, a user could toss a coin into a fountain and receive a random virtual item that way. It is kind of difficult to describe Roblox. The company says that Roblox offers experiences and the majority of the experiences involve playing games, but there is more to it. Instead of calling it a gaming platform, it is more appropriate to say that Roblox is a digital platform for everyone to hang out.
Hello malabdali.com owner, Thanks for the informative post!
Преимущества строительства дома из бруса 9х12 | Почему стоит построить дом из бруса 9х12 | Секреты уютного интерьера в доме из бруса 9х12 | Плюсы отопления в доме из бруса 9х12 | Выбор фундамента для дома из бруса 9х12 | Типы фундаментов для дома из бруса 9х12 | Дизайн ландшафта для дома из бруса 9х12 | Как выбрать мебель для дома из бруса 9х12 | Как обустроить зону отдыха в доме из бруса 9х12 | Как рассчитать бюджет на строительство дома из бруса 9х12
одноэтажный дом из бруса 9х12 https://domizbrusa-9x12spb.ru/ .
https://vyzov-santehnika-na-dom.ru.
лучшие средства для интимной гигиены IntiLINE каталог продукции
Привет всем)
Студенческая жизнь прекрасна, пока не приходит время писать диплом, как это случилось со мной. Не стоит отчаиваться, ведь существуют компании, которые помогают с написанием и защитой диплома на высокие оценки!
Сначала я искал информацию по теме: купить диплом юриста, купить диплом в нижним тагиле, купить диплом переводчика, купить диплом в волгограде, купить диплом в новочебоксарске, а потом наткнулся на https://communityofbabel.com/en/forums/discussion/language-learning-tips/kupit-attestat-h854n/, где все мои учебные проблемы были решены!
Удачи!
As I website possessor I believe the content here is really fantastic, regards for your efforts.
a8娛樂城
NGolo Kante https://ngolokante.prostoprosport-ar.com is a French footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Ittihad and the French national team. His debut for the first team took place on May 18, 2012 in a match against Monaco (1:2). In the 2012/13 season, Kante became the main player for Boulogne, which played in Ligue 3.
슬롯 킹
장황후는 거의 매일 정시에 양에 따라 생선 간을 먹는다.
Ruben Diogo da Silva Neves https://ruben-neves.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Portuguese footballer who plays as a midfielder for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Hilal and the Portuguese national team. Currently, Ruben Neves plays for the Al-Hilal club wearing number 8. His contract with the Saudi club is valid until the end of June 2026.
Здравствуйте!
Задался вопросом: можно ли на самом деле купить диплом государственного образца в Москве? Был приятно удивлен — это реально и легально!
Сначала искал информацию в интернете на тему: купить диплом магистра, купить диплом в миассе, купить диплом в северодвинске, можно ли купить диплом , купить диплом в владивостоке и получил базовые знания. В итоге остановился на материале: https://telegra.ph/Priobresti-diplom-libo-attestat-stalo-gorazdo-proshche-05-02
Хорошей учебы!
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your site offered us with valuable information to work on. You have done a formidable job and our whole community will be grateful to you.
To the malabdali.com owner, You always provide great insights.
Всем привет)
Будучи студентом, я наслаждался учебой до тех пор, пока не пришло время писать диплом. Но паниковать не стоило, ведь существуют компании, которые помогают с написанием и защитой диплома на отличные оценки!
Изначально я искал информацию по теме: купить диплом в комсомольске-на-амуре, купить диплом в рязани, купить диплом в ижевске, дешево купить диплом, купить диплом учителя физической культуры, затем наткнулся на https://aviaservis.biz/2024/06/08/Где-купить-диплом-Рѕ-среднем-образовании, где все мои учебные вопросы были решены!
Хорошей учебы!
Lebron Ramone James https://lebronjames.prostoprosport-ar.com American basketball player who plays the positions of small and power forward. He plays for the NBA team Los Angeles Lakers. Experts recognize him as one of the best basketball players in history, and a number of experts put James in first place. One of the highest paid athletes in the world.
In the past few years, Africa has surfaced as a vibrant hub for audio and celebrity culture, gaining international reputation and influencing worldwide trends. African audio, with its rich tapestry of genres like as Afrobeats, Amapiano, and highlife, offers captivated audiences globally. Major artists just like Burna Boy, Wizkid, and Tiwa Savage have not simply dominated the charts in Africa but have also made important inroads into typically the global music field. Their collaborations with international stars in addition to performances at key music festivals possess highlighted the continent’s musical prowess. The rise of electronic platforms and interpersonal media has further more amplified the reach of African songs, allowing artists in order to connect with followers across the world and share their unique sounds and reports – https://histoires-africaines.africa/annonce-d-embauche-juriste-debutant-h-f/.
In addition to be able to its musical talent, Africa’s celebrity traditions is flourishing, along with entertainers, influencers, plus public figures requesting large followings. Famous people such as Lupita Nyong’o, Trevor Noah, and Charlize Theron, who have origins in Africa, will be making waves worldwide in film, tv, and fashion. These types of figures not merely take attention to their very own work but in addition reveal important sociable issues and ethnical heritage. Their accomplishment stories inspire a new new generation involving Africans to go after careers in typically the entertainment industry, fostering a feeling of pride and ambition across typically the continent.
Moreover, African celebrities are progressively using their platforms to advocate with regard to change and provide returning to their residential areas. From Burna Son’s activism around interpersonal justice issues to Tiwa Savage’s attempts to promote education intended for girls, these public figures are utilizing their influence regarding positive impact. They can be involved in several philanthropic activities, promoting causes such as healthcare, education, plus environmental sustainability. This specific trend highlights typically the evolving role involving celebrities in Photography equipment, who are not just entertainers but also key players inside driving social transformation and development.
General, the landscape regarding music and celeb culture in Cameras is dynamic in addition to ever-evolving. The continent’s rich cultural diversity and creative talent carry on and garner worldwide acclaim, positioning Photography equipment as a major push inside the global enjoyment industry. As African artists and celebrities always break limitations and achieve brand-new heights, they pave just how for the more inclusive plus diverse representation throughout global media. With regard to those interested in staying updated upon the latest tendencies and news within this vibrant field, numerous platforms and publications offer complex coverage of Africa’s music and celeb happenings, celebrating the particular continent’s ongoing contributions to the entire world stage.
Maria Sharapova https://maria-sharapova.prostoprosport-ar.com Russian tennis player. The former first racket of the world, winner of five Grand Slam singles tournaments from 2004 to 2014, one of ten women in history who has the so-called “career slam”.
Привет, друзья!
Всегда считал, что покупка диплома о высшем образовании — это миф. Но, оказалось, что все возможно! Сначала искал информацию по теме: купить диплом в екатеринбурге, купить диплом в перми, купить диплом ветеринара, купить диплом в челябинске, купить диплом в пензе, а затем перешел на дипломы вузов. Подробнее можно узнать здесь: https://say.la/read-blog/33520
Оказалось, что все возможно и официально, с упрощенными программами обучения. Теперь у меня диплом московского вуза нового образца, и я рекомендую вам воспользоваться этим шансом!
Успешной учебы!
Kevin De Bruyne https://kevin-de-bruyne.prostoprosport-ar.com Belgian footballer, midfielder of the Manchester club City” and the Belgian national team. A graduate of the football clubs “Ghent” and “Genk”. In 2008 he began his adult career, making his debut with Genk.
Quincy Anton Promes https://quincy-promes.prostoprosport-br.com Dutch footballer, attacking midfielder and forward for Spartak Moscow . He played for the Dutch national team. He won his first major award in 2017, when Spartak became the champion of Russia.
[url=https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru]https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru[/url] вызов сантехника в спб.
вызов сантехника в спб [url=https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru]https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru[/url].
срочный вызов сантехника [url=https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru]https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru[/url].
сантехника в спб [url=https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru]https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru[/url].
[url=https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru]https://vyzov-santehnika-spb.ru[/url] спб сантехника на дом.
Секс-работа в городе Москве является запутанной и сложноустроенной проблемой. Невзирая на данная деятельность противозаконна законодательством, это занятие остаётся важным теневым сектором.
Прошлый
В советские эру интимные услуги процветала подпольно. После Советского Союза, в обстановке рыночной нестабильной ситуации, секс-работа стала быть явной.
Сегодняшняя Ситуация
В настоящее время секс-работа в городе Москве имеет различные формы, вплоть до люксовых эскорт-сервисов и до на улице интимных услуг. Высококлассные обслуживание часто осуществляются через сеть, а публичная интимные услуги располагается в определённых районах столицы.
Социально-экономические аспекты
Большинство девушки занимаются в эту деятельность вследствие материальных трудностей. Коммерческий секс может быть привлекательным из-за перспективы мгновенного заработка, но она влечет за собой вред для здоровья и охраны здоровья.
Правовые Вопросы
Проституция в стране не законна, и за эту деятельность занятие предусмотрены серьёзные наказания. Коммерческих секс-работников зачастую привлекают к дисциплинарной ответственности.
Поэтому, несмотря на запреты, коммерческий секс является сегментом теневой экономики города с большими социальными и правовыми последствиями.
красивые проститутки
What Is FitSpresso? The effective weight management formula FitSpresso is designed to inherently support weight loss. It is made using a synergistic blend of ingredients chosen especially for their metabolism-boosting and fat-burning features.
What Is FitSpresso? The effective weight management formula FitSpresso is designed to inherently support weight loss. It is made using a synergistic blend of ingredients chosen especially for their metabolism-boosting and fat-burning features.
Hello malabdali.com administrator, Keep it up!
Larry Joe Bird https://larry-bird.prostoprosport-br.com American basketball player who spent his entire professional career in the NBA ” Boston Celtics.” Olympic champion (1992), champion of the 1977 Universiade, 3-time NBA champion (1981, 1984, 1986), three times recognized as MVP of the season in the NBA (1984, 1985, 1986), 10 times included in the symbolic teams of the season (1980-88 – first team, 1990 – second team).
Секреты успешной перетяжки мебели, стильных
Уникальные идеи для перетяжки мебели, мебель, которая будет радовать вас долгие годы
Сделай свой дом уютным с помощью перетяжки мебели, закажите услугу профессионалов
Какой стиль выбрать для перетяжки мебели, которые понравятся каждому
Как не ошибиться с выбором ткани для перетяжки мебели, применить в деле
Мебель “КакСвоим”.
What Is Sugar Defender? Sugar Defender is a meticulously crafted natural health supplement aimed at helping individuals maintain balanced blood sugar levels. Developed by Jeffrey Mitchell, this liquid formula contains 24 scientifically backed ingredients meticulously chosen to target the root causes of blood sugar imbalances.
https://win-line.net/מכונות-מזל-על-כסף-אמיתי/
לשלוח, ראיה לדבריך.
ההתמודדות באינטרנט הפכה לתחום מושך מאוד בעשור האחרון, המציע אפשרויות שונות של אלטרנטיבות פעילות, לדוגמה קזינו אונליין.
בניתוח זה נבדוק את תופעת ההתמודדות המקוונת ונספק לכם פרטים חשובים שיעזור לכם להבין בנושא מעניין זה.
הימורי ספורט – קזינו באינטרנט
קזינו אונליין כולל אופציות שונות של אפשרויות מוכרים כגון חריצים. ההתמודדות באינטרנט מספקים לשחקנים ליהנות מחוויית פעילות מקצועית מכל מקום.
סוג המשחק פירוט קצר
מכונות פירות הימורי גלגל
רולטה הימור על מספרים וצבעים על גלגל מסתובב
משחק קלפים 21 משחק קלפים בו המטרה היא להשיג 21
משחק הפוקר משחק קלפים מורכב
באקרה משחק קלפים פשוט ומהיר
הימורים בתחום הספורט – התמודדות באינטרנט
הימורים בתחום הספורט הם אחד האזורים המתפתחים המרכזיים ביותר בהתמודדות באינטרנט. מבקרים מורשים לסחור על תוצאים של אתגרי ספורט מושכים כגון כדורסל.
העסקאות ניתן לתמוך על תוצאת האירוע, מספר הנקודות ועוד.
סוג ההימור הסבר תחומי ספורט מובילים
ניחוש התפוקה ניחוש התוצאה הסופית של התחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, קריקט
הפרש ביצועים ניחוש ההפרש בסקורים בין הקבוצות כל ענפי הספורט
כמות הסקורים ניחוש כמות הסקורים בתחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, הוקי קרח
המנצח בתחרות ניחוש איזו קבוצה תנצח (ללא קשר לתוצאה) מספר ענפי ספורט
התמודדות דינמית התמודדות במהלך האירוע בזמן אמת מגוון ענפי ספורט
פעילות מעורבת שילוב של מספר הימורים שונים מספר ענפי ספורט
משחקי קלפים אונליין – קזינו באינטרנט
משחקי קלפים אונליין הוא אחד ממשחקי הקזינו המשגשגים הגדולים ביותר בתקופה הנוכחית. מבקרים מסוגלים להשתתף מול משתתפים אחרים מאזורי הכדור הארצי בסוגים ש
Khvicha Kvaratskhelia https://khvicha-kvaratskhelia.prostoprosport-br.com Georgian footballer, winger for Napoli and captain of the Georgian national team. A graduate of Dynamo Tbilisi. He made his debut for the adult team on September 29, 2017 in the Georgian championship match against Kolkheti-1913. In total, in the 2017 season he played 4 matches and scored 1 goal in the championship.
What Is Neotonics? Neotonics is a skin and gut supplement made of 500 million units of probiotics and 9 potent natural ingredients to support optimal gut function and provide healthy skin.
bocor88
bocor88
Jack Peter Grealish https://jackgrealish.prostoprosport-br.com English footballer, midfielder of the Manchester City club and the England national team. A graduate of the English club Aston Villa from Birmingham. In the 2012/13 season he won the NextGen Series international tournament, playing for the Aston Villa under-19 team
Son Heung Min https://sonheung-min.prostoprosport-br.com South Korean footballer, striker and captain of the English Premier League club Tottenham Hotspur and the Republic of Korea national team. In 2022 he won the Premier League Golden Boot. Became the first Asian footballer in history to score 100 goals in the Premier League
Jude Victor William Bellingham https://jude-bellingham.prostoprosport-fr.com English footballer, midfielder of the Spanish club Real Madrid and the England national team. In April 2024, he won the Breakthrough of the Year award from the Laureus World Sports Awards. He became the first football player to receive it.
Antoine Griezmann https://antoine-griezmann.prostoprosport-fr.com French footballer, striker and midfielder for Atletico Madrid. Player and vice-captain of the French national team, as part of the national team – world champion 2018. Silver medalist at the 2016 European Championship and 2022 World Championship.
Привет всем)
Хорошо быть студентом, пока не придет пора писать диплом, что и произошло со мной, но не стоит отчаиваться, ведь есть хорошие компании что помогают с написанием и сдачей диплома на хорошие оценки!
Изначально искал информацию про купить диплом в москве, купить диплом бакалавра, купить диплом в москве, купить диплом инженера по охране труда, купить диплом в евпатории, потом попал на http://c99596qr.beget.tech/2024/05/14/kupit-diplom-vasha-dver-k-uspeshnomu-buduschemu.html и там решили все мои учебные заботы!
Успешной учебы!
Karim Mostafa Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-fr.com French footballer, striker for the Saudi club Al-Ittihad . He played for the French national team, for which he played 97 matches and scored 37 goals.
Sweet Bonanza https://sweet-bonanza.prostoprosport-fr.com is an exciting slot from Pragmatic Play that has quickly gained popularity among players thanks to its unique gameplay, colorful graphics and the opportunity to win big prizes. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at all aspects of this game, from mechanics and bonus features to strategies for successful play and answers to frequently asked questions.
Bernardo Silva https://bernardo-silva.prostoprosport-fr.com Portuguese footballer, midfielder. Born on August 10, 1994 in Lisbon. Silva is considered one of the best attacking midfielders in the world. The football player is famous for his endurance and performance. The athlete’s diminutive size is more than compensated for by his creativity, dexterity and foresight.
Philip Walter Foden https://phil-foden.prostoprosport-fr.com better known as Phil Foden English footballer, midfielder of the Premier club -League Manchester City and the England national team. On December 19, 2023, he made his debut at the Club World Championship in a match against the Japanese club Urawa Red Diamonds, starting in the starting lineup and being replaced by Julian Alvarez in the 65th minute.
Перетяжка мягкой мебели
https://www.liveinternet.ru/tags/%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%8F%D0%B6%D0%BA%D0%B0%20%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8/ .
Kylian Mbappe Lotten https://kylian-mbappe.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur francais, attaquant du Paris Saint-Germain et capitaine de l’equipe de France. Le 1er juillet 2024, il deviendra joueur du club espagnol du Real Madrid.
FitSpresso: What Is It? FitSpresso is a natural weight loss aid designed for individuals dealing with stubborn weight gain. It is made using only science-backed natural ingredients.
Mohamed Salah Hamed Mehrez Ghali https://mohamed-salah.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur egyptien, attaquant du club anglais de Liverpool et l’equipe nationale egyptienne. Considere comme l’un des meilleurs footballeurs du monde
Declan Rice https://declan-rice.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur anglais, milieu defensif du club d’Arsenal et de l’equipe nationale equipe d’Angleterre. Originaire de Kingston upon Thames, Declan Rice s’est entraine a l’academie de football de Chelsea des l’age de sept ans. En 2014, il devient joueur de l’academie de football de West Ham United.
Jamal Musiala https://jamal-musiala.prostoprosport-fr.com footballeur allemand, milieu offensif du club allemand du Bayern et du equipe nationale d’Allemagne. Il a joue pour les equipes anglaises des moins de 15 ans, des moins de 16 ans et des moins de 17 ans. En octobre 2018, il a dispute deux matchs avec l’equipe nationale d’Allemagne U16. En novembre 2020, il a fait ses debuts avec l’equipe d’Angleterre U21.
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois https://thhibaut-courtois.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur belge, gardien de but du club espagnol du Real Madrid . Lors de la saison 2010/11, il a ete reconnu comme le meilleur gardien de la Pro League belge, ainsi que comme joueur de l’annee pour Genk. Triple vainqueur du Trophee Ricardo Zamora
https://win-line.net/nextbet7-נקסט-בט-7/
להעביר, אסמכתא לדבריך.
ההמרה באינטרנט הפכה לנישה מושך מאוד לאחרונה, המציע מבחר רחב של חלופות הימורים, לדוגמה קזינו אונליין.
במאמר זה נבדוק את עולם ההתמודדות המקוונת ונייעץ לכם פרטים חשובים שיתרום לכם להתמצא בתחום מסקרן זה.
קזינו אונליין – התמודדות באינטרנט
קזינו אונליין מציע מגוון רחב של אפשרויות קלאסיים כגון פוקר. הקזינו באינטרנט מאפשרים למשתתפים להתנסות מחווית משחק מקצועית בכל עת ומקום.
סוג המשחק תיאור מקוצר
מכונות מזל משחקי מזל עם גלגלים
רולטה הימור על מספרים וצבעים על גלגל מסתובב
משחק קלפים 21 משחק קלפים להשגת ניקוד של 21
משחק הפוקר משחק קלפים אסטרטגי
משחק קלפים באקרה משחק קלפים קל וזריז
הימורי ספורט – פעילות באינטרנט
הימורי ספורט מהווים אחד הענפים המתפתחים הגדולים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. מבקרים יכולים להשקיע על תוצאים של משחקי ספורט מושכים כגון טניס.
השקעות יכולים להיות על תוצאת המשחק, מספר האירועים ועוד.
המשחק פירוט משחקי ספורט מרכזיים
ניחוש התפוצאה ניחוש התוצאה הסופית של האירוע כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס
הפרש סקורים ניחוש ההפרש בתוצאות בין הקבוצות כדורגל, כדורסל, הוקי
כמות הסקורים ניחוש כמות הביצועים בתחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, קריקט
הצד המנצח ניחוש מי יהיה הזוכה (ללא קשר לתוצאה) מרבית ענפי הספורט
הימורים דינמיים התמודדות במהלך התחרות בזמן אמת כדורגל, טניס, כדורסל
פעילות מעורבת שילוב של מספר הימורים שונים מרבית ענפי הספורט
פוקר אונליין – הימורים באינטרנט
התמודדות בפוקר מקוון מכיל אחד מסוגי הקזינו הפופולריים המשפיעים ביותר כיום. משתתפים מסוגלים להשתלב עם שחקנים אחרים מרחבי הכדור הארצי במגוון
Declan Rice https://declan-rice.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur anglais, milieu defensif du club d’Arsenal et de l’equipe nationale equipe d’Angleterre. Originaire de Kingston upon Thames, Declan Rice s’est entraine a l’academie de football de Chelsea des l’age de sept ans. En 2014, il devient joueur de l’academie de football de West Ham United.
What is Tea Burn? Tea Burn is a new market-leading fat-burning supplement with a natural patent formula that can increase both speed and efficiency of metabolism. Combining it with Tea, water, or coffee can help burn calories quickly.
Ronaldo de Asis Moreira https://ronaldinhogaucho.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, played as an attacking midfielder and striker. World Champion (2002). Winner of the Golden Ball (2005). The best football player in the world according to FIFA in 2004 and 2005.
Erling Breut Haaland https://erling-haaland.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista noruegues, atacante do clube ingles Manchester City e Selecao da Noruega. Detentor do recorde da Premier League inglesa em gols por temporada.
Philippe Coutinho Correia https://philippecoutinho.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, midfielder of the English club Aston Villa, playing on loan for the Qatari club Al-Duhail. He is known for his vision, passing, dribbling and long-range ability.
월드 슬롯
Fang Jifan은 그를 쫓아 냈습니다. “개, 다시 울면 거세하겠습니다.”
Carlos Henrique Casimiro https://carloscasemiro.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista brasileiro, volante do clube ingles Manchester United e capitao do Selecao Brasileira. Pentacampeao da Liga dos Campeoes da UEFA, campeao mundial e sul-americano pela selecao juvenil brasileira.
Kaka https://kaka.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista brasileiro, meio-campista. O apelido “Kaka” e um diminutivo de Ricardo. Formado em Sao Paulo. De 2002 a 2016, integrou a Selecao Brasileira, pela qual disputou 92 partidas e marcou 29 gols. Campeao mundial 2002.
Karim Mostafa Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista frances, atacante do clube saudita Al-Ittihad . Jogou pela selecao francesa, pela qual disputou 97 partidas e marcou 37 gols.
Топ-5 материалов для перетяжки мебели, проверенных временем
Уникальные идеи для перетяжки мебели, мебель, которая будет радовать вас долгие годы
Топ-3 причины для перетяжки мебели в доме, пригласите в гости дизайнера
Вдохновляющие идеи для перетяжки мебели, применяемые в современном дизайне
Как не ошибиться с выбором ткани для перетяжки мебели, применить в деле
“КакСвоим”.
1win казино сайт
Lionel Messi https://lionelmessi.prostoprosport-br.com e um jogador de futebol argentino, atacante e capitao do clube da MLS Inter Miami. , capitao da selecao argentina. Campeao mundial, campeao sul-americano, vencedor da Finalissima, campeao olimpico. Considerado um dos melhores jogadores de futebol de todos os tempos.
Harry Kane https://harry-kane.prostoprosport-br.com recebeu um convite para a selecao sub-alterna da Inglaterra pela primeira vez tempo 17 para o torneio juvenil em Portugal. Ao mesmo tempo, o atacante, devido a doenca grave, nao compareceu ao triunfante Campeonato Europeu Sub-17 masculino de 2010 pelos britanicos.
Jude Bellingham https://jude-bellingham.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista ingles, meio-campista do clube espanhol Real Madrid e do Selecao da Inglaterra. Em abril de 2024, ele ganhou o premio Breakthrough of the Year do Laureus World Sports Awards. Ele se tornou o primeiro jogador de futebol a recebe-lo.
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois https://thhibaut-courtois.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur belge, gardien de but du club espagnol du Real Madrid . Lors de la saison 2010/11, il a ete reconnu comme le meilleur gardien de la Pro League belge, ainsi que comme joueur de l’annee pour Genk. Triple vainqueur du Trophee Ricardo Zamora
Luis Alberto Suarez Diaz https://luis-suarez.prostoprosport-br.com Uruguayan footballer, striker for Inter Miami and Uruguay national team. The best scorer in the history of the Uruguay national team. Considered one of the world’s top strikers of the 2010s
Robert Lewandowski https://robert-lewandowski.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista polones, atacante do clube espanhol Barcelona e capitao da selecao polonesa. Considerado um dos melhores atacantes do mundo. Cavaleiro da Cruz do Comandante da Ordem do Renascimento da Polonia.
банный камень пироксенит для бани
блог шкода
Ederson Santana de Moraes https://edersonmoraes.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista brasileiro, goleiro do clube Manchester City e da Selecao Brasileira . Participante do Campeonato Mundial 2018. Bicampeao de Portugal pelo Benfica e pentacampeao de Inglaterra pelo Manchester City.
Получай азарт и адреналин в 1win казино, зарабатывай деньги.
Лучшие игровые автоматы в 1win казино, которые захватят тебя на долгие часы.
1win казино – ключ к финансовой независимости, попробуй и убедись сам.
Почувствуй вкус победы вместе с 1win казино, получай крупные выигрыши.
1win казино – это мир азарта и возможностей, воплоти свои мечты в реальность.
Наслаждайся азартом без ограничений в 1win казино, получай награды без границ.
1win казино – это мир азарта и фортуны, претворить свои мечты в реальность.
Удовольствие и адреналин в 1win казино, сталкивайся с удачей и побеждай.
1win 1win .
Virgil van Dijk https://virgilvandijk.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista holandes, zagueiro central, capitao do clube ingles Liverpool e capitao do a selecao holandesa.
Antoine Griezmann https://antoine-griezmann.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista frances, atacante e meio-campista do Atletico de Madrid. Jogador e vice-capitao da selecao francesa, integrante da selecao – campea mundial 2018. Medalhista de prata no Europeu de 2016 e no Mundial de 2022.
Victor James Osimhen https://victor-osimhen.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista nigeriano que atua como atacante. O clube italiano Napoli e a selecao nigeriana.
Лучшее казино для игры – 1win, не упустите свой шанс!
1win казино: ваш ключ к азартным играм, выигрывайте крупные суммы вместе с 1win казино!
1win казино – где каждый становится победителем, попробуйте сами и убедитесь!
Играйте и выигрывайте с 1win казино, получите удовольствие от азарта!
1win казино – ваш первый шаг к успеху, получите удовольствие от азарта с 1win казино!
1win скачать 1win скачать .
Romelu Menama Lukaku Bolingoli https://romelulukaku.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista belga, atacante do clube ingles Chelsea e da selecao belga . Por emprestimo, ele joga pelo clube italiano Roma.
Roberto Carlos da Silva Rocha https://roberto-carlos.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, left back. He was also capable of playing as both a central defender and a defensive midfielder. World champion 2002, silver medalist at the 1998 World Championships.
Thomas Mueller https://thomasmueller.prostoprosport-br.com is a German football player who plays for the German Bayern Munich. Can play in different positions – striker, attacking midfielder. The most titled German footballer in history
온라인 슬롯 게임 추천
Xiao Jing은 눈을 가늘게 떴습니다. “오, Mou 사령관, 당신은 매우 잘 알고 있습니다.”
Что нужно знать перед походом к стоматологу, советуем.
Современные технологии в стоматологии, профессиональный уход за зубами.
Как избежать боли при лечении зубов, изучить.
Мифы о стоматологии, в которые верят все, качественные советы стоматолога.
Как сохранить здоровье зубов на долгие годы, прочитать.
Лечение зубов без боли: реальность или миф?, качественные методики стоматологии.
Как избежать неприятного запаха изо рта, ознакомиться.
лікування зубів https://klinikasuchasnoistomatologii.vn.ua/ .
Neymar da Silva Santos Junior https://neymar.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista brasileiro que atua como atacante, ponta e atacante. meio-campista do clube saudita Al-Hilal e da selecao brasileira. Considerado um dos melhores jogadores do mundo. O maior artilheiro da historia da Selecao Brasileira.
Edson Arantes do Nascimento https://pele.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, forward (attacking midfielder. Played for Santos clubs) and New York Cosmos. Played 92 matches and scored 77 goals for the Brazilian national team.
Jude Victor William Bellingham https://jude-bellingham.prostoprosport-cz.org anglicky fotbalista, zaloznik spanelskeho klubu Real Madrid a anglicky narodni tym. V dubnu 2024 ziskal cenu za prulom roku z Laureus World Sports Awards. Stal se prvnim fotbalistou, ktery ji obdrzel.
Erling Breut Haaland https://erling-haaland.prostoprosport-cz.org je norsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za Anglicky klub Manchester City a norska reprezentace. Rekordman anglicke Premier League v poctu golu za sezonu.
Kylian Mbappe is a French professional footballer who plays as a forward for Paris Saint-Germain and the French national team. Renowned for his speed, dribbling, and finishing, Mbappe has won numerous titles, including multiple Ligue 1 championships and the FIFA World Cup in 2018. Find out more about him here – https://kylianmbappe.paris-saint-germain-ar.com/
Kylian Mbappe Lotten https://kylian-mbappe.prostoprosport-cz.org Francouzsky fotbalista, utocnik Paris Saint-Germain a kapitan tymu francouzskeho tymu. 1. cervence 2024 se stane hracem spanelskeho klubu Real Madrid.
Harry Kane https://harry-kane.prostoprosport-cz.org dostal pozvanku do anglickeho tymu nezletilych jako prvni cas 17. na turnaj mladeze v Portugalsku. Utocnik se zaroven kvuli vazne nemoci neobjevil na triumfalnim mistrovstvi Evropy muzu do 17 let 2010 pro Brity.
Mohamed Salah https://mohamed-salah.prostoprosport-cz.org je egyptsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za anglictinu. klub Liverpool a egyptsky narodni tym. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich fotbalistu na svete.
Vinicius Jose Paixan de Oliveira Junior vinicius-junior.prostoprosport-cz.org bezne znamy jako Vinicius Junior je brazilsky a spanelsky fotbalista , utocnik klubu Real Madrid a brazilsky reprezentant.
Kevin De Bruyne https://kevin-de-bruyne.prostoprosport-cz.org Belgicky fotbalista, zaloznik Manchesteru klub City” a belgicky narodni tym. Absolvent fotbalovych klubu „Ghent” a „Genk”. V roce 2008 zahajil svou karieru dospelych, debutoval v Genku.
Great post! We are linking to this great post on our site. Keep up the great writing.
Секреты выбора материала для перетяжки мебели: экспертные советы и рекомендации, для достижения идеального результата.
Горячие тенденции в мире перетяжки мебели: эксклюзивные идеи для дома, которые поразят ваших гостей.
Творческий процесс перетяжки мебели: самодельные идеи для уникального результата, для создания уютной и гармоничной обстановки.
Почему перетяжка мебели становится все популярнее: основные преимущества и плюсы, чтобы ваш дом стал уютным и уникальным.
Как выбрать подходящего мастера для перетяжки мебели: советы и рекомендации, для успешного завершения вашего проекта.
Какие материалы выбрать для перетяжки мебели в стиле минимализм: легкие и стильные способы, для оформления вашего дома в едином стиле.
Секреты перетяжки мебели в скандинавском стиле: как создать атмосферу комфорта, для создания атмосферы уюта и спокойствия.
Как сделать перетяжку мебели экономично и эффективно: секреты и советы, для привлечения внимания качественно выполненной работы.
Советы по перетяжке мебели в провансальском стиле: как создать атмосферу загородного уюта, для создания уютного и романтичного интерьера.
Как создать интерьер высокого класса с помощью перетяжки мебели: роскошный подход, которые добавят вашему дому роскошь и утонченность.
Профессиональные секреты перетяжки мебели: как сделать работу максимально эффективной, для успешной реализации вашего проекта и получения отличного результата.
перетяжка мягкой мебели мебели перетяжка мягкой мебели мебели .
outsourced sales team
How Can A Business Process Outsourcing Company Achieve At Minimum One Transaction From Ten Meetings?
BPO firms can enhance their sales rates by concentrating on a several important tactics:
Understanding Client Requirements
Before appointments, carrying out detailed analysis on possible customers’ enterprises, challenges, and unique demands is crucial. This readiness allows outsourcing firms to tailor their offerings, thereby making them more enticing and pertinent to the customer.
Clear Value Proposition
Offering a clear, compelling value offer is vital. BPO firms should emphasize how their solutions provide cost reductions, increased effectiveness, and niche skills. Clearly demonstrating these advantages assists clients understand the measurable advantage they would gain.
Building Trust
Trust is a cornerstone of effective transactions. BPO companies could build reliability by displaying their history with case histories, reviews, and sector accreditations. Verified success stories and reviews from content clients might significantly bolster credibility.
Efficient Follow Through
Steady follow-up subsequent to meetings is key to maintaining interest. Customized post-meeting communication emails that reiterate important discussion points and address any questions help keep the client interested. Using customer relationship management tools makes sure that no prospect is forgotten.
Unconventional Lead Acquisition Method
Creative strategies like content marketing might establish outsourcing companies as thought leaders, drawing in prospective clients. Interacting at sector events and utilizing social media platforms like professional networks can extend impact and establish significant relationships.
Advantages of Contracting Out Technical Support
Delegating technical support to a BPO organization could cut expenses and give entry to a skilled labor force. This enables businesses to prioritize core activities while maintaining excellent support for their clients.
Optimal Methods for App Development
Adopting agile methods in app creation guarantees more rapid completion and progressive improvement. Interdisciplinary units improve teamwork, and ongoing feedback helps detect and address challenges early on.
Relevance of Personal Branding for Employees
The individual brands of staff improve a outsourcing company’s trustworthiness. Recognized market experts within the firm draw client credibility and add to a good reputation, helping with both customer acquisition and keeping talent.
Worldwide Impact
These tactics help BPO companies by pushing effectiveness, enhancing customer relations, and promoting Ways Could A Business Process Outsourcing Firm Make At A Minimum Of One Transaction From Ten Sessions?
BPO companies can enhance their sales success rates by concentrating on a several key tactics:
Understanding Customer Demands
Before appointments, carrying out comprehensive investigation on potential clients’ enterprises, issues, and specific demands is vital. This preparation enables BPO organizations to customize their offerings, making them more enticing and relevant to the customer.
Transparent Value Offer
Offering a clear, compelling value statement is vital. BPO organizations should highlight how their solutions yield economic benefits, increased effectiveness, and niche knowledge. Explicitly illustrating these advantages assists customers grasp the measurable advantage they would receive.
Building Confidence
Reliability is a foundation of successful transactions. BPO organizations can create trust by displaying their track record with case histories, reviews, and sector accreditations. Demonstrated success narratives and reviews from happy customers can significantly strengthen trustworthiness.
Productive Follow-Up
Regular follow through following sessions is crucial to maintaining interaction. Tailored post-meeting communication communications that recap key topics and answer any questions assist maintain client interest. Employing CRM systems guarantees that no lead is neglected.
Unconventional Lead Generation Approach
Original methods like content strategies could establish BPO companies as thought leaders, attracting potential clients. Networking at industry events and leveraging online platforms like professional networks might expand impact and create significant contacts.
Advantages of Contracting Out Tech Support
Contracting Out technical support to a outsourcing company might cut expenses and provide access to a talented staff. This permits businesses to focus on primary tasks while ensuring high-quality service for their users.
Best Approaches for Application Creation
Embracing agile methodologies in application development ensures quicker completion and progressive improvement. Cross-functional groups improve teamwork, and constant feedback helps spot and fix issues early on.
Importance of Individual Employee Brands
The personal brands of workers enhance a BPO organization’s credibility. Known sector experts within the organization pull in client trust and increase a favorable reputation, aiding in both new client engagement and employee retention.
Global Effect
These tactics benefit BPO companies by promoting effectiveness, improving client relationships, and fostering
Lionel Messi https://lionel-messi.prostoprosport-cz.org je argentinsky fotbalista, utocnik a kapitan klubu MLS Inter Miami. , kapitan argentinske reprezentace. Mistr sveta, vitez Jizni Ameriky, vitez finale, olympijsky vitez. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich fotbalistu vsech dob.
Bernardo Silva https://bernardo-silva.prostoprosport-cz.org Portugalsky fotbalista, zaloznik. Narozen 10. srpna 1994 v Lisabonu. Silva je povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich utocnych zalozniku na svete. Fotbalista je povestny svou vytrvalosti a vykonem.
Antoine Griezmann https://antoine-griezmann.prostoprosport-cz.org Francouzsky fotbalista, utocnik a zaloznik za Atletico de Madrid. Hrac a vicekapitan francouzskeho narodniho tymu, clen tymu – mistr sveta 2018 Stribrny medailista z mistrovstvi Evropy 2016 a mistrovstvi sveta 2022.
Robert Lewandowski https://robert-lewandowski.prostoprosport-cz.org je polsky fotbalista, utocnik spanelskeho klubu Barcelona a kapitan polskeho narodniho tymu. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich utocniku na svete. Rytir krize velitele polskeho renesancniho radu.
立即访问Telegram官网,下载全球最受欢迎的即时通讯应用。Telegram以其高安全性和易用性闻名,提供文本、语音消息和视频通话等多种通讯方式。支持各种文件类型的分享,无论是照片、视频还是文档,都能快速发送。界面简洁,多语言支持,让您的通讯无国界限。现在就来体验!Visit the official Telegram website now and download the world’s most popular instant messaging app. Known for its high security and ease of use, Telegram offers various communication methods including text, voice messages, and video calls. It supports sharing of all file types, whether photos, videos, or documents, with fast delivery. The interface is clean and supports multiple languages, making your communication boundless. Experience it today! https://www.telegramkd.com z2t0qwx7uo
Son Heung Min https://son-heung-min.prostoprosport-cz.org Jihokorejsky fotbalista, utocnik a kapitan anglickeho klubu Premier League Tottenham Hotspur a narodniho tymu Korejske republiky. V roce 2022 vyhral Zlatou kopacku Premier League.
Luka Modric https://luka-modric.prostoprosport-cz.org je chorvatsky fotbalista, stredni zaloznik a kapitan spanelskeho tymu. klub Real Madrid, kapitan chorvatskeho narodniho tymu. Uznavan jako jeden z nejlepsich zalozniku nasi doby. Rytir Radu prince Branimira. Rekordman chorvatske reprezentace v poctu odehranych zapasu.
Cristiano Ronaldo https://cristiano-ronaldo.prostoprosport-cz.org je portugalsky fotbalista, utocnik, kapitan Saudske Arabie klubu An-Nasr a portugalskeho narodniho tymu. Mistr Evropy. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich fotbalistu vsech dob. Nejlepsi strelec v historii fotbalu podle IFFIS a ctvrty podle RSSSF
Проститутки Тюмени
Pablo Martin Paez Gavira https://gavi.prostoprosport-cz.org Spanelsky fotbalista, zaloznik barcelonskeho klubu a spanelske reprezentace. Povazovan za jednoho z nejtalentovanejsich hracu sve generace. Ucastnik mistrovstvi sveta 2022. Vitez Ligy narodu UEFA 2022/23
Pedro Gonzalez Lopez https://pedri.prostoprosport-cz.org lepe znamy jako Pedri, je spanelsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocny zaloznik. za Barcelonu a spanelskou reprezentaci. Bronzovy medailista z mistrovstvi Evropy 2020 a zaroven nejlepsi mlady hrac tohoto turnaje.
Rodrigo Silva de Goiz https://rodrygo.prostoprosport-cz.org Brazilsky fotbalista, utocnik Realu Madrid a brazilskeho narodniho tymu. V breznu 2017 byl Rodrigo povolan do narodniho tymu Brazilie U17 na zapasy Montague Tournament.
Alison Ramses Becker https://alisson-becker.prostoprosport-cz.org Brazilsky fotbalista nemeckeho puvodu, brankar klubu Liverpool a brazilsky narodni tym. Je povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich brankaru sve generace a je znamy svymi vynikajicimi zakroky, presnosti prihravek a schopnosti jeden na jednoho.
Karim Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-cz.org je francouzsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za Saudskou Arabii. Arabsky klub Al-Ittihad. Hral za francouzsky narodni tym, za ktery odehral 97 zapasu a vstrelil 37 branek. V 17 letech se stal jednim z nejlepsich hracu rezervy, nastrilel tri desitky golu za sezonu.
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois https://thibaut-courtois.prostoprosport-cz.org Belgicky fotbalista, brankar spanelskeho klubu Real Madrid . V sezone 2010/11 byl uznan jako nejlepsi brankar v belgicke Pro League a take hrac roku pro Genk. Trojnasobny vitez Ricardo Zamora Trophy
Virgil van Dijk https://virgil-van-dijk.prostoprosport-cz.org Nizozemsky fotbalista, stredni obrance, kapitan anglickeho klubu Liverpool a kapitan nizozemskeho narodniho tymu.
Bruno Guimaraes Rodriguez Moura https://bruno-guimaraes.prostoprosport-cz.org Brazilsky fotbalista, defenzivni zaloznik Newcastlu United a Brazilsky narodni tym. Vitez olympijskych her 2020 v Tokiu.
Toni Kroos https://toni-kroos.prostoprosport-cz.org je nemecky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako stredni zaloznik za Real Madrid a nemecky narodni tym. Mistr sveta 2014. Prvni nemecky hrac v historii, ktery sestkrat vyhral Ligu mistru UEFA.
Toni Kroos https://toni-kroos.prostoprosport-cz.org je nemecky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako stredni zaloznik za Real Madrid a nemecky narodni tym. Mistr sveta 2014. Prvni nemecky hrac v historii, ktery sestkrat vyhral Ligu mistru UEFA.
Darwin Gabriel Nunez Ribeiro https://darwin-nunez.prostoprosport-cz.org Uruguaysky fotbalista, utocnik anglickeho klubu Liverpool a Uruguaysky narodni tym. Bronzovy medailista mistrovstvi Jizni Ameriky mezi mladeznickymi tymy.
Romelu Menama Lukaku Bolingoli https://romelu-lukaku.prostoprosport-cz.org Belgicky fotbalista, utocnik anglickeho klubu Chelsea a Belgican vyber. Na hostovani hraje za italsky klub Roma.
온라인 슬롯 사이트
철갑선에 소식이 전해진 후 Fang Jifan은 안도의 한숨을 쉬었습니다.
русские проститутки https://prostitutki-213.ru
buy tiktok account 1000 followers https://tiktok-followers-buy.com
buy followers on tiktok https://buy-tiktok-followers.com
отчаянные домохозяйки сериал https://domohozyayki-serial.ru
регистрация рио бет казино регистрация Rio Bet Casino
драгон мани казино https://trucktir.ru
Большой выбор игровых автоматов, рабочее зеркало сайта playfortuna играть на реальные деньги онлайн
Здравствуйте!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом по заказу аттестата ПТУ. Думал, что это невозможно, и начал искать информацию в интернете по теме: купить диплом парикмахера, купить диплом в каменске-уральском, купить диплом фармацевта, купить аттестат школы, купить диплом в петропавловске-камчатском. Постепенно углубляясь в тему, нашел отличный ресурс здесь: http://steklo.by/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=olisuhob и остался очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом сварщика о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь!
Успешной учебы!
Качественная и недорогая https://mebelvam-nn.ru лучшие цены, доставка и сборка.
Здравствуйте!
Для определенных людей, купить диплом о высшем образовании – это острая необходимость, возможность получить достойную работу. Впрочем для кого-то – это желание не терять время на учебу в ВУЗе. С какой бы целью вам это не понадобилось, мы готовы помочь. Оперативно, профессионально и выгодно сделаем диплом любого ВУЗа и года выпуска на настоящих бланках со всеми подписями и печатями.
Мы предлагаем выгодно купить диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Данный диплом способен пройти лубую проверку, даже с использованием специфических приборов. Решите свои задачи максимально быстро с нашим сервисом.
О преимуществах наших дипломов:
• используются настоящие бланки “Гознак”;
• все подписи руководства;
• все печати университета;
• специальные водяные знаки, нити и иные степени защиты;
• идеальное заполнение и оформление – ошибки полностью исключены;
• любые проверки оригинальности документа.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
http://openmotonews.ru/kak-priobresti-diplom-podrobnoe-rukovodstvo
Успешной учебы!
Pin Up casino https://pin-up.salexy.kz official website, Pin Up slot machines play for money online, Pin Up mirror working for today.
Slot machines on the official website and mirrors of the Pin Up online casino https://pin-up.tr-kazakhstan.kz are available for free mode, and after registering at Pin Up Casino Ru you can play for money.
Pin up entry to the official website. Play online casino Pin Up https://pin-up.prostoprosport.ru for real money. Register on the Pin Up Casino website and claim bonuses!
Sports in Azerbaijan https://idman-xeberleri.com.az development and popular sports Azerbaijan is a country with rich sports traditions and outstanding achievements on the international stage.
купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена vm-tver.ru .
Добрый день!
Для некоторых людей, купить диплом о высшем образовании – это острая необходимость, удачный шанс получить достойную работу. Однако для кого-то – это желание не терять время на учебу в институте. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на это решение, мы готовы помочь вам. Максимально быстро, профессионально и недорого изготовим документ любого ВУЗа и любого года выпуска на подлинных бланках с реальными подписями и печатями.
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы имеете возможность в нашем сервисе. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых университетов РФ. Вы получите необходимый диплом по любым специальностям, включая документы Советского Союза. Гарантируем, что в случае проверки документов работодателем, никаких подозрений не появится.
Преимущества наших документов:
• используем только настоящие бланки “Гознака”;
• все подписи руководства;
• мокрые печати учебного заведения;
• водяные знаки, нити и иные степени защиты;
• безупречное заполнение и оформление – ошибок не будет;
• любые проверки документов.
Наша компания предлагает быстро заказать диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Наш диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже при использовании профессиональных приборов. Достигайте свои цели максимально быстро с нашим сервисом.
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
http://dom-nam.ru/index.php/forum/dizajn-interera/23134-voplotite-svoi-professionalnye-mechty-v-zhizn-kup#44171
Успехов в учебе!
World of Games https://onlayn-oyunlar.com.az provides the latest news about online games, game reviews, gameplay and ideas, game tactics and tips. The most popular and spectacular
The main sports news of Azerbaijan https://idman.com.az. Your premier source for the latest news, exclusive interviews, in-depth analysis and live coverage of everything happening in sports in Azerbaijan.
UFC in Azerbaijan https://ufc.com.az news, schedule of fights and tournaments 2024, rating of UFC fighters, interviews, photos and videos. Live broadcasts and broadcasts of tournaments, statistics.
NHL (National Hockey League) News https://nhl.com.az the latest and greatest NHL news for today. Sports news – latest NHL news, standings, match results, online broadcasts.
Привет!
Для многих людей, заказать диплом университета – это острая необходимость, уникальный шанс получить хорошую работу. Однако для кого-то – это желание не терять время на учебу в ВУЗе. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на такой шаг, наша компания готова помочь. Оперативно, качественно и недорого сделаем документ любого года выпуска на подлинных бланках с реальными подписями и печатями.
Наша компания предлагает быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашими дипломами.
Преимущества наших дипломов:
• используются лишь настоящие бланки “Гознак”;
• подлинные подписи должностных лиц;
• все печати университета;
• водяные знаки, нити и другие степени защиты;
• безупречное заполнение и оформление – ошибок не бывает;
• любые проверки оригинальности документа.
Дипломы об окончании ВУЗов и ССУЗов РФ:
– Способны повысить статус своего владельца;
– Открывают большие возможности на рынке труда;
– Повышают рейтинг в глазах граждан;
– Повышают самооценку.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
https://www.intelivisto.com/forum/posts/list/0/86604.page#159267
Успешной учебы!
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your site by accident, and I’m shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Привет, друзья!
Наши специалисты предлагают максимально быстро приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Наш диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже с использованием специфических приборов. Достигайте цели быстро с нашим сервисом.
Где приобрести диплом по нужной специальности?
http://onlaintelevizia.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=426
Хорошей учебы!
메가 슬롯 사이트
그때 개가 한 말이 아닙니다.
blackpanther77 login
본즈 카지노 앱을 다운로드하여 모바일에서 편리하게 게임을 즐기세요. Bons Casino는 다양한 슬롯 게임과 BONS 보너스를 제공합니다. 간편한 본즈 카지노 로그인을 통해 언제든지 게임에 접속할 수 있습니다. BONS 보너스 코드로 더 많은 혜택을 누리세요. 본즈와 함께 즐거운 게임 시간을 보내세요. 앱을 통해 손쉽게 로그인하고 다양한 게임을 즐길 수 있습니다. https://xn--bons-e68pp97i14g.com/bons-registration/
ремонт смартфонов в москве
Погрузитесь в мир берців зсу, Чем примечательны берці зсу?, освойте, значении, Берці зсу: символ верности и чести, Берці зсу: путь к мудрости, найдите, мощью, освойте, в суть, Берець зсу – це не просто взуття!, значення
бєрци зсу https://bercitaktichnizsu.vn.ua/ .
https://intim.nskxxx.me/
купить диплом в пензе vm-tver.ru .
Добрый день!
Для многих людей, приобрести диплом ВУЗа – это острая необходимость, удачный шанс получить достойную работу. Однако для кого-то – это желание не терять огромное количество времени на учебу в институте. С какой бы целью вам это не понадобилось, мы готовы помочь. Оперативно, профессионально и выгодно сделаем документ нового или старого образца на государственных бланках со всеми требуемыми печатями.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Документ пройдет любые проверки, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро с нашей компанией.
Превосходства наших документов:
• используются лишь качественные бланки “Гознака”;
• оригинальные подписи руководства;
• мокрые печати ВУЗа;
• водяные знаки, нити и прочие степени защиты;
• безупречное качество оформления – ошибок не будет;
• любая проверка документа.
Дипломы и аттестаты об окончании учебных учреждений Российской Федерации:
– Способны повысить статус владельца;
– Открывают большие возможности на рынке труда;
– Повышают уважение в глазах окружающих;
– Повышают личную уверенность и самооценку.
Где купить диплом по актуальной специальности?
https://ragingbookmarks.com/story17338277/%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%83%D1%87%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%BA%D0%B8
Хорошей учебы!
Здравствуйте!
Для некоторых людей, приобрести диплом о высшем образовании – это острая необходимость, уникальный шанс получить достойную работу. Но для кого-то – это банальное желание не терять огромное количество времени на учебу в институте. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на такой шаг, мы готовы помочь. Быстро, профессионально и выгодно изготовим документ любого ВУЗа и года выпуска на настоящих бланках с реальными подписями и печатями.
Мы предлагаем быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Диплом способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при использовании специфических приборов. Решите свои задачи быстро и просто с нашим сервисом.
Преимущества наших дипломов:
• используются только фирменные бланки “Гознака”;
• оригинальные подписи руководства;
• мокрые печати ВУЗа;
• специальные водяные знаки, нити и прочие степени защиты;
• идеальное качество оформления – ошибки исключены;
• любая проверка оригинальности документа.
Где приобрести диплом по нужной специальности?
http://koxma.4adm.ru/viewtopic.php?f=251&t=5119
Удачи!
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
Для многих людей, приобрести диплом ВУЗа – это острая необходимость, возможность получить достойную работу. Но для кого-то – это желание не терять массу времени на учебу в ВУЗе. С какой бы целью вам это не потребовалось, наша компания готова помочь вам. Максимально быстро, профессионально и выгодно изготовим документ нового или старого образца на подлинных бланках с реальными печатями.
[b]Приобрести документ[/b] о получении высшего образования вы можете в нашей компании в столице. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов РФ. Вы получите необходимый диплом по любой специальности, включая документы старого образца. Даем 100% гарантию, что в случае проверки документов работодателем, каких-либо подозрений не появится.
Преимущества наших дипломов:
• используются лишь качественные бланки “Гознака”;
• подлинные подписи должностных лиц;
• все печати учебного заведения;
• специальные водяные знаки, нити и другие степени защиты;
• идеальное качество оформления – ошибок не будет;
• любая проверка документа.
[b]Наша компания предлагает[/b] быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже с применением профессиональных приборов. Решайте свои задачи максимально быстро с нашими дипломами.
[b]Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?[/b]
https://woman.0bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=813#p2220
[b]Удачи![/b]
Здравствуйте!
Задался вопросом: можно ли на самом деле купить диплом государственного образца в Москве? Был приятно удивлен — это реально и легально!
Сначала искал информацию в интернете на тему: купить диплом с занесением в реестр, купить диплом в дзержинске, купить диплом в октябрьском, купить диплом автомеханика , куплю диплом и получил базовые знания. В итоге остановился на материале: http://forestsnakes.teamforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=2784&p=7477#p7477
Хорошей учебы!
ремонт стиральных машин на дому [url=http://centr-remonta-stiralnyh-mashin.ru]http://centr-remonta-stiralnyh-mashin.ru[/url] .
Добрый день!
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро купить диплом, который выполняется на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Диплом способен пройти любые проверки, даже при помощи специального оборудования. Решите свои задачи максимально быстро с нашими дипломами.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
http://izumrudnoeozero.listbb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=8
Успехов в учебе!
데지 슬롯
Xie Qian과 다른 사람들은 무표정했고 Zhu Houzhao와 Fang Jifan과 헤어졌습니다!
Привет!
Для многих людей, приобрести диплом о высшем образовании – это острая потребность, уникальный шанс получить достойную работу. Но для кого-то – это желание не терять массу времени на учебу в ВУЗе. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на такой шаг, мы готовы помочь. Максимально быстро, качественно и недорого сделаем диплом любого года выпуска на государственных бланках с реальными печатями.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро заказать диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Наш документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании специального оборудования. Решите свои задачи максимально быстро с нашими дипломами.
Преимущества наших дипломов:
• используем лишь настоящие бланки “Гознака”;
• оригинальные подписи руководства;
• мокрые печати учебного заведения;
• водяные знаки, нити и прочие степени защиты;
• безупречное заполнение и оформление – ошибки исключены;
• любые проверки оригинальности документа.
Где купить диплом специалиста?
http://sea.2bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=1123#p3049
Хорошей учебы!
bocor88 login
먹튀 검증
Fang Jifan은 “폐하, 농민을 설득하는 원본 편지를 아직도 기억하십니까?”
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Добрый день!
Мы предлагаем выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием специального оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро с нашими дипломами.
Где приобрести диплом по актуальной специальности?
https://woman.build2.ru/viewtopic.php?id=13913#p43380
Успехов в учебе!
[b]Здравствуйте[/b]!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом по заказу аттестата ПТУ. Думал, что это невозможно, и начал искать информацию в интернете по теме: купить диплом товароведа, купить диплом в киселевске, купить диплом инженера строителя, купить диплом в люберцах, купить диплом в биробиджане. Постепенно углубляясь, нашел отличный ресурс здесь: http://www.senbernar.ru/profile/10913-izigot/, и остался очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом сварщика о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь!
Успешной учебы!
와일드 바운티 쇼다운
Hongzhi 황제는 Liu Jian을 바라 보았지만 그의 시선은 더욱 이상했습니다!
Забронируйте перфектен мотел веднага безотлагателно
Перфектно дестинация за туризъм по выгодной такса
Заявете най-добри оферти подслон и квартири в момента с гарантией на наша обслужване заемане. Разгледайте за ваше удоволствие специални предложения и ексклузивни скидки на бронирование жилища по всему земен кръг. Без значение желаете уреждате почивка до море, деловую мисия или любовен уикенд, у нас ще откриете идеальное дестинация для проживания.
Истински кадри, оценки и мнения
Наблюдавайте оригинални изображения, цялостни рейтинги и откровени препоръки об отелях. Имаме обширен выбор вариантов размещения, за да имате възможност подберете съответния, который максимално соответствует вашему средства и тип туризъм. Нашата услуга предоставя достъпно и доверие, предоставляя вам желаната сведения за вземане на най-добро решение.
Лекота и безопасность
Отминете о долгих поисках – заявете незабавно просто и безопасно у нас, с возможностью оплаты в отеле. Нашата система резервиране лесен и надежден, что позволяет вам да се фокусирате за планиране вашего путешествия, без на деталях.
Главные забележителности света за пътуване
Идентифицирайте перфектното место за нощуване: отели, гостевые дома, бази – всичко на едно място. Над 2М оферти за Ваш подбор. Инициирайте Вашето пътуване: резервирайте места за настаняване и исследуйте най-добрите места из цял земята! Нашата система осигурява непревзойденные условия за престой и богат выбор оферти за различни уровня бюджет.
Разгледайте отблизо Европейския континент
Разследвайте туристическите центрове Европейската география за идентифициране на варианти за престой. Разкрийте для себя места размещения в Стария свят, от крайбрежни на Средиземном море до алпийски убежищ в Алпите. Нашите препоръки ще ви доведат към най-добрите възможности престой на старом регион. Незабавно кликнете връзките по-долу, чтобы найти хотел във Вашата предпочитана европейской стране и инициирайте Вашето европейско опознаване
Заключение
Резервирайте идеальное дестинация за туризъм при изгодна ставка веднага
Поиск отелей по всему миру
Предварително заявете превъзходен хотел уже незабавно
Идеальное пункт за почивка с атрактивна цене
Бронируйте топ оферти отелей и престой незабавно със сигурност на нашата система бронирования. Откройте за ваше удоволствие уникальные варианти и специални отстъпки за заявяване отелей из цял миру. Без значение того, планируете уреждате отпуск до плаж, бизнес мисия или романтический уикенд, при нас ще откриете перфектно дестинация за отсядане.
Подлинные снимки, рейтинги и препоръки
Наблюдавайте автентични кадри, детайлни отзиви и правдиви препоръки за настаняванията. Имаме голям выбор опции отсядане, за да сте в състояние изберете съответния, същия наилучшим образом покрива вашите средства и стилю дейност. Наш сервис осигурява достъпно и доверие, предоставляя вам желаната сведения за вземане на правильного решения.
Простота и стабилност
Отхвърлете за отнемащите разглеждания – заявете веднага удобно и надеждно у нас, с алтернатива плащане в отеле. Нашата система резервиране безпроблемен и надежден, правещ Ви способни сосредоточиться в планирането на вашето приключение, без в подробностите.
Водещи обекти света за туристически интерес
Найдите отличното место за настаняване: отели, гостевые дома, общностни ресурси – всичко наблизо. Более 2 000 000 оферти за Ваш подбор. Инициирайте Вашето пътуване: резервирайте отели и разгледайте топ места на територията на миру! Нашето предложение предлагает непревзойденные оферти по жилью и многообразен выбор дестинации за различни размер финансов ресурс.
Опознайте лично Стария континент
Обхождайте туристическите центрове Европа за намиране на варианти за престой. Изследвайте для себя възможности за подслон на Европейския континент, от курортов на Средиземно море до алпийски прибежища в Алпийските планини. Нашите съвети ще ви доведат към най-добрите вариантам подслон в стария континенте. Лесно посетете линковете ниже, за да откриете хотел във Вашата избрана европейской стране и инициирайте Вашето пътуване по приключение
Обобщение
Забронируйте перфектно локация за туризъм при изгодна ставка безотлагателно
Major thanks for the article post. Much thanks again.
My website: анал порно
Добрый день!
Где приобрести диплом по необходимой специальности?
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы можете у нас в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов России. Вы сможете получить диплом по любым специальностям, включая документы образца СССР. Даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа работодателем, никаких подозрений не возникнет.
http://vecmir.ru/index.php?option=com_community
Успехов в учебе!
Привет, друзья!
Всегда считал, что покупка диплома о высшем образовании — это миф. Но, оказалось, что все возможно! Сначала искал информацию по теме: купить диплом университета, купить диплом в рязани, купить диплом в якутске, купить диплом в новошахтинске, купить диплом автомеханика, а затем перешел на дипломы вузов. Подробнее можно узнать здесь: http://rogerfilms.com/index.php?title=Желаете получить работу своей мечты
Оказалось, что все возможно и официально, с упрощенными программами обучения. Теперь у меня диплом московского вуза нового образца, и я рекомендую вам воспользоваться этим шансом!
Хорошей учебы!
Great blog here! Also your site loads up fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Добрый день!
Где заказать диплом по актуальной специальности?
Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Они будут заверены необходимыми печатями и подписями.
http://www.prepody.ru/topic19138.html
Успешной учебы!
Привет, друзья!
Купить диплом о высшем образовании.
Наша компания предлагает приобрести диплом высокого качества, который невозможно отличить от оригинала без использования специального оборудования и квалифицированного специалиста.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
http://ostome.ru/forumbb/posting.php?mode=post&f=12
Успехов в учебе!
The very root of your writing while sounding reasonable originally, did not sit very well with me personally after some time. Someplace within the paragraphs you managed to make me a believer but just for a while. I however have got a problem with your leaps in logic and one would do well to fill in all those breaks. If you can accomplish that, I could surely end up being impressed.
게이츠 오브 올림푸스
오늘날의 세계에서 황제와 왕자 사이에 어떤 차이가 있습니까? 그렇다보니…
raid carry wow raid carry wow .
Привет!
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Купить документ о получении высшего образования можно в нашей компании в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых университетов России. Вы сможете получить диплом по любой специальности, любого года выпуска, в том числе документы старого образца. Гарантируем, что при проверке документа работодателями, подозрений не появится.
http://www.dancerussia.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=24656
Удачи!
[url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] доставка товаров из сша.
доставка товаров из сша в россию [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] .
посредники по доставке из сша [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] .
посредники по доставке из сша в россию [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] .
[url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] мейлфорвадеры доставка из сша.
[url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] мейлфорвадеры доставка из сша в россию.
[url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] доставка посылок из сша.
доставка посылок из сша в россию [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] .
доставка посылок из америки [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url] .
доставка товаров из америки [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url]
доставка товаров из америки в россию [url=https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08]https://telegra.ph/Dostavka-tovarov-iz-SSHA-v-Rossiyu-07-08[/url]
Привет!
Купить документ о получении высшего образования можно в нашей компании. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов РФ. Вы сможете получить диплом по любой специальности, включая документы СССР. Гарантируем, что при проверке документов работодателем, каких-либо подозрений не возникнет.
Наша компания предлагает выгодно купить диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями. Наш диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже при использовании специфических приборов. Решайте свои задачи быстро с нашей компанией.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
https://biznet.kz/discussion/1288/kupit-diplom-v-novosibirske/p1?new=1
Успехов в учебе!
Привет!
Для многих людей, приобрести диплом о высшем образовании – это острая потребность, удачный шанс получить выгодную работу. Однако для кого-то – это желание не терять огромное количество времени на учебу в ВУЗе. С какой бы целью вам это не понадобилось, наша фирма готова помочь. Оперативно, качественно и выгодно сделаем документ любого ВУЗа и года выпуска на настоящих бланках со всеми необходимыми подписями и печатями.
Мы предлагаем быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже при использовании профессионального оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро с нашим сервисом.
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
http://seriallove.bbok.ru/viewtopic.php?id=6746#p122710
Успешной учебы!
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Где заказать диплом по актуальной специальности?
Приобретение диплома университета РФ в нашей компании является надежным делом, ведь документ [b]заносится в государственный реестр[/b]. При этом печать производится на официальных бланках, установленных государством.
Вы покупаете документ [b]через надежную фирму.[/b]
https://graph.org/Kupit-diplom-06-13-2
[b]Удачи![/b]
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
Привет, друзья!
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Приобрести документ о получении высшего образования можно у нас в Москве. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов Российской Федерации. Вы сможете получить диплом по любым специальностям, включая документы старого образца. Даем гарантию, что при проверке документа работодателями, каких-либо подозрений не возникнет.
http://forexrassia.ru/page/4
Хорошей учебы!
Добрый день!
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
Мы предлагаем документы техникумов, расположенных на территории всей Российской Федерации. Можно заказать качественно сделанный диплом за любой год, указав актуальную специальность и хорошие оценки за все дисциплины. Дипломы и аттестаты выпускаются на “правильной” бумаге самого высшего качества. Это дает возможность делать настоящие дипломы, которые невозможно отличить от оригинала. Они заверяются необходимыми печатями и подписями.
gerincservdebrecen.hu/informaciok/a-kezeles-menete
MetaMask小狐狸钱包https://www.metamaskb.com Oh2Y4
Just what I needed to know thank you for this.
child abusechild abuse xvlUCATv2
Привет!
Где купить диплом по необходимой специальности?
Приобрести документ университета вы имеете возможность в нашей компании. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации.
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по приятным ценам. Стоимость зависит от конкретной специальности, года получения и ВУЗа. Всегда стараемся поддерживать для заказчиков адекватную ценовую политику.
https://blog.traftop.biz/2024/03/01/premiums-diploms/
Хорошей учебы!
tuan88 slot
telegram pornchild abuse AUAoLPx
Привет, друзья!
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Купить документ ВУЗа можно в нашей компании. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых университетов Российской Федерации. Вы сможете получить необходимый диплом по любым специальностям, включая документы образца СССР. Гарантируем, что в случае проверки документов работодателем, подозрений не возникнет.
http://led119.ru/forum/user/104667/
Успешной учебы!
how to abuse childrenhow to abuse children THwRrYn
Здравствуйте!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по разумным тарифам.
Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе России. Можно приобрести диплом от любого учебного заведения, за любой год, указав необходимую специальность и оценки за все дисциплины. Дипломы и аттестаты печатаются на “правильной” бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможность делать государственные дипломы, которые невозможно отличить от оригиналов. Документы будут заверены всеми обязательными печатями и штампами.
Гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа работодателем, подозрений не появится.
Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?
asktourist.ru/viewtopic.php?id=5095#p19135
child abusechild abuse Rdx3kBua
I’ll immediately clutch your rss as I can not to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognise so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Здравствуйте!
Где заказать диплом по нужной специальности?
Приобрести документ ВУЗа вы можете в нашей компании в Москве. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов РФ. Вы получите необходимый диплом по любой специальности, любого года выпуска, включая документы образца СССР. Гарантируем, что в случае проверки документов работодателями, каких-либо подозрений не появится.
http://foro.turismo.org/post281274.html
Хорошей учебы!
Добрый день!
Для многих людей, купить диплом ВУЗа – это острая необходимость, удачный шанс получить выгодную работу. Однако для кого-то – это осмысленное желание не терять время на учебу в ВУЗе. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на это решение, мы готовы помочь. Быстро, профессионально и по доступной цене изготовим документ нового или старого образца на подлинных бланках со всеми печатями.
Наша компания предлагает выгодно заказать диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти любые проверки, даже при помощи профессионального оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро с нашими дипломами.
Где приобрести диплом по актуальной специальности?
https://www.soft-clouds.com/blogs/96403/??????????-???????????-????-??????-?-????????-?????-?????-???????
Хорошей учебы!
Здравствуйте!
Купить документ университета можно в нашей компании в столице. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов России. Вы получите необходимый диплом по любым специальностям, любого года выпуска, в том числе документы образца СССР. Гарантируем, что при проверке документов работодателем, подозрений не возникнет.
Наши специалисты предлагают быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями. Диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием профессионального оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашей компанией.
Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?
https://ratingforex.ru/forum-forex/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=35616&sid=f68caf2cc1c72d393fe7b0bd77673496
Успехов в учебе!
child abusechild abuse ZGqGFz
child abusechild abuse OoXW3Hn
Glory Casino
Здравствуйте!
Хочу рассказать о своем опыте по заказу аттестата пту, думал это не реально и стал искать информацию в сети, про купить диплом старого образца, старые дипломы купить, купить диплом в салавате, купить диплом в ельце, купить диплом в омске, постепенно вникая в суть дела нашел отличный материал здесь https://549mtbr.com/ivanjdan-slava-garde-panteri-iz-bijeljine/#comment-270838 и был очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом столяра о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь)
Успешной учебы!
I want to to thank you for this very good read!! I absolutely enjoyed every little bit of it. I have you book marked to look at new things you post…
child abusechild abuse vA15WAwG
child abusechild abuse q0fqnHzZ
Привет!
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы имеете возможность у нас в столице. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов РФ.
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам. Цена будет зависеть от конкретной специальности, года получения и университета. Всегда стараемся поддерживать для покупателей адекватную политику тарифов.
https://plarium.com/forum/ru/nords-heroes-of-the-north-browser/351_taverna/1638295_dokumenti-o-srednem-obrazovanii/
Хорошей учебы!
https://aoseulado.net/
sunmory 33
child abusechild abuse Dz3B1A1R
виза цифрового кочевника https://vnzh24.ru/
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com ajLeWnzI
child abusechild abuse iPFjPH
child abusechild abuse Wmad8
Привет, друзья!
Где приобрести диплом по необходимой специальности?
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Документы будут заверены всеми необходимыми печатями и подписями.
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
https://www.bibliogemma.com/cb-profile/pluginclass/cbblogs?action=blogs&func=show&id=248
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
child abusechild abuse Xed2eUuxAq
Привет!
Для многих людей, заказать диплом университета – это острая потребность, уникальный шанс получить достойную работу. Но для кого-то – это очевидное желание не терять множество времени на учебу в ВУЗе. С какой бы целью вам это не понадобилось, наша компания готова помочь. Быстро, профессионально и недорого сделаем документ любого года выпуска на подлинных бланках с реальными печатями.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро приобрести диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями должностных лиц. Данный документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при помощи специфических приборов. Решайте свои задачи быстро и просто с нашими дипломами.
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
http://gazeta.ekafe.ru/viewtopic.php?f=48&t=25396
Хорошей учебы!
[u][b] Привет, друзья![/b][/u]
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
[b]Приобрести документ[/b] о получении высшего образования вы можете у нас. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов России. Вы получите диплом по любой специальности, включая документы образца СССР. Даем 100% гарантию, что в случае проверки документа работодателями, подозрений не появится.
http://www.topfoto.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=36&show_all=yes
[b]Успехов в учебе![/b]
Привет!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по доступным ценам.
Мы предлагаем документы техникумов, расположенных на территории всей РФ. Вы сможете купить качественно сделанный диплом от любого заведения, за любой год, включая документы старого образца СССР. Дипломы и аттестаты выпускаются на бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможность делать настоящие дипломы, которые невозможно отличить от оригиналов. Они будут заверены всеми требуемыми печатями и штампами.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
buldingnews.ru/page/3
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/217171028/detail.aspx
Добрый день!
Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?
Приобрести документ о получении высшего образования вы можете в нашей компании в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов РФ. Вы получите диплом по любой специальности, любого года выпуска, включая документы старого образца. Гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа работодателями, подозрений не возникнет.
http://alltheraige.com/highlights-of-nepal/016d376e-9d36-41d3-a3fd-965986e4b768-jpg/#comment-1020523/
Успехов в учебе!
Привет!
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным ценам.
Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Вы можете купить диплом от любого заведения, за любой год, в том числе документы старого образца. Документы делаются на бумаге самого высокого качества. Это дает возможности делать государственные дипломы, не отличимые от оригиналов. Они заверяются всеми необходимыми печатями и подписями.
Даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа работодателем, никаких подозрений не появится.
Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?
b98385gb.beget.tech/2024/05/16/poluchite-diplom-kotoryy-otkroet-vam-novye-gorizonty-prosto-dostupno-udobno.html
child abusechild abuse UkJnmOj6q
Привет, друзья!
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Купить документ ВУЗа вы имеете возможность в нашем сервисе. Мы оказываем услуги по производству и продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов РФ.
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по выгодным тарифам. Стоимость зависит от выбранной специальности, года получения и образовательного учреждения. Стараемся поддерживать для заказчиков адекватную политику тарифов.
http://www.diablomania.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=558189#post558189
Удачи!
child abusechild abuse huyS1oF
child abusepornographic movies Uaujfdbl
child abusechild abuse NTf3Uyei
Undeniably consider that which you stated. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the internet the simplest factor to bear in mind of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people consider worries that they just don’t know about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top and also outlined out the entire thing without having side effect , other people could take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
Привет, друзья!
Купить диплом о высшем образовании.
Мы предлагаем купить диплом высочайшего качества, неотличимый от оригинального документа без участия специалиста высокой квалификации со специальным оборудованием.
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
http://bank-garantiya.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=eqywytu
Хорошей учебы!
Здравствуйте!
Задался вопросом: можно ли на самом деле купить диплом государственного образца в Москве? Был приятно удивлен — это реально и легально!
Сначала искал информацию в интернете на тему: купить аттестаты за 11, купить диплом института, купить диплом с внесением в реестр, купить диплом в балашихе , купить диплом в оренбурге и получил базовые знания. В итоге остановился на материале: https://ya.7bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=11586#p33250
Удачи!
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Для многих людей, приобрести [b]диплом[/b] университета – это необходимость, возможность получить достойную работу. Однако для кого-то – это очевидное желание не терять время на учебу в ВУЗе. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на такой шаг, мы готовы помочь. Быстро, качественно и по доступной цене изготовим диплом любого года выпуска на государственных бланках со всеми требуемыми подписями и печатями.
[b]Наша компания предлагает[/b] быстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями. Документ способен пройти любые проверки, даже с использованием профессионального оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашей компанией.
[b]Где купить диплом специалиста?[/b]
https://www.cyberpinoy.net/read-blog/9041
[b]Успешной учебы![/b]
Привет, друзья!
Купить документ о получении высшего образования можно в нашей компании в Москве. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов РФ. Вы сможете получить необходимый диплом по любой специальности, любого года выпуска, включая документы образца СССР. Даем гарантию, что при проверке документов работодателем, подозрений не появится.
Наша компания предлагает быстро и выгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже с использованием профессиональных приборов. Достигайте своих целей быстро и просто с нашими дипломами.
Где приобрести диплом по необходимой специальности?
http://pokupki.bestforums.org/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=17800
Удачи!
child abusechild abuse HXjDUWA
child abusepornographic movies nark1lkvp
child abusechild abuse a7nXDI
Здравствуйте!
Где купить диплом по необходимой специальности?
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы имеете возможность у нас в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых университетов Российской Федерации. Вы получите диплом по любой специальности, включая документы СССР. Даем 100% гарантию, что в случае проверки документа работодателями, подозрений не появится.
http://anomalnews.ru/wp-login.php?action=rp&key=icqTRMlZSxWyUnOdAr2Q&login=miguelpAcags
Хорошей учебы!
child abusechild abuse Jf4sAz4e
child abusechild abuse H6Oz8zeF
child abusepornographic movies CT3OXLKYN
wow raid carry service https://kreativwerkstatt-esens.de/ .
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com KIIZ7m8
child abusechild abuse ARwGnl0
child abusechild abuse 0Bi7yQ9
child abusepornographic movies faB8Y
child abusechild abuse 1AlfrP
There’s a list of the best casinos with PayPal available. The bonuses of these sites are also listed. So, all you need to do is compare them. Naturally, there’s a filter that will make your search a lot easier. Once you find what you’re looking for, you can dive in whether it is PayPal Bingo, PayPal betting, or any other form of PayPal gambling. PayPal casino deposits are pretty much instant, but you’ll have to wait approximately 1 to 2 days for a PayPal withdrawal to show up in your balance, if you choose PayPal as your withdrawal method. This is faster than most wire transfers, but it’s fair to say that PayPal is not the fastest withdrawal method. In some casinos, withdrawals to internet wallets like Neteller or Skrill are instant, so PayPal is no match for these in terms of speed.
https://andersonsqgf900115.blogdiloz.com/27218539/play-casino-online-win-real-money
Coupons such as ‘BIGGERISBETTER’ will let you make the most of your first deposit. You can visit their website to know about the latest codes that you can use to redeem exclusive offers. The online casino has been delivering a wide range of wagering solutions and table games since its official launch. It is believed to be one of the most trustworthy Realtime Microgaming sites. The gaming house has earned great prestige recently in 2017, 2018, 2023, and 2023. This section of the review of Raging Bull casino app will talk all about the mobile experience provided by this casino platform. Sign up to Raging Bull Slots casino to grab one of three casino welcome bonuses and some free spins. Claim the offer that suits your bankroll and play slots and keno. Our Raging Bull Slots reviewers believe this is a top promotion for all new players.
Привет!
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Мы можем предложить документы техникумов, которые находятся на территории всей Российской Федерации. Документы заверяются всеми требуемыми печатями и подписями.
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа:
http://myweektour.ru/realnyie-diplomyi-v-vashih-rukah-nadezhnoe-priobretenie-dokumentov-ob-obrazovanii/
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Finding the time and actual effort to produce a great article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
Добрый день!
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Заказать документ о получении высшего образования можно у нас в Москве. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов РФ. Вы сможете получить необходимый диплом по любой специальности, включая документы СССР. Гарантируем, что при проверке документа работодателями, подозрений не возникнет.
https://stoligra.ru/products/golovolomka-kubik–cast-puzzle-cuby-uroven-slozhnosti-4/#comment_67394
Успехов в учебе!
панели армстронг https://armstrong-ceiling24.ru/
Крайне советую Mihaylov digital, их основная сфера это продвижение сайтов в Yandex, а также web разработка!
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com 3REjSxZ4A
Привет!
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании.
Наша компания предлагает приобрести диплом в высоком качестве, неотличимый от оригинала без участия специалиста высокой квалификации со специальным оборудованием.
Где купить диплом специалиста?
http://olddle.orkclub.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=obemyzale
Успешной учебы!
Добрый день!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по доступным ценам.
Мы можем предложить документы техникумов, расположенных на территории всей России. Вы можете купить диплом от любого учебного заведения, за любой год, указав необходимую специальность и оценки за все дисциплины. Документы выпускаются на “правильной” бумаге самого высшего качества. Это дает возможности делать государственные дипломы, не отличимые от оригинала. Документы заверяются необходимыми печатями и штампами.
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
77lub.ru/products/small-engine-oils/
Защитите свои данные с помощью резидентских прокси, воспользоваться этим инструментом.
В чем особенность резидентских прокси?, узнайте подробностями.
Как выбрать лучший резидентский прокси, инструкция для пользователей.
Какие задачи решают резидентские прокси?, узнайте возможностями.
В чем преимущество безопасности резидентских прокси?, обзор функций безопасности.
Как резидентские прокси защищают от опасностей?, анализируем важные аспекты.
Какие преимущества дает использование резидентских прокси?, рассмотрим основные плюсы.
Как улучшить скорость Интернета с резидентским прокси, рекомендации для оптимизации работы.
Зачем использовать резидентский прокси для сбора информации?, анализ возможностей для парсеров.
Как оставаться анонимным в Интернете с резидентским прокси, шаги к безопасности онлайн.
Секреты эффективной работы в соцсетях с резидентским прокси, практические советы функционала.
Какие преимущества дает аренда резидентских прокси, рассмотрим лучшие варианты.
Как избежать DDoS с резидентским прокси?, подробно изучим меры безопасности.
Почему резидентские прокси пользуются популярностью, рассмотрим основные факторы.
Сравнение резидентских и дата-центровых прокси, рекомендации для выбора.
резидентские прокси https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/ .
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com FKIcydsI
Защитите свои данные с помощью резидентских прокси, как это работает.
Обходите географические блокировки с резидентскими прокси, полномасштабным контентом.
Оптимизируйте работу сети благодаря резидентским прокси, в чем преимущество.
Скройте свой реальный IP-адрес от хакеров с резидентскими прокси, и будьте уверены в своей безопасности.
Защитите свою личную жизнь и данные с резидентскими прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Используйте резидентские прокси для безопасного серфинга в интернете, и не бойтесь за свою приватность.
индивидуальные резидентские прокси https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/ .
Привет, друзья!
Приобрести диплом университета.
Наша компания предлагает заказать диплом высочайшего качества, который не отличить от оригинала без использования дорогостоящего оборудования и опытного специалиста.
Где заказать диплом специалиста?
https://forum.theabyss.ru/index.php?showtopic=739694
Удачи!
Ставки на спорт с высокими коэффициентами | Легальные ставки на 1win | 1win дает возможность выиграть крупный приз | Стань частью 1win| Ставь на победу с 1win| Ставки на 1win – это ваша удача| 1win предлагает лучшие условия для игры| 1win – выбор успешных игроков| На 1win вы всегда находитесь в выигрыше| 1win – это ваш верный партнер в ставках
1win беларусь 1win беларусь .
온라인 슬롯
따라서 Ouyang Zhiren과 다른 사람들은 희망이 거의 없을 수 있습니다.
1win – лучший выбор для онлайн-ставок
Выигрывайте с 1win без усилий
Завоюйте свою удачу вместе с 1win
1win – надежный партнер для всех любителей ставок
Букмекерская контора 1win радует своих клиентов каждый день
Ваши ставки всегда успешные с 1win
Ставки на спорт с 1win – высокие коэффициенты и увлекательные матчи
Сделайте свою жизнь ярче с помощью 1win
Победы становятся легко доступными с 1win
Доверьте свои ставки профессионалам из 1win
1win – это лучший способ сделать свою игру еще более захватывающей
1win делает вашу игру более прибыльной и увлекательной
Ставки на спорт становятся простыми с 1win
1win делает ставки доступными для всех|1win – это ваша дверь в мир азарта и прибыли
1win – ваш путь к большим выигрышам|Увлекательные ставки и азартные игры на платформе 1win|1win – ваш верный партнер в мире ставок|Увеличивайте свои выигрыши с 1win|Играйте и выигрывайте с 1win|1win делает вашу игру максимально увлекательной и выгодной|1win – ваш путь к успеху и богатству|1win предлагает вам только лучшие условия для игры|1win – идеальное место для вашего успеха|Начните свой путь к победе с 1win|1win – ваш партнер в мире ставок и азарта|1win делает вашу игру увлекательной и прибыльной|1win – ваш верный ход к выигрышу|1win – это ваш путь к азарту и прибыли|1win – ваш верный партнер в мире ставок|1win – лучший выбор для начинающих и профессионалов|1win – ваш проводник в мире азарта|Ув
1win зеркало https://1win-ofitsialnyy.by/ .
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always exciting to read articles from other authors and use something from their sites.
Большие шансы на успех с 1win: высокие коэффициенты и удобный интерфейс, испытать.
Большой выбор игровых автоматов и карточных игр на 1win, проверить свои навыки.
1win: быстрый и удобный способ заработать деньги, начать играть.
Участвуйте в ставках на киберспорт с 1win, попробовать.
Удобный и надежный сервис для азартных развлечений – 1win, попробовать.
1win 1win .
child abusepornographic movies f3vMo
child abusechild abuse ao9TPqYey3
child abusechild abuse LIRGQKaCc
child abusechild abuse xDW1Ze
Good article! We are linking to this great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
child abusechild abuse YSl0lPEbMU
child abusechild abuse pHbQ9IbNS
child abusechild abuse YoE2G
child abusepornographic movies 0mPS8n0
child abusepornographic movies nJ8aefc
child abusechild abuse p3QZhJMCbv
child abusepornographic movies pIL7cJNkd
child abusechild abuse LW55b0
child abusepornographic movies juYlvPZ0
child abusepornographic movies Rnt38a5cWa
child abusechild abuse 26AYkMJ9
After looking over a number of the blog posts on your web page, I truly appreciate your way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my web site as well and tell me what you think.
온라인 슬롯 게임 추천
그들은 모두 괜찮은 사람들입니다. 어떻게 그런 자세를 볼 수 있습니까?
You are one talented writer thank you for the post.
купить справку
I need to to thank you for this fantastic read!! I absolutely enjoyed every bit of it. I’ve got you book marked to check out new things you post…
купить справку о болезни
child abusechild abuse BtfPIk0f
child abusechild abuse Dd5LCMwO
child abusechild abuse lwJNoO
child abusechild abuse qxikTpZhXX
Hi, I do think this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I may come back once again since I book marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
child abusepornographic movies WN6D2WoN9
I saw a similar post on another website but the points were not as well articulated.
ремонт телефонов в москве
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both equally educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that too few people are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy I found this during my search for something regarding this.
Интеграция мультимедийных систем Интеграция мультимедийных систем .
Truly many of helpful tips.
입플 사이트
Hongzhi 황제는 잠시 생각한 다음 Xiao Jing을 바라 보았습니다. “모집 부 장관 Ma Wensheng”.
Very fine blog.
ремонт мобильных телефонов рядом
child abusechild abuse 4dE3JDU
child abusepornographic movies k7Wwdkd4MQ
child abusechild abuse kOH0c8
child abusepornographic movies dOwsc
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I have to disagree with most of the comments here, but maybe I’m just a contrarian.
срочно починить телефон
приложение zenit
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com BtFiVP
child abusepornographic movies ybnc2
child abusechild abuse 0hYN0
Next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesn’t disappoint me as much as this particular one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, however I really thought you would probably have something useful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
ремонт сотовых адреса
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com eDzdpZ3
MetaMask小狐狸钱包https://www.metamaskb.com CRCuecE0
child abusechild abuse Ac1UqejX
child abusepornographic movies JJKi5m2
child abusechild abuse wrRmO8Fm8l
I would really like to appreciate the endeavors you cash in on written this article. I’m going for the similar best product from you finding out in the foreseeable future as well. Actually your creative writing abilities has urged me to begin my very own blog now. Genuinely the blogging is distributing its wings rapidly. Your write down is often a fine illustration showing it.
фоновое озвучивание помещений фоновое озвучивание помещений .
Very good post! We will be linking to this particularly great article on our site. Keep up the great writing.
Respect to post author, some fantastic information
My website: analporno.club
very good publish, i definitely love this web site, carry on it
telegram下载:https://www.telegrampw.com 9IAWj7ZMZ
child abusepornographic movies aRzSjIo
I want to to thank you for this good read!! I absolutely loved every little bit of it. I have you book marked to look at new things you post…
child abusechild abuse KTZrzKC4u
I really love your site.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you develop this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m wanting to create my own personal site and want to find out where you got this from or exactly what the theme is called. Thanks.
Erling Haaland is banging in the goals for fun, and the Norway international striker will be massive for City against Leeds. Haaland scored against Liverpool, and it is going to be extremely hard for Leeds to keep the striker quiet. 26 09 2020 15:00 Sheffield United v Leeds United All fixtures are subject to change once live TV schedule has been finalised. Registered Company: WherestheMatch Ltd, First Floor, 264 Manchester Road, Warrington, Cheshire WA1 3RB, United Kingdom | Company No. 06683937 | VAT No. 330 9458 02 Our website is temporarily unavailable in your location. 06 03 2021 15:00 West Ham United (a) With the overwhelming American presence in the Leeds United camp, it is now a common occurrence to see the Whites on USA Network or NBC for American audiences. Regardless, the best way to watch Leeds is to have a subscription to Peacock Premium in addition to a TV subscription. Peacock has 180 exclusive Premier League games every season, with the rest either airing on USA Network or NBC.
https://en-web-directory.com/listings12765638/saints-fc-fixtures
Fabrizio Romano is often referred to as the “King of Football Transfer News”. He has been working with Sky Sports in… read more Despite both players now being back, Liverpool should look to invest in this area, which could lead to the club considering a move for Aït-Nouri, who has impressed in Gary O'Neil's side this season. Wolves predominantly operate in a 3-4-3 formation, which is similar to Xabi Alonso's Bayer Leverkusen squad, as the former midfielder continues to be linked with the Liverpool role. Earlier on Thursday, it was confirmed that Quansah’s Liverpool team-mate Curtis Jones had left the England camp after being informed he was not going to be part of the squad heading to Germany. Jurgen Klopp discusses his emotions ahead of his final game as Liverpool manager, saying he would love to put on a great match against Wolves as a final send-off.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thanks, However I am encountering troubles with your RSS. I don’t know why I cannot join it. Is there anybody having the same RSS issues? Anybody who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanks.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this post and also the rest of the site is very good.
ремонт мобильных телефонов
лучшее порево бесплатно лучшее порево бесплатно .
починить телефон
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It is the little changes that make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
After looking over a handful of the blog posts on your blog, I truly like your technique of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site too and let me know your opinion.
I blog frequently and I truly appreciate your information. This great article has really peaked my interest. I will book mark your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Spot on with this write-up, I actually assume this website needs far more consideration. I will in all probability be once more to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve been to your blog before but after browsing through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly delighted I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
газоблок наро фоминск https://gazobeton-moskow.ru/
locowin casino
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I come across a blog that’s equally educative and interesting, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something not enough folks are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy I came across this in my hunt for something concerning this.
топовые порно видео https://apteka-porno.ru/ .
смотреть порно коллекции смотреть порно коллекции .
Лучшие автомобили из Кореи | Секреты выбора авто из Кореи | Новинки автомобильного рынка Кореи | Самые популярные авто Кореи | За что полюбили автомобили Кореи | Топ-3 востребованных автомобиля из Кореи | Топ-7 подержанных авто из Кореи | Лучшие по соотношению цена-качество корейские авто | Какой авто из Кореи подойдет именно вам? | Лучшие внедорожники из Кореи | Выбор современного кроссовера Кореи | Корейские авто для долгих поездок: комфорт и безопасность | Лучшие корейские машины для города | Проверка корейского автомобиля перед приобретением | Как сделать уникальным свой корейский автомобиль
машины из кореи купить https://avtodom63.ru/ .
גוף חטוב וקימורים מושלמים. ועם הנשים הללו אתה תבלה ותיהנה. איתן תוכל להגשים את כל החלומות. דירות דיסקרטיות בתל אביב הן המקום שיגרום לשניכם להתנשף ולהתרגש מרוב אושר. הנערה יודעת כיצד לפנק את גוף הגבר. היא יודעת היכן לגעת והיכן ללחוץ, והיא תעשה זאת עד read contentsays:
I just sent this post to a bunch of my friends as I agree with most of what you’re saying here and the way you’ve presented it is awesome.
What’s up to every body, it’s my first pay a visit of this blog; this website contains awesome and genuinely excellent material in support of visitors.
драгон мани казино
Helpful information. Fortunate me I discovered your site by chance, and I am stunned why this twist of fate did not took place earlier! I bookmarked it.
xslot guncel
זהו שירות המספק את הצרכים של הגוף הגברי ואת המהות של להיות גבר. בילוי עם נערות ליווי בתל אביב מאפשר לגבר להשתחרר ולהתפרק. זוהי לבילוי מפנק ואינטימי סצנת הבילוי של חיפה היא לא רק מועדונים וברים טרנדיים, היא כוללת גם נערות ליווי בחיפה. זהו שירות סקס באר שבע
שתפנק אותך ותגרום לך להרגיש טוב. אם אין לך תכניות לסוף השבוע, אתה חייב לנסות נערות ליווי בתל אביב. במקום להיות לבד בבית, הזמן נערות חרמניות וסקסיות עם חזה וישבן כמו בסרטים. אתה עומד ליהנות מכל רגע. אתה תחווה תחושות נעימות של חום והתרגשות ורק תרצה עוד שירותי ליווי
Защитите свою конфиденциальность с резидентским прокси, предлагаем этим инструментом.
Какие преимущества у резидентских прокси?, прочитайте подробностями.
Советы по выбору резидентского прокси, рекомендации для пользователей.
Какие задачи решают резидентские прокси?, ознакомьтесь с возможностями.
В чем преимущество безопасности резидентских прокси?, обзор функций безопасности.
Как резидентские прокси защищают от опасностей?, разберем важные аспекты.
Как резидентский прокси помогает повысить эффективность?, рассмотрим основные плюсы.
Как улучшить скорость Интернета с резидентским прокси, советы для оптимизации работы.
Почему резидентский прокси стоит использовать для парсинга, обзор возможностей для парсеров.
Секреты анонимности с резидентским прокси, практические шаги к безопасности онлайн.
Секреты эффективной работы в соцсетях с резидентским прокси, рекомендации функционала.
Какие преимущества дает аренда резидентских прокси, рассмотрим лучшие варианты.
Как избежать DDoS с резидентским прокси?, рассмотрим меры безопасности.
В чем причина популярности резидентских прокси?, проанализируем основные факторы.
Как выбрать между резидентским и дата-центровым прокси?, советы для выбора.
качественные резидентские прокси https://rezidentnieproksi.ru/ .
Glory Casino
슬롯 사이트 추천
그러나 일단 시작되면 강력하고 멈출 수 없을 것입니다.
оснащение конференц зала оснащение конференц зала .
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
You have made some decent points there. I looked on the net for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
תהיה בטוח שאתה הולך ליהנות. יש הרבה סיבות מדוע לבקר דירות דיסקרטיות בחיפה, ולא צריך תכניות מיוחדות. זהו מסוג הבילויים שניתן זהו שירות המספק את הצרכים של הגוף הגברי ואת המהות של להיות גבר. בילוי עם נערות ליווי בתל אביב מאפשר לגבר להשתחרר ולהתפרק. זוהי good page
Spot on with this write-up, I actually assume this website needs far more consideration. I will in all probability be once more to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
I blog frequently and I really appreciate your content. The article has truly peaked my interest. I will book mark your site and keep checking for new details about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Безопасность данных с резидентскими прокси, для чего это нужно.
Обходите географические блокировки с резидентскими прокси, и наслаждайтесь контентом.
Оптимизируйте работу сети благодаря резидентским прокси, в чем преимущество.
Обезопасьте свои онлайн-платежи с резидентскими прокси, и чувствуйте себя спокойно.
Сделайте свои онлайн-активности невидимыми благодаря резидентским прокси, и наслаждайтесь анонимностью.
Скачивайте файлы анонимно через резидентские прокси, и не тревожьтесь за свою приватность.
резидентский прокси https://rezidentnie-proksi.ru/ .
שחזרו הביתה לסוף השבוע ורוצים קצת לפרוק את הלחץ מהצבא. לפעמים אלו הם גברים נשואים שקיבלו סוף סוף חופש מהאישה ונותרו לבד בביתם. בילוי טובה. כך שאם אין לך דירה פנויה או שאינך נמצא בבית מלון – זהו הפתרון עבורך. דירות דיסקרטיות בתל אביב זה פינוק מהסרטים מכון ליווי בראשון לציון שמתאים לכל אחד
סידורים בתל אביב ויש לו קצת זמן פנוי. אולי אלו בחורים שהגיעו לבלות במועדונים של תל אביב ומרגישים חרמנים אחרי המועדון. אלו עם נערות ליווי בחיפה הנערות מעניקות שירות לכל הגברים, לרבות אנשי עסקים מכובדים, עורכי דין, רופאים, פרופסורים, אנשים דתיים linked here
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the best blogs on the net. I will highly recommend this site!
оборудование для конференц залов оборудование для конференц залов .
оборудование для переговорных оборудование для переговорных .
The Narrative Concerning Solana’s Creator Yakovenko’s Success
Post Two Mugs of Coffees with a Ale
Yakovenko, the visionary the innovator behind Solana, commenced his path with a modest practice – coffee and beer. Unaware to him, these moments would spark the machinery of his journey. At present, Solana is as a significant competitor in the digital currency world, boasting a market value of billions.
First Sales of Ethereum ETF
The Ethereum ETF recently made its debut with a staggering trading volume. This significant event observed multiple spot Ethereum ETFs from various issuers start trading in the U.S., bringing extraordinary activity into the typically calm ETF trading environment.
SEC’s Approval of Ethereum ETF
The SEC has formally approved the spot Ethereum ETF to be listed. As a cryptographic asset that includes smart contracts, Ethereum is projected to significantly impact the crypto industry thanks to this approval.
Trump’s Bitcoin Tactics
With the election nearing, Trump portrays himself as the ‘Cryptocurrency President,’ constantly highlighting his advocacy for the cryptocurrency industry to attract voters. His method contrasts with Biden’s approach, intending to capture the interest of the cryptocurrency community.
Elon Musk’s Influence
Musk, a notable figure in the blockchain world and a backer of Trump, stirred things up once again, promoting a meme coin related to his antics. His actions continues to shape market dynamics.
Recent Binance News
A subsidiary of Binance, BAM, has been permitted to use customer funds into U.S. Treasuries. Furthermore, Binance noted its 7th anniversary, showcasing its progress and securing various compliance licenses. At the same time, the corporation also disclosed plans to delist several notable cryptocurrency trading pairs, impacting various market participants.
Artificial Intelligence and Economic Outlook
Goldman Sachs’ top stock analyst recently commented that artificial intelligence won’t trigger an economic transformation
נמצאות בכל מקום, דירות דיסקרטיות בתל אביב גם מציעות חווית אירוח 24 שעות ביממה. כאשר אתה מרגיש חרמן בבוקרו של יום, או רוצה נעימה, וגם נערות שיודעות לפנק את הגבר. זה מתאים לכל הגברים הנשואים או אלו שאין להם פרטיות ואינם יכולים להזמין לביתם את הנערות. ליווי נערה עצמאית וסקסית
Like the way you’ve outlined things. Easy to follow. Not cluttered.
The Hidden Tale Concerning Solana’s Founder Toly’s Accomplishment
Subsequent to 2 Cups of Espresso plus a Pint
Toly, the mastermind behind Solana, began his quest with an ordinary routine – a couple of coffees and an ale. Little did he know, those moments would ignite the cogs of his future. Currently, Solana stands as an influential competitor in the crypto sphere, having a billion-dollar market value.
First Sales of Ethereum ETF
The new Ethereum ETF lately started with a substantial volume of trades. This milestone event experienced several spot Ethereum ETFs from various issuers begin trading in the U.S., introducing extraordinary activity into the generally calm ETF trading market.
Ethereum ETF Approval by SEC
The SEC has given the nod to the Ethereum exchange-traded fund for being listed. Being a cryptographic asset with smart contracts, Ethereum is anticipated to have a profound impact the blockchain sector due to this approval.
Trump and Bitcoin
With the election nearing, Trump frames himself as the “Crypto President,” repeatedly showing his advocacy for the digital currency sector to gain voters. His strategy contrasts with Biden’s approach, intending to capture the focus of the cryptocurrency community.
Musk’s Influence on Crypto
Elon Musk, a well-known figure in the blockchain world and a supporter of Trump, created a buzz yet again, boosting a meme coin associated with his antics. His actions continues to shape the market landscape.
Binance Updates
Binance’s subsidiary, BAM, is now allowed to channel customer funds into U.S. Treasury instruments. Moreover, Binance noted its 7th anniversary, underscoring its journey and achieving several compliance licenses. Simultaneously, Binance also made plans to delist several notable cryptocurrency trading pairs, impacting various market participants.
Artificial Intelligence and Economic Outlook
Goldman Sachs’ top stock analyst recently observed that AI won’t spark an economic revolution
Tips and tools you offer are so helpful to agencies in our community.
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all of us you actually recognise what you’re speaking about! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally consult with my website =). We will have a link alternate contract between us
онлайн казино Dragon Money
видеостена купить в москве видеостена купить в москве .
https://derbayerischelowe.info/
оборудование для актовых залов оборудование для актовых залов .