THEORETICAL CONSIDERATIONS The concept of circuit loading The emitter-follower circuit Calculation of the effective (load) input impedance Zin in the emitter-follower circuit
Common Emitter Amplifier
The most common amplifier configuration for an NPN transistor is that of the Common Emitter Amplifier circuit All types of transistor amplifiers
inductor and capacitor formulas
Capacitor Inductor
Norton’s Theorem
What is Norton’s Theorem? Norton’s Theorem states that it is possible to simplify any linear circuit, no matter how complex, to an
Superposition theorem
Superposition theorem is one of those strokes of genius that takes a complex subject and simplifies it in a way that makes
Mesh Current Method and Analysis
The Mesh-Current Method, also known as the Loop Current Method, is quite similar to the Branch Current method in that it uses simultaneous equations,
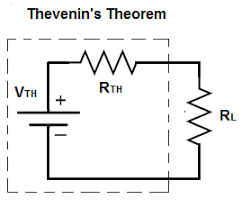
Thevenin’s Theorem
Thevenin’s Theorem states that it is possible to simplify any linear circuit, no matter how complex, to an equivalent circuit with just
Millman theorem
In Millman’s Theorem, the circuit is re-drawn as a parallel network of branches, each branch containing a resistor or series battery/resistor combination. Millman’s Theorem is applicable
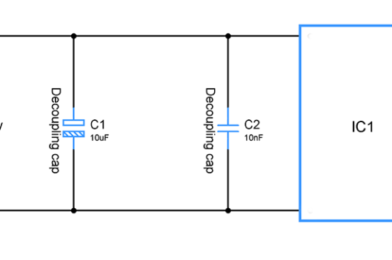
Decoupling Capacitors or bypass capacitor
Electronic Byte: What are Decoupling Capacitors, in Only 5 Minutes It’s pretty standard for beginner electronic designers to forget just how unstable
10 circuit design tips every designer must know
1) USING DECOUPLING AND COUPLING CAPACITORS: Capacitor are widely known for its timing properties, however filtering is another important property of this component
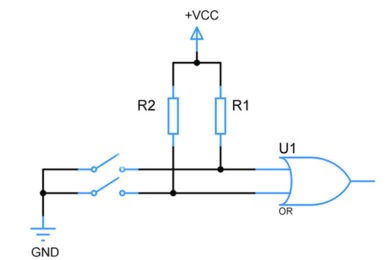
PULL UP OR PULL DOWN RESISTORS
WHAT IS PULL UP OR PULL DOWN RESISTORS: (active high or active low) These are common resistors that connects the digital input
DC to DC buck-boost converter
DC to DC buck-boost converter The buck–boost converter is a type of DC-to-DC converter that has an output voltage magnitude that is
DC to DC buck converter
DC to DC buck converter A buck converter (step-down converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter which steps down voltage (while stepping up
DC to DC boost converter
DC to DC boost converter A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage (while stepping down